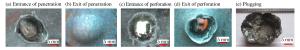
High-speed impact of low-carbon alloy steel plates by ultra-high strength blunt projectiles
-
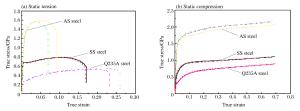
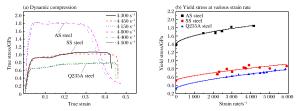
摘要: 为分析不同组分低碳合金钢板抗超高强度低碳合金钢弹体的高速撞击性能及破坏模式,以两种典型防弹特种钢SS、AS以及常见的Q235A钢为研究对象,通过静态拉伸、静态压缩及动态压缩测试,获得静态拉伸和压缩性能参数以及1 000~6 000 s-1应变率范围内的力学行为,分析了材料组分与力学性能的相关性。采用弹道枪加载撞击方法,获得了两种超高强度合金钢平头圆柱形弹体对3种钢板(14.5~15.9 mm厚)的弹道极限速度,通过分析获得了不同工况下的极限比吸收能,讨论了合金钢板在弹体高速撞击下破坏模式的差异,分析了材料力学性能与破坏模式的相关性。研究表明:3种合金钢板抗弹体撞击性能与材料屈服强度正相关,但其性能间的差异远小于屈服强度间的差异;在超高强度合金钢平头圆柱形弹体的高速撞击下,3种钢板的失效机制与其力学性能密切相关,Si和Mn含量高的AS钢呈硬脆性特征,其断裂失效主要取决于材料的剪切强度,而Si和Mn含量较低的SS钢和Q235A钢具有良好的塑性,其断裂失效主要取决于材料的压缩强度和剪切强度。Abstract: To investigate the ballistic resistance and failure mode of three different low-carbon alloy steel plates subjected to ultra-high strength low alloy steel projectiles, we used the typical bulletproof special steels SS and AS and the commonly used Q235A steel for our study in the present research, obtained their static tensile and compression performance and the dynamic mechanical behavior at the strain rate of 1 000 to 6 000 s-1 by static tension, compression and split Hopkinson pressure bar tests respectively, and analyzed the relationship between material composition and mechanical performance. We also obtained the ballistic limits of these plates (14.5~15.9 mm thick) subjected to two ultra-high strength low alloy steel projectiles by ballistic gun experiments. Furthermore, we compared the specific energy absorption and failure mode of the steel plates under various conditions and analyzed the relationship between the mechanical performance and the failure mode. The results showed a positive correlation between the ballistic resistance and the yield strength, but the differences between the ballistic resistances of the three steel plates are less than that between the yield strength. Finally, the failure mechanism of different steel plates is correlated with different mechanical parameters: for the AS steel plates with a high content of Si and Mn, the main determinant of fracture failure is its shear strength, as is characterized by great hardness and brittleness, while for SS and Q235A steel plate with a low content of Si and Mn the main determinant is its compressive and shear strength, as is characterized by good plasticity.
-
表 1 实验用35CrMnSiA的基本力学性能
Table 1. Basic mechanical properties of test 35CrMnSiA
σy/MPa σu/MPa E/GPa HRC δ/% ψ/% 1 387 1 770 187.21 45.3 9.08 40.8 表 2 3种钢的主要化学组分
Table 2. Main chemical compositions of three kinds of steel
材料 质量分数/% C Si Mn Cr Ni S P SS钢 0.07~0.14 0.17~0.37 0.30~0.60 0.90~1.20 2.60~3.00 ≤0.015 ≤0.020 AS钢 0.19~0.25 0.70~1.00 1.50~1.85 ≤0.025 ≤0.020 Q235A钢 0.14~0.22 ≤0.30 0.30~0.65 ≤0.050 ≤0.045 表 3 3种合金钢板的力学性能
Table 3. Mechanical properties of three kinds of alloy steel plate
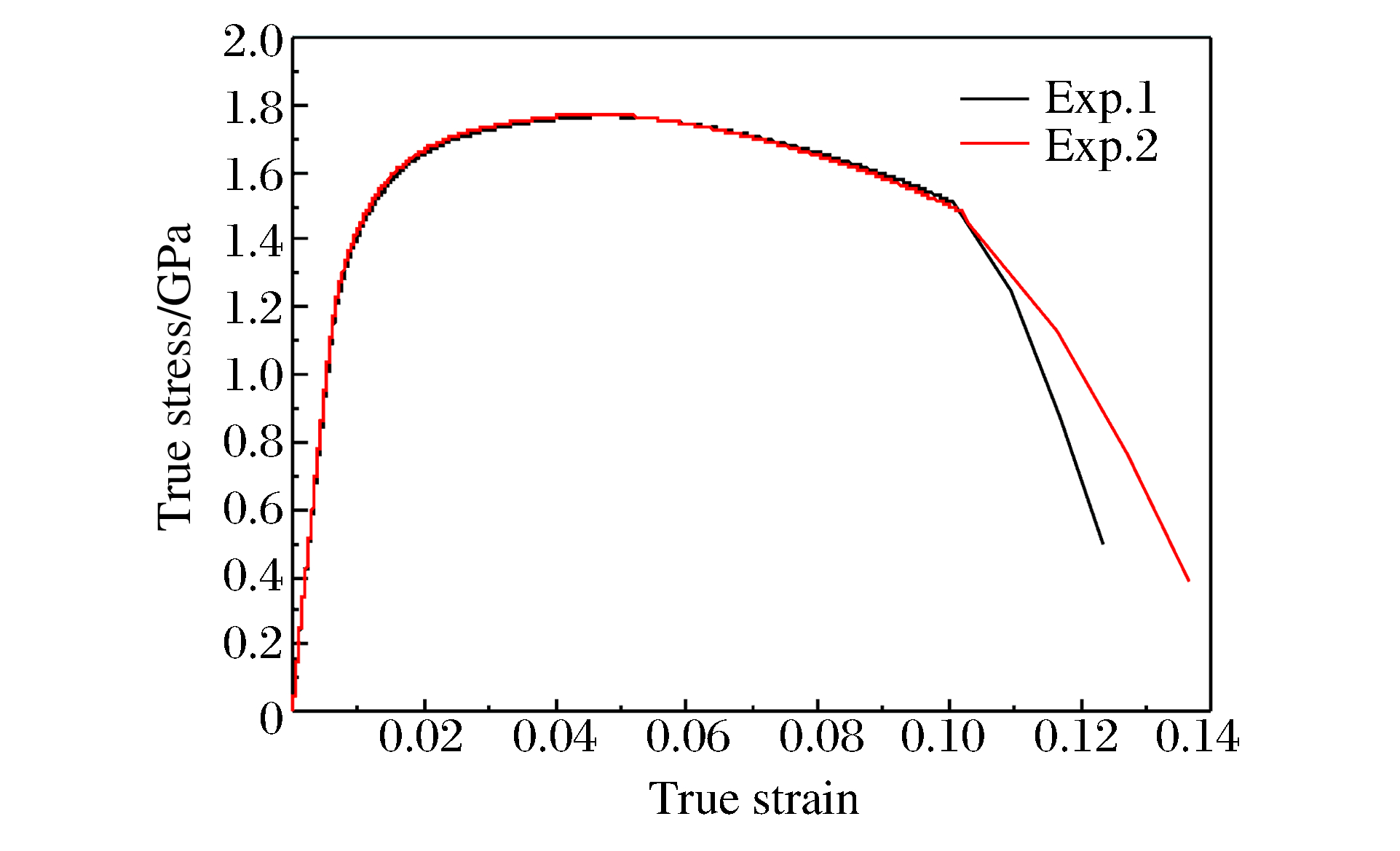
材料 静态压缩与静态拉伸 动态压缩 σy/MPa σu/MPa σy/σu δ/% E/GPa Et/GPa σyc/MPa Ec/GPa Etc/GPa σyc/σy σyd/MPa ${{\dot \varepsilon }_{\rm{t}}}$/s-1 SS钢 665 787 0.84 22.20 204.49 1.358 526 63.35 0.321 0.79 860(4 300~4 450 s-1) 5 900(未断) AS钢 1 211 1 579 0.77 9.00 191.50 9.820 1 387 128.17 0.618 1.15 1 832(4 150~4 800 s-1) 4 150(断裂) Q235A钢 274 546 0.50 31.75 196.26 1.308 321 64.10 0.436 1.17 649(4 400~4 500 s-1) 5 850(未断) 表 4 两种结构弹体撞击3种合金钢板的实验结果
Table 4. Experimental results of three kinds of alloy steel plate impacted by two different projectiles
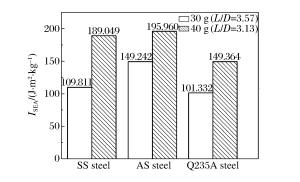
靶体材料 d/mm m/g v/(m·s-1) 穿透情况 v50/(m·s-1) ISEA/(J·m2·kg-1) AS钢 15.0 30 1 177.36
939.58
1 095.07
1 117.86
1 102.47贯穿
未穿
未穿
贯穿
贯穿1 083.27 149.242 40 1 016.34
1 209.30
1 126.35
1 061.22
1 006.47
975.00未穿
贯穿
贯穿
贯穿
贯穿
未穿1 085.55 195.960 SS钢 14.5 30 780.56
884.55
1 054.97
974.56
917.28未穿
未穿
贯穿
贯穿
未穿921.36 109.811 40 891.43
914.96
1 006.45
1 050.51未穿
未穿
未穿
未穿1 050.51 189.049 Q235A钢 15.9 30 696.06
876.83
1 068.10
1 000.00
931.14
974.92
978.06
957.06未穿
未穿
贯穿
贯穿
未穿
贯穿
贯穿
贯穿929.82 101.971 40 1 087.11
959.88
878.87贯穿
贯穿
未穿980.43 150.303 -
[1] Dey S, Børvik T, Hopperstad O S, et al. The effect of target strength on the perforation of steel plates using three different projectile nose shapes[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2004, 30(8/9):1005-1038. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0734743X04000971 [2] Deng Y F, Zhang W, Qing G H, et al. The ballistic performance of metal plates subjected to impact by blunt-nosed projectiles of different strength[J]. Materials & Design, 2014, 54(2):1056-1067. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0261306913008753#! [3] Deng Y F, Zhang W, Yang Y G, et al. The ballistic performance of metal plates subjected to impact by projectiles of different strength[J]. Materials & Design, 2014, 58(6):305-315. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0261306914000119 [4] Dikshit S N, Kutumbarao V V, Sundararajan G. The influence of plate hardness on the ballistic penetration of thick steel plates[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1995, 16(2):293-320. doi: 10.1016/0734-743X(94)00041-T [5] Jena P K, Mishra B, Kumar K S, et al. An experimental study on the ballistic impact behavior of some metallic armour materials against 7.62 mm deformable projectile[J]. Materials & Design, 2010, 31(7):3308-3316. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=662aeef21468aa69a6668ef113c27fbc [6] Jena P K, Mishra B, Rameshbabu M, et al. Effect of heat treatment on mechanical and ballistic properties of a high strength armour steel[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2010, 37(3):242-249. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2009.09.003 [7] Børvik T, Dey S, Clausen A H. Perforation resistance of five different high-strength steel plates subjected to small-arms projectiles[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2009, 36(7):948-964. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2008.12.003 [8] 马鸣图, 黎明, 黄镇如.金属防弹材料的研究进展[J].材料导报, 2005, 19(增刊2):423-424. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cldb2005z2133Ma Mingtu, Li Ming, Huang Zhenru. Research progress of the bulletproof metal materials[J]. Materials Review, 2005, 19(Suppl 2):423-424. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cldb2005z2133 [9] Prytz A K, Odegardstuen G, Sogstad E, et al. Fragmentation of 155 mm artillery grenade, simulations and experiment[C]//26th International Symposium on Ballistics. Miami, Florida, United States, 2011. [10] 黄经伟, 李文彬, 郑宇, 等.大口径榴弹自然破片形成过程[J].兵工自动化, 2013, 32(11):20-23. doi: 10.7690/bgzdh.2013.11.005Huang Jingwei, Li Wenbin, Zheng Yu, et al. Formation of natural fragments from large caliber shells[J]. Ordnance Industry Automation, 2013, 32(11):20-23. doi: 10.7690/bgzdh.2013.11.005 [11] 阎建国, 闵恩泽, 张树才.大口径榴弹钢破片的分析[J].金属材料与热加工工艺, 1983(1):49-57.Yan Jianguo, Min Enze, Zhang Shucai. Analysis of fragments of large caliber grenade steel[J]. Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 1983(1):49-57. [12] 范长刚, 董瀚, 雍岐龙, 等.低合金超高强度钢的研究进展[J].机械工程材料, 2006, 30(8):1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3738.2006.08.001Fan Changgang, Dong Han, Yong Qilong, et al. Research development of ultra-high strength low alloy steels[J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 2006, 30(8):1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3738.2006.08.001 [13] 王富山, 吉嘉龙, 何武, 等.潜艇用10CrNi3MoV、10CrNi3MoCu和10CrNi2MoCu钢板规范: GJB 1663─93[S].北京: 国防科学技术工业委员会, 1993. [14] 杜晨阳, 丛长斌, 张斯博.22SiMn2TiB特种钢板热处理工艺研究[J].金属加工:热加工, 2011(19):58-59. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXRG201119027.htm [15] 吕广庶, 张远明.工程材料及成形技术基础[M].2版.北京:高等教育出版社, 2006:129. [16] 曹柏桢, 凌玉崑, 蒋浩征, 等.飞航导弹战斗部与引信[M].北京:中国宇航出版社, 1995:140. -






 下载:
下载: