Experimental study of fuel-air mixture explosion characteristics in the short pipe containing weakly confined face at the end
-
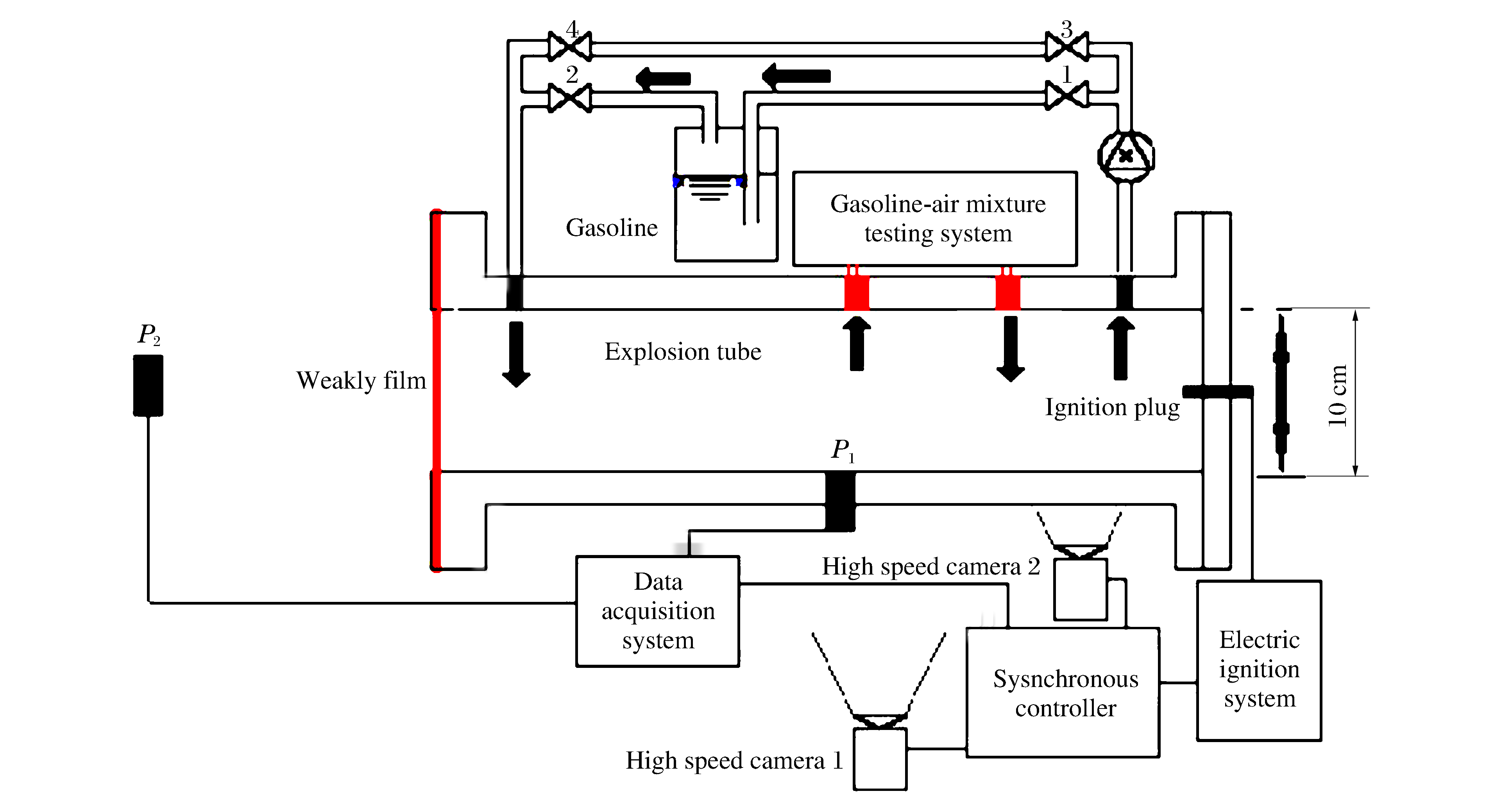
摘要: 构建了长径比为4的含弱约束端面的短管道实验系统,对短管道油气爆炸特性进行了实验研究,得到油气爆炸压力和火焰的变化规律。实验结果表明:(1)受破膜、泄流、外部爆炸等因素的影响,含弱约束端面短管道油气爆炸具有多个超压峰值,并产生Helmholtz振荡;(2)弱约束端面对管道内外爆炸超压均具有增强作用,内部最大超压为24.23 kPa,外部最大超压为5.45 kPa,分别为无约束条件下的4.9和2.7倍;(3)火焰变化过程可划分为“层流燃烧-突变加速-外部爆炸-衰弱熄灭”4个阶段;由于湍流、界面不稳定、斜压效应等因素的影响,火焰在突变加速和外部爆炸两个阶段会发生剧烈的拉伸褶皱和卷曲变形,形成Tulip火焰和蘑菇云状火焰。(4)在层流燃烧阶段,弱约束端面对火焰速度有减弱作用,此阶段最大火焰速度为3.5 m/s,相比于无约束时减弱了41.3%;而在突变加速和外部爆炸阶段,弱约束端面破坏产生的强泄流对火焰传播速度有增强作用,此阶段最大火焰速度为80.2 m/s,相比于无约束时增强了106.2%。(5)不同初始油气浓度条件下火焰发展模式具有显著差异,在低浓度和中浓度条件下火焰能够冲出弱约束端面形成外部火球,而在高浓度条件下,火焰无法冲出管道。Abstract: In this paper, we studied the characteristics of the fuel-air mixture explosion using an experiment system built in a short pipe containing a weakly confined face at the end, with the following results achieved. (1) Multiple pressure peaks were observed due to the rupture, discharge, external explosion, accompanied with the Helmholtz oscillation. (2) The constraint surface produced a strengthening effect on the explosion overpressure, the maximum internal overpressure being 24.23 kPa and the maximum external overpressure being 5.45 kPa, respectively 4.9 and 2.7 times that of the pressure as compared in an unconstrained structure. (3) The morphological changes of the flame can be divided into four stages, those of the laminar combustion, the mutation and acceleration, the external explosion, and the extinction. Due to the influence of such factors as turbulence, interface instability and baroclinic effects, the flame shape was folded and crimped, forming a tulip during the mutation and acceleration stage and a sphere during the external explosion stage. (4) During the laminar combustion stage, the weakly confined face had a lessening effect on the flame speed, with 3.5 m/s as its maximum, which is reduced by 41.3%. In the states of mutation-acceleration and external explosion, the destruction of the confined surface had a strengthening effect on the flame speed, with 80.2 m/s as its maximum, which is enhanced by 106.2%. (5) The flame development made a significant difference at different concentrations. The flame can break through the weak confinement and form an external explosion at low and medium concentration, while at high concentration, the flame was unable to do so.
-
Key words:
- fuel-gas mixture /
- short pipe /
- weakly confined film /
- overpressure /
- flame propagation speed
-
表 1 管道内部爆炸特性对比
Table 1. Comparison of internal explosion characteristics
端部条件 pb/kPa pfv/kPa tfv/s pext/kPa text/s pref/kPa 振荡期 Δt/s T/s 有约束 24.23 22.07 0.047 22.07 0.047 6.71 有 0.009 0.003 无约束 - 1.28 0.016 4.97 0.051 - 无 - - 注:pb为破膜超压峰值;pfv为泄流冲击超压峰值;tfv为泄流冲击超压峰值时刻;pext为外部爆炸超压峰值;text为外部爆炸超压峰值时刻;pref为回流燃烧超压;Δt为震荡持续时间;T为振荡周期。 表 2 管道外部爆炸特性对比
Table 2. Comparison of external explosion characteristics
端部条件 pb/kPa pext/kPa text/s 振荡期 Δt/s T/s 有约束 1.94 5.45 0.048 有 0.009 0.003 无约束 - 2.02 0.053 无 - - 表 3 不同油气体积分数下的油气爆燃火焰发展特性
Table 3. Flame development at different oil volume fraction
CCH/
%火焰发展类型 封闭爆炸阶段 开口发展阶段 衰弱阶段 1.07 A D G 1.23 A D G 1.50 A E G 1.83 B F G 2.07 B F G 2.20 B E G 2.45 C E G 2.60 C - - 2.76 C - - 2.90 C - - 3.15 Null Null Null 注:A-光滑椭球形层流火焰,B-鳞状褶皱椭球层流火焰,C-卷曲絮状火焰,D-射流火焰,E-球形火焰,F蘑菇云状火焰,G-衰弱熄灭,Null-未燃 -
[1] 王引群.矿井瓦斯爆炸火焰传播试验研究[J].山西煤炭, 2012(9):52-53. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=sxmt201209019&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQWANG Yinqun. Experimental study on flame propagation of gas explosion in mines[J]. Shanxi Coal, 2012(9):52-53. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=sxmt201209019&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [2] 温小萍, 武建军, 解茂昭.瓦斯爆炸火焰结构与压力波的耦合规律[J].化工学报, 2013(10):3871-3877. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=hgsz201310057&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQWEN Xiaoping, WU Jianjun, XIE Maozhao. Coupled relationship between flame structure and pressure wave of gas explosion[J]. CIESC Journal, 2013(10):3871-3877. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=hgsz201310057&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [3] CAO W, Gao W, LIANG J, et al. Flame-propagation behavior and a dynamic model for the thermal-radiation effects in coal-dust explosions[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2014, 29(1):65-71. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0950423014000254 [4] KIM W K, MOGI T, DOBASHI R. Flame acceleration in unconfined hydrogen/air deflagrations using infrared photography[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2013, 26(6):1501-1505. doi: 10.1016/j.jlp.2013.09.009 [5] NISHIMURA I, MOGI T, DOBASHI R. Simple method for predicting pressure behavior during gas explosions in confined spaces considering flame instabilities[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2013, 26(2):351-354. doi: 10.1016/j.jlp.2011.08.009 [6] SNOEYS J, GOING J E, TAVEAU J M R. Advances in dust explosion protection techniques: flameless venting[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2012, 45(3):403-413. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1877705812031906 [7] YAN X, YU J, GAO W. Flame behaviors and pressure characteristics of vented dust explosions at elevated static activation overpressures[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2015, 33:101-108. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0950423014002058 [8] TOMLIN G, JOHNSON D M, CRONIN P, et al. The effect of vent size and congestion in large-scale vented natural gas/air explosions[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2015, 35:169-181. doi: 10.1016/j.jlp.2015.04.014 [9] MOLKOV V, MAKAROV D. LES modelling of an unconfined large-scale hydrogen-air deflagration[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2006, 39(18):4366-4376. https://www.mendeley.com/research-papers/les-modelling-unconfined-largescale-hydrogenair-deflagration/ [10] QIAO A, ZHANG S. Advanced CFD modeling on vapor dispersion and vapor cloud explosion[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2010, 23(6):843-848. doi: 10.1016/j.jlp.2010.06.006 [11] DADASHZADEH M, KHAN F, HAWBOLDT K, et al. An integrated approach for fire and explosion consequence modelling[J]. Fire Safety Journal, 2013, 61(5):324-337. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0379711213001586 [12] TOMIZUKA T, KUWANA K, SHIMIZU K, et al. Estimation of turbulent flame speed during DME/air premixed gaseous explosions[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2013, 26(2):369-373. doi: 10.1016/j.jlp.2011.09.004 [13] 齐圣. 受限空间油气爆燃及其细水雾抑制实验研究与数值仿真[D]. 重庆: 解放军后勤工程学院, 2014. [14] FAKANDU B M, ANDREWS G E, PHYLAKTOU H N. Vent burst pressure effects on vented gas explosion reduced pressure[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2015, 36: 429-438. doi: 10.1016/j.jlp.2015.02.005 [15] CHAO J, BAUWENS C R, DOROFEEV S B. An analysis of peak overpressures in vented gaseous explosions[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2011, 33(2):2367-2374. doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2010.06.144 [16] 姜孝海. 泄爆外流场的动力学机理研究[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2004. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10288-2005031547.htm -







 下载:
下载: