Response of reinforced concrete slabs to low-velocity projectile impact investigated using upper bound method
-
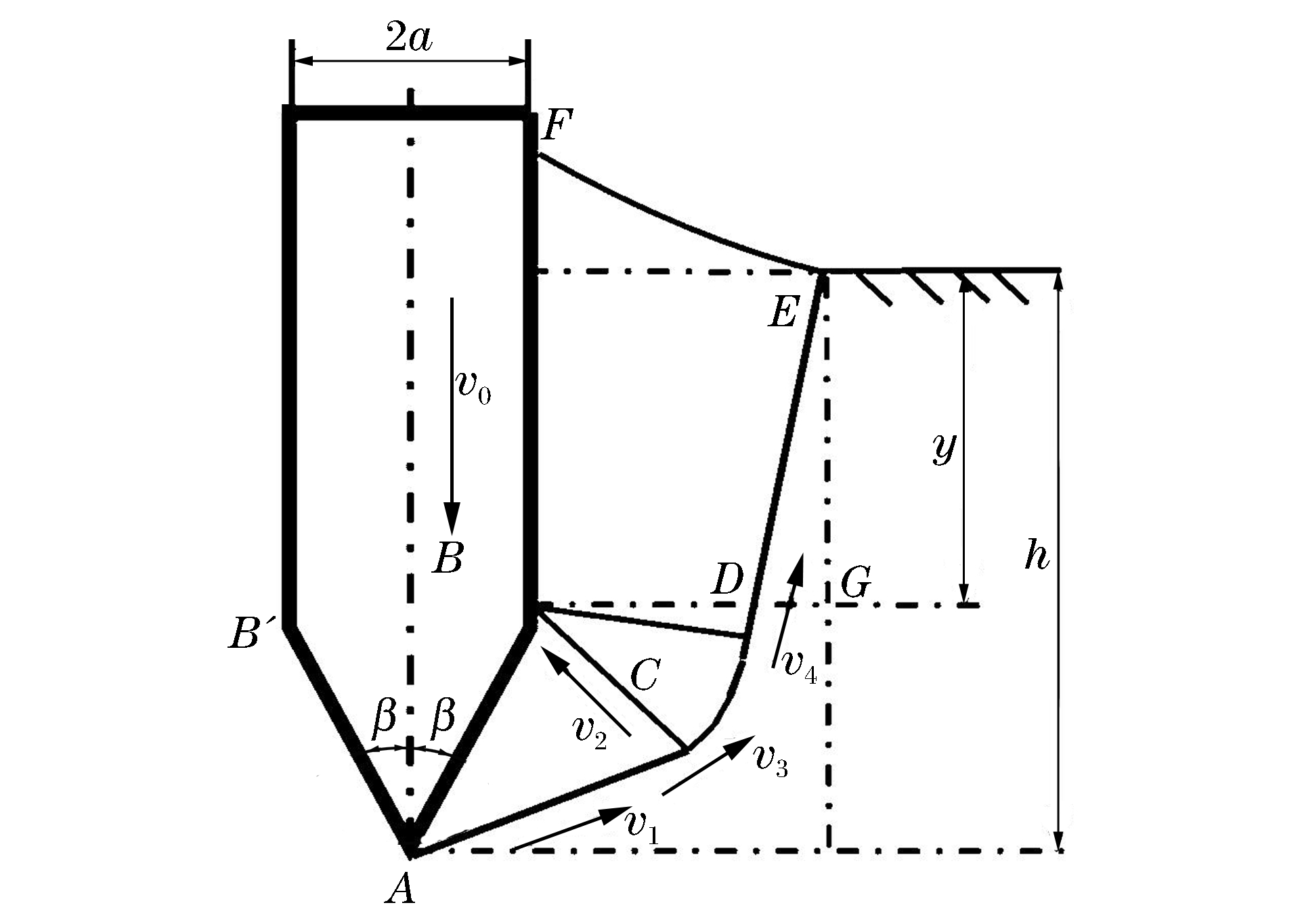
摘要: 基于不可压缩刚塑性材料模型和滑移线场理论,获得了单一容许速度场条件下刚性弹低速侵彻半无限介质的阻力函数。在此基础上,基于多速度容许场得到了刚性弹侵彻有限厚度靶的三阶段阻力曲线,并提出了震塌与贯穿的临界条件,通过与实验结果、UMIST公式及古比雪夫的对比,验证了本文方法在钢筋混凝土板低速撞击问题中的适用性,分析了弹头形状、冲击因子和钢筋阻力系数等参数对临界震塌(贯穿)厚度的影响。Abstract: Based on the incompressible-rigid-plastic material assumption and the slip line field theory, the resistance function of a rigid projectile penetrating a semi-infinite target at a low velocity was obtained with a single admissible velocity field. A three-stage resistance curve of a rigid projectile impacting on a thin target was analyzed under multiple velocity fields, where the critical conditions for scabbing or perforation were calculated. The methods and formulae for local effects on reinforced concrete slab under low-velocity impact were further verified using comparative analysis of the results from the experiments, the UMIST formulae, the Kuibyshev formulae, and the present paper's calculations. The relationships between the normalized critical scabbing/perforation thickness, and the nose-shape factor, the impact factor and the reinforcement factor were examined to present potential guide to experimental studies.
-
Key words:
- rigid-plasticity limit analysis /
- low velocity penetration /
- concrete /
- scabbing /
- perforation
-
实验 L/2a fc /MPa ft/MPa τs/MPa IBL vBL/(m·s-1) 实验 本文计算 T-1 2 25.0 2.6 4.0 10.5 27.0~35.7 47 T-2 2 25.2 3.1 4.4 10.5 41.7~56.8 49 T-3 2 161.9 7.3 17.2 10.5 34.7~58.5 97 T-4 2 175.3 13.8 24.6 10.5 76.0~104.0 116 表 2 本文计算结果与普通混凝土实验[11]的比较
Table 2. Comparison between experimental results [11] of normal strength concrete and present method
实验 L/2a fc /MPa ft/MPa τs/MPa IBL φ/mm @/mm fs/MPa μ vBL/(m·s-1) 配筋 实验 本文计算 D-1-1 2.0 35.0 3.0 5.12 15.9 2.5 34 382 0.43 165 103 D-1-2 2.0 35.0 3.0 5.12 15.4 3.0 25 183 0.40 222 101 D-1-3 2.4 35.0 3.0 5.12 20.8 3.0 25 183 0.40 232 117 D-1-4 2.4 35.0 3.0 5.12 127.1 5.0 27 473 2.68 236 291 D-1-5 2.0 34.0 3.4 5.38 53.6 3.25 21 600 1.76 210 193 D-1-6 2.0 34.0 3.4 5.38 34.8 2.5 20 650 1.19 162 156 表 3 本文计算结果与高性能混凝土实验[12]的比较
Table 3. Comparison between experimental results[12] of high performance concrete and present method
实验 L/2a fc /MPa ft/MPa τs/MPa IBL φ/mm @/mm fs/MPa μ vBL/(m·s-1) 配筋 实验 本文计算 D-2-1 4 40.0 4.0 6.3 66.5 8 100 400 0.64 204~245 187 D-2-2 4 108.0 10.8 17.1 38.3 8 100 400 0.24 273~276 233 D-2-3 4 102.0 10.2 16.1 39.1 8 100 400 0.25 281~289 229 D-2-4 4 104.0 10.4 16.4 38.9 8 100 400 0.24 287~291 231 D-2-5 4 113.0 11.3 17.9 37.7 8 100 400 0.22 262~289 237 D-2-6 4 106.0 10.6 16.8 38.6 8 100 400 0.24 291~307 232 D-2-7 4 101.0 10.1 16.0 39.3 8 100 400 0.25 286~292 229 D-2-8 4 93.0 9.3 14.7 40.7 8 100 400 0.27 292~313 223 D-2-9 4 94.0 9.4 14.9 40.5 8 100 400 0.27 313~314 224 D-2-10 4 102.0 10.2 16.1 39.2 8 100 400 0.25 287~289 229 D-2-11 4 103.0 10.3 16.3 39.0 8 100 400 0.25 287~292 230 -
[1] Hill R. The mathematical theory of plasticity[M]. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1950. [2] Ravid M, Bodner S R. Dynamic perforation of visco-plastic plates by rigid projectiles[J]. International Journal of Engineering Science, 1983, 21(6):577-591. doi: 10.1016/0020-7225(83)90105-2 [3] Amini A, Anderson J. Modeling of projectile penetration into geologic targets based on energy tracking and momentum impulse principles[C]//Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium on Interaction of Nonnuclear Munitions with Structures. Germany, 1993. [4] Tirosh J, Tylis A, Davidi G. Foreign object damage: Penetration of rigid projectiles into solids[J]. Mechanics of Materials, 2009, 41(5):535-544. doi: 10.1016/j.mechmat.2009.01.024 [5] 陈士林, 王明洋, 潘越峰.锥形端部弹体在岩石(混凝土)介质层中侵彻实用计算方法[J].爆炸与冲击, 2004, 24(1):7-15. http://www.bzycj.cn/article/id/9912Chen Shilin, Wang Mingyang, Pan Yuefeng. The method of calculation for penetration of conical nosed projectile in rock (concrete) layers[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2004, 24(1):7-15. http://www.bzycj.cn/article/id/9912 [6] 王明洋, 施翠英, 陈士林.事故型撞击混凝土板的临界震塌与贯穿厚度计算方法[J].工程力学, 2009, 26(11):238-246. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GCLX200911042.htmWang Mingyang, Shi Cuiying, Chen Shilin. Method of calculating critical spalling and penetration thickness of concrete slab of block under accident impact[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2009, 26(11):238-246. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GCLX200911042.htm [7] 冯淑芳, 王明洋, 任广昊, 等.深地下坑道衬砌结构抗局部冲击计算方法研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2011, 30(6):1150-1156. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yslxygcxb201106008Feng Shufang, Wang Mingyang, Ren Guanghao, et al. Research on calculation method for local impact of deep tunnel lining structure[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2011, 30(6):1150-1156. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yslxygcxb201106008 [8] 咸玉席, 文鹤鸣.平头弹侵彻半无限混凝土靶的工程模型[J].防护工程, 2012, 34(2):35-38. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10358-1014432193.htmXian Yuxi, Wen Heming. An engineering model for the penetration of flat-nosed projectiles into semi-infinite concrete targets[J]. Protective Engineering, 2012, 34(2):35-38. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10358-1014432193.htm [9] Li Q M, Ye Z Q, Ma G W, et al. Influence of overall structural response on perforation of concrete targets[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2007, 34(5):926-941. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2006.03.005 [10] Tai Y S. Flat ended projectile penetrating ultra-high strength concrete plate target[J]. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics, 2009, 51(2):117-128. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ0214989790/ [11] Dancygier A N. Effect of reinforcement ratio on the resistance of reinforced concrete to hard projectile impact[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 1997, 172(1):233-245. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=723b6881b18fa7ba33bf200ca91ae81f&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [12] Dancygier A N, Yankelevsky D Z, Jaegermann C. Response of high performance concrete plates to impact of non-deforming projectiles[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2007, 34(11):1768-1779. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2006.09.094 [13] 卡恰诺夫L M.塑性理论基础(第二版)[M].周承倜, 译.北京: 人民教育出版社, 1982: 332-385. [14] 冯淑芳.深埋地下结构抗爆动力计算方法研究[D].南京: 解放军理工大学, 2011. [15] 徐秉业, 刘信声.应用弹塑性力学[M].北京:清华大学出版社, 1995:510-512. [16] Wen H M, Xian Y U. A unified approach for concrete impact[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2015, 77:84-96. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2014.11.015 -







 下载:
下载: