Experimental and numerical study on projectiles’ high-velocity penetration into reinforced concrete
-
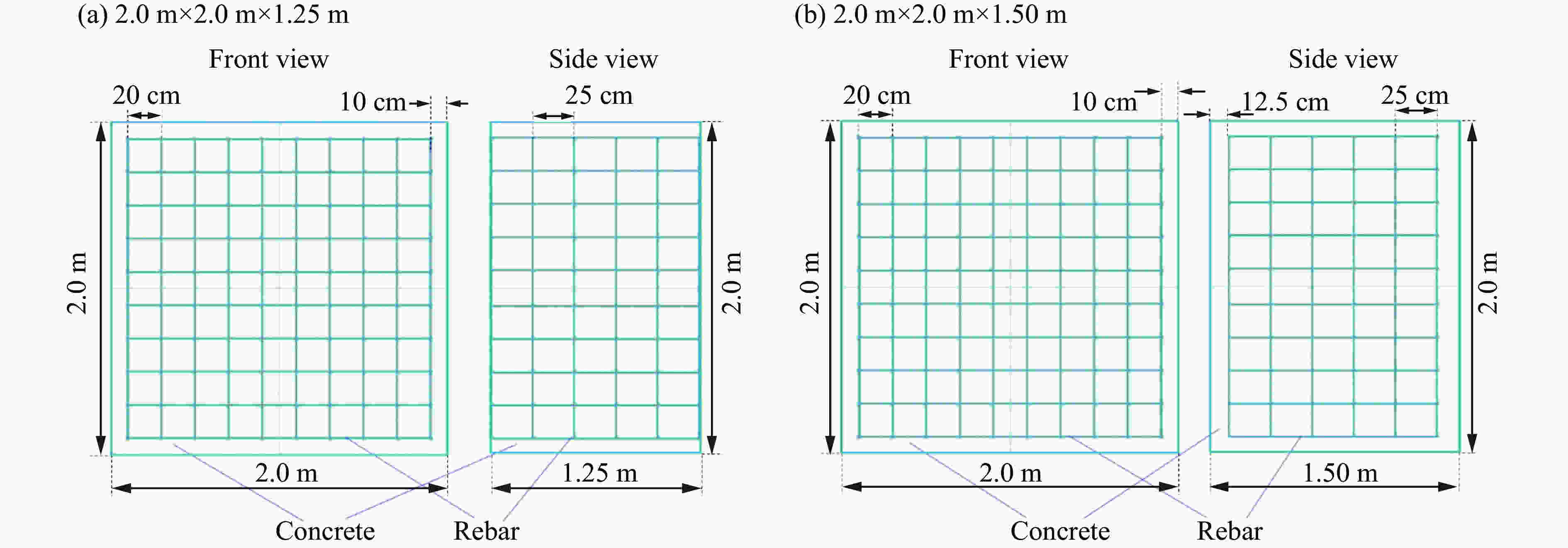
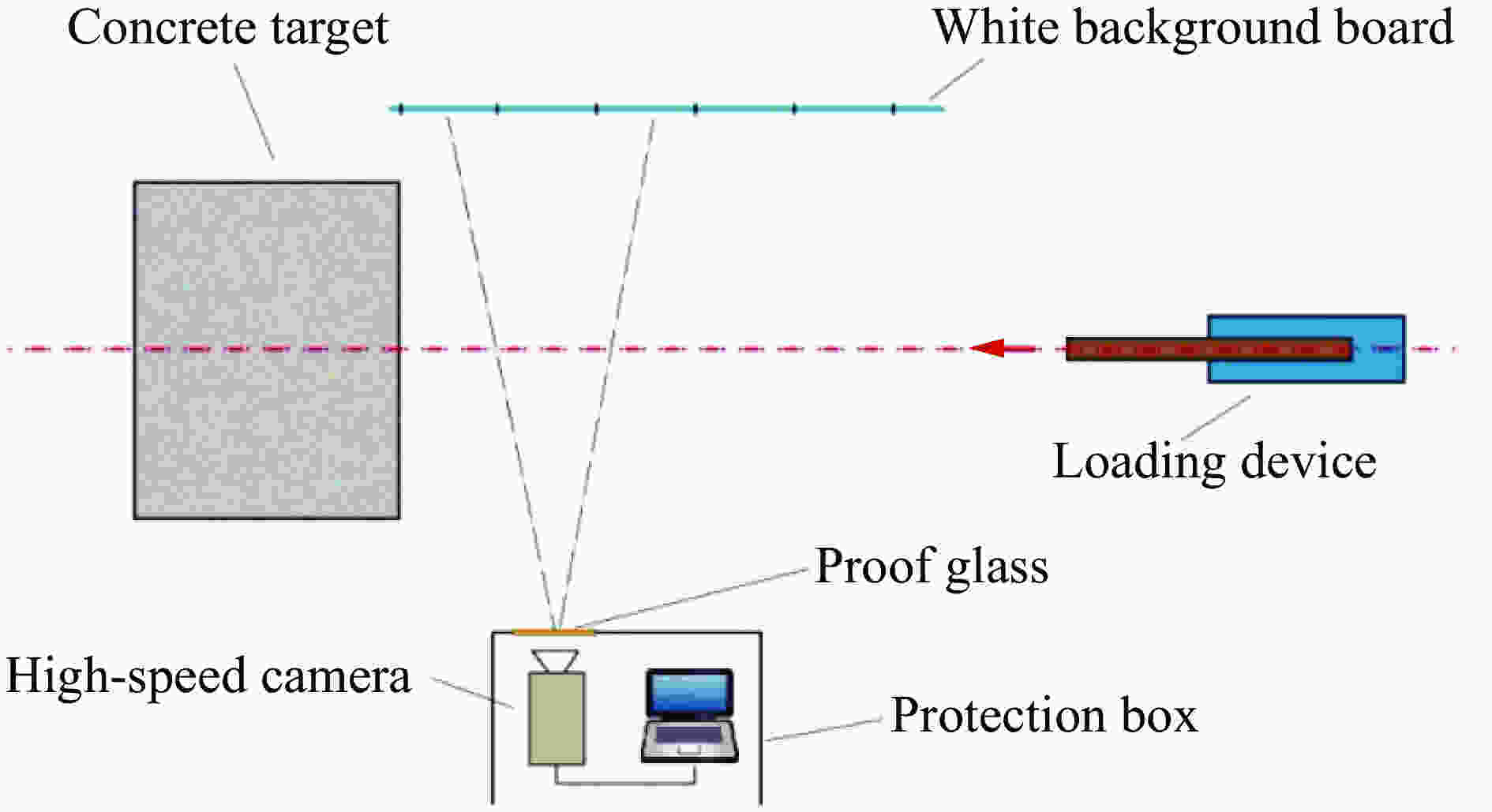
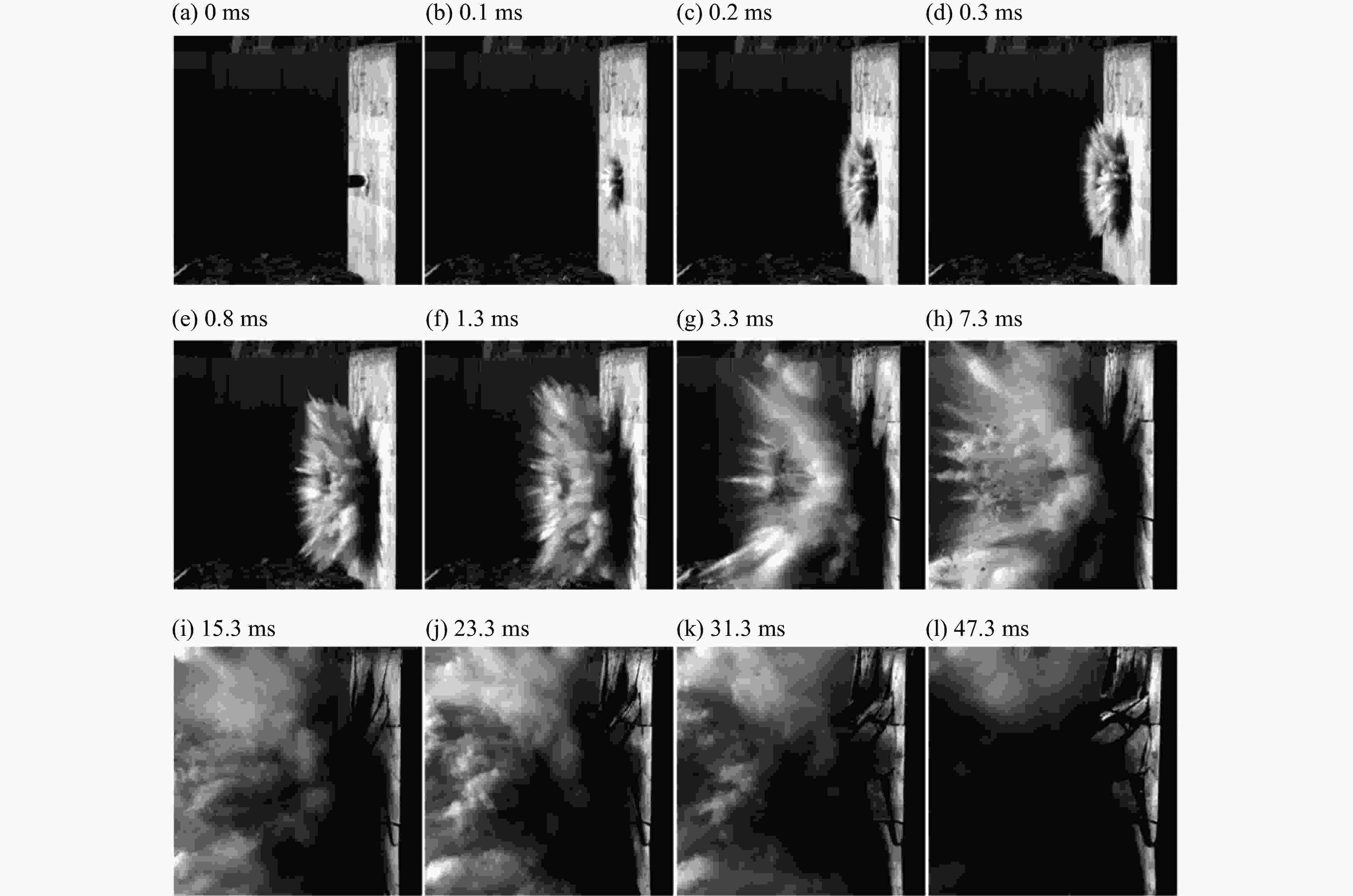
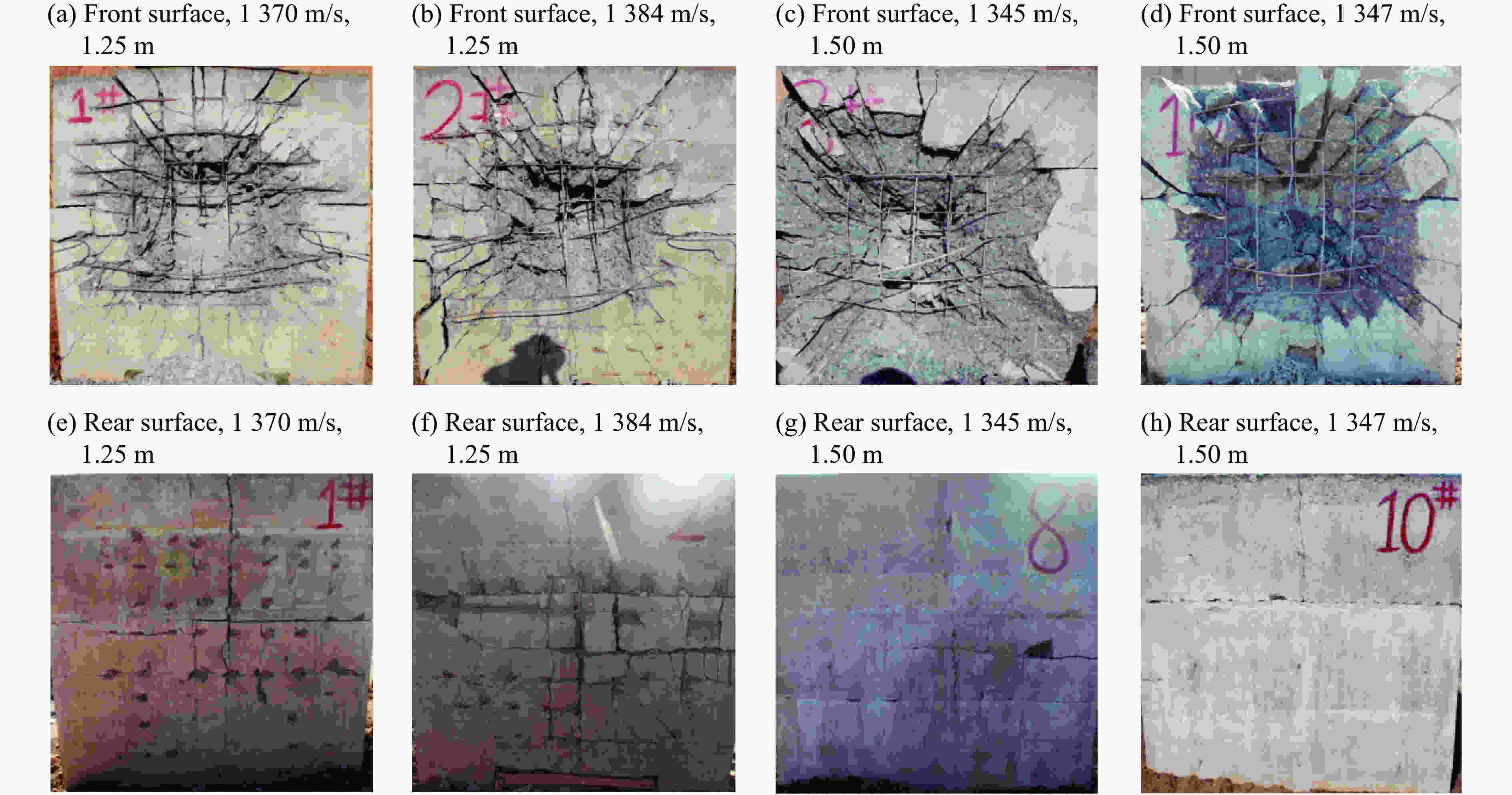
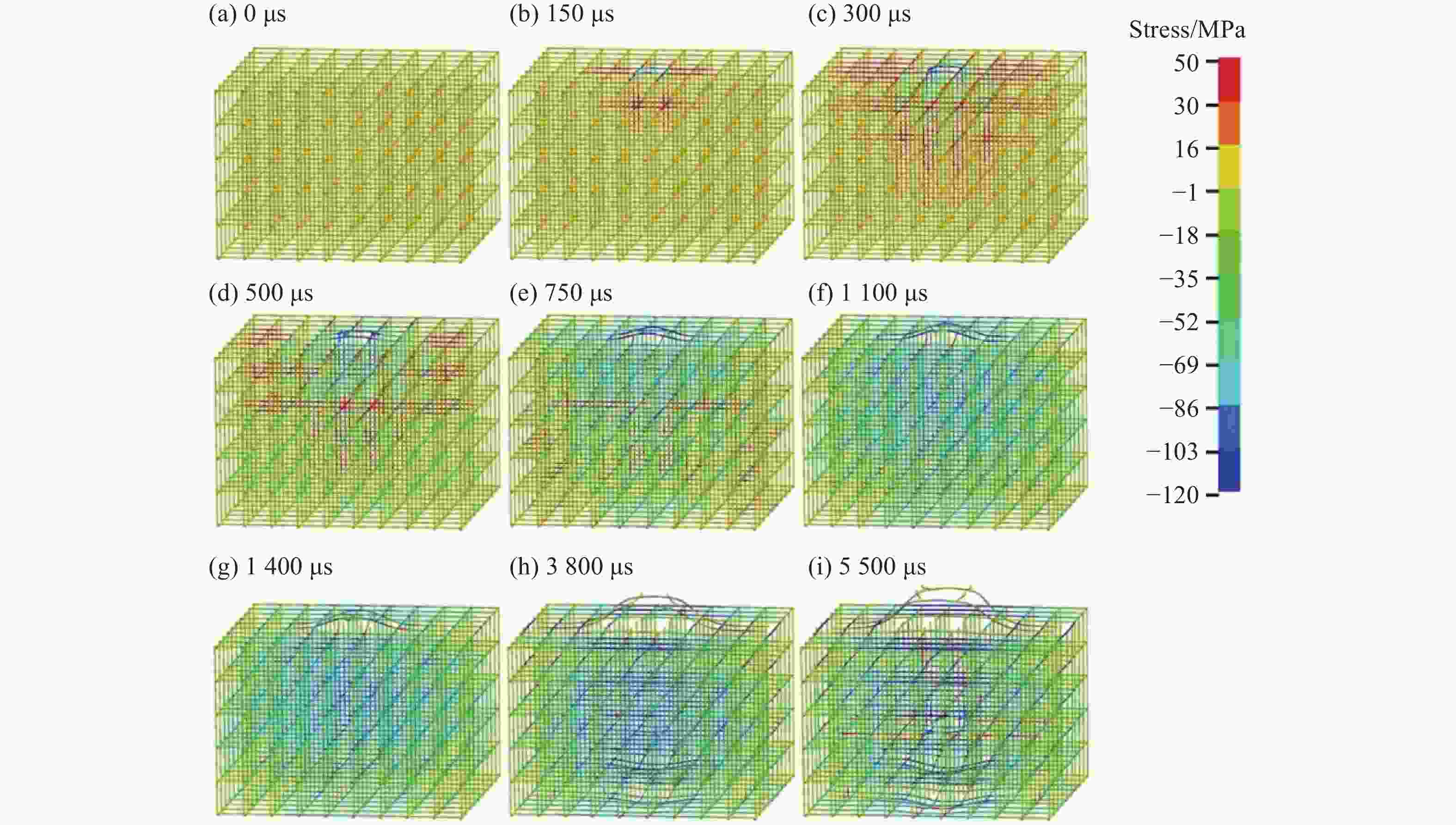
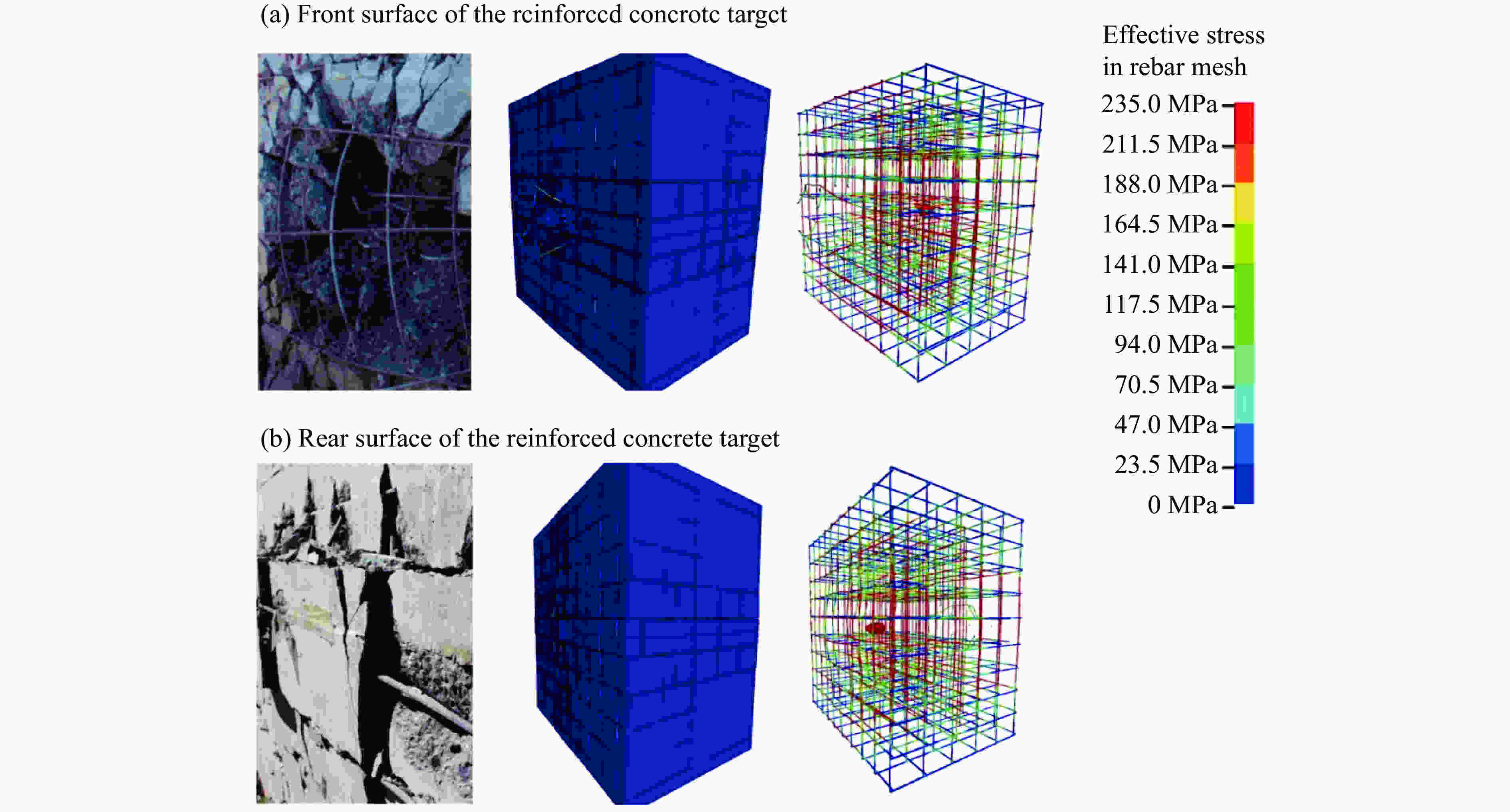
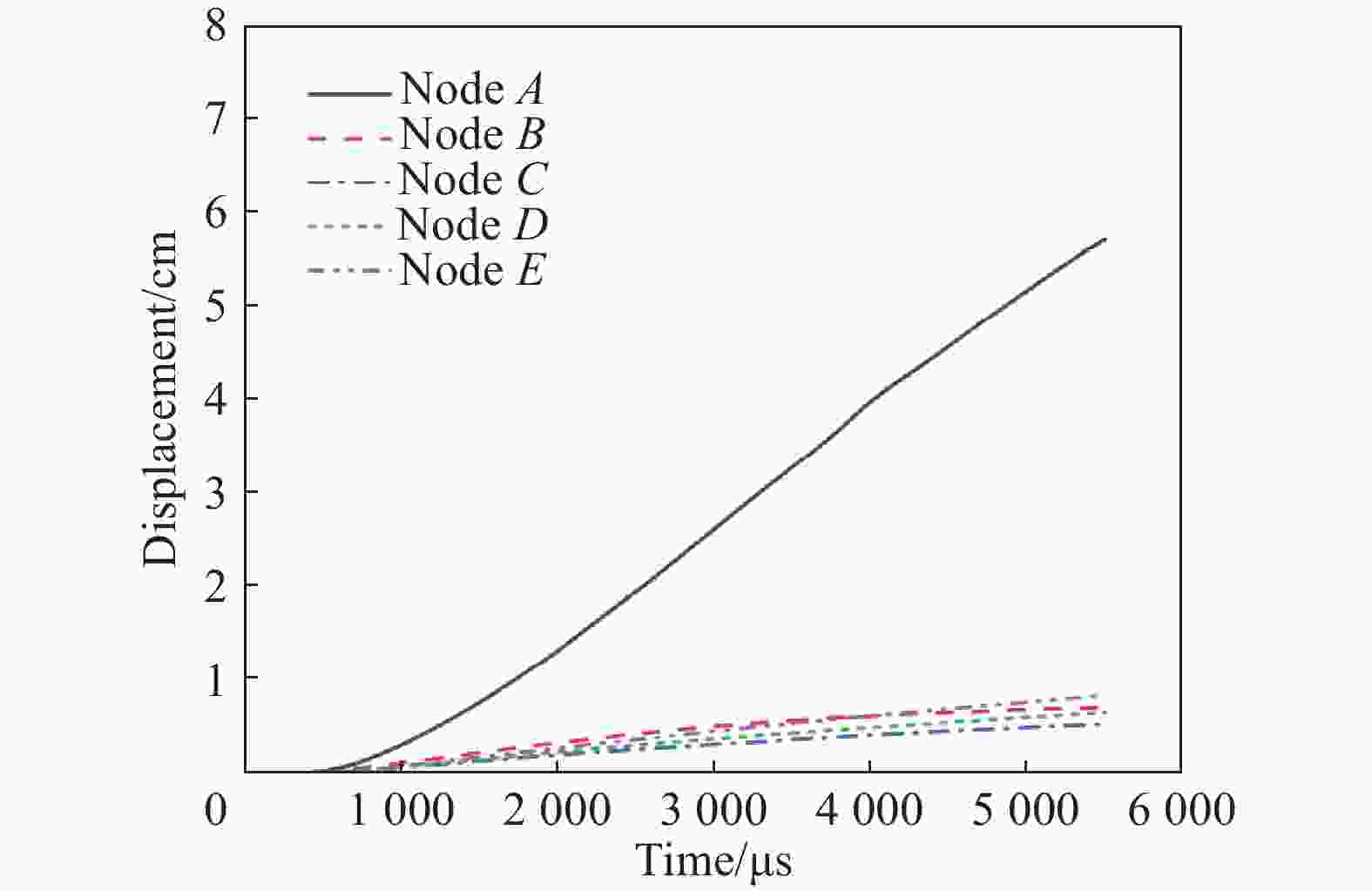
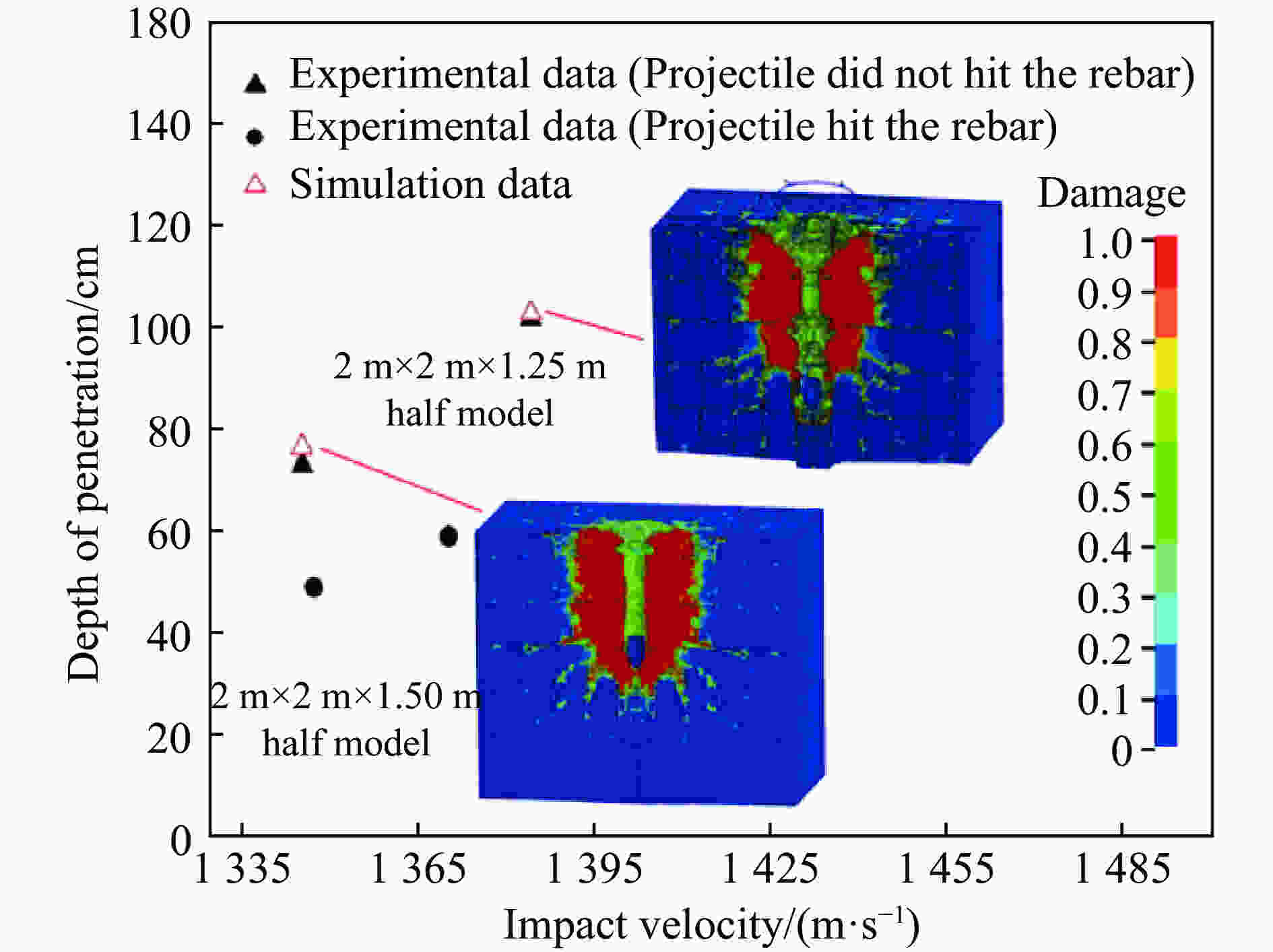
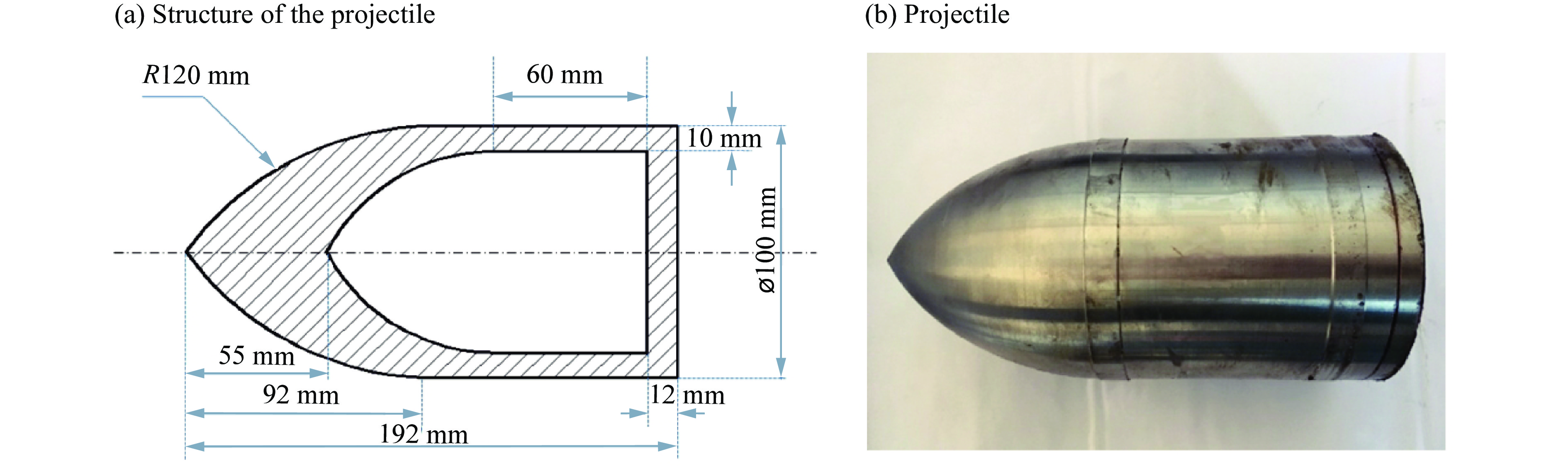
摘要: 为了得到钢筋混凝土目标在动能弹高速冲击作用下的破坏数据,基于大口径发射平台进行了100 mm口径卵形弹体高速侵彻钢筋混凝土靶体的实验,弹体质量为5.4 kg,靶体尺寸分为2 m × 2 m × 1.25 m 和 2 m × 2 m × 1.50 m两种,混凝土抗压强度为50 MPa,弹体侵彻速度为1 345~1 384 m/s,实验获得了弹体的侵彻深度及钢筋混凝土靶体的破坏数据。通过“钢筋混凝土全体单元分离式共节点建模方法”建立钢筋混凝土靶体模型,结合Riedel-Hiermaier-Thoma本构模型对实验工况进行计算。数值模拟给出了侵彻过程中钢筋的拉压力变化和分布规律,很好地模拟出贴近迎弹面钢筋在弹体高速冲击作用下伴随混凝土反向飞溅而产生的反向拉伸现象及靶体背面钢筋在混凝土崩落作用下发生的拉伸现象;数值模拟得到的弹体侵深数据、现象与实验结果吻合良好,实验验证了“钢筋混凝土全体单元分离式共节点建模方法”的可靠性。Abstract: In order to obtain the damage data of reinforced concrete targets subjected to high-velocity impact of kinetic-energy projectiles, based on the large-caliber launch platform, penetration experiments were carried out by applying 100-mm-caliber oval projectiles with high velocity penetrating into reinforced concrete targets. The projectile mass is 5.4 kg, and the target dimensions have two kinds: 2 m × 2 m × 1.25 m and 2 m × 2 m × 1.50 m. The compressive strength of the concrete is 50 MPa, and the penetration velocity of the projectile ranges from 1 345 to 1 384 m/s. The penetration depths of the projectiles and the damage data of the reinforced concrete targets were obtained by the experiment. The reinforced concrete target model was established through the reinforced concrete all solid hexahedral separation common node modeling. The numerical simulation was then carried out by this modeling method combined with the Riedel-Hiermaier-Thoma constitutive model. Numerical simulation results display the variation and distribution of the tensile and compressive stresses in the steel bars in the penetration process. The reverse stretching phenomenon of the rebar mesh near the front surface and the tensile phenomenon of the rebar mesh near the rear surface are perfectly simulated by this method. The simulated penetration depth and the damage phenomenon of the reinforced concrete are in good agreement with the experimental results. It proves the reliability of the reinforced concrete all solid hexahedral separation common node modeling.
-
Key words:
- penetration /
- reinforced concrete /
- structural damage /
- common node modeling
-
表 1 实验工况及结果
Table 1. Experimental conditions and results
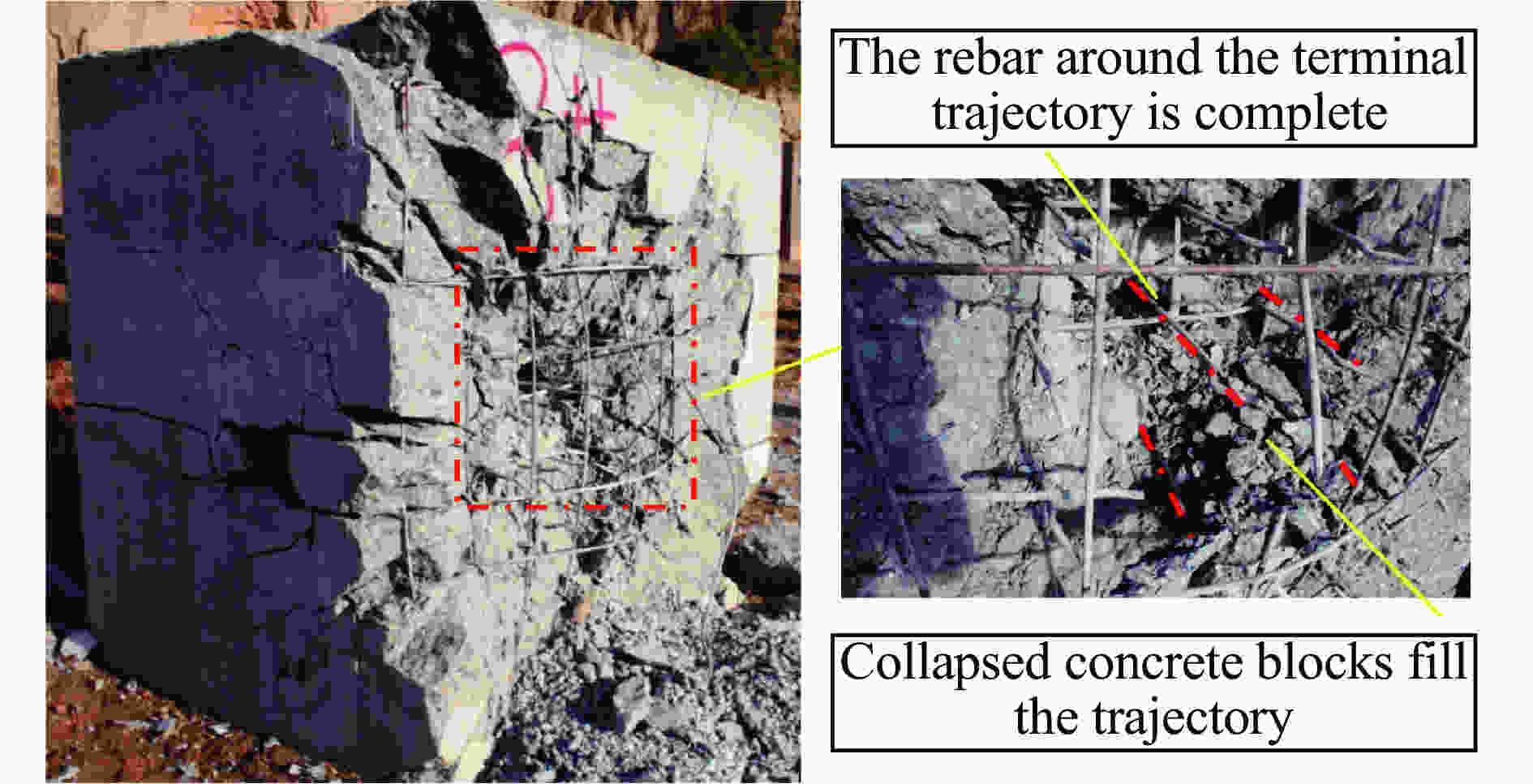
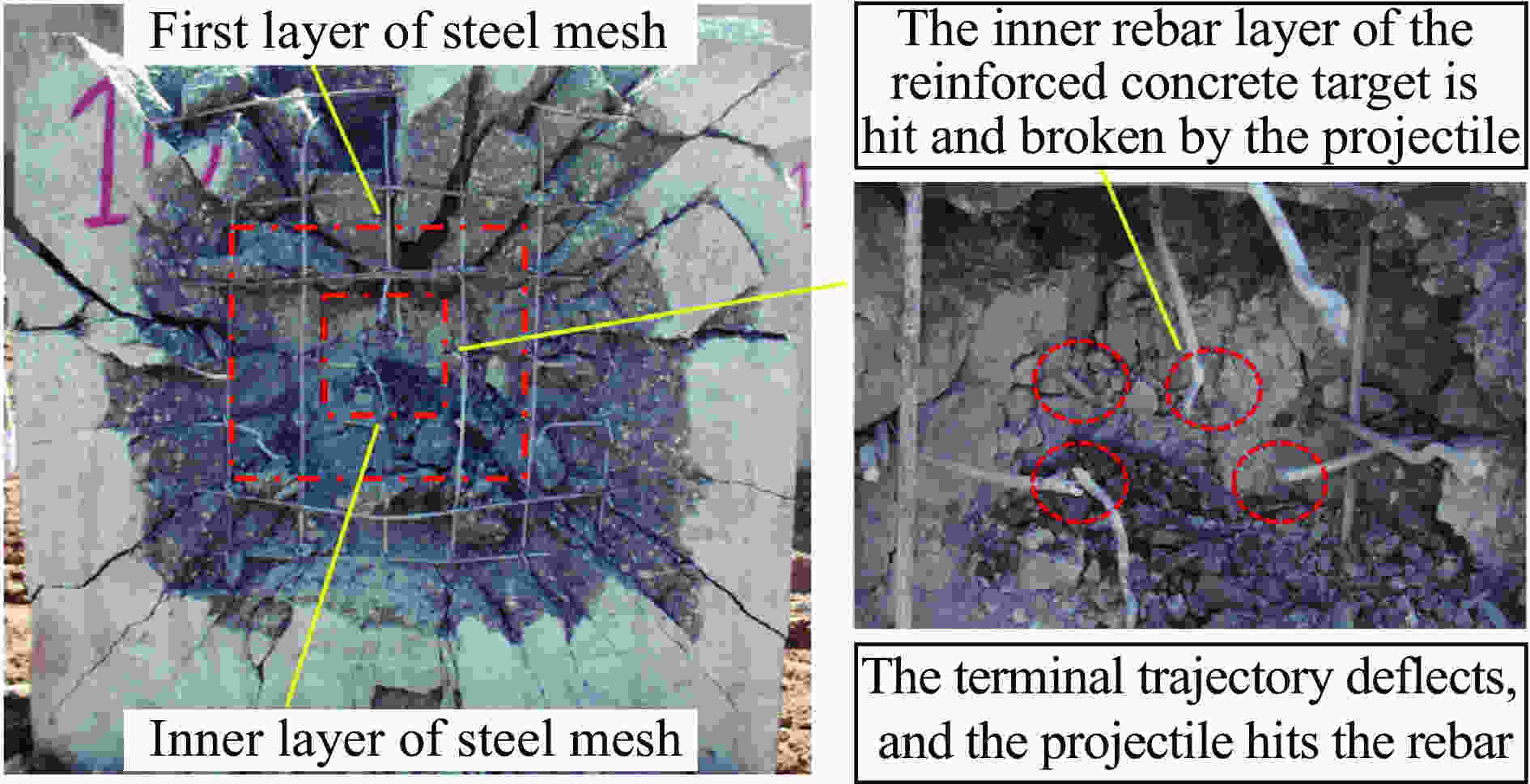
实验编号 靶板尺寸 弹体速度/(m·s−1) 弹体深度/cm 状态 1 2 m × 2 m × 1.25 m 1 370 59 击中钢筋 2 2 m × 2 m × 1.25 m 1 384 102 未击中钢筋 3 2 m × 2 m × 1.50 m 1 345 73 未击中钢筋 4 2 m × 2 m × 1.50 m 1 347 49 击中钢筋 表 2 靶体迎弹面混凝土崩落数据
Table 2. Concrete caving data of target front surface
实验编号 D1/cm D2/cm D3/cm D4/cm D/cm 1 116.2 111.7 151.9 127.4 126.8 2 110.0 107.1 134.2 127.7 119.8 3 161.3 148.4 264.5 197.4 192.9 4 148.4 138.5 160.5 173.6 155.3 表 3 弹体和钢筋的材料参数
Table 3. Material parameters of projectiles and rebar
材料 密度/(g·cm−3) 弹性模量/GPa 泊松比 屈服强度/MPa 弹体 7.85 207 0.3 835 钢筋 7.80 210 0.3 235 -
[1] HANCHAK S J, FORRESTAL M J, YOUNG E R, et al. Perforation of concrete slabs with 48 MPa (7 ksi) and 140 MPa (20 ksi) unconfined compressive strengths [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1992, 12(1): 1–7. DOI: 10.1016/0734-743X(92)90282-X. [2] FORRESTAL M J, FREW D J, HANCHAK S J, et al. Penetration of grout and concrete targets with ogive-nose steel projectiles [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1996, 18(5): 465–476. DOI: 10.1016/0734-743X(95)00048-F. [3] 武海军, 黄风雷, 王一楠. 高速弹体非正侵彻混凝土试验研究 [C] // 第八届全国爆炸力学学术会议论文集. 江西吉安: 中国力学学会爆炸力学专业委员会, 2007: 488−494. [4] 梁斌, 陈小伟, 姬永强, 等. 先进钻地弹概念弹的次口径高速深侵彻实验研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2008, 28(1): 1–9. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2008)01-0001-09.LIANG Bin, CHEN Xiaowei, JI Yongqiang, et al. Experimental study on deep penetration of reduced-scale advanced earth penetrating weapon [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2008, 28(1): 1–9. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2008)01-0001-09. [5] 何翔, 徐翔云, 孙桂娟, 等. 弹体高速侵彻混凝土的效应实验 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2010, 30(1): 1–6. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2010)01-0001-06.HE Xiang, XU Xiangyun, SUN Guijuan, et al. Experimental investigation on projectiles’ high-velocity penetration into concrete targets [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2010, 30(1): 1–6. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2010)01-0001-06. [6] 王可慧, 宁建国, 李志康. 高速弹体非正侵彻混凝土靶的弹道偏转实验研究 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2013, 27(4): 561–566. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.2013.04.015.WANG Kehui, NING Jianguo, LI Zhikang, et al. Ballistic trajectory of high-velocity projectile obliquely penetrating concrete target [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2013, 27(4): 561–566. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.2013.04.015. [7] 武海军, 张爽, 黄风雷. 钢筋混凝土靶的侵彻与贯穿研究进展 [J]. 兵工学报, 2018, 39(1): 182–208. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2018.01.020.WU Haijun, ZHANG Shuang, HUANG Fenglei. Research progress in penetration/perforation into reinforced concrete targets [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2018, 39(1): 182–208. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2018.01.020. [8] 王明洋, 钱七虎, 赵跃堂. 接触爆炸作用下钢板-钢纤维钢筋混凝土遮弹层设计方法: Ⅱ [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2002, 22(2): 163–168.WANG Mingyang, QIAN Qihu, ZHAO Yuetang. Design method of steel fiber concrete shelter plate under contact detonation: Ⅱ [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2002, 22(2): 163–168. [9] Livermore Software Technology Corporation. LS-DYNA keyword user’s manual[M]. Version 971. Livermore, CA : Livermore Software Technology Corporation, 2012. [10] TAYLOR L M, CHEN E P, KUSZMAUL J S. Microcrack-include damage accumulation in brittle rock under dynamic loading [J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 1986, 55(3): 301–320. DOI: 10.1016/0045-7825(86)90057-5. [11] HOLMQUIST T J, JOHNSON G R, COOK W H. A computational constitutive model for concrete subjected to large strains, high strain rates and high pressure [C] // Proceedings of the fourteenth International Symposium on Ballistics. Quebec, Canada: ISIEMS, 1993: 591−600. DOI: 10.1115/1.4004326. [12] RIEDEL W, THOMA K, HIERMAIER S, et al. Penetration of reinforced concrete by BETA-B-500: numerical analysis using a new macroscopic concrete model for hydrocodes [C] // Proceedings of the Ninth International Symposiumon on Interaction of the Effects of Munitions with Structures. Berlin, Germany: ISIEMS, 1999: 315−322. [13] BORRVALL T, RIEDEL W. The RHT concrete model in LS-DYNA [C] // Proceedings of the Eighth European LS-DYNA User Conference. Strasbourg, France: LSTC, 2011: 1−14. [14] HECKÖTTER C, SIEVERS J. Simulation of impact tests with hard, soft and liquid filled missiles on reinforced concrete structures [J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2013, 80(3): 1805. [15] XU H, WEN H M. A computational constitutive model for concrete subjected to dynamic loadings [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2016, 91: 116–125. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2016.01.003. -







 下载:
下载: