Influence of structural interspace on anti-penetration performance of sandwich composite armor system
-
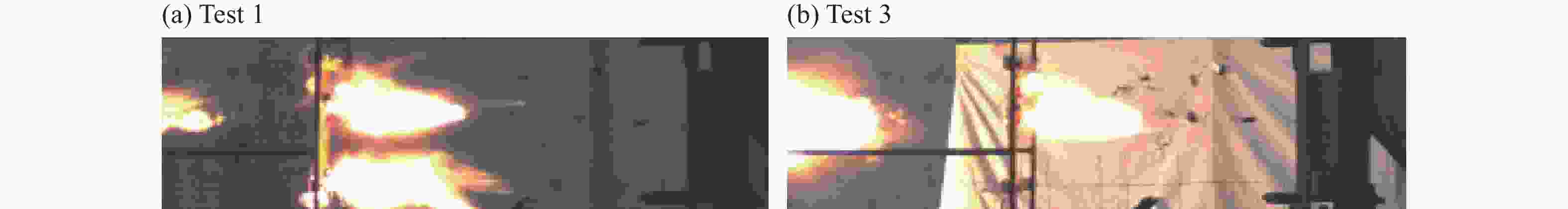
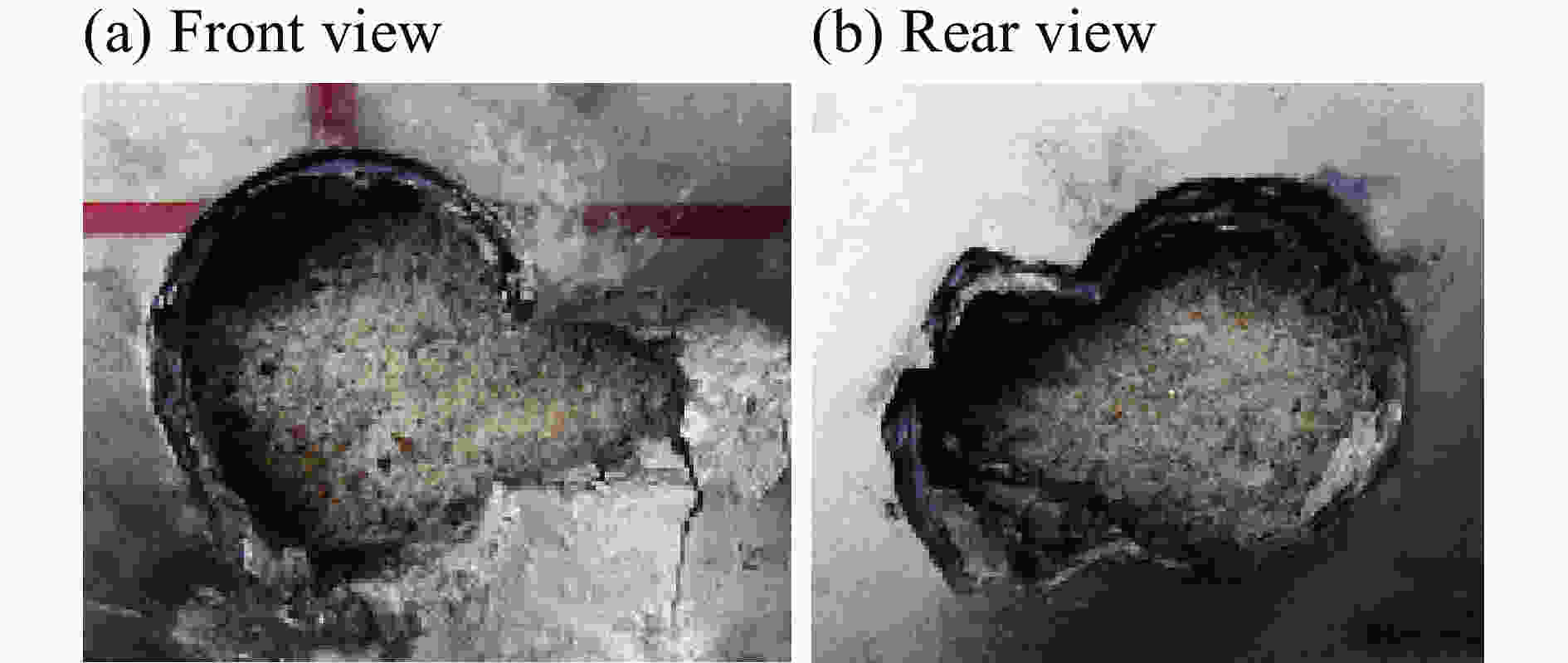
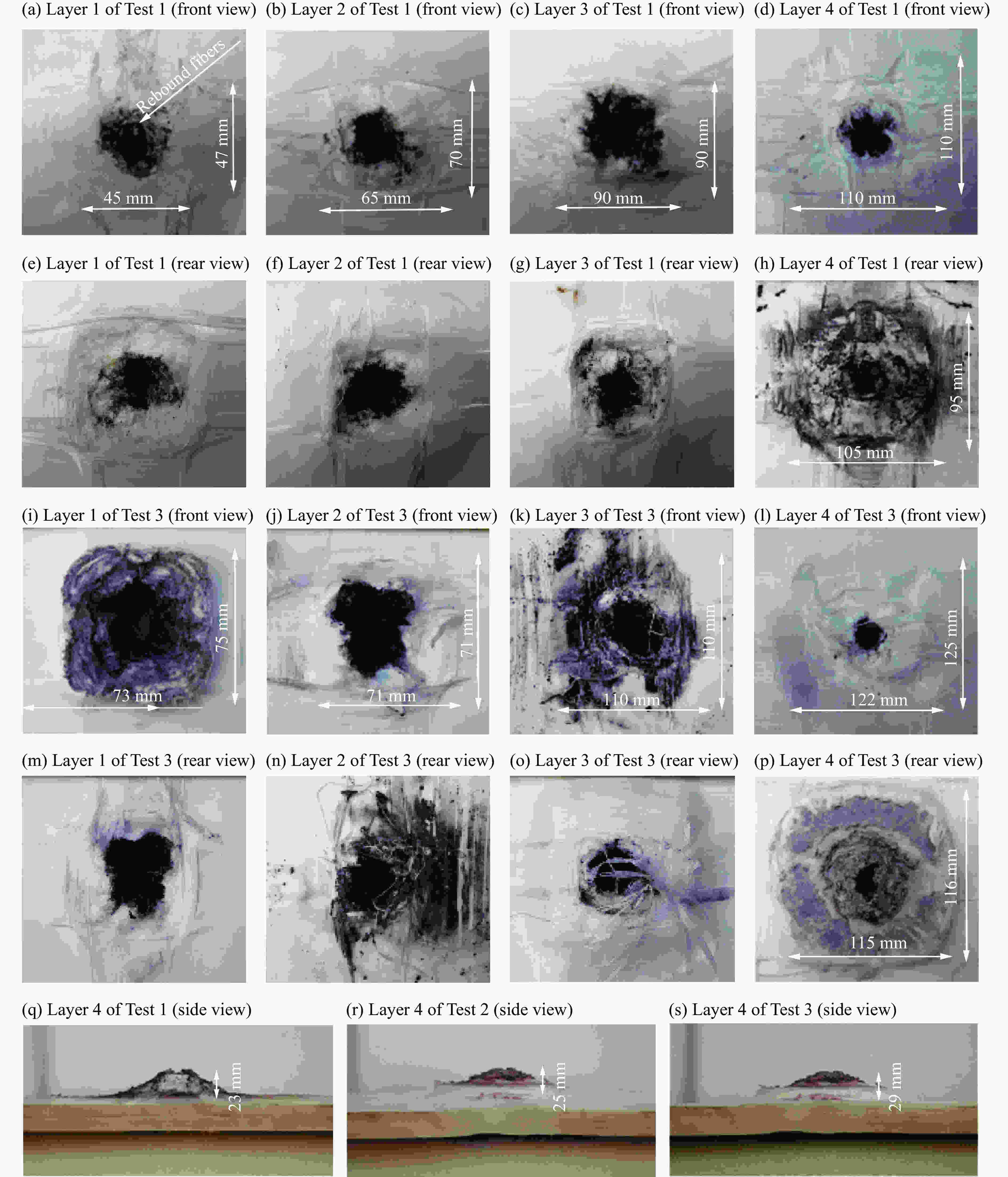
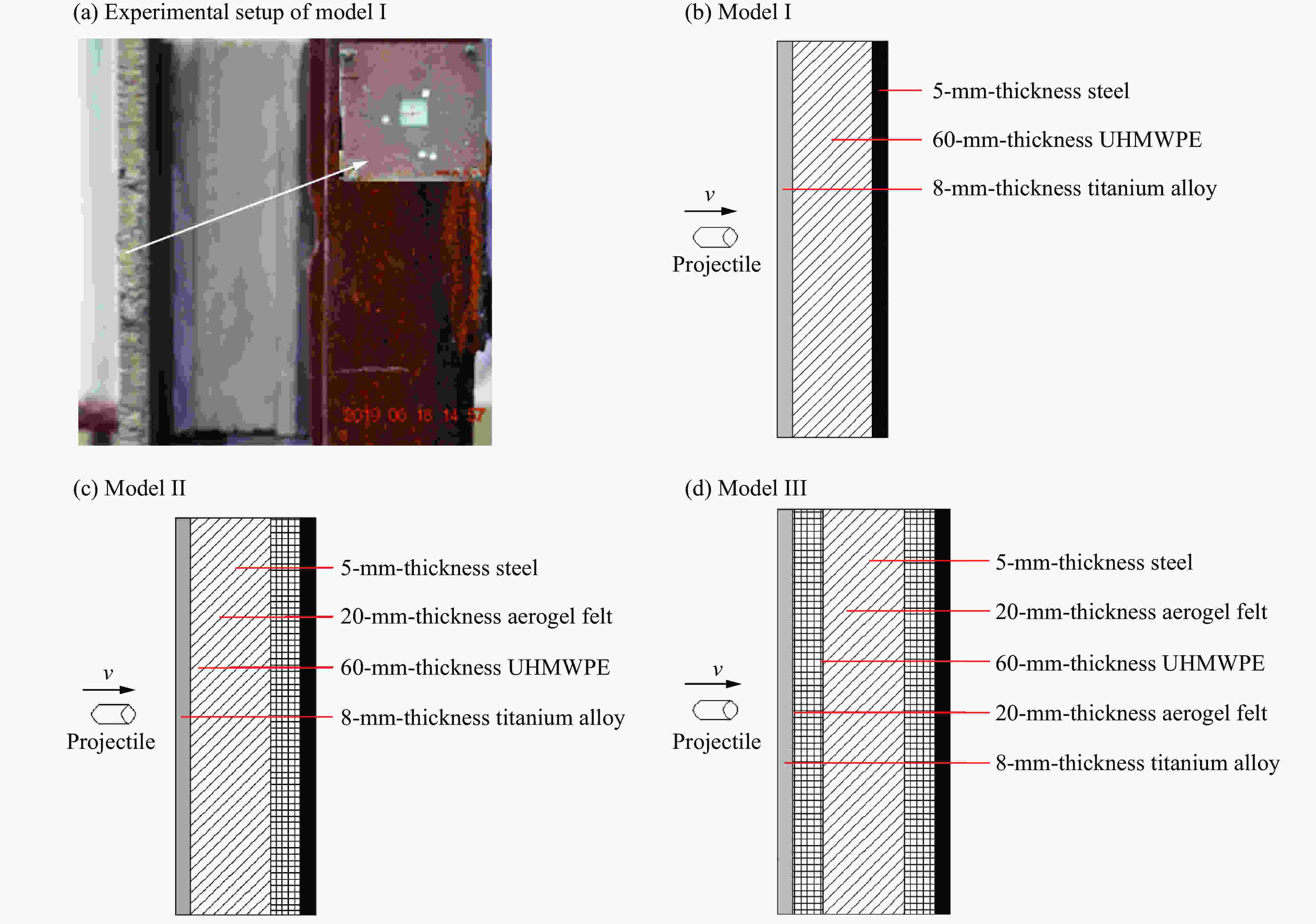
摘要: 采用由厚度为8 mm的前置钛合金板、面密度为60 kg/m2的高强聚乙烯纤维增强复合材料层合板抗弹芯层、厚度为8 mm的后置钢板构成的夹芯式复合装甲,模拟舰船舷侧复合夹芯舱壁结构。根据面板与芯层间是否设置20 mm的间隙,将复合装甲结构定义为无间隙式、后间隙式及前后间隙式。为研究以上3种结构在55 g圆柱体弹高速冲击下的抗弹性能及破坏机理,开展了系列弹道实验,分析了钛合金板、高强聚乙烯纤维增强复合材料层合板芯层及钢质面板的破坏模式,探讨了结构间隙对复合装甲结构抗弹性能的影响。结果表明:前置钛合金板的破坏模式为剪切冲塞,靶板背弹面产生脆性断裂并伴随碎块崩落现象;聚乙烯纤维增强复合材料板的破坏模式及钢质背板的变形范围受间隙的影响较大,前置钛合金板受间隙影响较小;相同载荷侵彻下,间隙的存在有利于提高复合装甲结构的抗弹性能。
-
关键词:
- 复合装甲 /
- 结构间隙 /
- 钛合金 /
- 高强聚乙烯纤维增强复合材料 /
- 高速冲击
Abstract: A sandwich composite armor consisting of an 8 mm thickness front titanium alloy plate, a 60 kg/m2 planar density high-strength polyethylene fiber reinforced composite laminate core layer and an 8 mm thickness rear steel plate was used to simulate the structures of composite sandwich bulkheads on ship sides. According to whether there was an interspace of 20 mm between the panel and the core, the composite armor structures were defined as non-interspace type, back interspace type and front-back interspace type. In order to study the anti-penetration performance and failure mechanism of the above three structures under high-speed impact of a cylindrical projectile with the mass of 55 g, a series of ballistic tests were carried out. The failure modes of the titanium alloy plate, the ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fiber-reinforced composite laminate core, and the steel panel were analyzed, and the influence of the structural interspace on the anti-penetration performances of the composite armor structures was obtained. The results show that the failure mode of the front titanium alloy plate is shear plugging, brittle fracture occurs on the bullet surface of the target plate and is accompanied by debris collapse; that the failure mode of the polyethylene fiber reinforced composite plate and the deformation range of the steel back plate are greatly affected by the interspace, while the front titanium alloy plate is less affected by the interspace; and that the existence of interspace is beneficial to improve the anti-penetration performances of the composite armor structures. -
表 1 面板材料力学性能
Table 1. Mechanical properties of panel materials
材料 E/GPa ρ/(kg·m−3) µ σy/MPa σb/MPa δs/% 钛合金 110 4 500 0.36 922 986 15.5 921A 钢 210 7 800 0.30 590 750 23 表 2 实验结果
Table 2. Experimental results
试验工况 靶板类型 厚度/mm ρa/(kg·m−2) v0/(m·s−1) vr/(m·s−1) Ea/(J·m2·kg−1) 1 Ⅰ 8/60/8 162.09 1 628.0 713.1 363.39 2 II 8/60/20/8 161.45 1 687.0 752.9 388.20 3 III 8/20/60/20/8 161.93 1 657.0 632.6 398.32 注:未计算气凝胶毡面密度。 -
[1] CORBETT G G, REID S R, JOHNSON W. Impact loading of plates and shells by free-flying projectiles: a review [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1996, 18(2): 141–230. DOI: 10.1016/0734-743x(95)00023-4. [2] CHEN X W, LI Q M. Shear plugging and perforation of ductile circular plates struck by a blunt projectile [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2003, 28(5): 513–536. DOI: 10.1016/s0734-743x(02)00077-5. [3] WEN H M. Penetration and perforation of thick FRP laminates [J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2001, 61(8): 1163–1172. DOI: 10.1016/s0266-3538(01)00020-3. [4] NUNES L M, PACIORNIK S, D’ALMEIDA J R M. Evaluation of the damaged area of glass-fiber-reinforced epoxy-matrix composite materials submitted to ballistic impacts [J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2004, 64(7/8): 945–954. DOI: 10.1016/s0266-3538(03)00105-2. [5] 王元博, 王肖钧, 胡秀章, 等. Kevlar层合材料抗弹性能研究 [J]. 工程力学, 2005, 22(3): 76–81. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4750.2005.03.015.WANG Yuanbo, WANG Xiaojun, HU Xiuzhang, et al. Experimental study of ballistic resistance of Kevlar laminates [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2005, 22(3): 76–81. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4750.2005.03.015. [6] 梅志远, 朱锡, 张立军. FRC层合板抗高速冲击机理研究 [J]. 复合材料学报, 2006, 23(2): 143–149. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2006.02.025.MEI Zhiyuan, ZHU Xi, ZHANG Lijun. Ballistic protective mechanism of FRC laminates [J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2006, 23(2): 143–149. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2006.02.025. [7] WAMBUA P, VANGRIMDE B, LOMOV S, et al. The response of natural fibre composites to ballistic impact by fragment simulating projectiles [J]. Composite Structures, 2007, 77(2): 232–240. DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2005.07.006. [8] 覃悦, 文鹤鸣, 何涛. 卵形弹丸撞击下 FRP层合板的侵彻和穿透 [J]. 复合材料学报, 2007, 24(2): 131–136. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2007.02.023.QIN Yue, WEN Heming, HE Tao. Penetration and perforation of FRP laminates under normal impact by ogival-nosed projectiles [J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2007, 24(2): 131–136. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2007.02.023. [9] 王晓强, 朱锡, 梅志远, 等. 超高分子量聚乙烯纤维增强层合厚板抗弹性能实验研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2009, 29(1): 29–34. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2009)01-0029-06.WANG Xiaoqiang, ZHU Xi, MEI Zhiyuan, et al. Ballistic performances of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fiber-reinforced thick laminated plates [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2009, 29(1): 29–34. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2009)01-0029-06. [10] 虢忠仁, 杜文泽, 钟蔚华, 等. 芳纶复合材料对球形弹丸的抗贯穿性能研究 [J]. 兵工学报, 2010, 31(4): 458–463.GUO Zhongren, DU Wenze, ZHONG Weihua, et al. Anti-perforation performance of aramid composite against spheric projectile [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2010, 31(4): 458–463. [11] CARRILLO J G, GAMBOA R A, FLORES-JOHNSON E A, et al. Ballistic performance of thermoplastic composite laminates made from aramid woven fabric and polypropylene matrix [J]. Polymer Testing, 2012, 31(4): 512–519. DOI: 10.1016/j.polymertesting.2012.02.010. [12] 彭刚, 王绪财, 刘原栋, 等. 复合材料层板的抗贯穿机理与模拟研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2012, 32(4): 337–345. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2012)04-0337-09.PENG Gang, WANG Xucai, LIU Yuandong, et al. Research on anti-perforating mechanism and simulation of composite laminates [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2012, 32(4): 337–345. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2012)04-0337-09. [13] 胡年明, 陈长海, 侯海量, 等. 高速弹丸冲击下复合材料层合板损伤特性仿真研究 [J]. 兵器材料科学与工程, 2017, 40(3): 66–70. DOI: 10.14024/j.cnki.1004-244x.20170427.008.HU Nianming, CHEN Changhai, HOU Hailiang, et al. Simulation on damage characteristic of composite laminates under high-velocity projectile impact [J]. Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2017, 40(3): 66–70. DOI: 10.14024/j.cnki.1004-244x.20170427.008. [14] 胡年明, 朱锡, 侯海量, 等. 高速破片侵彻下高分子聚乙烯层合板的弹道极限估算方法 [J]. 中国舰船研究, 2014, 9(4): 55–62. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3185.2014.04.009.HU Nianming, ZHU Xi, HOU Hailiang, et al. Estimating method for the ballistic limit of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fiber-reinforced laminates under high-velocity fragment penetration [J]. Chinese Journal of Ship Research, 2014, 9(4): 55–62. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3185.2014.04.009. [15] 朱锡, 梅志远, 刘润泉, 等. 舰用轻型复合装甲结构及其抗弹实验研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2003, 23(1): 61–66.ZHU Xi, MEI Zhiyuan, LIU Runquan, et al. Warship's light composite armor structure resistibility for ballistic impact [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2003, 23(1): 61–66. [16] 陈长海, 朱锡, 侯海量, 等. 弹丸低速贯穿纤维与金属组合薄靶板的试验研究 [J]. 兵工学报, 2012, 33(12): 1473–1479.CHEN Changhai, ZHU Xi, HOU Hailiang, et al. An experimental research on low-velocity projectiles perforating fiber and metal combined thin targets [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2012, 33(12): 1473–1479. [17] 陈长海, 朱锡, 侯海量, 等. 球头弹低速贯穿金属/FRP组合薄板的实验研究 [J]. 弹道学报, 2012, 24(4): 51–55. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-499X.2012.04.011.CHEN Changhai, ZHU Xi, HOU Hailiang, et al. Experimental research on low-velocity ball projectile perforating metal/FRP combined-thin-plates [J]. Journal of Ballistics, 2012, 24(4): 51–55. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-499X.2012.04.011. [18] 张元豪, 陈长海, 朱锡. 钢/玻璃钢组合结构对高速弹丸的抗侵彻特性 [J]. 中国舰船研究, 2017, 12(1): 93–100. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3185.2017.01.014.ZHANG Yuanhao, CHEN Changhai, ZHU Xi. GFRP and steel compounded structure subjected to impact by high velocity projectiles [J]. Chinese Journal of Ship Research, 2017, 12(1): 93–100. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3185.2017.01.014. [19] 徐豫新, 王树山, 严文康, 等. 纤维增强复合材料三明治板的破片穿甲实验 [J]. 复合材料学报, 2012, 29(3): 72–78. DOI: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.2012.03.019.XU Yuxin, WANG Shushan, YAN Wenkang, et al. Armor-piercing experiment on fragment against sandwich plate with fiber reinforced composite cores [J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2012, 29(3): 72–78. DOI: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.2012.03.019. [20] 徐豫新, 戴文喜, 王树山, 等. 纤维增强复合材料三明治板破片穿甲数值仿真 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2014, 33(2): 134–140. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2014.02.026.XU Yuxin, DAI Wenxi, WANG Shushan, et al. Numerical simulation on fragment armor-piercing against sandwich plate with fiber reinforced composite cores [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2014, 33(2): 134–140. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2014.02.026. [21] 李茂, 侯海量, 朱锡, 等. 结构间隙对芳纶纤维增强复合装甲结构抗侵彻性能的影响 [J]. 兵工学报, 2017, 38(9): 1797–1805. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2017.09.017.LI Mao, HOU Hailiang, ZHU Xi, et al. Influence of structural interspace on anti-penetration performance of para-aramid fiber-reinforced composite armor system [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2017, 38(9): 1797–1805. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2017.09.017. [22] O'MASTA M R, DESHPANDE V S, WADLEY H N G. Mechanisms of projectile penetration in Dyneema® encapsulated aluminum structures [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2014, 74: 16–35. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2014.02.002. -






 下载:
下载: