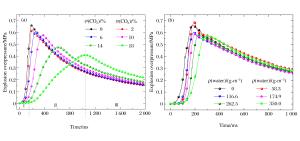
| [1] |
郑立刚, 苏洋, 李刚, 等.点火位置对氢气/甲烷/空气预混气体爆燃特性的影响[J].化工学报, 2017, 68(12):4874-4881. DOI: 10.11949/j.issn.0438-1157.20170369.ZHENG Ligang, SU Yang, LI Gang, et al. Effect of ignition position on deflagration characteristics of premixed hydrogen/methane/air[J]. CIESC Journal, 2017, 68(12):4874-4881. DOI: 10.11949/j.issn.0438-1157.20170369.
|
| [2] |
SCHWER D A, KAILASANATH K. Numerical simulations of the mitigation of unconfined explosions using water-mist[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2007, 31(2):2361-2369. DOI: 10.1016/j.proci.2006.07.145.
|
| [3] |
ANANTH R, WILLAUER H D, FARLEY J P, et al. Effects of fine water mist on a confined blast[J]. Fire Technology, 2012, 48(3):641-675. DOI: 10.1007/s10694-010-0156-y.
|
| [4] |
HOLBORN P G, BATTERSBY P, INGRAM J M, et al. Modelling the mitigation of lean hydrogen deflagrations in a vented cylindrical rig with water fog[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2012, 37(20):15406-15422. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.07.131.
|
| [5] |
LENTATI A M, CHELLIAH H K. Physical, thermal, and chemical effects of fine-water droplets in extinguishing counterflow diffusion flames[J]. Symposium on Combustion, 1998, 27(2):2839-2846. DOI: 10.1016/S0082-0784(98)80142-2.
|
| [6] |
YOSHIDA A, OKAWA T, EBINA W, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation of flame speed retardation by water mist[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2015, 162(5):1772-1777. DOI: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2014.11.038.
|
| [7] |
CAO X Y, REN J J, BI M S, et al. Experimental research on methane/air explosion inhibition using ultrafine water mist containing additive[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2016, 43:352-360. DOI: 10.1016/j.jlp.2016.06.012.
|
| [8] |
GU R, WANG X S, XU H L. Experimental study on suppression of methane explosion with ultra-fine water mist[J]. Fire Safety Science, 2010, 19(2):51-59. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5309.2010.02.001.
|
| [9] |
HOLBORN P G, BATTERSBY P, INGRAM J M, et al. Modelling the mitigation of hydrogen deflagrations in a vented cylindrical rig with water fog and nitrogen dilution[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2013, 38(8):3741-3487. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.12.134.
|
| [10] |
MODAK A U, ABBUD-MADRID A, DELPLANQUE J P, et al. The effect of mono-dispersed water mist on the suppression of laminar premixed hydrogen-, methane-, and propane-air flames[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2006, 144(1):103-111. DOI: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2005.07.003.
|
| [11] |
BOECK L R, KINK A, OEZDIN D, et al. Influence of water mist on flame acceleration, DDT and detonation in H2-air mixtures[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40(21):6995-7004. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.03.129.
|
| [12] |
BATTERSBY P N, AVERILL A F, INGRAM J M, et al. Suppression of hydrogen-oxygen-nitrogen explosions by fine water mist:Part 2. Mitigation of vented deflagrations[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2012, 37(24):19258-19267. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.10.029.
|
| [13] |
INGRAM J M, AVERILL A F, BATTERSBY P N, et al. Suppression of hydrogen-oxygen-nitrogen explosions by fine water mist:Part 1. Burning velocity[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2012, 37(24):19250-19257. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.09.092.
|
| [14] |
VOLLMER K G, ETTNER F, SATTELMAYER T. Deflagration-to-detonation transition in hydrogen/air mixtures with a concentration gradient[J]. Combustion Science and Technology, 2012, 184(10/11):1903-1915. DOI: 10.1080/00102202.2012.690652.
|
| [15] |
GIERAS M. Flame acceleration due to water droplets action[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2008, 21(4):472-477. DOI: 10.1016/j.jlp.2008.03.004.
|
| [16] |
余明高, 安安, 游浩.细水雾抑制管道瓦斯爆炸的实验研究[J].煤炭学报, 2011, 36(3):417-422. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2011.03.025.YU Minggao, AN An, YOU Hao. Experimental study on inhibiting the gas explosion by water spray in tube[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2011, 36(3):417-422. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2011.03.025.
|
| [17] |
曹兴岩, 任婧杰, 周一卉, 等.超细水雾增强与抑制甲烷/空气爆炸的机理分析[J].煤炭学报, 2016, 41(7):1711-1719. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2015.1726.CAO Xingyan, REN Jingjie, ZHOU Yihui, et al. Analysis on the enhancement and suppression of methane/air explosions by ultrafine water mist[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2016, 41(7):1711-1719. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2015.1726.
|
| [18] |
CAO X Y, REN J J, ZHOU Y H, et al. Suppression of methane/air explosion by ultrafine water mist containing sodium chloride additive[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 285:311-318. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.11.016.
|
| [19] |
PEI B, YU M G, CHEN L W, et al. Experimental study on the synergistic inhibition effect of nitrogen and ultrafine water mist on gas explosion in a vented duct[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2016, 40:546-553. DOI: 10.1016/j.jlp.2016.02.005.
|
| [20] |
CHELLIAH H K, LAZZARINI A K, WANIGARATHNE P C, et al. Inhibition of premixed and non-premixed flames with fine droplets of water and solutions[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2002, 29(1):369-376. DOI: 10.1016/S1540-7489(02)80049-9.
|
| [21] |
暴秀超, 刘福水, 孙作宇.预混火焰胞状不稳定性研究[J].西华大学学报:自然科学版, 2014, 33(1):79-83. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-159X.2014.01.019.BAO Xiuchao, LIU Fushui, SUN Zuoyu. Study on instability of outwardly propagating spherical premixed flame[J]. Journal of Xihua University:Natural Science Edition, 2014, 33(1):79-83. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-159X.2014.01.019.
|
| [22] |
张鹏鹏.超细水雾增强与抑制瓦斯爆炸的实验研究[D].大连: 大连理工大学, 2013: 35-37. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10141-1013201707.htm
|
| [23] |
暴秀超, 刘福水, 张正芳.不同初始压力下氢气燃烧的胞状不稳定性及自加速性[J].燃烧科学与技术, 2014, 20(1):38-43. DOI: 10.11715/rskxjs.R201307020.BAO Xiuchao, LIU Fushui, ZHANG Zhengfang. Cellular instability and self-acceleration of hydrogen combustionat various initial pressure[J]. Journal of Combustion Science and Technology, 2014, 20(1):38-43. DOI: 10.11715/rskxjs.R201307020.
|







 下载:
下载: