A multi-stage computational inverse technique for identification of the dynamic constitutive parameters of concrete
-
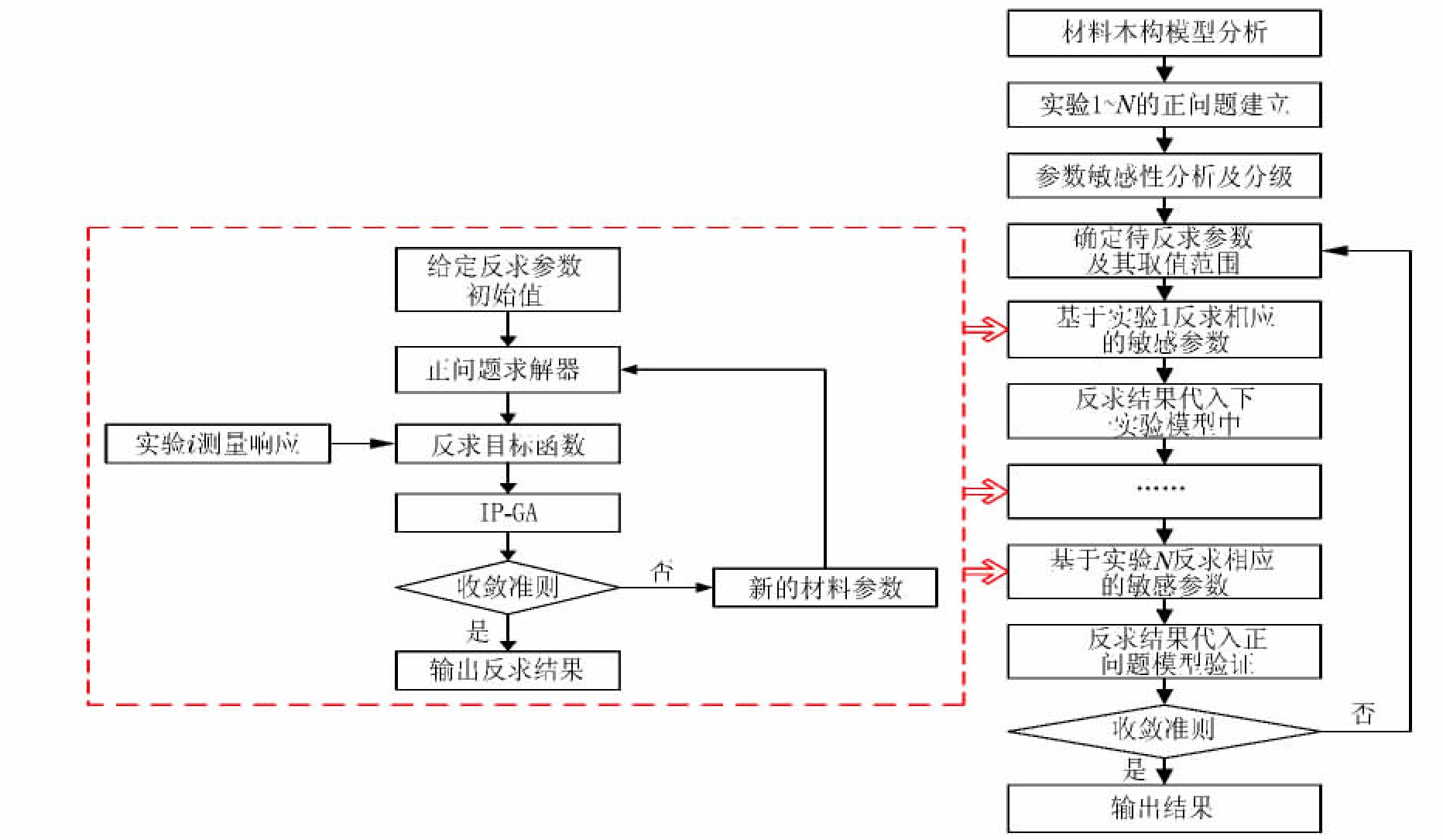
摘要: 基于不同应变率下的分离式Hopkinson压杆实验,提出了一种混凝土材料动态本构参数的分阶段反求方法。该分阶段反求方法中,结合不同的实验模型对未知参数进行敏感性分析,并依据敏感程度对参数进行分类,每类参数对应于1组实验,再利用反求方法分阶段确定各类参数,在每一类参数反求时均将上一次反求结果作为已知条件。结果表明,该分阶段反求方法充分利用所有实验的测量响应信息,能快速获取混凝土本构中较难确定的关键参数,为参数的确定提供了一种有效的途径。Abstract: A multi-stage computational inverse technique is presented to determine the dynamic constitutive parameters of concrete based on the split Hopkinson pressure bar tests at different strain rate loadings.In this method, sensitivity analysis for parameters is carried out based on different experimental models and classification for the parameters is performed according to sensitivity, then the parameters are determined step by step through the inverse method.During parameters identification by multi-stage inverse method, last identified results are applied to current parameters identification.The results indicate that this method obtains the parameters rapidly, which are determined difficultly and expensively by traditional method, combining with different experiments.It is a potentially effective and useful tool to identify material constitutive parameters.
-
Key words:
- solid mechanics /
- inverse problem /
- multi-stage /
- parameters identification /
- SHPB test /
- HJC constitutive model
-
表 1 混凝土HJC本构模型的基本参数
Table 1. The material parameters for HJC concrete constitutive model
ρ0/(g·cm-3) fc/MPa E/GPa G/GPa T/MPa D1 D2 Smax 2.405 57.7 37.93 15.8 4.53 0.04 1.0 7 Pcrush/MPa μcrush Plock/GPa μplock μlock K1/GPa K2/GPa K3/GPa 19.23 0.9×10-3 6.0 0.238 5 0.143 5 85 -171 208 表 2 分阶段参数反求的结果
Table 2. The inversed results by multi-stage inverse technique
反求阶段 实验 反求参数 搜索区间 反求结果 第1阶段 低应变率实验, case 1 A [0.2, 1.0] 0.828 6 B [0.4, 1.5] 0.671 0 N [0.5, 1.2] 0.628 2 第2阶段 高应变率实验, case 3 C [0.05, 0.2] 0.150 0 -
[1] Ross C A, Thompson P Y, Tedesco J W. Split-Hopkinson pressure-bar tests on concrete and mortar in tension and compression[J]. ACI Materials Journal, 1989, 86(5): 475-481. [2] Bischoff P H, Perry S H. Compressive behaviour of concrete at high strain rates[J]. Materials and Structures, 1991, 24(6): 425-450. doi: 10.1007/BF02472016 [3] Tedesco J W, Hughes M L, Ross C A. Numerical simulation of high strain rate concrete compression tests[J]. Computers & Structures, 1994, 51(1): 65-77. [4] Holmquist T J, Johnson G R, Cook W H. A computational constitutive model for concrete subjected to large strains, high strain rates, and high pressures[C]//Jackson N. Proceedings of the 14th International Symposium on Ballistics. USA: American Defense Preparedness Association, 1993: 591-600. [5] Riedel W, Thoma K, Hiermaier S, et al. Penetration of reinforced concrete by BETA-B-500 numerical analysis using a new macroscopic concrete model for hydrocodes[C]//Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on Interaction of the Effects of Munitions with Structures. Berlin, Germany, 1999: 315-322. [6] Taylor L M, Chen E P, Kuszmaul J S. Microcrack-induced damage accumulation in brittle rock under dynamic loading[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 1986, 55(3): 301-320. doi: 10.1016/0045-7825(86)90057-5 [7] Han X, Liu G R. Computational inverse technique for material characterization of functionally graded materials[J]. American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2003, 41(2): 288-295. doi: 10.2514/2.1942 [8] Cooreman S, Lecompte D, Sol H, et al. Elasto-plastic material parameter identification by inverse methods: Calculation of the sensitivity matrix[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2007, 44(13): 4329-4341. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2006.11.024 [9] Sedighi M, Khandaei M, Shokrollahi K H. An approach in parametric identification of high strain rate constitutive model using Hopkinson pressure bar test results[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2010, 527(15): 3521-3528. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2010.02.025 [10] 伍乾坤, 韩旭, 胡德安.一种陶瓷脆性材料动态本构参数的计算反求方法[J].固体力学学报, 2009, 30(3): 280-285.Wu Qian-kun, Han Xu, Hu De-an. An inverse technique for identification of dynamic constitutive parameters of ceramic brittle material[J]. Acta Mechanica Solida Sinica, 2009, 30(3): 280-285. [11] Chen R, Han X, Liu J, et al. A computational inverse technique to determine the dynamic constitutive model parameters of concrete[J]. Computers Materials & Continua, 2011, 25(2): 135-157. [12] Liu G R, Han X. Computational inverse techniques in nondestructive evaluation[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2003. [13] Hao Y F, Hao H, Li Z X. Numerical analysis of lateral inertial confinement effects on impact test of concrete compressive material properties[J]. International Journal of Protective Structures, 2010, 1(1): 145-167. doi: 10.1260/2041-4196.1.1.145 [14] 巫绪涛, 李耀, 李和平.混凝土HJC本构模型参数的研究[J].应用力学学报, 2010, 27(2): 340-344.Wu Xu-tao, Li Yao, Li He-ping. Research on the material constants of the HJC dynamic constitutive model for concrete[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2010, 27(2): 340-344. -







 下载:
下载: