Effect of surface roughness on impact expansion fracture of 6061 aluminum alloy thin-walled cylindrical tube
-
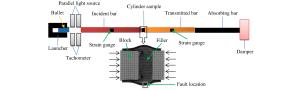
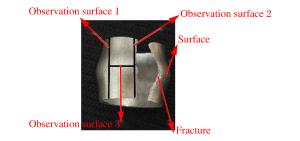
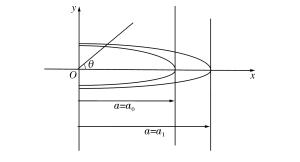
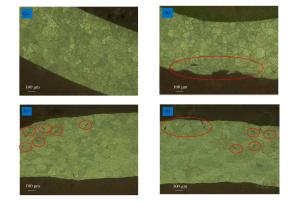
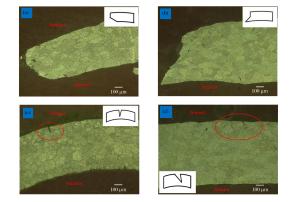
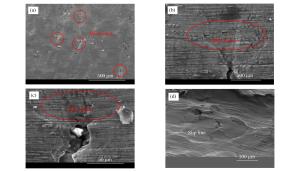
摘要: 采用分离式霍普金森杆实验技术,对表面加工后不同粗糙度的6061铝合金薄壁圆柱管进行动态膨胀断裂冻结回收实验,并对薄壁金属圆柱管动态膨胀断裂过程中裂纹萌生、扩展情况以及最终断裂模式等进行了研究。结果表明:相同冲击压力条件下,薄壁金属圆柱管表面粗糙度越大,材料越容易发生膨胀破裂;裂纹萌生于外壁面,由外向内扩展,并且裂纹的扩展主要受裂纹处应力状态的影响;薄壁金属圆柱管的断裂模式由拉伸和剪切断裂机制起主导作用,其断口为拉剪混合型断口。Abstract: Dynamic expansion crack freezing recovery tests of 6061 aluminum alloy thin-walled cylindrical tubes with different roughnesses after surface processing were carried out with the split Hopkinson pressure bar experimental technique, and the crack initiation, propagation and final fracture mode of the thin-walled metal cylindrical tubes of dynamic expansion fracture process were studied. The results show that: under the same impact pressure, the greater the surface roughness of the thin-walled metal cylindrical tube, the more prone to the expansion of the material in the process of expanding fracture; the crack initiating on the surface of the outer wall is extended from the outside to the inside, and the crack propagation is mainly affected by the stress state at the crack; the fracture mode is dominated by the tensile and shear fracture mechanism, the fracture mode is a mixed type of tension and shear fracture.
-
表 1 6061铝合金主要化学成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of 6061 aluminum alloy
化学元素 Mg Si Fe Cu Cr Zn Mn Ti 质量分数/% 0.8~1.2 0.4~0.8 0.7 0.15~0.40 0.04~0.35 0.25 0.15 0.15 表 2 6061铝合金物理性能参数
Table 2. Physical property parameters of 6061 aluminum alloy
ρ/(g·cm-3) ν 延伸率 Tm/℃ σt/MPa E/GPa 2.69 0.330 > 10% 582~652 > 205 68.9 表 3 薄壁圆柱管实验参数
Table 3. Experimental parameters of thin-walled cylindrical tubes
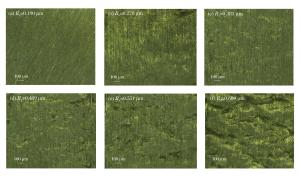
No. Ra/μm 1 0.190 2 0.243 3 0.278 4 0.314 5 0.385 6 0.414 7 0.489 8 0.551 9 0.689 -
[1] MOTT N F. A theory of fragmentation of shells and bombs[M]. Berlin: Springer Publishing, 2006:243-294. [2] TAYLOR G I. The fragmentation of tubular bombs[G]//Batchelor G K. The Scientific Papers of Sir Geoffrey Ingram Taylor: Vol. 3. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1963: 387-390. [3] 马晓青.冲击动力学[M].北京:北京理工大学出版社, 1992:282-294. [4] 汤铁钢, 李庆忠, 孙学林, 等.45钢柱壳膨胀断裂的应变率效应[J].爆炸与冲击, 2006, 26(2):35-39. http://www.bzycj.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9208.shtmlTANG Tiegang, LI Qingzhong, SUN Xuelin, et al. Strain-rate effects of expanding fracture of 45 steel cylinder shells driven by detonation[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2006, 26(2):35-396. http://www.bzycj.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9208.shtml [5] 汤铁钢, 李庆忠, 陈永涛, 等.实现材料高应变率拉伸加载的爆炸膨胀环技术[J].爆炸与冲击, 2009, 29(1):45-46. doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2009)01-0045-04TANG Tiegang, LI Qingzhong, CHEN Yongtao, et al. An improved technique for dynamic tension of metal ring by explosive loading[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2009, 29(1):45-46. doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2009)01-0045-04 [6] 汤铁钢, 谷岩, 李庆忠, 等.爆轰加载下金属柱管膨胀破裂过程研究[J].爆炸与冲击, 2003, 23(6):529-533. http://www.bzycj.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10103.shtmlTANG Tiegang, GU Yan, LI Qingzhong, et al. Expanding fracture of steel cylinder shell by detonation driving [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2003, 23(6):529-533. http://www.bzycj.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10103.shtml [7] HOGGATT C R, RECHT R F. Fracture behavior of tubular bombs[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1968, 39(3):1856-1862. doi: 10.1063/1.1656442 [8] 胡八一, 董庆东, 韩长生, 等.内部爆轰加载下的钢管膨胀断裂研究[J].爆炸与冲击, 1993, 13(1):49-54. http://www.bzycj.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10657.shtmlHU Bayi, DONG Qingdong, HAN Changsheng, et al. Studies of expansion and fracture of explosive-filled steel cylinders[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 1993, 13(1):49-54. http://www.bzycj.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10657.shtml [9] 叶想平, 李英雷, 张祖根.45钢薄壁圆柱管的冲击膨胀断裂机理研究[J].爆炸与冲击, 2014, 31(3):322-327. doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2014)03-0322-06YE Xiangping, LI Yinglei, ZHANG Zugen, et al. Study on the fracture mechanism of 45 steel thin walled cylindrical tube[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2014, 31(3):322-327. doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2014)03-0322-06 [10] 叶想平. 薄壁金属圆柱管的冲击膨胀断裂行为研究[D]. 绵阳: 中国工程物理研究院, 2012. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-82818-1012499404.htm [11] 叶想平, 李英雷, 李英华.基于SHPB装置的膨胀圆柱管实验技术[J].爆炸与冲击, 2012, 32(5):528-534. doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2012)05-0528-07YE Xiangping, LI Yinglei, LI Yinghua. Experimental technique of expanding cylinder tube based on SHPB device[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2012, 32(5):528-534. doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2012)05-0528-07 [12] 熊峻江.疲劳断裂可靠性工程学[M].北京:国防工业出版社, 2008:15-17. [13] 孙兆霞.6061铝合金冲击载荷作用下的变形断裂行为[J].轻合金加工技术, 2012, 40(7):65-69. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qhjjgjs201207015SUN Zhaoxia. Deformation and fracture behavior of 6061 aluminum alloy under impact load[J]. Light Alloy Fabrication Technology, 2012, 40(7):65-69. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qhjjgjs201207015 [14] 朱浩, 吕丹, 朱亮, 等.6061铝合金断裂机理的原位拉伸研究[J].机械工程学报, 2009, 45(2):94-99. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jxgcxb200902017ZHU Hao, LV Dan, ZHU Liang, et al. Study on the fracture mechanism of 6061 aluminum alloy by in-situ tension[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2009, 45(2):94-99. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jxgcxb200902017 [15] 高重阳, 施惠基, 姚振汉, 等.薄壁柱壳在内部爆炸载荷下膨胀断裂的研究[J].爆炸与冲击, 2000, 20(2):160-167. http://www.bzycj.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10273.shtmlGAO Chongyang, SHI Huiji, YAO Zhenhan, et al. Study on the expansion fracture of thin walled cylindrical shell under internal explosion load[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2000, 20(2):160-167. http://www.bzycj.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10273.shtml -







 下载:
下载: