Nose-shape optimization and simulation of projectiles penetrating into concrete target based on local interaction theory
-
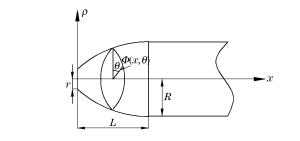
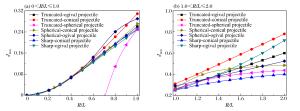
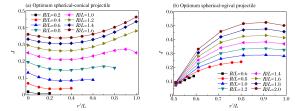
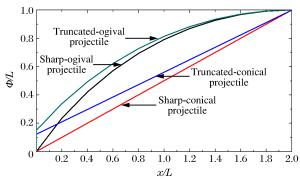
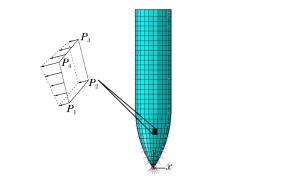
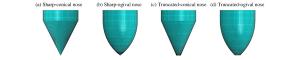
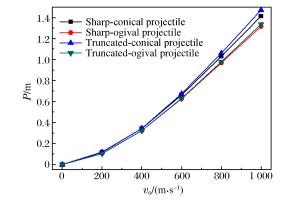
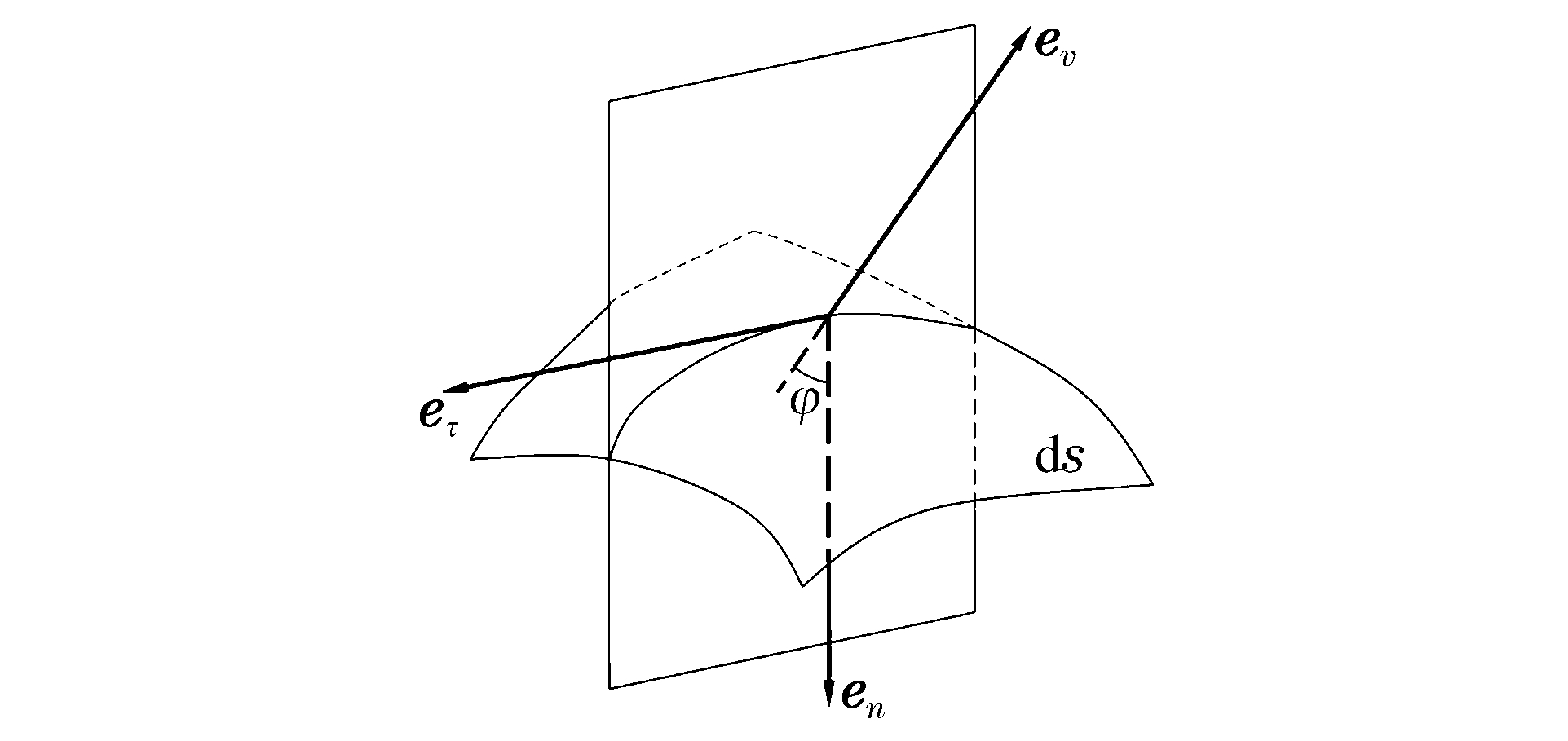
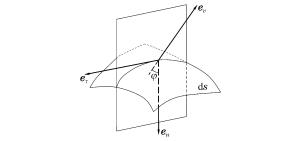
摘要: 以局部相互作用理论为基础,引入与弹体头部形状相关的开坑计算方法和归一化弹体头部形状方程,给出了任意头部形状弹体侵彻混凝土深度的计算模型。利用最大侵深法,得到了无量纲头部形状控制参数表达式及经典变分头部形状优化设计方法。理论计算及弹靶分离仿真模拟计算结果与实验结果吻合较好。研究结果表明:弹体头部相对半径较小时,球头锥形和球头卵形弹体优化后得到的头部形状分别为尖头锥形和尖头卵形;优化截头弹体的侵彻深度大于优化尖头弹体,而优化截锥形弹体的侵彻深度最大;弹体头部形状对弹体侵彻过载的影响显著,优化弹体头部形状可以有效地提高侵彻深度。Abstract: Based on the local interaction theory, we proposed a penetration depth model for projectiles with an arbitrary nose-shape penetrating into a concrete target in consideration of the cratering stage related to nose-shape and normalized nose-shape function. Furthermore, using the method of maximum depth of penetration, we presented an expression about the normalized control parameter of the nose-shape and the classical variational optimization of the nose-shape. The local interaction model prediction and simulation results accord well with the experimental data of different projectile nose shapes. The optimal analysis and simulation show that, when the relative radius of the projectile nose is small, the optimal spherical-tip projectile is similar to corresponding optimal sharp-tip projectile, and the optimized truncated-tip projectiles have better penetration performance than that of the corresponding sharp-tip projectile. Compared with other nose-shaped projectiles, the optimized truncated-conical projectile has a relatively greater penetration depth. As the shape of the projectile nose affects its overload in the penetration process, the optimized shape of the projectile nose can effectively improve the penetration depth of the projectile.
-
表 1 弹体模型参数及混凝土材料参数
Table 1. Parameters for projectile geometry model and concrete material
弹体头部形状 实验编号 弹体模型参数 混凝土材料参数 m/kg dp/mm 弹体头形方程 σc/MPa ρt/(kg·m-3) 尖卵形 1[24] 4.43 57.0 Φ=[228.02-(x-110.4)2]1/2-199.5 35 2 450 2[25] 12.90 76.2 Φ=[228.62-(x-126.4)2]1/2-190.5 39 2 300 截卵形 3[26] 0.28 25.3 Φ=[90.12-(x-33.2)2]1/2-83.8 40 2 300 尖锥形 4[27] 0.08 10.0 Φ=x tan22.5° 44 2 200 5[27] 0.08 10.0 Φ=x 44 2 200 -
[1] Bunimovich A I, Dubinskii A V. Mathematical models and methods of localized interaction theory[M]. Singapore: World Scientific Publishing, 1995. [2] Ben-Dor G, Dubinsky A, Elperin T. Applied high-speed plate penetration dynamics[M]. Netherlands: Springer, 2006. [3] Ben-Dor G, Dubinsky A, Elperin T. High-speed penetration dynamics: Engineering models and methods[M]. Singapore: World Scientific Publishing, 2013. [4] Ben-Dor G, Dubinsky A, Elperin T. High-speed penetration modeling and shape optimization of the projectile penetrating into concrete shields[J]. Mechanics Based Design of Structures and Machines, 2009, 37(4):538-549. doi: 10.1080/15397730903272830 [5] Ben-Dor G, Dubinsky A, Elperin T. Localized interaction models with non-constant friction for rigid penetrating impactors[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2007, 44(7):2593-2607. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ026134457/ [6] Ben-Dor G, Dubinsky A, Elperin T. Numerical solution for shape optimization of an impactor penetrating into a semi-infinite target[J]. Computers & Structures, 2003, 81(1):9-14. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=971c54e8a853179f371f74951cb55a0b [7] Ben-Dor G, Dubinsky A, Elperin T. Shape optimization of impactor penetrating into concrete or limestone targets[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2003, 40(17):4487-4500. doi: 10.1016/S0020-7683(03)00212-9 [8] Ben-Dor G, Dubinsky A, Elperin T. Optimization of the nose shape of an impactor against a semi-infinite FRP laminate[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2002, 62(5):663-667. doi: 10.1016/S0266-3538(02)00006-4 [9] Ben-Dor G, Dubinsky A, Elperin T. Optimization of layered shields with a given areal density[J]. International Journal of Fracture, 1998, 91(1):L9-L14. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=5f80f37c9160d323597558e848e52019 [10] Yakunina G E. The dynamics of pyramidal bodies within the framework of the local interaction model[J]. Journal of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2003, 67(1):11-23. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=5f03b377af7205b50e3688ccdd3dab47&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [11] Yakunina G Y. The three-dimensional motion of optimalpyramidal bodies[J]. Journal of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2005, 69(2):234-243. doi: 10.1016/j.jappmathmech.2005.03.009 [12] Yakunina G. Optimum three-dimensional hypersonic bodies within the framework of a local interaction model[C]//10th AIAA/NAL-NASDA-ISAS International Space Planes and Hypersonic Systems and Technologies Conference, 2001: 11. [13] Yakunna G Y. Effects of sliding friction on the optimal 3D-nose geometry of rigid rods penetrating media[J]. Optimization and Engineering, 2005, 6(3):315-338. doi: 10.1007/s11081-005-1742-6 [14] Ragnedda F, Serra M. Optimum shape of high speed impactor for concrete targets using PSOA heuristic[J]. Engineering, 2010, 2(4):257-262. doi: 10.4236/eng.2010.24035 [15] Jones S E, Rule W K. On the optimal nose geometry for a rigid penetrator, including the effects of pressure-dependent friction[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2000, 24(4):403-415. doi: 10.1016/S0734-743X(99)00157-8 [16] Chen X W, Li Q M. Deep penetration of a non-deformable projectile with different geometrical characteristics[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2002, 27(6):619-637. doi: 10.1016/S0734-743X(02)00005-2 [17] 皮爱国, 黄风雷.基于变分法原理的侵彻弹体头部形状优化设计[J].弹箭与制导学报, 2007, 27(4):126-130. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9728.2007.04.037Pi Aiguo, Huang Fenglei. Based on variation method for the shape optimization of penetrator nose shape[J]. Journal of Projectiles, Rockets, Missiles and Guidance, 2007, 27(4):126-130. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9728.2007.04.037 [18] 刘坚成, 黄风雷, 皮爱国, 等.异型头部弹体增强侵彻性能机理研究[J].爆炸与冲击, 2014, 34(4):409-414. doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2014)04-0409-06Liu Jiancheng, Huang Fenglei, Pi Aiguo, et al. On enhanced penetration performance of modified nose projectiles[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2014, 34(4):409-414. doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2014)04-0409-06 [19] Liu J, Pi A, Huang F. Penetration performance of double-ogive-nose projectiles[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2015, 84:13-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2015.05.003 [20] Forrestal M J, Tzou D Y. A spherical cavity-expansion penetration model for concrete targets[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 1997, 34(31):4127-4146. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=15bb10f7d851f075588b20216506d45c [21] Luk V K, Forrestal M J. Penetration into semi-infinite reinforced-concrete targets with spherical and ogival nose projectiles[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1987, 6(4):291-301. doi: 10.1016/0734-743X(87)90096-0 [22] Li Q M, Chen X W. Dimensionless formulae for penetration depth of concrete target impacted by a non-deformable projectile[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2003, 28(1):93-116. doi: 10.1016/S0734-743X(02)00037-4 [23] Teland J A, Sjøl H. Penetration into concrete by truncated projectiles[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2004, 30(4):447-464. doi: 10.1016/S0734-743X(03)00073-3 [24] 黄民荣.刚性弹体对混凝土靶的侵彻与贯穿机理研究[D].南京: 南京理工大学, 2011. http: //cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10288-1012320967.htm [25] Forrestal M J, Frew D J, Hickerson J P, et al. Penetration of concrete targets with deceleration-time measurements[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2003, 28(5):479-497. doi: 10.1016/S0734-743X(02)00108-2 [26] Qian L, Yang Y, Tong L. A semi-analytical model for truncated-ogive-nose projectiles penetration into semi-infinite concrete targets[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2000, 24(9):947-955. doi: 10.1016/S0734-743X(00)00008-7 [27] 石志勇, 汤文辉, 赵国民, 等.混凝土靶中侵彻深度的相似性研究[J].弹道学报, 2005, 17(1):62-66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-499X.2005.01.012Shi Zhiyong, Tang Wenhui, Zhao Guomin, et al. Similarity study of the penetration depth for the concrete targets[J]. Journal of Ballistics, 2005, 17(1):62-66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-499X.2005.01.012 [28] Ben-Dor G, Dubinsky A, Elperin T. Shape optimization of high-speed penetrators: A review[J]. Central European Journal of Engineering, 2012, 2(4):473-482. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=52a17f483d9239a276eed9a7f8370cd5&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [29] Forrestal M J, Tzou D Y. A spherical cavity-expansion penetration model for concrete targets[J]. International Journal of Solids & Structures, 1997, 34(31):4127-4146. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=9f6cbc41cc8e41622e2eccbe35f1dfdd&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [30] 何涛, 文鹤鸣.卵形钢弹对铝合金靶板侵彻问题的数值模拟[J].高压物理学报, 2006, 20(4):408-414. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5773.2006.04.012He Tao, Wen Heming. Numerical simulations of the penetration of aluminum targets by ogive-nosed steel projectiles[J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2006, 20(4):408-414. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5773.2006.04.012 [31] Fang Q, Kong X, Hong J, et al. Prediction of projectile penetration and perforation by finite cavity expansion method with the free-surface effect[J]. Acta Mechanica Solida Sinica, 2014, 27(6):597-611. doi: 10.1016/S0894-9166(15)60005-2 [32] Li Q M, Flores-Johnson E A. Hard projectile penetration and trajectory stability[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2011, 38(10):815-823. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2011.05.005 -






 下载:
下载: