Trend removing methods of vibration signals of deep hole bench blasting in near field
-
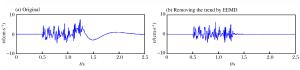
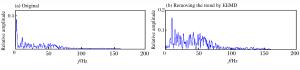
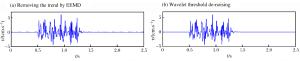
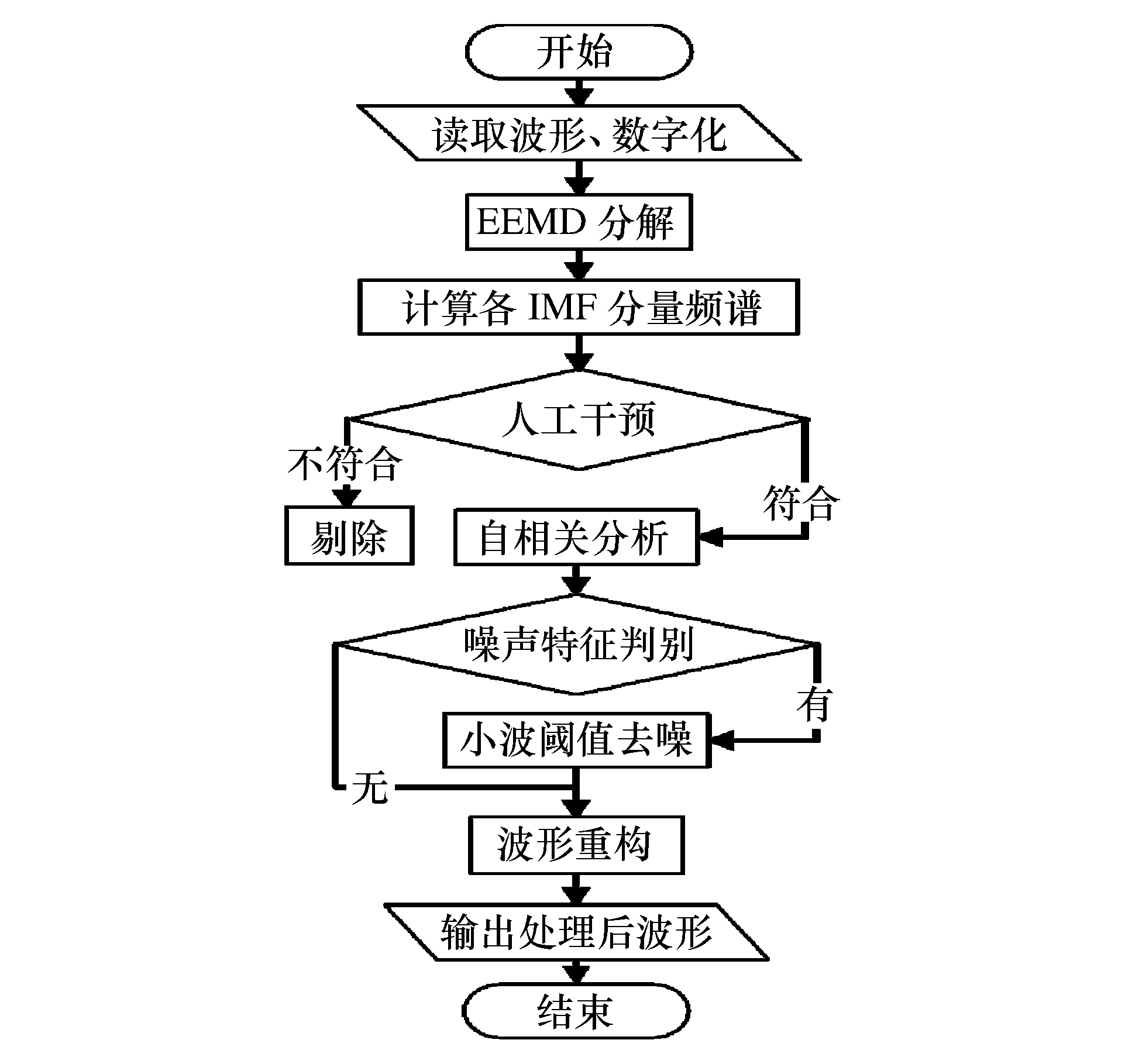
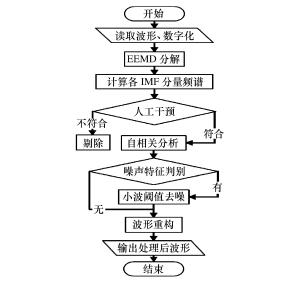
摘要: 基于深孔台阶爆破近区大量实测振动信号,总结了趋势项产生的原因主要为大振幅脉冲输入下的非线性失真及低频干扰叠加,在此基础上以测试仪器有效监测范围作为识别趋势项组成部分的判别准则。利用集合经验模态分解(ensemble empirical mode decomposition,EEMD)、小波分解等信号分析手段,提出了以固有模态函数(intrinsic mode function,IMF)的频带分布为指标、人工判别的趋势项去除方法,以及基于自相关分析识别噪声特征的小波阈值去噪方法。实例证明该方法切实有效,可实现爆破信号的批量化预处理。Abstract: Based on a large number of measured vibration signals of deep hole bench blasting in near field, this paper has contributed the trend mainly to the nonlinear distortion and the low frequency interference superposition with a large amplitude pulse input. On this basis, the effective monitoring range of test instruments has been chosen as criteria to identify the part of the trend. Using ensemble empirical mode decomposition (EEMD), the wavelet analysis, and other signal analysis methods, a trend elimination method is proposed here, which is based on the combination of the frequency band distribution of each intrinsic mode function component and artificial identification. In addition, a wavelet threshold denoising method is also proposed based on autocorrelation analysis to identify noise characteristics. Examples show that the methods are effective and can be realized by batch pretreatment of blasting signals.
-
Key words:
- near field /
- blasting vibration /
- trend /
- EEMD /
- autocorrelation analysis /
- wavelet /
- denoising
-
表 1 信号测试条件
Table 1. Conditions of the test signal
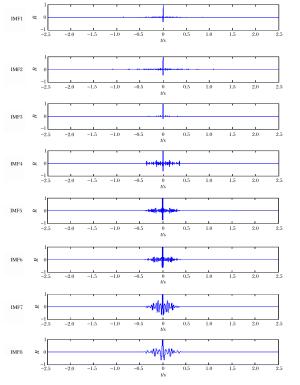
测区 爆心距/m 最大段药量/kg 近区 65 2280 表 2 各IMF分量主频
Table 2. Dominant frequency of each IMF component
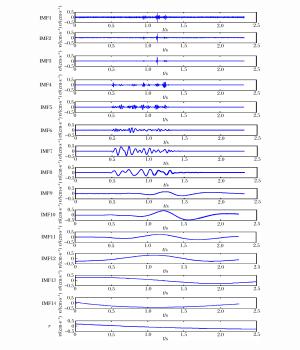
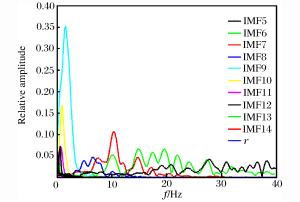
IMF分量 主频/Hz IMF1 33.40 IMF2 14.40 IMF3 39.20 IMF4 32.40 IMF5 36.40 IMF6 19.40 IMF7 10.40 IMF8 7.60 IMF9 1.60 IMF10 1.00 IMF11 0.80 IMF12 0.60 IMF13 0.40 IMF14 0.20 r 0.00 -
[1] 陈燕, 刘哲, 郑宾, 等.基于LabVIEW的测试信号预处理方法研究[J].国外电子测量技术, 2008, 27(10):4-5, 16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8978.2008.10.002CHEN Yan, LIU Zhe, ZHENG Bin, et al. Study on test signal pre-processing method based on LabVIEW[J]. Foreign Electronic Measurement Technology, 2008, 27(10):4-5, 16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8978.2008.10.002 [2] 王若平, 杨彦朋, 王国林, 等. EMD在路面不平度信号趋势中的应用[J].拖拉机与农用运输车, 2010, 27(10):64-66. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=tljynyysc201004024WANG Ruoping, YANG Yanpeng, WANG Guolin, et al. Application of EMD to road routhness trend[J]. Tractor and Farm Transporter, 2010, 27(10):64-66. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=tljynyysc201004024 [3] 朱学峰, 韩宁.基于经验模态分解的非平稳信号趋势项消除[J].飞行器测控学报, 2012, 31(1):65-70. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fxqckxb201201016ZHU Xuefeng, HAN Ning. Removal of non-stationary signal trend items by empirical mode decomposition[J]. Journal of Spacecraft TT&C Technology, 2012, 31(1):65-70. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fxqckxb201201016 [4] 龙源, 谢全民, 钟明寿, 等.爆破震动测试信号预处理分析中趋势项去除方法研究[J].工程力学, 2012, 29(10):63-68. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK201205321457LONG Yuan, XIE Quanmin, ZHONG Mingshou, et al. Research on trend removing methods in preprocessing analysis of blasting vibration monitoring signals[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2012, 29(10):63-68. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK201205321457 [5] WU Zhaohua, HUANG N E. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition:a noise assisted data analysis method[J]. Advances in Adaptive Data Analysis, 2009, 1(1):1-41.DOI: 10.1142/S1793536909000047 [6] 朱艳芹, 杨先麟.几种基于小波阈值去噪的改进方法[J].电子测试, 2008(2):18-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8519.2008.02.005ZHU Yanqin, YANG Xianlin. Several new methods based on wavelet thresholding denoising[J]. Electronic Test, 2008(2):18-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8519.2008.02.005 [7] 李夕兵, 张义平, 刘志祥.爆破震动信号的小波分析与HHT变换[J].爆炸与冲击, 2005, 25(6):528-535. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1455.2005.06.008LI Xibing, ZHANG Yiping, LIU Zhixiang. Wavelet analysis and Hilbert-Huang transform of blasting vibration signal[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2005, 25(6):528-535. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1455.2005.06.008 [8] 肖立波, 任建亭, 杨海峰.振动信号预处理方法研究及其MATLAB实现[J].计算机仿真, 2010, 27(8):330-337. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2010.08.081XIAO Libo, REN Jianting, YANG Haifeng. Study on vibration signal pre-processing method based on Matlab[J]. Computer Simulation, 2010, 27(8):330-337. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2010.08.081 [9] 徐长发, 李国宽.实用小波方法[M].武汉:华中科技大学出版社, 2005. [10] 陈隽, 李杰.振动信号趋势项提取的几种方法及其比较[J].福州大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 33(增刊):42-45. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fzdxxb2005z1009CHEN Jun, LI Jie. Methods for signal trend extraction and their comparison[J]. Journal of Fuzhou University (Natural Sciences Edtion), 2005, 33(Suppl):42-45. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fzdxxb2005z1009 -






 下载:
下载: