Reduced mechanism and analysis for thermal deflagration of C1-C4 alkane mixture
-
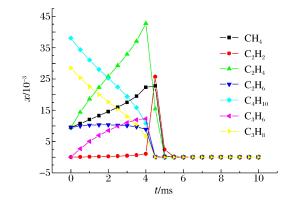
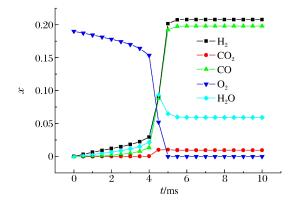
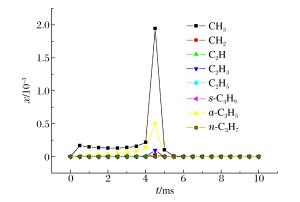
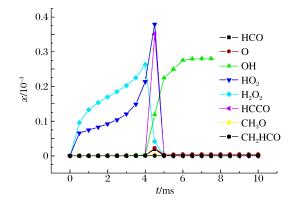
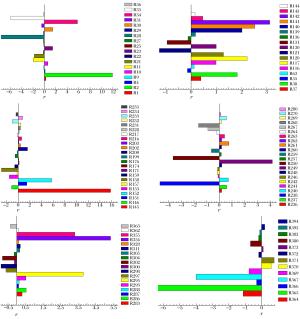
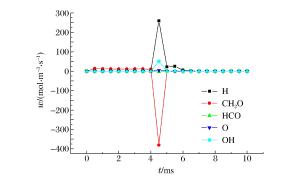
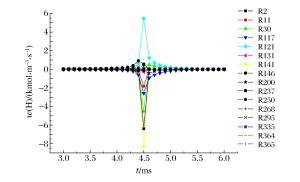
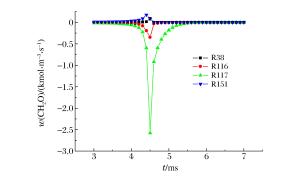
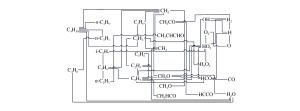
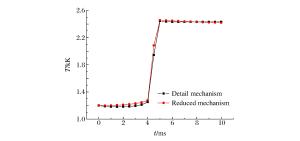
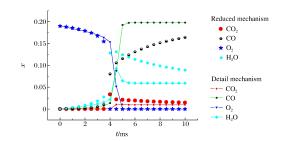
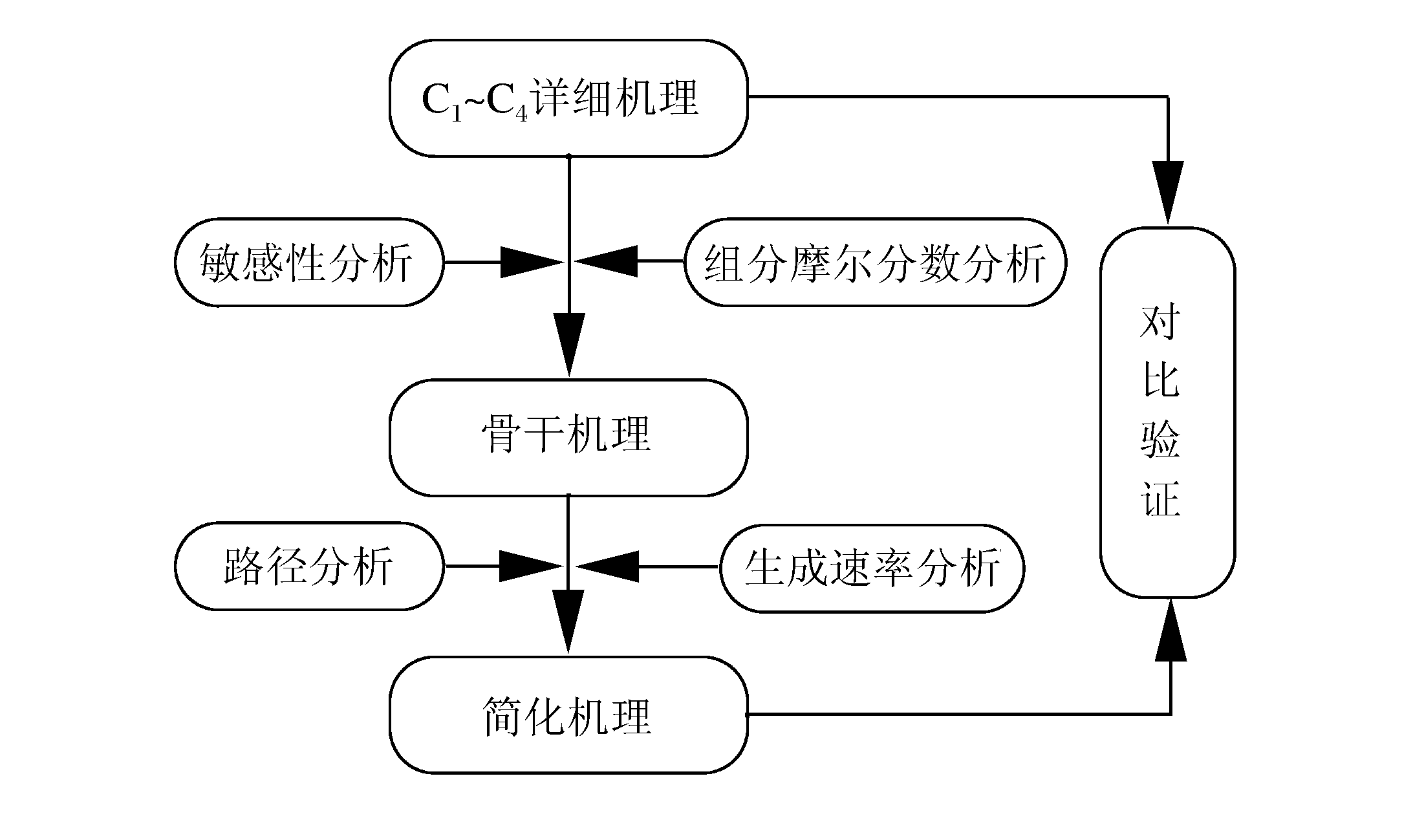
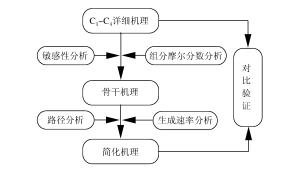
摘要: 为了探索油气在受限空间热爆燃发生的化学反应机理,以CHEMICAL4.1为平台,分析了C1~C4烷烃混合气体热爆燃过程的系统温度、主要组分浓度和中间产物生成率的变化规律。通过敏感性分析、生成速率分析和路径分析等方法,简化了C1~C4烷烃混合气体的详细机理,得到了一个包含37种组分、80个基元反应组成的简化机理,并进行了对比验证。在反应机理上印证了气体热爆燃过程存在缓慢氧化、快速氧化和反应平衡3个阶段。发现与超氧化氢和过氧化氢有关的基元反应是热爆燃发生的关键反应,而大量产生的氢基和羟基最终导致了热爆燃的发生。Abstract: For studying the chemical mechanism of thermal deflagration of gasoline-air mixture in the confined space, the temperature of the system, the concentration of main components and the generation rate of production in the deflagration process of C1-C4 alkane were simulated with CHEMICAL4.1 as a platform. Based on the analysis for the simulated data of the chemical mechanism, three results were obtained as follows. (1)By sensitivity analysis, rate-of-production analysis, path analysis and so on, the detailed oxidation mechanism of C1-C4 alkane was studied, and drew a reduced mechanism which consisted of 37 species and 80 reactions. The comparison of the two mechanisms was presented. (2) There existed three distinct stages in the thermal deflagration process based on the analysis for the mechanism, namely slow oxidation, rapid oxidation and reaction equilibrium. (3) In the whole chain reaction process, the reactions generating hydroperoxyl and hydrogen peroxide were the key reactions because the hydrogen and hydroxyl groups were largely generated from them so that they induced the deflagration happen finally.
-
表 1 C1~C4简化机理的反应方程
Table 1. Reaction equations for reduced mechanism of C1~ C4
反应编号 反应方程 R2* O+OH=O2+H R10 H+HO2=OH+OH R11* H+HO2=H2+O2 R12 H+HO2=O+H2O R14 OH+OH=O+H2O R16 H+H+H2=H2+H2 R20 O+O+M=O2+M R21* HO2+HO2=H2O2+O2 R23* OH+OH(+M)=H2O2(+M) R24 H2O2+H=HO2+H2 R26 H2O2+O=OH+HO2 R28* CH3+CH3(+M)=C2H6(+M) R29 CH3+H(+M)=CH4(+M) R30* CH4+H=CH3+H2 R32 CH4+O=CH3+OH R34* CH3+HO2=CH3O+OH R38* CH3+O2=CH2O+OH R55 CH3O+M=CH2O+H+M R76 CH2+O=CO+H+H R77 CH2+O=CO+H2 R100 CH+O2=HCO+O R101 CH+O=CO+H R102 CH+OH=HCO+H R107 CH+CH2O=CH2CO+H R112 C+O2=CO+O R113 C+OH=CO+H R115 C+CH2=C2H+H R116* CH2O+H=HCO+H2 R120* HCO+O2=HO2+CO R121* HCO+M=H+CO+M R123 HCO+H=CO+H2 R124 HCO+O=CO+OH R126 CO+OH=CO2+H R127 CO+O+M=CO2+M R130* C2H6+CH3=C2H5+CH4 R131* C2H6+H=C2H5+H2 R140* C2H5+O2=C2H4+HO2 R141 C2H4+H=C2H3+H2 R142* C2H4+OH=C2H3+H2O R143 C2H4+O=CH3+HCO R145* C2H4+CH3=C2H3+CH4 R146* C2H4+H(+M)=C2H5(+M) R151* C2H3+O2=CH2O+HCO R152* C2H3+O2=CH2HCO+O R157* C2H3+O2=C2H2+HO2 R158* C2H3+CH3=C3H6 R166 C2H2+OH=CH2CO+H R168 C2H2+OH=CH3+CO R183 CH2HCO+H=CH2CO+H2 R184 CH2HCO+O=CH2O+HCO R187 CH2HCO+CH3=>C2H5+CO+H R200* CH2CO+H=HCCO+H2 R215 HCCO+O=CH+CO2 R229 C3H8+O2=i-C3H7+HO2 R230 C3H8+O2=n-C3H7+HO2 R231 C3H8+HO2=n-C3H7+H2O2 R233* C3H8+OH=n-C3H7+H2O R238* C3H8+H=n-C3H7+H2 R247 n-C3H7+M=C2H4+CH3+M R248 n-C3H7+O2=C3H6+HO2 R249* i-C3H7+O2=C3H6+HO2 R250* C3H6+H(+M)=i-C3H7(+M) R251 i-C3H7+H=C2H5+CH3 R252 n-C3H7+H=C2H5+CH3 R257 C3H6+HO2=a-C3H5+H2O2 R263 C3H6+O=C2H5+HCO R264 C3H6+O=a-C3H5+OH R268* C3H6+H=a-C3H5+H2 R273 C3H6+O2=a-C3H5+HO2 R284 CH2CHCHO+O=CH2CHCO+OH R290 CH2CHCO+O=C2H3+CO2 R295* a-C3H5+HO2=CH2CHCHO+H+OH R354* C4H10=C2H5+C2H5 R355* C4H10=n-C3H7+CH3 R359 C4H10+O2=s-C4H9+HO2 R361 C4H10+a-C3H5=s-C4H9+C3H6 R364* C4H10+H=s-C4H9+H2 R367* C4H10+OH=s-C4H9+H2O R369 C4H10+O=s-C4H9+OH R372 s-C4H9+M=C3H6+CH3+M 表 2 C1~C4简化机理反应速率方程的参数
Table 2. Parmeters of reaction rate equations for reduced mechanism of C1-C4
反应编号 A b Ea/(J·mol-1) R2* 2.02×1014 -0.4 0.0 R10 1.50×1014 0.0 1 000.0 R11 8.45×1011 0.7 1 241.0 R12 3.01×1013 0.0 1 721.0 R14 3.57×104 2.4 -2 112.0 R16 9.20×1016 -0.6 0.0 R20 1.89×1013 0.0 -1 788.0 R21* 4.20×1014 0.0 11 982.0 R23* 1.24×1014 -0.4 0.0 R24 1.98×106 2.0 2 435.0 R26 9.55×106 2.0 3 970.0 R28* 9.22×1016 -1.2 636.0 R29 2.14×1015 -0.4 0.0 R30* 2.20×104 3.0 8 750.0 R32 6.92×108 1.6 8 485.0 R34* 7.00×1012 0.0 0.0 R38* 2.51×1011 0.0 14 640.0 R55 5.45×1013 0.0 13 497.0 R76 5.00×1013 0.0 0.0 R77 3.00×1013 0.0 0.0 R100 3.30×1013 0.0 0.0 R101 5.70×1013 0.0 0.0 R102 3.00×1013 0.0 0.0 R107 9.46×1013 0.0 -515.0 R112 2.00×1013 0.0 0.0 R113 5.00×1013 0.0 0.0 R115 5.00×1013 0.0 0.0 R116* 2.19×108 1.8 3 000.0 R120* 7.58×1012 0.0 410.0 R121* 1.86×1017 -1.0 17 000.0 R123 1.19×1013 0.2 0.0 R124 3.00×1013 0.0 0.0 R126 9.42×103 2.2 -2 351.0 R127 6.17×1014 0.0 3 000.0 R130* 5.50×10-1 4.0 8 300.0 R131* 5.40×102 3.5 5 210.0 R140* 3.00×1020 -2.9 6 760.0 R141 3.36×10-7 6.0 1 692.0 R142* 2.02×1013 0.0 5 936.0 R143 1.02×107 1.9 179.0 R145* 6.62 3.7 9 500.0 R146* 1.08×1012 0.5 1 822.0 R151* 1.70×1029 -5.3 6 500.0 R152* 3.50×1014 -0.6 5 260.0 R157* 2.12×10-6 6.0 9 484.0 R158* 4.46×1056 -13.0 13 865.0 R166 2.18×10-4 4.5 -1 000.0 R168 4.83×10-4 4.0 -2 000.0 R183 4.00×1013 0.0 0.0 R184 1.00×1014 0.0 0.0 R187 4.90×1014 -0.5 0.0 R200* 2.00×1014 0.0 8 000.0 R215 2.95×1013 0.0 1 113.0 R229 4.00×1013 0.0 48 610.0 R230 4.00×1013 0.0 51 360.0 R231 4.76×104 2.5 16 492.0 R233* 3.16×107 1.8 934.0 R238* 1.33×106 2.5 6 756.0 R247 1.23×1013 -0.1 30 202.0 R248 3.58×109 0.0 -3 532.0 R249* 6.10×1020 -2.9 7 910.0 R250* 5.70×109 1.2 874.0 R251 5.00×1013 0.0 0.0 252 1.00×1014 0.0 0.0 R257 9.64×103 2.6 13 910.0 R263 1.58×107 1.8 -1 216.0 R264 5.24×1011 0.7 5 884.0 R268* 1.73×105 2.5 2 492.0 R273 2.00×1013 0.0 44 000.0 R284 7.24×1012 0.0 1 970.0 R290 1.00×1014 0.0 0.0 R295* 1.00×1013 0.0 0.0 R354* 2.00×1016 0.0 81 300.0 R355* 1.74×1017 0.0 85 700.0 R359 4.00×1013 0.0 47 600.0 R361 3.16×1011 0.0 16 400.0 R364* 5.68×105 2.4 3 765.0 R367* 7.23×107 1.6 -247.0 R369 5.62×1013 0.0 5 200.0 R372 2.14×1012 0.7 30 856.0 -
[1] Battin-Leclerc F. Detailed chemical kinetic models for the low-temperature combustion of hydrocarbons with application to gasoline and diesel fuel surrogates[J]. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 2008, 34: 440-498. doi: 10.1016/j.pecs.2007.10.002 [2] Wang Yi-feng, Yao Ming-fa, Zheng Zun-qing. A semi-detailed chemical kinetic model of a gasoline surrogate fuel for internal combustion engine applications[J]. Fuel, 2013, 113(2): 347-356. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016236113004882 [3] 刘合, 陈方, 刘洪, 等.甲烷/空气预混超声速燃烧的18步简化机理[J].燃烧科学与技术, 2012, 18(5): 467-472. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-RSKX201205015.htmLiu He, Chen Fang, Liu Hong, et al. 18-step reduced mechanism for methane/air premixed supersonic combustion[J]. Journal of Combustion Science and Technology, 2012, 18(5): 467-472. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-RSKX201205015.htm [4] 梁运涛.封闭空间瓦斯爆炸过程的反应动力学分析[J].中国矿业大学学报, 2010, 39(2): 196-200. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkydxxb201002009Liang Yun-tao. Analysis of reaction kinetic for gas explosion in enclosed space[J]. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology, 2010, 39(2): 196-200. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkydxxb201002009 [5] 刘耀东, 解茂昭, 贾明, 等.一个改进的异辛烷氧化化学动力学骨架模型[J].工程热物理学报, 2013, 34(4): 791-795. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GCRB201304049.htmLiu Yao-dong, Xie Mao-zhao, Jia Ming, et al. An improved skeletal chemical kinetic model for iso-octane oxidation[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2013, 34(4): 791-795. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GCRB201304049.htm [6] 方亚梅, 王全德, 王繁, 等.正十二烷高温燃烧详细化学动力学机理的系统简化[J].物理化学学报, 2012, 28(11): 2536-2542. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-WLHX201211006.htmFang Ya-mei, Wang Quan-de, Wang Fan, et al. Reduction of the detailed kinetic mechanism for high-temperature combustion of n-dodecane[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2012, 28(11): 2536-2542. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-WLHX201211006.htm [7] 姚通, 钟北京.正癸烷着火及燃烧的化学动力学模型[J], 物理化学学报, 2013, 29(2): 237-244.Yao Tong, Zhong Bei-jing. Chemical kinetic model for auto-ignition and combustion of n-decane[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2013, 29(2): 237-244. [8] 雒婧, 尧命发.正庚烷甲苯混合物燃烧简化机理分析[J].燃烧科学与技术, 2012, 18(4): 367-374. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rskxyjs201204013Luo Jing, Yao Ming-fa. Reduced combustion mechanism of n-heptane/toluene mixtures[J]. Journal of Combustion Science and Technology, 2012, 18(4): 367-374. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rskxyjs201204013 [9] 郑东, 钟北京.异辛烷/正庚烷/乙醇三组分燃料着火的化学动力学模型[J].物理化学学报, 2012, 28(9): 2029-2036. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wlhxxb201209003Zheng Dong, Zhong Bei-jing. Chemical kinetic model for ignition of three-component fuel comprising iso-octane/n-heptane/ethanol[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2012, 28(9): 2029-2036. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wlhxxb201209003 [10] Mehl M, Pitz W J, Westbrook C K, et al. Kinetic modeling of gasoline surrogate components and mixtures under engine conditions[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2011, 33(1): 193-200. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1540748910000787 [11] 曾文, 解茂昭.正庚烷HCCI燃烧下多环芳烃生成机理与影响因素分析[J].大连理工大学学报, 2012, 52(2): 183-190. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90724X/20122/41248426.htmlZeng Wen, Xie Mao-zhao. Analyses of influencing factors and formation mechanism of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in n-heptane HCCI combustion[J]. Journal of Dalian University of Technology, 2012, 52(2): 183-190. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90724X/20122/41248426.html [12] 张庆峰, 郑朝蕾, 何祖威, 等.适用于HCCI发动机的基础燃料化学动力学模型: Ⅱ:构造骨架机理[J].内燃机学报, 2011, 29(2): 133-138. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-NRJX201102007.htmZhang Qing-feng, Zheng Zhao-lei, He Zu-wei, et al. A chemical kinetic model of PRF oxidation for HCCI engine: Ⅱ: Structure of a skeletal model[J]. Transactions of CSICE, 2011, 29(2): 133-138. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-NRJX201102007.htm [13] Ra Y, Reitz R D. A reduced chemical kinetic model for IC engine combustion simulations with primary reference fuels[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2008, 155(4): 713-738. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2008.05.002 [14] Narayanaswamy K, Blanquart G, Pitsch H. A consistent chemical mechanism for oxidation of substituted aromatic species[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2010, 157(10): 1879-1898. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2010.07.009 [15] 贾宝山, 李艳红, 曾文, 等.受限空间瓦斯爆炸链式反应机理的敏感性分析[J].环境工程, 2011, 29(增刊): 318-323. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/93897X/2011S1/1003576782.htmlJia Bao-shan, Li Yan-hong, Zeng Wen, et al. Sensitive analysis of chain reaction mechanism of gas explosion[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2011, 29(Suppl): 318-323. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/93897X/2011S1/1003576782.html [16] Li Shan-ling, Jiang Yong, Qiu Rong. Detailed mechanism reduction for C3H8/DMMP/air flame based on path flux analysis-sensitivity analysis method[J]. Journal of Combustion Science and Technology, 2012, 18(5): 473-478. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_rskxyjs201205017.aspx [17] Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. C1-C4 mechanism with PAH formation[EB/OL]. [2014-2-10].https://combustion.llnl.gov/mechanisms/aromatic-and-pah-formation/c1c4-mechanism-with-pah-formation. -






 下载:
下载: