Numerical simulation on spallation and fragmentation of tin under explosive loading
-
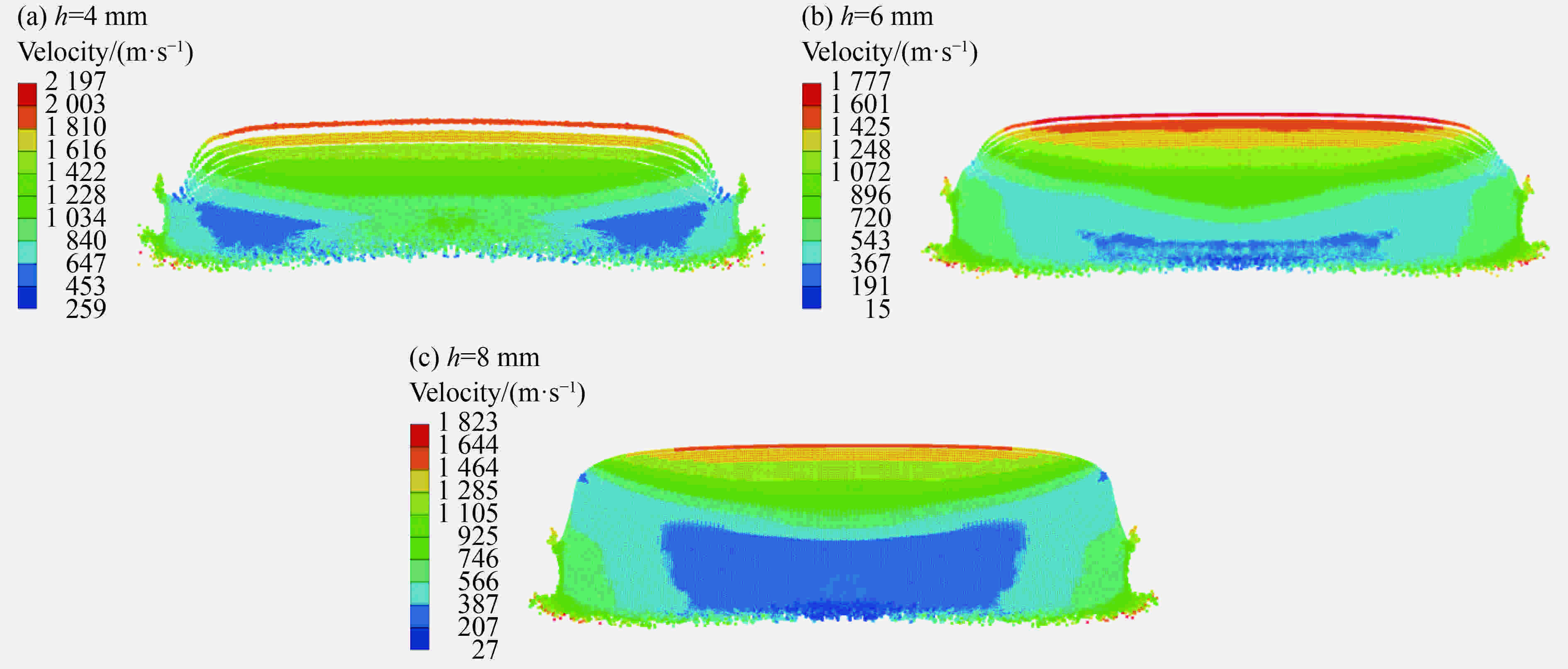
摘要: 对爆轰加载下低熔点金属锡的层裂破碎问题开展了数值模拟。在利用实验数据对所采用数值方法和材料模型开展对比验证的基础上,通过对样品内部物理量时间及空间分布演化对比分析,剖析了冲击加-卸载中样品内部应力波与材料相互作用过程。此外,通过对比分析不同厚度锡样品在爆轰加载下的动态行为特征,进一步认识了自由面反射稀疏波、边侧稀疏波和入射稀疏波共同作用下层裂破碎演化机制。结果表明,当样品较薄时,层裂破碎行为由反射稀疏波主导;随着样品厚度的增大,反射稀疏波主导区缩小,入射稀疏波和边侧稀疏波主导区逐渐增大。Abstract: Spallation and fragmentation of tin, a low-melting point metal under explosive loading were numerically simulated. The numerical method and material model used were validated by the experimental results. Thereby, the temporal evolution and spatial distribution of the physical quantities in the Sn specimens were compared to explore the interaction between the stress waves and the material in the specimen under impact loading and unloading. Furthermore, the dynamic behaviors of the specimens with various thicknesses under explosive loading were in-depth analyzed to further understand the evolution mechanism of the spallation and fragmentation under the combination action of the reflective rarefaction wave from the free surface, the lateral rarefaction wave and the incident rarefaction wave. The results show that for the thin specimen, the early spallation and fragmentation are dominated by the reflective rarefaction wave. With increasing the thickness of the specimen, the region dominated by the reflective rarefaction wave becomes smaller, and meanwhile the region dominated by the incident rarefaction wave and the lateral rarefaction wave becomes larger.
-
Key words:
- explosive loading /
- tin /
- spallation and fragmentation /
- stress wave /
- evolution mechanism
-
表 1 Sn和Al的SG本构参数
Table 1. The material parameters in SG constitutive relation for Sn and Al
材料 G0/GPa Y0/GPa Ymax/GPa $ \beta $ $ \eta $ $ {G_{{p}}'}$ $ {{{G}}_{{T}}'}/\rm{(MPa}\cdot {{\rm{K}}^{-1}}\rm{)}$ $ {Y_{{p}}'}$ $ {T_{{\rm{m0}}}}/{\rm{K}}$ Sn 17.9 0.16 0.22 2 000 0.06 1.55 −37.95 0.013 9 656.6 Al 2.86 0.26 0.76 310 0.185 1.86 −17.62 0.016 9 1 220 表 2 Sn和Al的Mie-Grüneisen状态方程参数
Table 2. The material parameters in Mie-Grüneisen equation of state for Sn and Al
材料 $ {{\rho }_{0}}\rm{/(g}\cdot \rm{c}{{\rm{m}}^{\rm{-3}}}\rm{)}$ $ {{c}_{0}}\rm{/(m}\cdot {{\rm{s}}^{-1}}\rm{)}$ $ {S_1}$ $ \gamma $ Sn 7.287 2 590 1.49 2.27 Al 2.785 5 328 1.338 2.0 表 3 高能炸药JWL状态方程参数
Table 3. The parameters in JWL equation of state for high explosive
$ {{\rho }_{\rm{e}}}/(\rm{g}\cdot \rm{c}{{\rm{m}}^{-3}}\rm{)}$ $ D/\rm{(m}\cdot {{\rm{s}}^{-1}}\rm{)}$ $ {p_{\rm{e}}}/{\rm{GPa}}$ $ A/{\rm{GPa}}$ $ B/{\rm{GPa}}$ $ {R_1}$ $ {R_2}$ $ \omega $ $ {{e}_{\rm{e}}}\rm{/(GJ}\cdot {{\rm{m}}^{\rm{-3}}}\rm{)}$ 1.85 8 710 34.4 824.8 7.06 4.3 0.79 0.28 10.2 -
[1] ANDRIOT P, CHAPRON P, LAMBERT V, et al. Influence of melting on shocked free surface behaviour using Doppler laser interferometry and X-ray densitometry [C] // AIP Conference Proceedings: Shock Waves in Condensed Matter, 1983: 277−280. DOI: 10.1016/b978-0-444-86904-3.50065-8. [2] ZHIEMBETOV A K, MIKHAYLOV A L, SMIRNOV G S. Experimental study of explosive fragmentation of metals melts [C] // AIP Conference Proceedings: Shock Compression of Condensed Matter, 2001: 547−552. DOI: 10.1063/1.1483598. [3] HOLTKAMP D B, CLARK D A, FERME N, et al. A survey of high explosive-induced damage and spall in selected metals using proton radiography [C] // AIP Conference Proceedings: Shock Compression of Condensed Matter, 2004: 477−482. DOI: 10.1063/1.1780281. [4] ANTOUN T, SEAMAN L, CURRAN D R, et al. Spall fracture [M]. New York: Springer, 2002: 1−34. [5] HOPKINSON B. A method of measuring the pressure produced in the detonation of high explosives or by the impact of bullets [J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1914, 213: 437–456. DOI: 10.1098/rsta.1914.0010. [6] SIGNOR L, RESSEGUIER T D, ROY G, et al. Fragment-size prediction during dynamic fragmentation of shock-melted tin: recovery experiments and modeling issues [C] // AIP Conference Proceedings: Shock Compression of Condensed Matter, 2007: 593−596. DOI: 10.1063/1.2833159. [7] RESSEGUIER T D, SIGNOR L, DRAGON A, et al. Dynamic fragmentation of laser shock-melted tin: experiment and modelling [J]. International Journal of Fracture, 2010, 163(1/2): 109–119. [8] 陈永涛, 任国武, 汤铁钢, 等. 爆轰加载下金属样品的熔化破碎现象诊断 [J]. 物理学报, 2013, 62(11): 116202 doi: 10.7498/aps.62.116202CHEN Yongtao, HONG Renwu, TANG Tiegang, et al. Experimental diagnostic of melting fragments under explosive loading [J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2013, 62(11): 116202 doi: 10.7498/aps.62.116202 [9] 陈永涛, 洪仁楷, 陈浩玉, 等. 爆轰加载下金属材料的微层裂现象 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2017, 37(1): 61–67. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2017)01-0061-07CHEN Yongtao, HONG Renkai, CHEN Haoyu, et al. Micro-spalling of metal under explosive loading [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2017, 37(1): 61–67. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2017)01-0061-07 [10] CHEN Y, HONG R, CHEN H, et al. An improved Asay window technique for investigating the micro-spall of an explosively-driven tin [J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2017, 88(1): 013904. doi: 10.1063/1.4973699 [11] 张林, 李英华, 张祖根, 等. 用于诊断材料微层裂的Asay窗技术 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2017, 37(4): 692–698. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2017)04-0692-07ZHANG Lin, LI Yinghua, ZHANG Zugen, et al. Asay window for probing the microspall of materials [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2017, 37(4): 692–698. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2017)04-0692-07 [12] SOULARD L. Molecular dynamics study of the micro-spallation [J]. The European Physical Journal D, 2008, 50(3): 241–251. DOI: 10.1140/epjd/e2008-00212-2. [13] XIANG M, HU H, CHEN J, et al. Molecular dynamics simulations of micro-spallation of single crystal lead [J]. Modelling and Simulation in Materials Science and Engineering, 2013, 21(5): 055005. doi: 10.1088/0965-0393/21/5/055005 [14] XIANG M, HU H, CHEN J. Spalling and melting in nanocrystalline Pb under shock loading: molecular dynamics studies [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2013, 113(14): 144312. doi: 10.1063/1.4799388 [15] 曹结东, 刘文韬, 张树道. 爆轰驱动锡微层裂的数值模拟研究 [C] // 第十四届全国激波与激波管学术会, 2010: 153−157. [16] 张锁春. 光滑质点流体动力学(SPH)方法: 综述 [J]. 计算物理, 1996, 13(4): 385–397ZHANG Suochun. Smoothedparticle hydrodynamics (SPH) method: a review [J]. Chinese Journal of Computation Physics, 1996, 13(4): 385–397 [17] 刘谋斌, 宗智, 常建忠. 光滑粒子动力学方法的发展与应用 [J]. 力学进展, 2011, 41(2): 217–234LIU Moubin, ZONG zhi, CHANG Jianzhong. Developements and applications of smoothed particle hydrodynamics [J]. Advances in Mechanics, 2011, 41(2): 217–234 [18] STEINBERG D J, COCHRAN S G, Guinan M W. A constitutive model for metals applicable at high-strain rate [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1980, 51(3): 1498–1504. doi: 10.1063/1.327799 [19] GRADY D E. The spall strength of condensed matter [J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 1988, 36(3): 353–384. doi: 10.1016/0022-5096(88)90015-4 -







 下载:
下载: