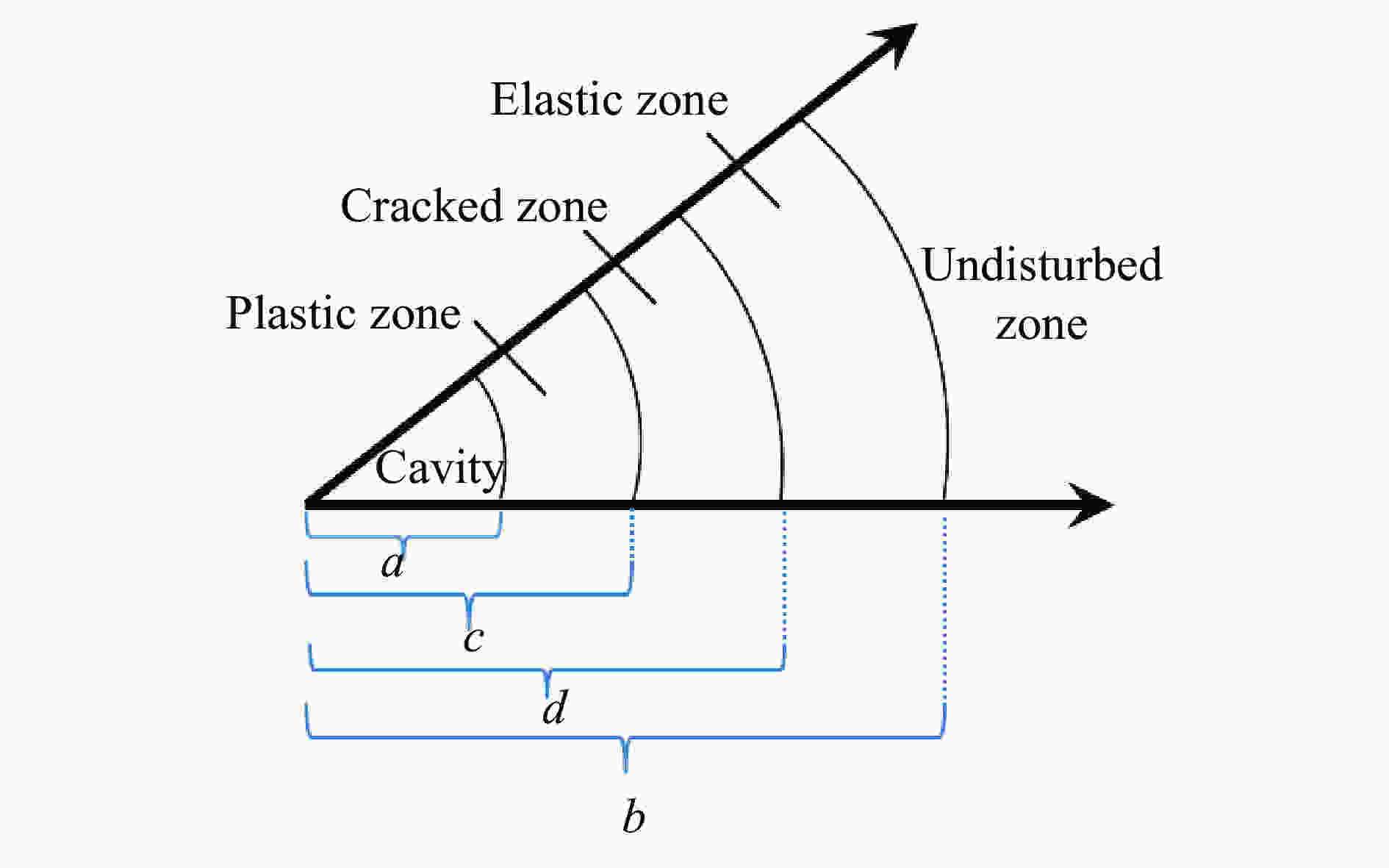
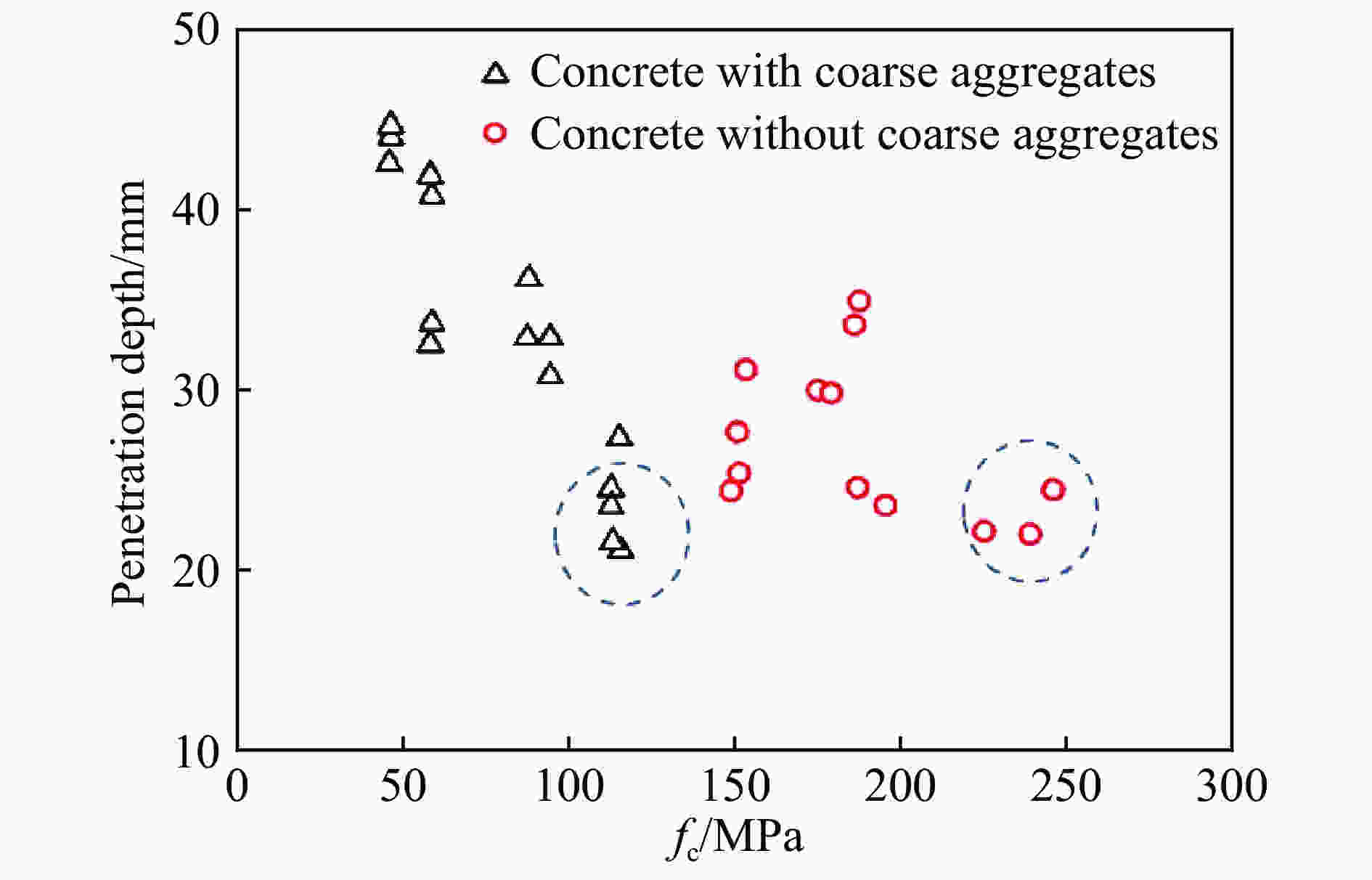
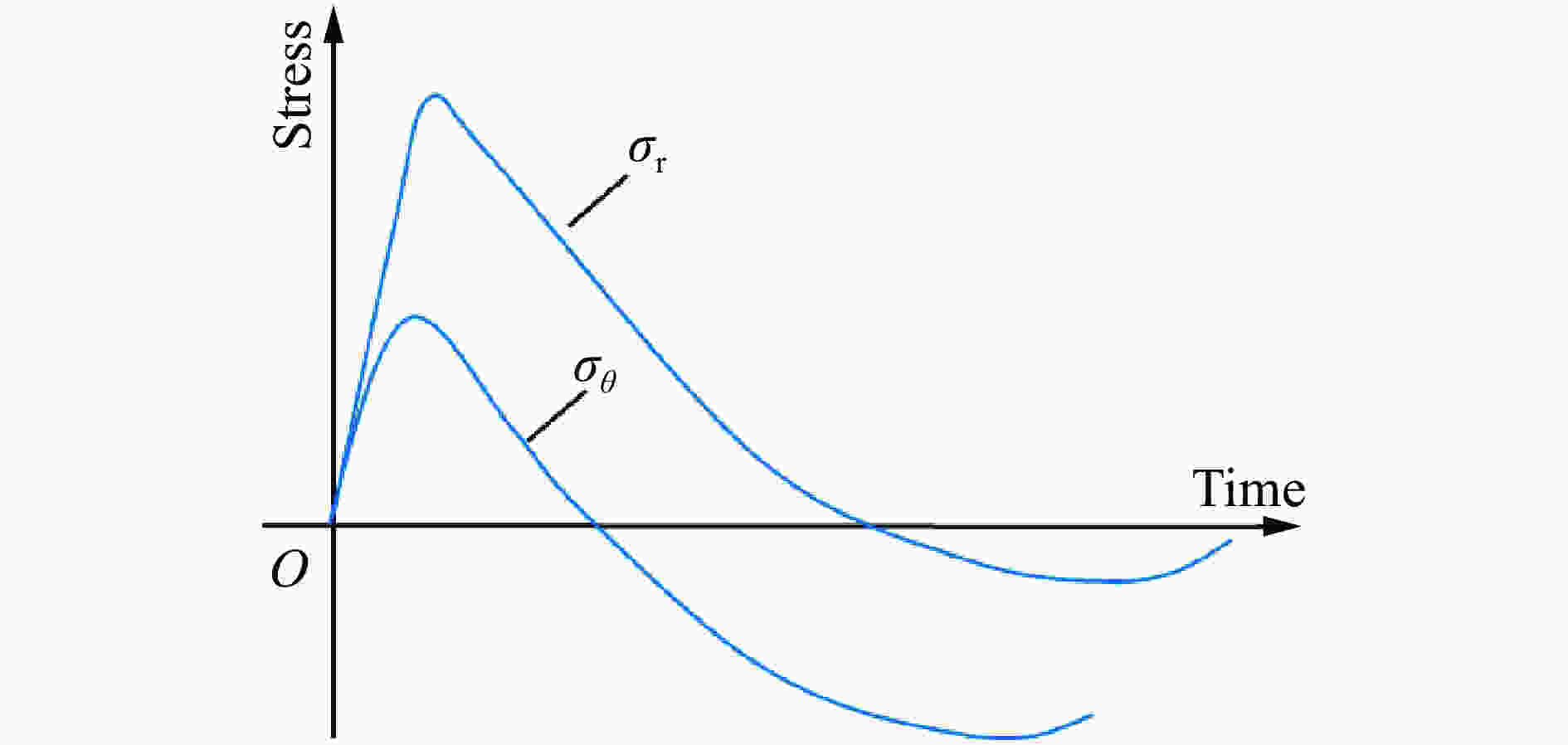
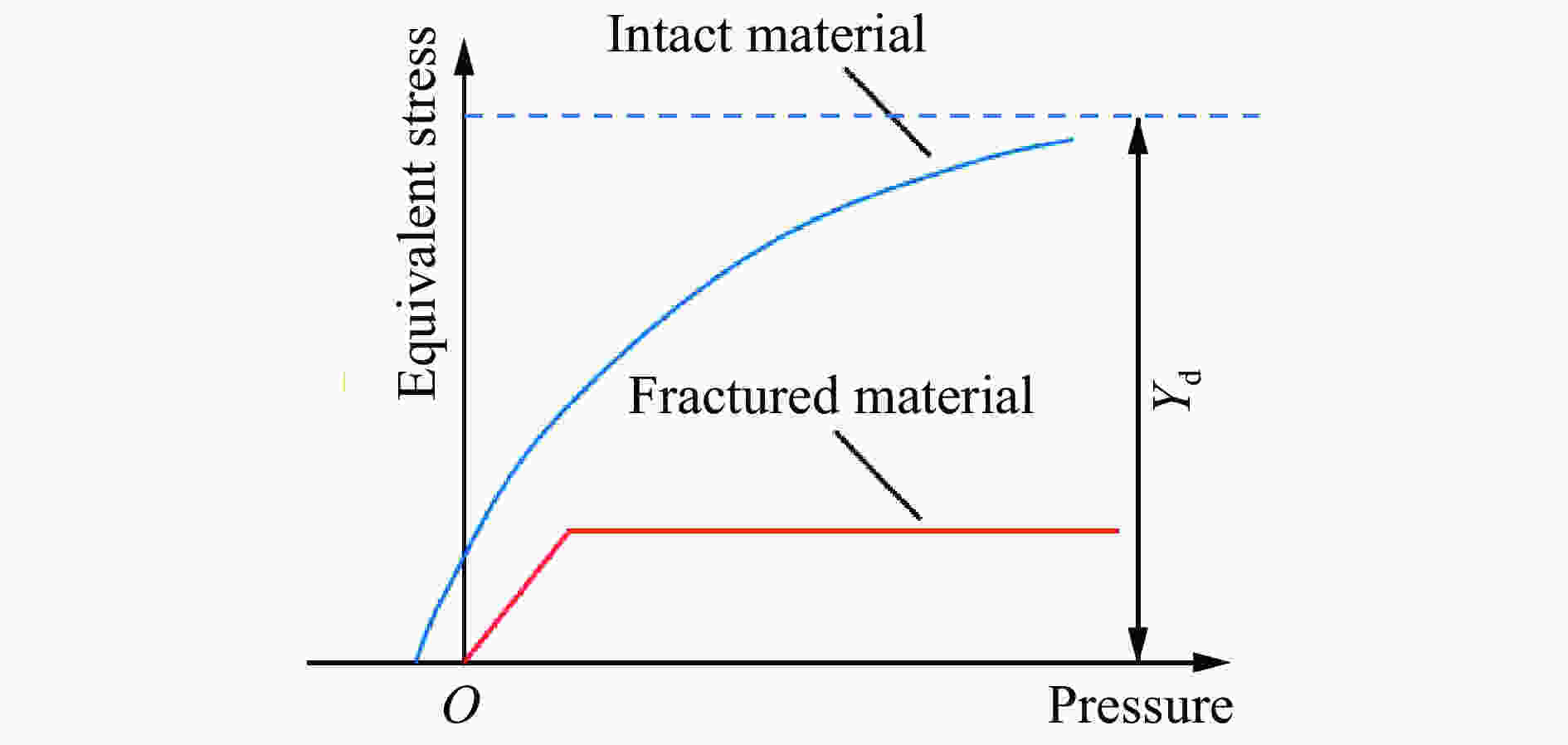
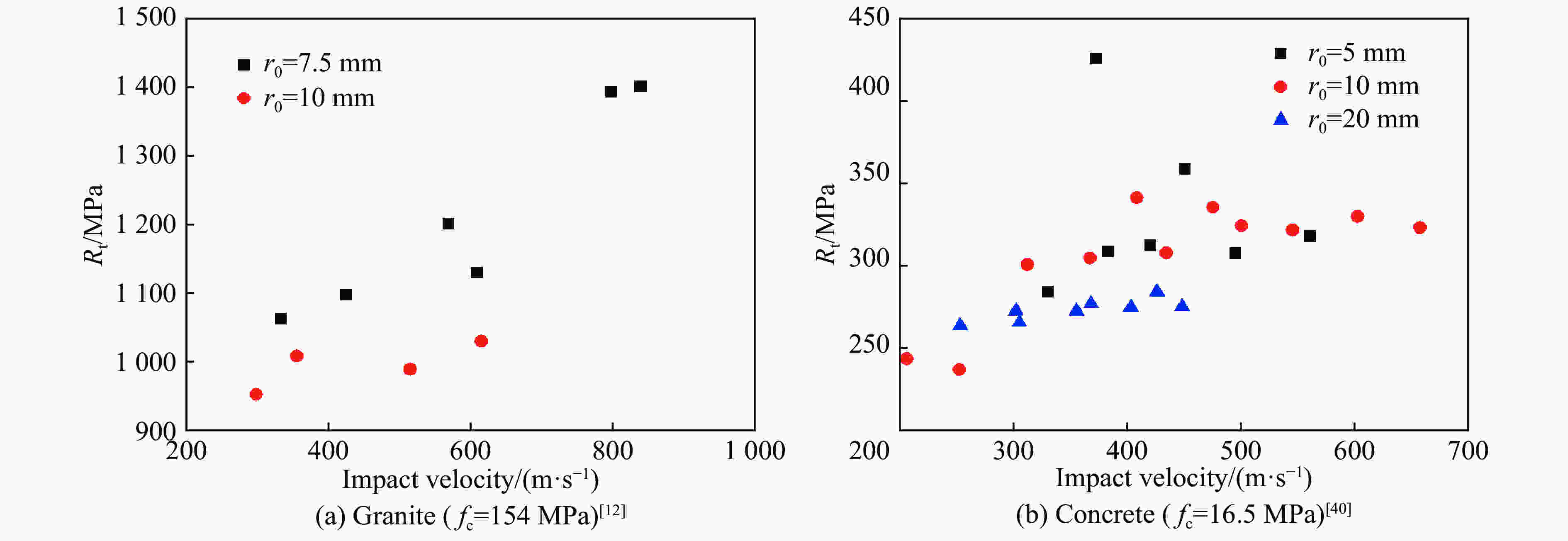
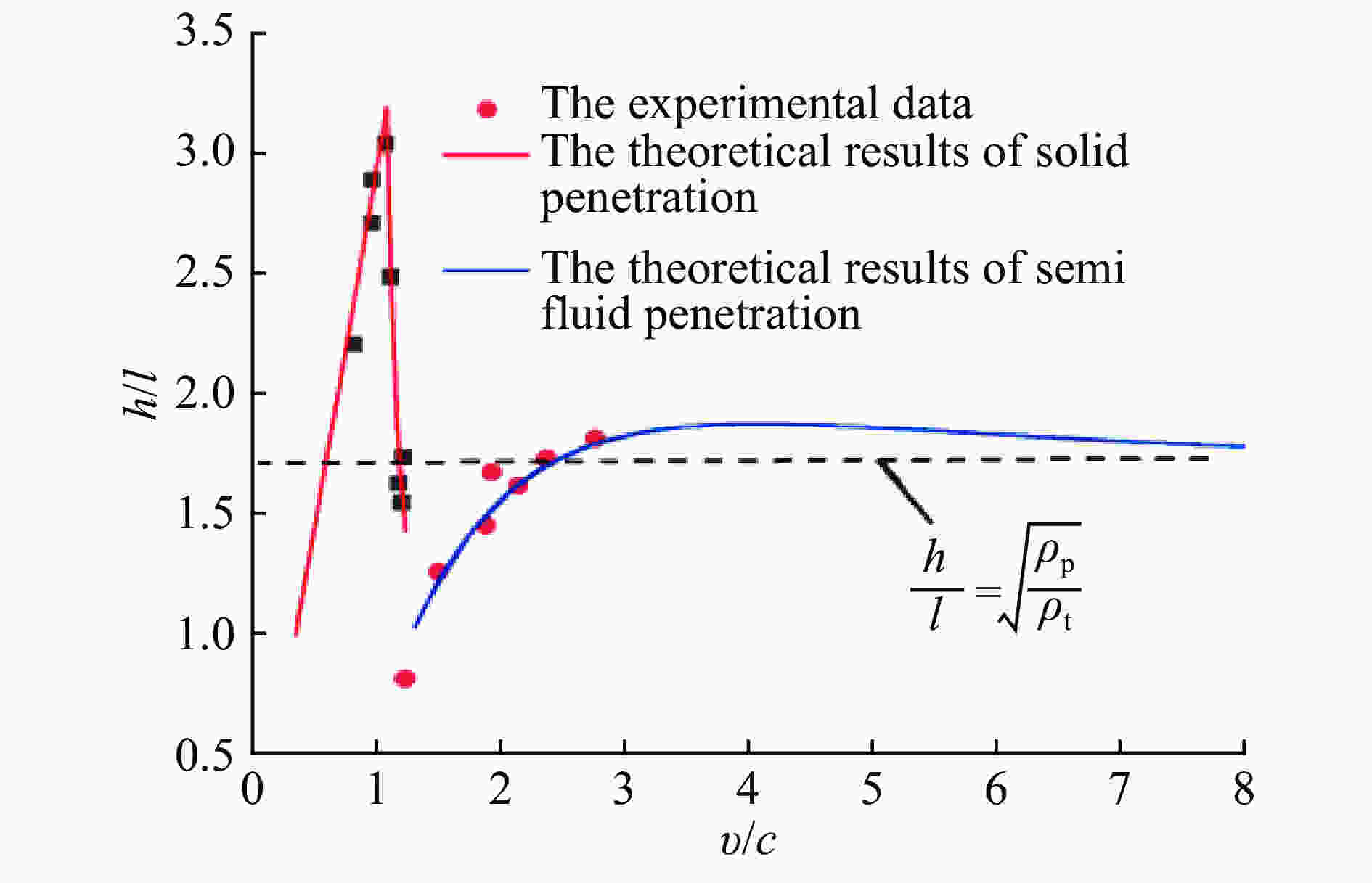
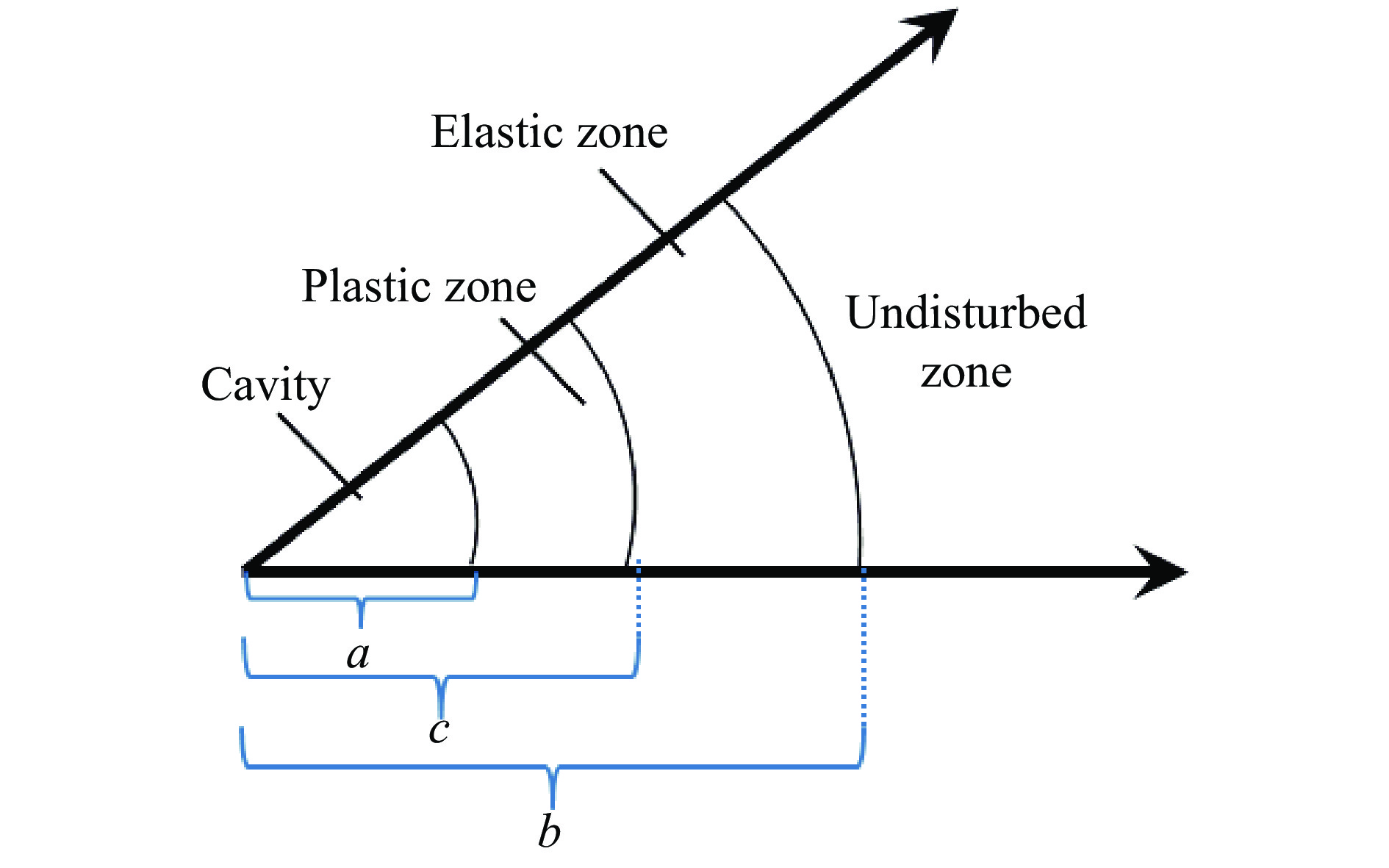
| [1] |
ANDERSON C E. Analytical models for penetration mechanics: a review [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2017, 108: 3–26. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2017.03.018.
|
| [2] |
FORRESTAL M J, LUK V K. Dynamic spherical cavity-expansion in a compressible elastic-plastic solid [J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 1988, 55(2): 275–279. DOI: 10.1115/1.3173672.
|
| [3] |
HILL R. The mathematical theory of plasticity [M]. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1998.
|
| [4] |
FORRESTAL M J, TZOU D Y. A spherical cavity-expansion penetration model for concrete targets [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 1997, 34(31/32): 4127–4146.
|
| [5] |
FORRESTAL M J, ALTMAN B S, CARGILE J D, et al. An empirical equation for penetration depth of ogive-nose projectiles into concrete targets [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1994, 15(4): 395–405. DOI: 10.1016/0734-743X(94)80024-4.
|
| [6] |
HE T, WEN H M, GUO X J. A spherical cavity expansion model for penetration of ogival-nosed projectiles into concrete targets with shear-dilatancy [J]. ActaMechanicaSinica, 2011, 27(6): 1001–1012.
|
| [7] |
彭永, 方秦, 吴昊, 等. 对弹体侵彻混凝土靶体阻力函数计算公式的探讨 [J]. 工程力学, 2015, 32(4): 112–119.PENG Y, FANG Q, WU H, et al. Discussion on the resistance forcing function of projectiles penetrating into concrete targets [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2015, 32(4): 112–119.
|
| [8] |
KONG X Z, WU H, FANG Q. Rigid and eroding projectile penetration into concrete targets based on am extended dynamic cavity expansion model [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2017, 100: 13–22. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2016.10.005.
|
| [9] |
卢正操, 张元迪, 文鹤鸣, 等. 长杆弹侵彻半无限混凝土靶的理论研究 [J]. 现代应用物理, 2018, 9(4): 040102.LU Z C, ZHANG Y D, WEN H M, et al. Theoretical study on the penetration of long rods into semi-infinite concrete target [J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2018, 9(4): 040102.
|
| [10] |
FORRESTAL M J. Penetration into dry porous rock [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 1986, 22(12): 1485–1986.
|
| [11] |
FREW D J, FORRESTAL M J, HANCHAK S J. Penetration experiments withlimestone targets and ogive-nose steel projectiles [J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2000, 67(4): 841–845. DOI: 10.1115/1.1331283.
|
| [12] |
张德志, 张向荣, 林俊德, 等. 高强钢弹对花岗岩正侵彻的实验研究 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2005, 24(9): 1612–1618. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.09.024.ZHANG D Z, ZHANG X R, LIN J D, et al. Penetration experiments for normal impact into granite targets with high-strength steel projectile [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2005, 24(9): 1612–1618. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.09.024.
|
| [13] |
LI J C, MA G W, YU M H. Penetration analysis for geo-material based on unified strength criterion [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2008, 35: 1154–1163. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2008.01.003.
|
| [14] |
SATAPATHY S, BLESS S. Calculation of penetration resistance of brittle materials using spherical cavity expansion analysis [J]. Mechanics of Materials, 1996, 23: 323–330. DOI: 10.1016/0167-6636(96)00022-1.
|
| [15] |
GALANOV B A, KARTUZOV V V, IVANOV S M. New analytical model of expansion of spherical cavity in brittle material basedon the concepts of mechanics of compressible porous and powder materials [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2008, 35: 1522–1528. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2008.07.016.
|
| [16] |
ROSENBERG Z, DEKEL E. A numerical study of the cavity expansion process and its application to long-rod penetration mechanics [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2008, 35: 147–154. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2007.01.005.
|
| [17] |
TATE A. A theory for the deceleration of long rods after impact [J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 1967, 15(6): 387–399. DOI: 10.1016/0022-5096(67)90010-5.
|
| [18] |
RIEDELW, WICKLEIN M, THOMA K. Shock properties of conventional and high strength concrete: experimental and mesomechanical analysis [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2008, 35: 155–171. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2007.02.001.
|
| [19] |
李干, 王明洋, 宋春明, 等. 超高速飞片撞击花岗岩实验及其动态力学性能研究 [C] // 第六届全国工程安全与防护学术会议. 湘潭: 中国岩石力学与工程学会工程安全与防护分会, 2018.
|
| [20] |
PETERSEN CF. Shock wave studies of selected rocks [D]. California: Stanford University, 1969.
|
| [21] |
王明洋, 李杰, 李海波, 等. 岩石的动态压缩行为与超高速动能弹毁伤效应计算 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2018, 38(6): 1200–1217. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0173.WANG M Y, LI J, LI H B, et al. Dynamic compression behavior of rock and simulation of damage effects of hypervelocity kinetic energy bomb [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2018, 38(6): 1200–1217. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0173.
|
| [22] |
ROSENBERG Z, TSALIAH J. Applying Tate’s model for the interaction of long rod projectiles with ceramic targets [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1990, 9(2): 247–251. DOI: 10.1016/0734-743X(90)90016-O.
|
| [23] |
FORRESTAL M J, TZOU D Y, ASKARI E, et al. Penetration into ductile metal targets with rigid spherical-nose rods [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1995, 16(5/6): 699–710.
|
| [24] |
ROSENBERG Z, DEKEL E. On the deep penetration of deforming long rods [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2010, 47: 238–250. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2009.09.030.
|
| [25] |
TATE A. Long rod penetration models: Part Ⅱ: extensions to the hydrodynamic theory of penetration [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 1986, 28(9): 599–612. DOI: 10.1016/0020-7403(86)90075-5.
|
| [26] |
WALKER J D, ANDERSON C E. A time-dependent model for long-rod penetration [J]. International Journal of ImpactEngineering, 1995, 16(1): 19–48.
|
| [27] |
ROSENBERG Z, DEKEL E. The deep penetration of concrete targets by rigid rods: revisited [J]. International Journal of Protective Structure, 2010, 1: 125–144. DOI: 10.1260/2041-4196.1.1.125.
|
| [28] |
ZHANG M H, SHIM V P, LU G, et al. Resistance of high-strength concrete to projectile impact [J]. International Journal of ImpactEngineering, 2005, 31: 825–841. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2004.04.009.
|
| [29] |
GRADY D E. Shock-wave compression of brittle solids [J]. Mechanics of Materials, 1998, 29: 181–203.
|
| [30] |
LUNDBORG N. Strength of rock-like materials [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 1968, 5: 427–454. DOI: 10.1016/0148-9062(68)90046-6.
|
| [31] |
ROSENBERG Z. On the relation between the Hugoniot elastic limit and the yield strength of brittle materials [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1993, 74(1): 752–753. DOI: 10.1063/1.355247.
|
| [32] |
王礼立. 应力波基础[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2005.
|
| [33] |
胡进军, 谢礼立. 地震超剪切破裂研究现状 [J]. 地球科学进展, 2011, 26(1): 39–47.HU J J, XIE L L. Review of the state-of-art researches on earthquake super-shear rupture [J]. Advance in Earth Science, 2011, 26(1): 39–47.
|
| [34] |
SATAPATHY S, BLESS S. Cavity expansion resistance of brittle materials obeying a two-curve pressure-shear behavior [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2000, 88(7): 4004–4012. DOI: 10.1063/1.1288007.
|
| [35] |
BAVDEKAR S, PARSARD G, SUBHASH G, et al. Animproved dynamic expanding cavity model for high-pressureand high-strain rate responseofceramics [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2017, 26: 39–47.
|
| [36] |
STERNBERG J. Material properties determining the resistance of ceramics to high velocity penetration [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1989, 65(9): 3417–3424. DOI: 10.1063/1.342659.
|
| [37] |
KOZHUSHKO A A, RYKOVA I I, SINANI A B. Resistance of ceramics to penetration at impact velocities above 5 km/s [J]. Journal de Physique IV, 1991, 1(C3): C3–117. 1.
|
| [38] |
ISBELL W M, ANDERSON C E, ASAY J R, et al. Penetration mechanics research in the former Soviet Union [R]. San Diego, California: Science Applications International Corp, 1992.
|
| [39] |
VLASOVA M V, KAKAZEI N G, KOVTUN V I. Failure of self-bonded silicon carbide under dynamic pressure [J]. Powder Metallurgy and Metal Ceramics, 1988, 27(4): 325–329.
|
| [40] |
徐建波. 长杆弹对混凝土的侵彻特性研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2001.
|
| [41] |
刘桂武, 倪长也, 金峰, 等. 陶瓷/金属复合装甲抗弹约束效应述评 [J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2011, 45(3): 7–15.LIU G W, NI C Y, JIN F, et al. Review of anti-ballistic confinement effects of ceramic-metal composite armor [J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2011, 45(3): 7–15.
|
| [42] |
徐松林, 单俊芳, 王鹏飞, 等. 三轴应力状态下混凝土的侵彻性能研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2019, 39(7): 071101. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0034.XU S L, SHAN J F, WANG P F, et al. Penetration performance of concrete under triaxial stress [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2019, 39(7): 071101. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0034.
|
| [43] |
蒙朝美, 宋殿义, 蒋志刚, 等. 多边形钢管约束混凝土靶抗侵彻性能试验研究 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2018, 37(13): 14–19.MENG C M, SONG D Y, JIANG Z G, et al. Tests for anti-penetration performance of polygonal steel tube-confined concrete targets [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2018, 37(13): 14–19.
|
| [44] |
任劼, 党发宁, 马宗源, 等. 复杂地应力条件下聚能射流装药侵彻深部砂岩穿透深度研究 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2018, 37(3): 679–688.REN J, DANG F N, MA Z Y, et al. Penetration depth of shaped charge into deep sandstone under complex geostress [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 37(3): 679–688.
|
| [45] |
FAN P X, WANG M Y, SONG C M. Anti-strike capability of steel-fiber reactive powder concrete [J]. Defence Science Journal, 2013, 63(4): 363–368. DOI: 10.14429/dsj.63.2407.
|






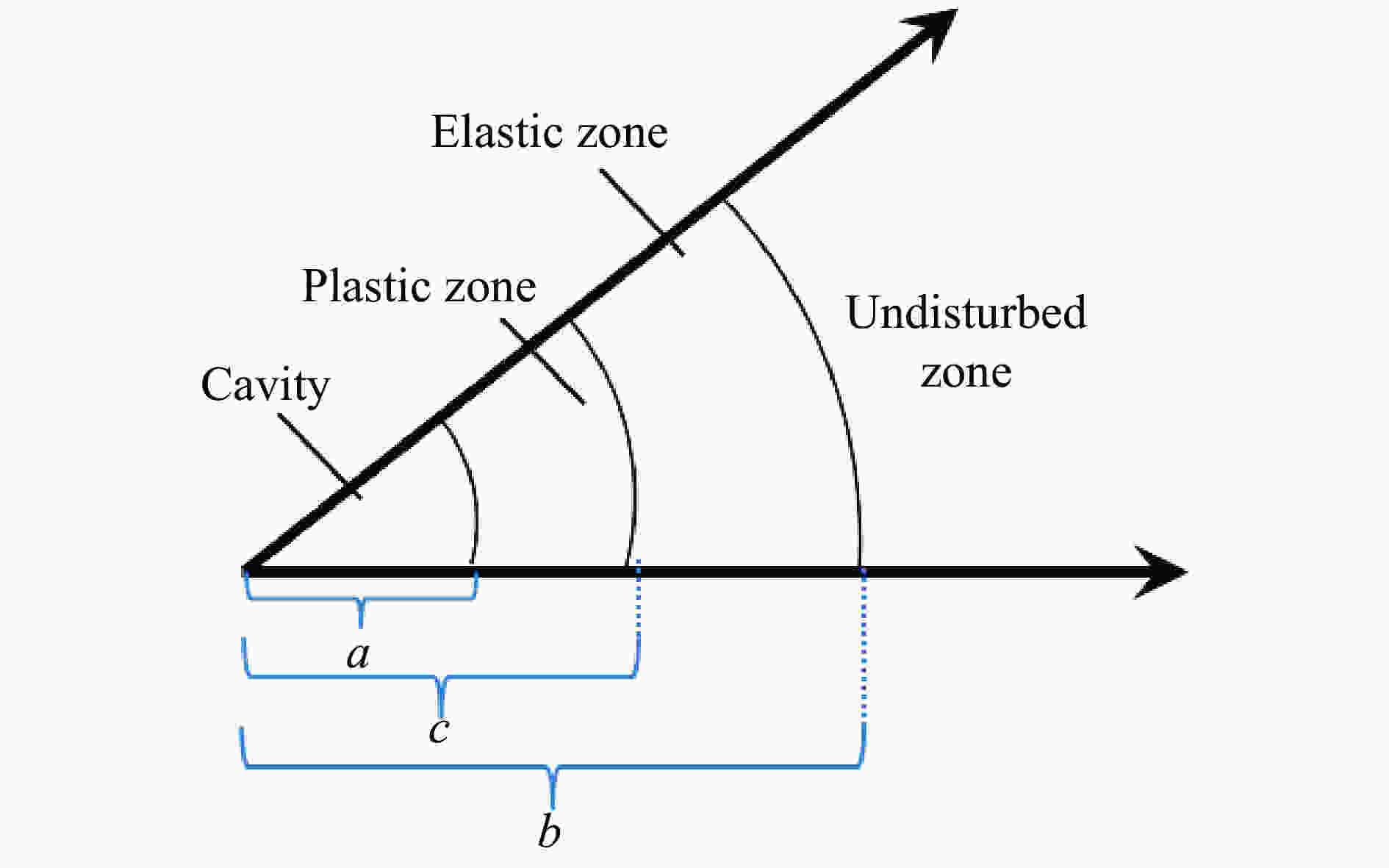
 下载:
下载: