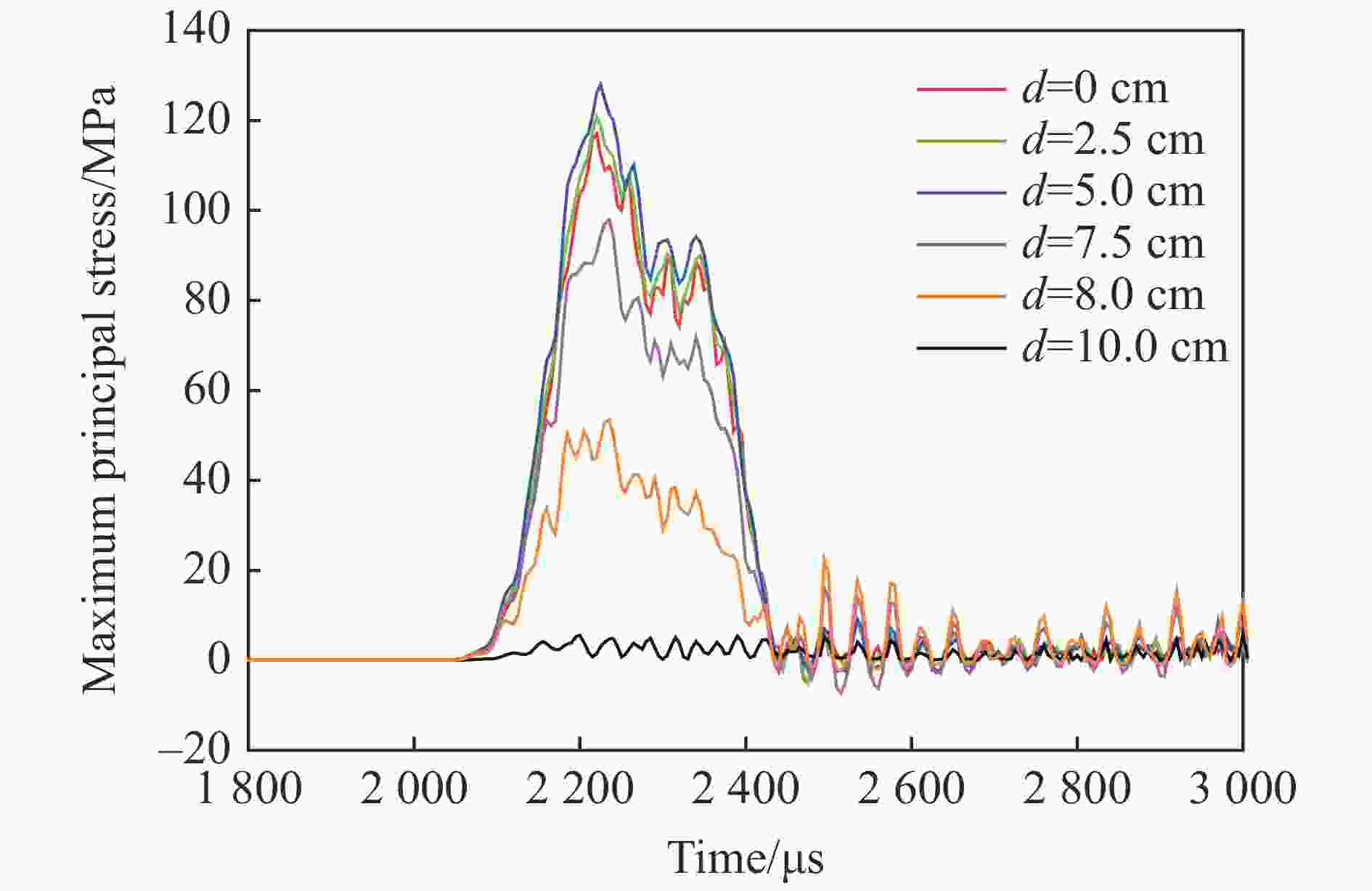
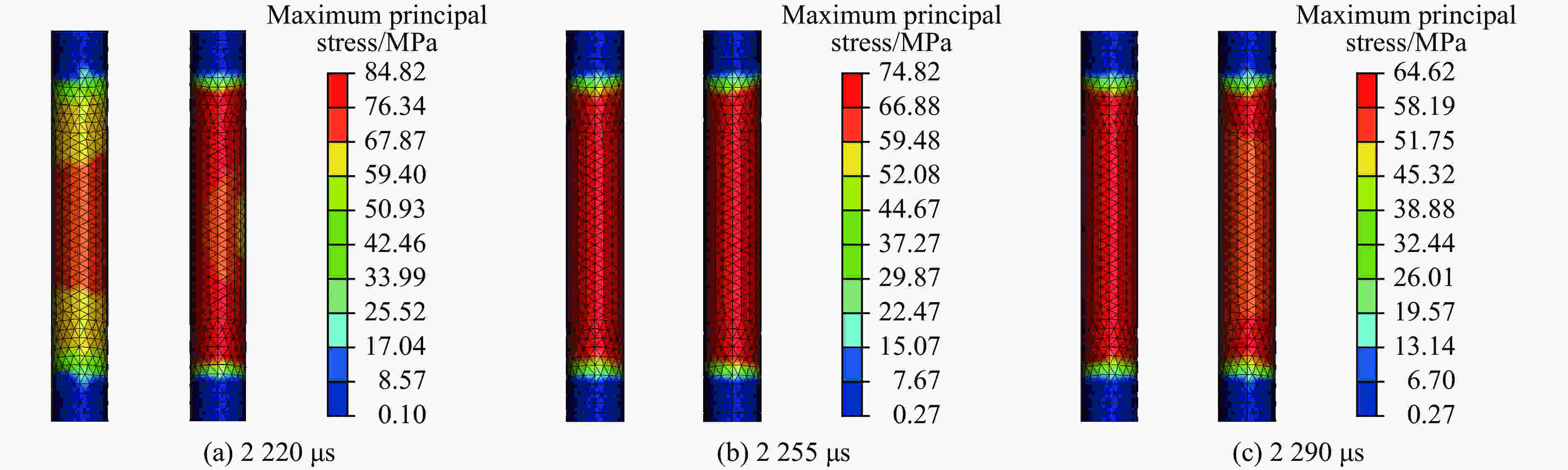
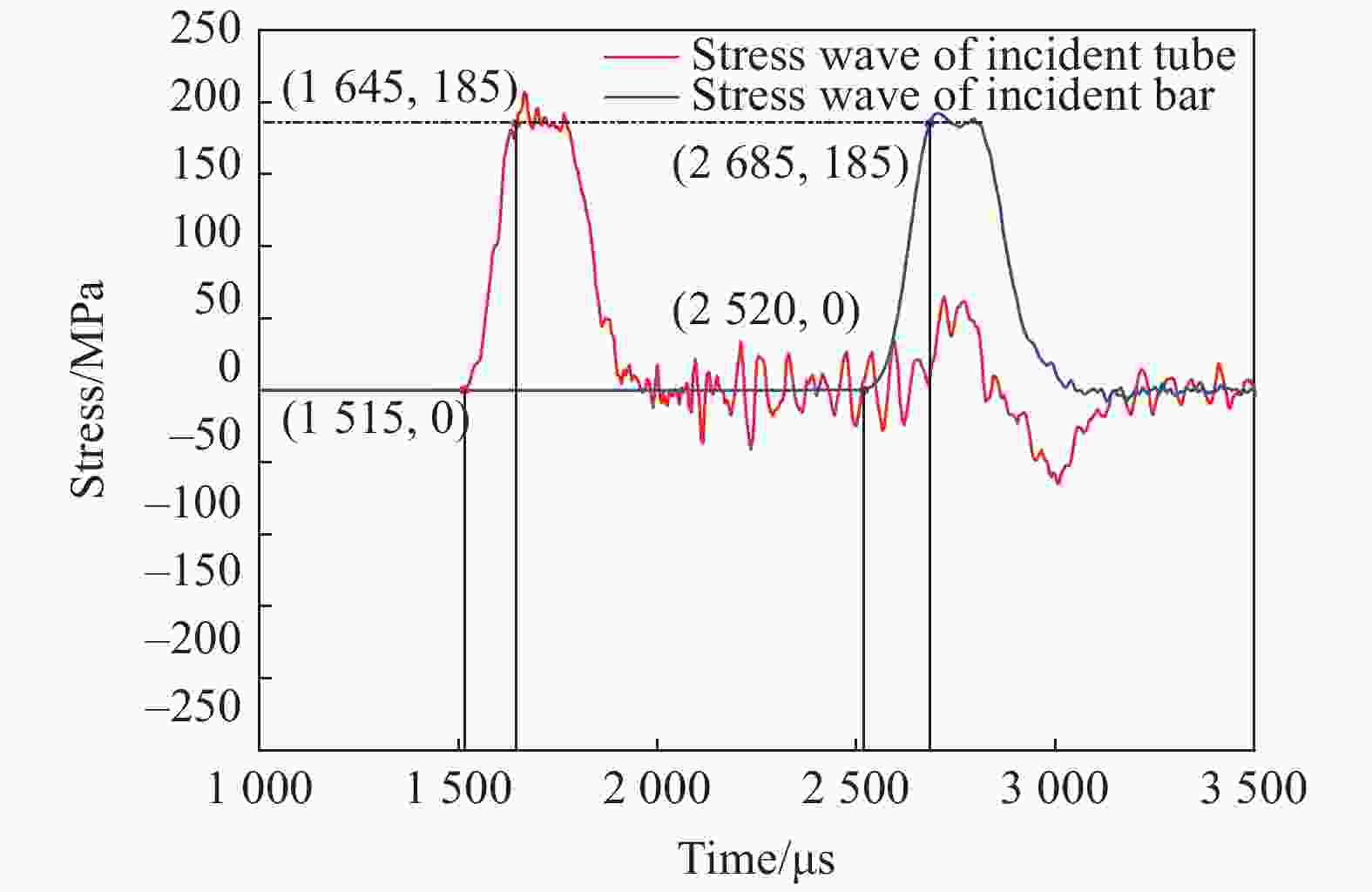
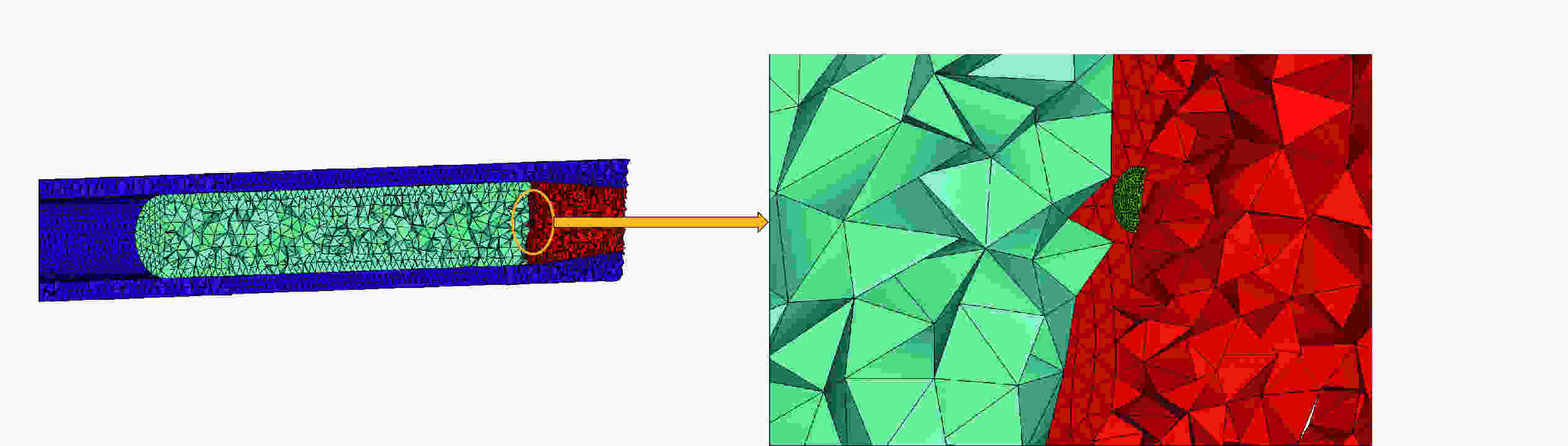
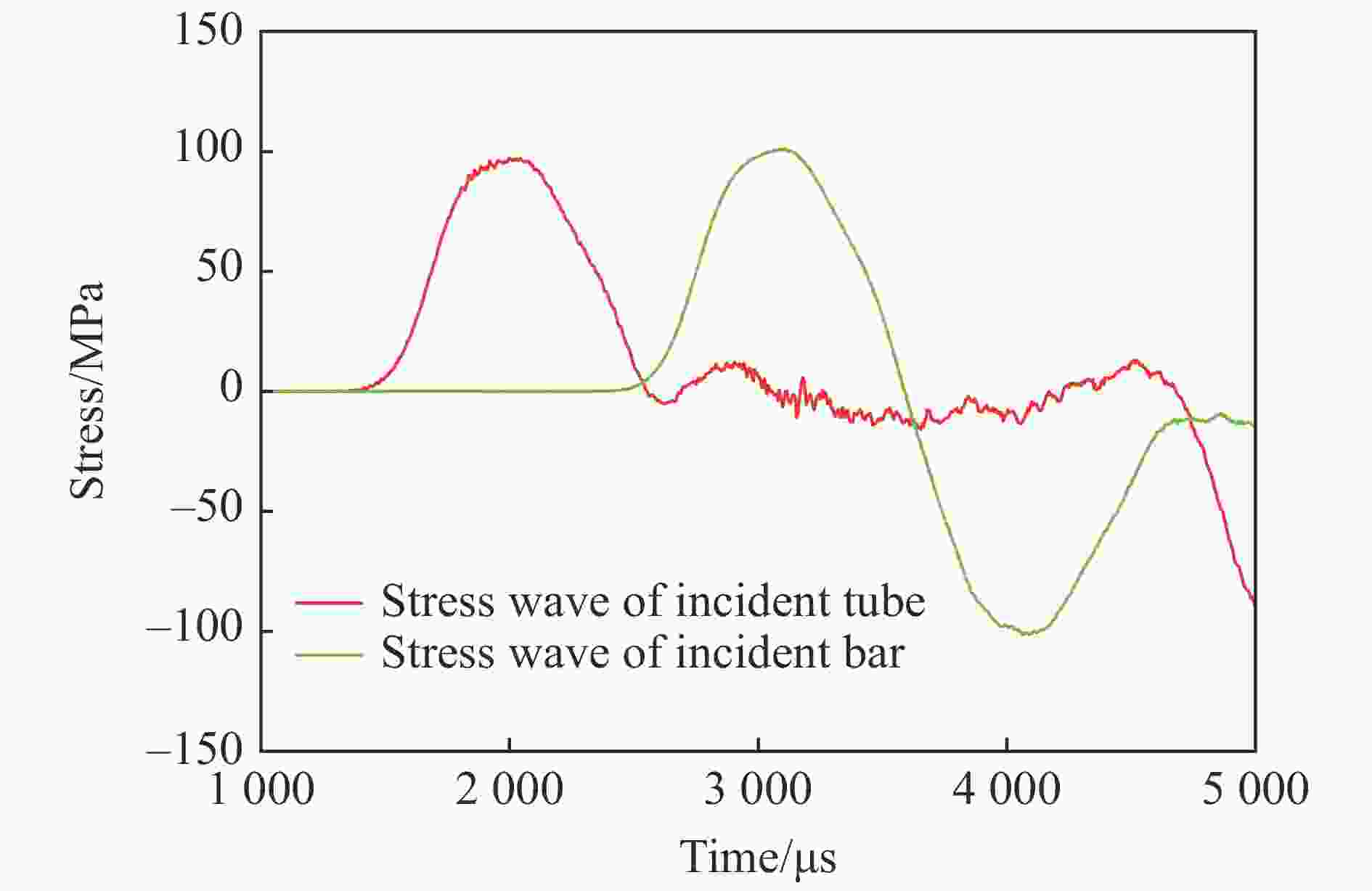
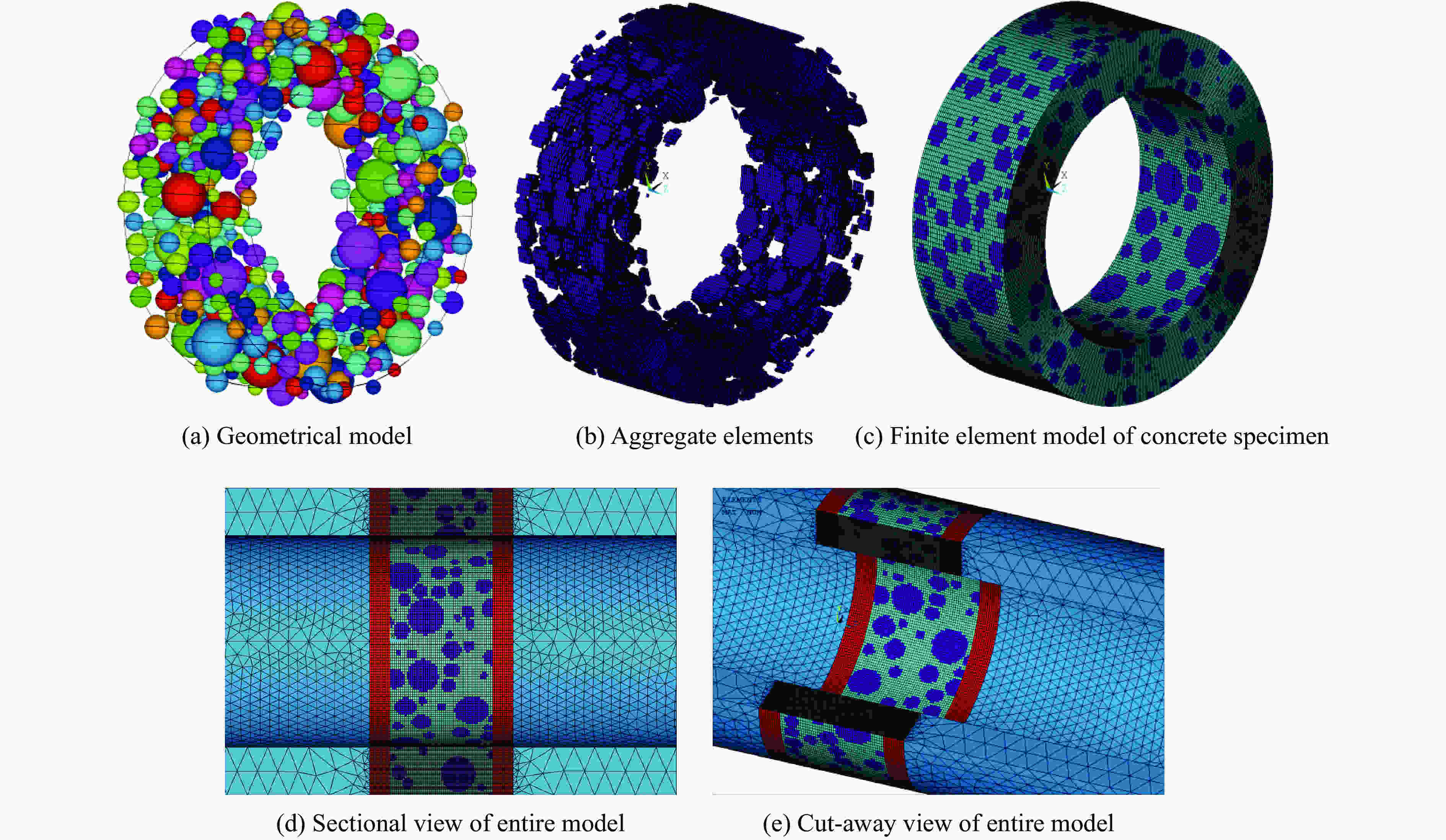
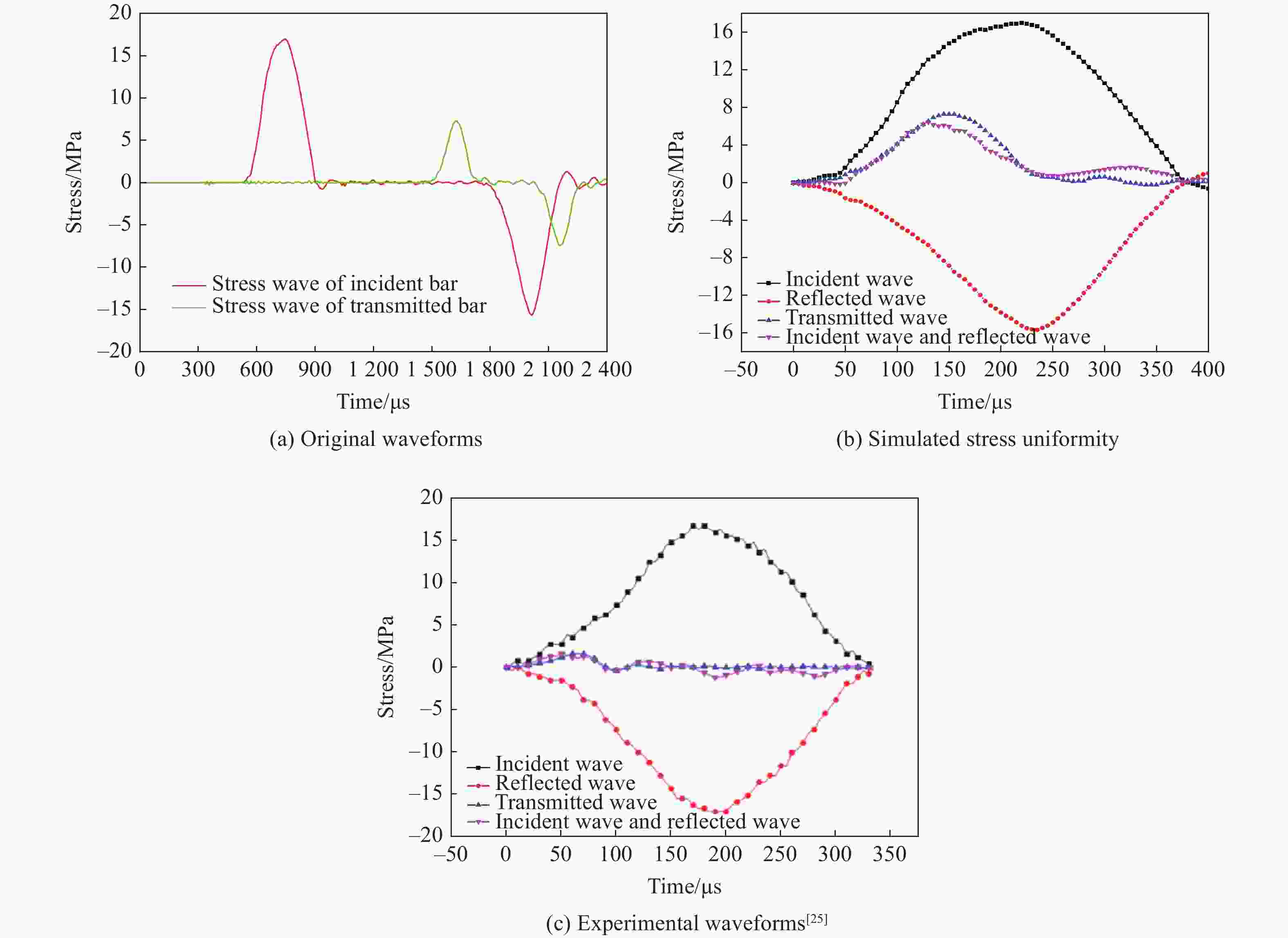
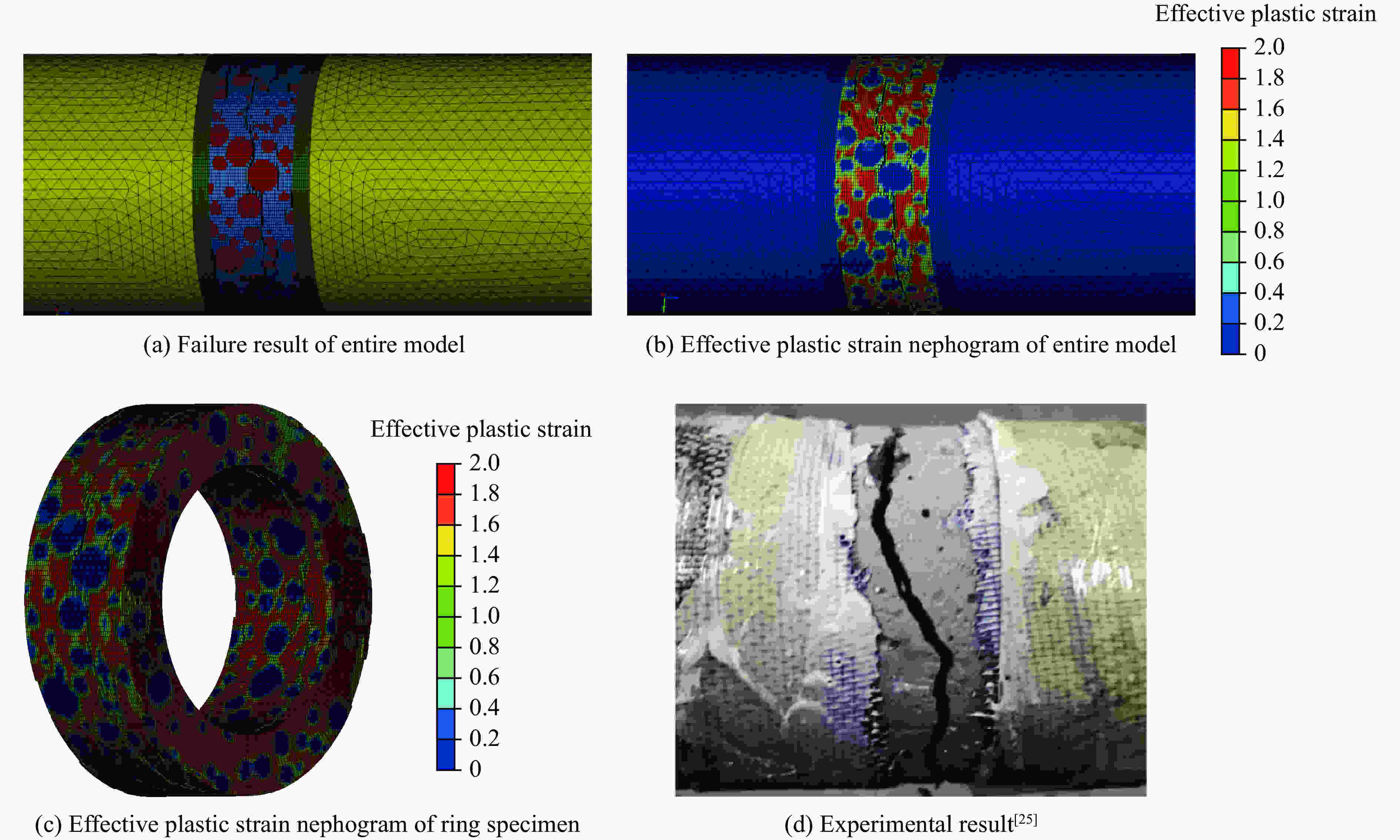
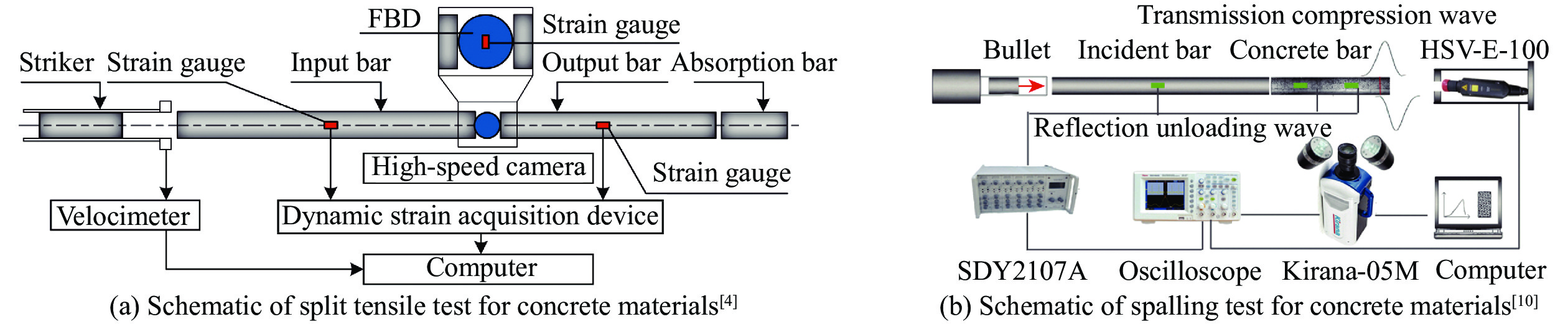
| [1] |
KHOSRAVANI M R, WEINBERG K. A review on split Hopkinson bar experiments on the dynamic characterisation of concrete [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 190: 1264–1283. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.09.187.
|
| [2] |
郭瑞奇, 任辉启, 张磊, 等. 分离式大直径Hopkinson杆实验技术研究进展 [J]. 兵工学报, 2019, 40(7): 1518–1536. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2019.07.023.GUO R Q, REN H Q, ZHANG L, et al. Research progress of large-diameter split Hopkinson bar experimental technique [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2019, 40(7): 1518–1536. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2019.07.023.
|
| [3] |
LAMBERT D E, ROSS C A. Strain rate effects on dynamic fracture and strength [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2000, 24(10): 985–998. DOI: 10.1016/S0734-743X(00)00027-0.
|
| [4] |
FENG W H, LIU F, YANG F, et al. Experimental study on dynamic split tensile properties of rubber concrete [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 165: 675–687. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.01.073.
|
| [5] |
曹海, 马芹永. 预制与后浇混凝土粘结后的动态劈拉性能 [J]. 建筑材料学报, 2018, 21(1): 150–153;164. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2018.01.024.CAO H, MA Q Y. Dynamic splitting tensile performance of post pouring concrete adhered on precast concrete [J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2018, 21(1): 150–153;164. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2018.01.024.
|
| [6] |
CHEN X D, GE L M, ZHOU J K, et al. Dynamic Brazilian test of concrete using split Hopkinson pressure bar [J]. Materials and Structures, 2017, 50(1): 1. DOI: 10.1617/s11527-016-0885-6.
|
| [7] |
胡时胜, 张磊, 武海军, 等. 混凝土材料层裂强度的实验研究 [J]. 工程力学, 2004, 21(4): 128–132. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4750.2004.04.023.HU S S, ZHANG L, WU H J, et al. Experimental study on spalling strength of concrete [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2004, 21(4): 128–132. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4750.2004.04.023.
|
| [8] |
张磊, 胡时胜. 混凝土层裂强度测量的新方法 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2006, 26(6): 537–542. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2006)06-0537-06.ZHANG L, HU S S. A novel experimental technique to determine the spalling strength of concretes [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2006, 26(6): 537–542. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2006)06-0537-06.
|
| [9] |
WU H J, ZHANG Q M, HUANG F L, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation on the dynamic tensile strength of concrete [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2005, 32(1-4): 605–617. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2005.05.008.
|
| [10] |
俞鑫炉, 付应乾, 董新龙, 等. 混凝土一维应力层裂实验的全场DIC分析 [J]. 力学学报, 2019, 51(4): 1064–1072. DOI: 10.6052/0459-1879-19-008.YU X L, FU Y Q, DONG X L, et al. Full field DIC analysis of one-dimensional spall strength for concrete [J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2019, 51(4): 1064–1072. DOI: 10.6052/0459-1879-19-008.
|
| [11] |
巫绪涛, 代仁强, 陈德兴, 等. 钢纤维混凝土动态劈裂试验的能量耗散分析 [J]. 应用力学学报, 2009, 26(1): 151–154. DOI: 1000-4939(2009)01-0151-04.WU X T, DAI R Q, CHEN D X, et al. Energy dissipation analysis on dynamic splitting-tensile test of steel fiber reinforced concrete [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2009, 26(1): 151–154. DOI: 1000-4939(2009)01-0151-04.
|
| [12] |
张磊,胡时胜,陈德兴,等. 混凝土材料的层裂特性 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2008, 28(3): 193–199. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2008)03-0193-07.ZHANG L, HU S S, CHEN D X, et al. Spall characteristics of concrete materials [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2008, 28(3): 193–199. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2008)03-0193-07.
|
| [13] |
张凯, 陈荣刚, 张威, 等. 混凝土动态直接拉伸实验技术研究 [J]. 实验力学, 2014, 29(1): 89–96. DOI: 10.7520/1001-4888-13-064.ZHANG K, CHEN R G, ZHANG W, et al. Study of experimental technique for concrete dynamic direct tension [J]. Journal of Experimental Mechanics, 2014, 29(1): 89–96. DOI: 10.7520/1001-4888-13-064.
|
| [14] |
LEVI-HEVRONI D, KOCHAVI E, KOFMAN B, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation on the dynamic increase factor of tensile strength in concrete [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2018, 114: 93–104. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2017.12.006.
|
| [15] |
姜锡权, 徐可立, 方文敏, 等. 新型分离式霍普金森拉杆装置: CN201310044304.3 [P]. 2013-05-08.
|
| [16] |
王礼立, 胡时胜, 杨黎明, 等. 材料动力学[M]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社, 2017.
|
| [17] |
郭瑞奇, 任辉启, 张磊, 等. 基于混凝土细观骨料模型的SHPB仿真模拟研究 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2019, 38(22): 107–116. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2019.22.015.GUO R Q, REN H Q, ZHANG L, et al. Simulation for SHPB tests based on a mesoscopic concrete aggregate model [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2019, 38(22): 107–116. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2019.22.015.
|
| [18] |
崔堃鹏, 夏超逸, 刘炎海, 等. 高速铁路桥墩汽车撞击力的数值模拟与特性分析 [J]. 桥梁建设, 2013, 43(6): 57–63. DOI: 1003-4722(2013)06-0057-07.CUI K P, XIA C Y, LIU Y H, et al. Numerical simulation and characteristic analysis of vehicle collision forces in high-speed railway bridge pier [J]. Bridge Construction, 2013, 43(6): 57–63. DOI: 1003-4722(2013)06-0057-07.
|
| [19] |
韩志伟, 周红杰, 李春, 等. 海上风力机与船舶碰撞的动力响应及防碰装置 [J]. 中国机械工程, 2019, 30(12): 1387–1394. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2019.12.001.HAN Z W, ZHOU H J, LI C, et al. Dynamic response and anti collision devices of an offshore wind turbine subjected to ship impacts [J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 30(12): 1387–1394. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2019.12.001.
|
| [20] |
王礼立. 应力波基础[M].2版.北京: 国防工业出版社, 2005.
|
| [21] |
果春焕, 周培俊, 陆子川, 等. 波形整形技术在Hopkinson杆实验中的应用 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2015, 35(6): 881–887. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2015)06-0881-07.GUO C H, ZHOU P J, LU Z C, et al. Application of pulse shaping technique in Hopkinson bar experiments [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2015, 35(6): 881–887. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2015)06-0881-07.
|
| [22] |
江德斐, 林国标, 舒大禹, 等. T2铜的动态力学性能及本构关系 [J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2016, 26(7): 1437–1443. DOI: 1004-0609(2016)-07-1437-07.JIANG D F, LIN G B, SHU D Y, et al. Dynamic mechanical property and constitutive relation of T2 copper [J]. Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2016, 26(7): 1437–1443. DOI: 1004-0609(2016)-07-1437-07.
|
| [23] |
ZHANG M, WU H J, LI Q M, et al. Further investigation on the dynamic compressive strength enhancement of concrete-like materials based on split Hopkinson pressure bar tests: part I: experiments [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2009, 36(12): 1327–1334. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2009.04.009.
|
| [24] |
LI Q M, LU Y B, MENG H. Further investigation on the dynamic compressive strength enhancement of concrete-like materials based on split Hopkinson pressure bar tests: part Ⅱ: numerical simulations [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2009, 36(12): 1335–1345. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2009.04.010.
|
| [25] |
ZHANG S, LU Y B, JIANG X Q, et al. Inertial effect on concrete-like materials under dynamic direct tension [J]. International Journal of Protective Structures, 2018, 9(3): 377–396. DOI: 10.1177/2041419618766156.
|
| [26] |
金浏, 杜修力. 加载速率对混凝土拉伸破坏行为影响的细观数值分析 [J]. 工程力学, 2015, 32(8): 42–49. DOI: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2013.08.0791.JIN L, DU X L. Meso-scale numerical analysis of the effect of loading rate on the tensile failure behavior of concrete [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2015, 32(8): 42–49. DOI: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2013.08.0791.
|
| [27] |
吴成, 沈晓军, 王晓鸣, 等. 细观混凝土靶抗侵彻数值模拟及侵彻深度模型 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2018, 38(6): 1364–1371. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2017-0123.WU C, SHEN X J, WANG X M, et al. Numerical simulation on anti-penetration and penetration depth model of mesoscale concrete target [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2018, 38(6): 1364–1371. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2017-0123.
|
| [28] |
邓勇军, 陈小伟, 姚勇, 等. 基于细观混凝土模型的刚性弹体正侵彻弹道偏转分析 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2017, 37(3): 377–386. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2017)03-0377-10.DENG Y J, CHEN X W, YAO Y, et al. On ballistic trajectory of rigid projectile normal penetration based on a meso-scopic concrete model [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2017, 37(3): 377–386. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2017)03-0377-10.
|
| [29] |
郭瑞奇. 三维混凝土骨料模型的p型自适应有限元及其快速求解算法[D]. 湘潭: 湘潭大学, 2017.
|
| [30] |
CHEN G, HAO Y F, HAO H. 3D meso-scale modelling of concrete material in spall tests [J]. Materials and Structures, 2015, 48(6): 1887–1899. DOI: 10.1617/s11527-014-0281-z.
|
| [31] |
XU Z, HAO H, LI H N. Mesoscale modelling of dynamic tensile behaviour of fibre reinforced concrete with spiral fibres [J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2012, 42(11): 1475–1493. DOI: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2012.07.006.
|
| [32] |
MALVAR L J, CRAWFORD J E, WESEVICH J W, et al. A plasticity concrete material model for DYNA3D [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1997, 19(9-10): 847–873. DOI: 10.1016/S0734-743X(97)00023-7.
|
| [33] |
MALVAR L J, CRAWFORD J E, MORRILL K B. K&C concrete material model release Ⅲ: automated generation of material model input[R]. Karagozian and Case Structural Engineers, 2000.
|






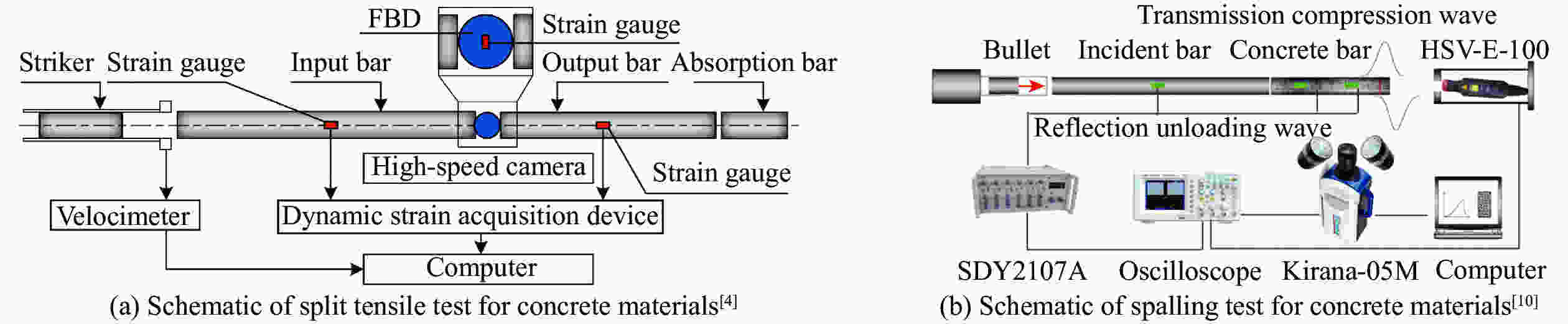
 下载:
下载: