Experimental investigation on characteristics of layered ice spheres under high-velocity impact
-
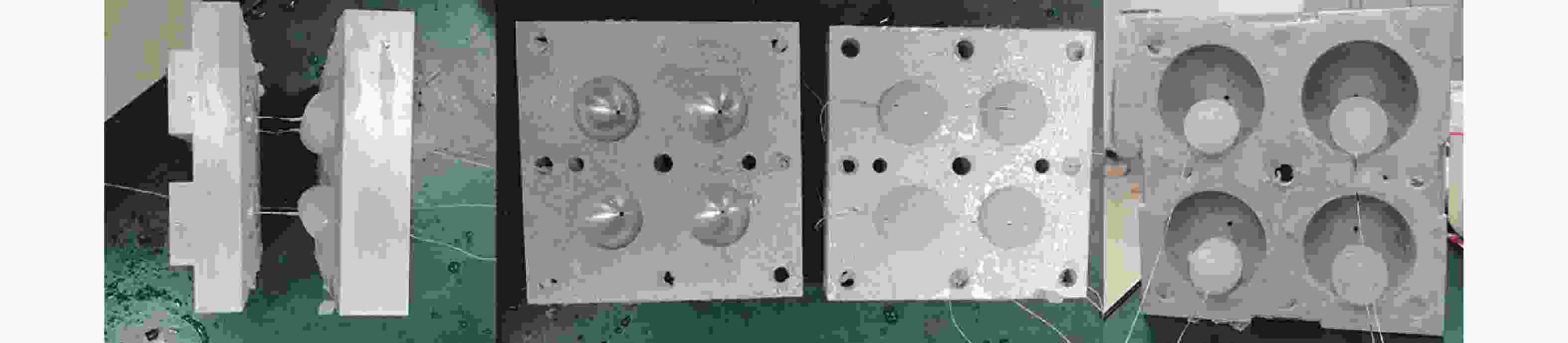
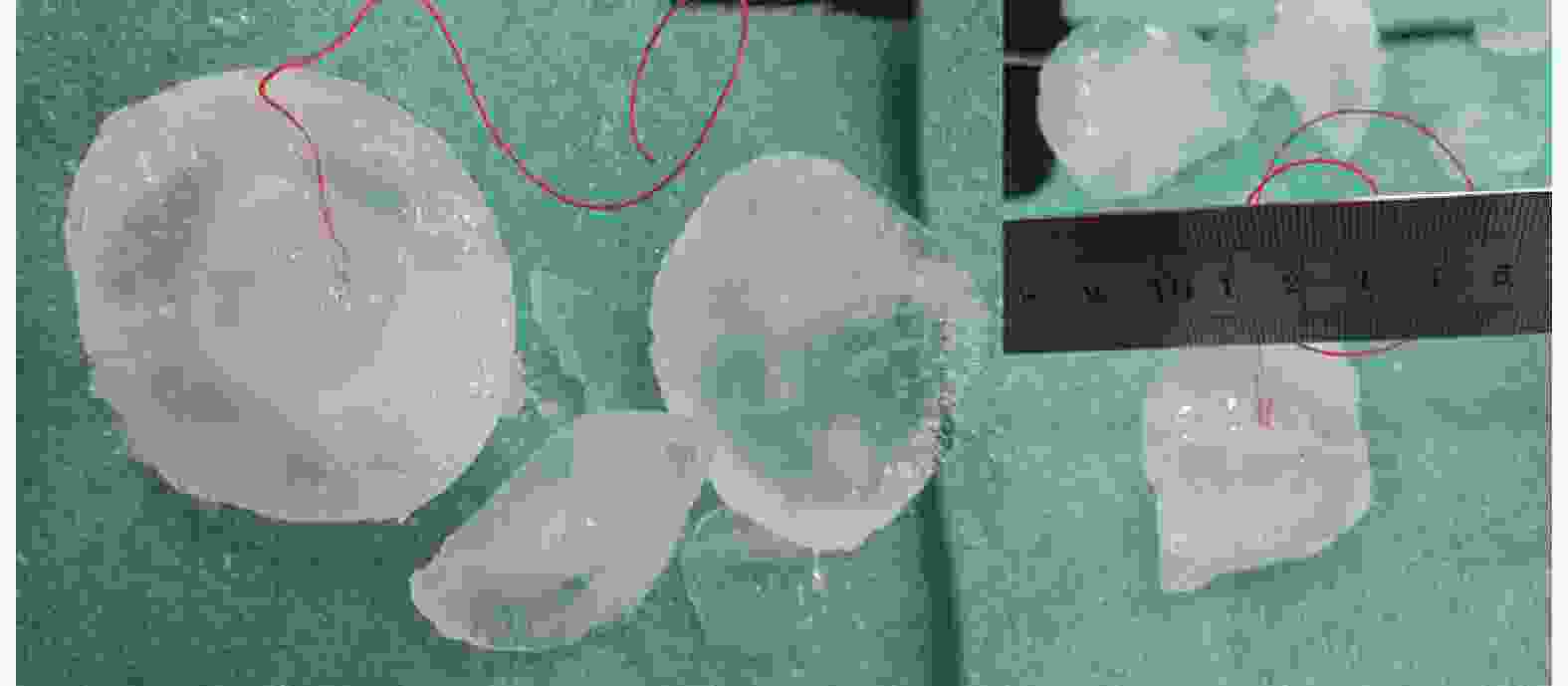
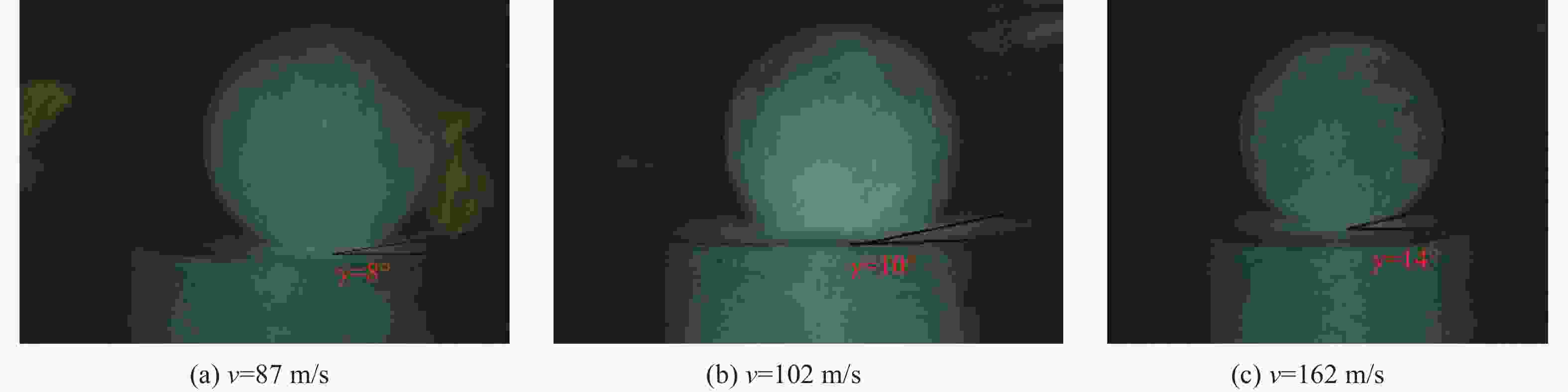
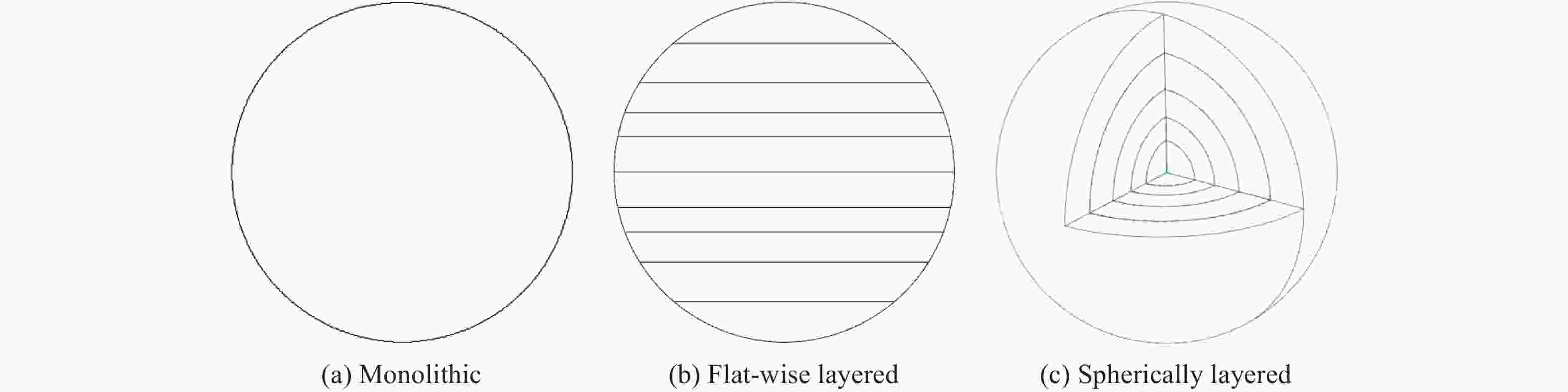
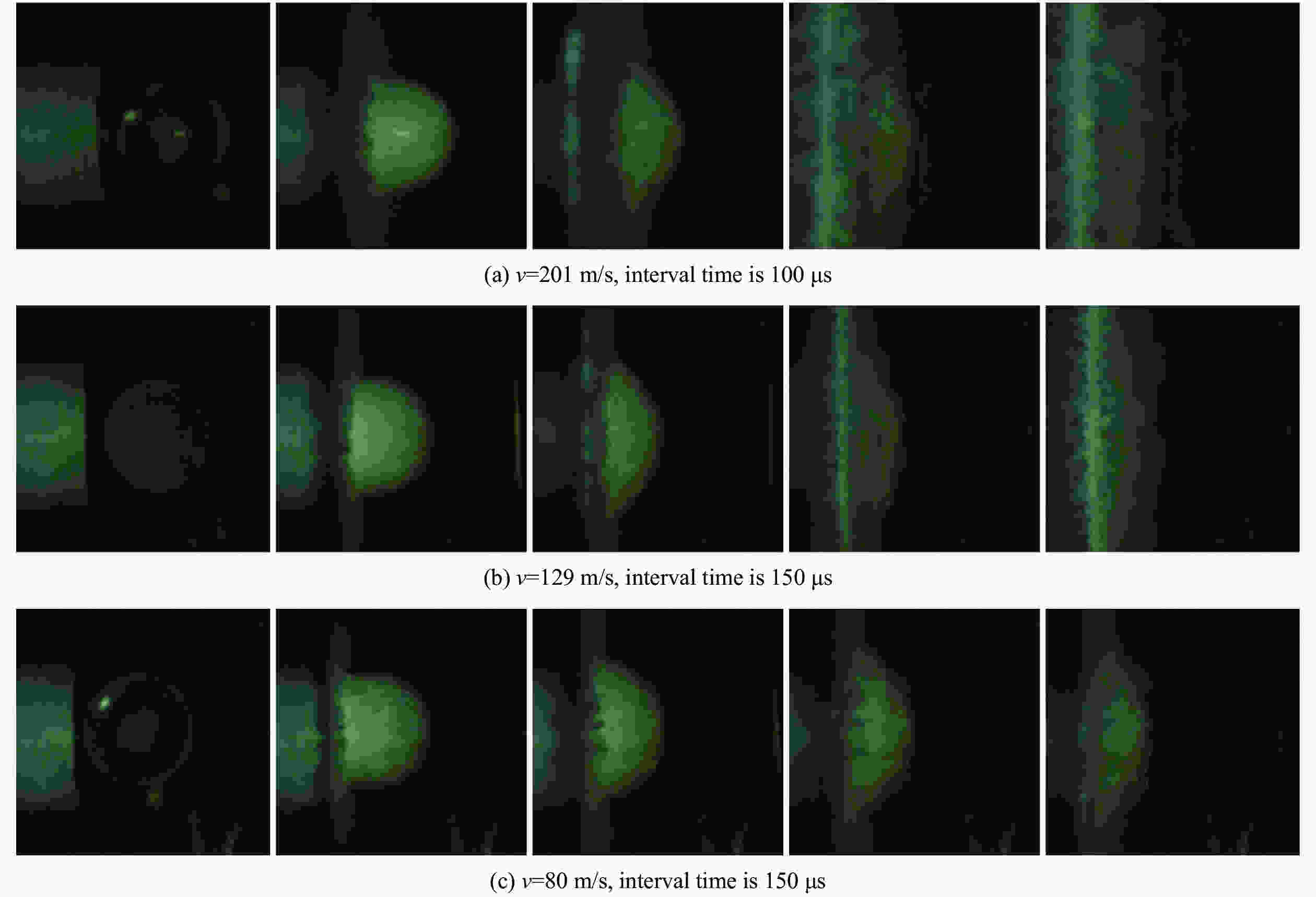
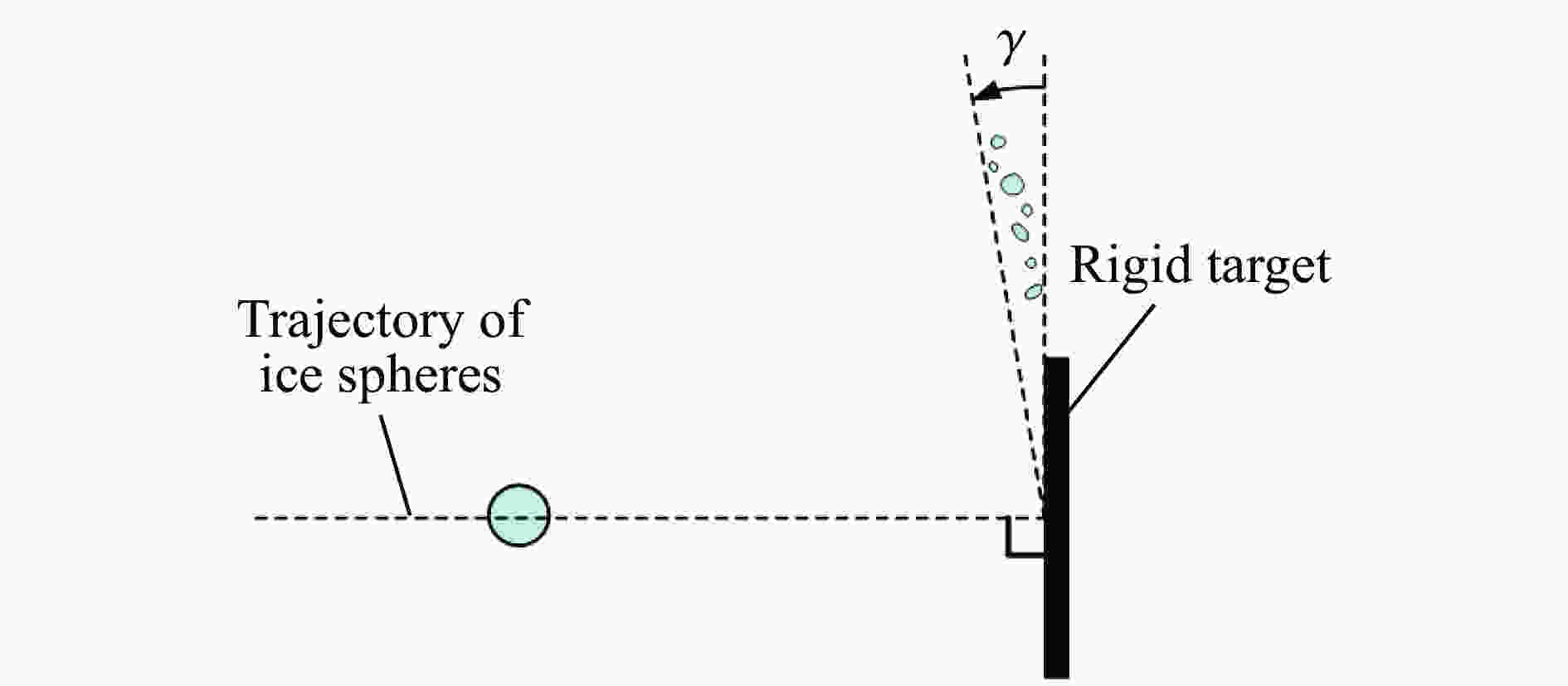
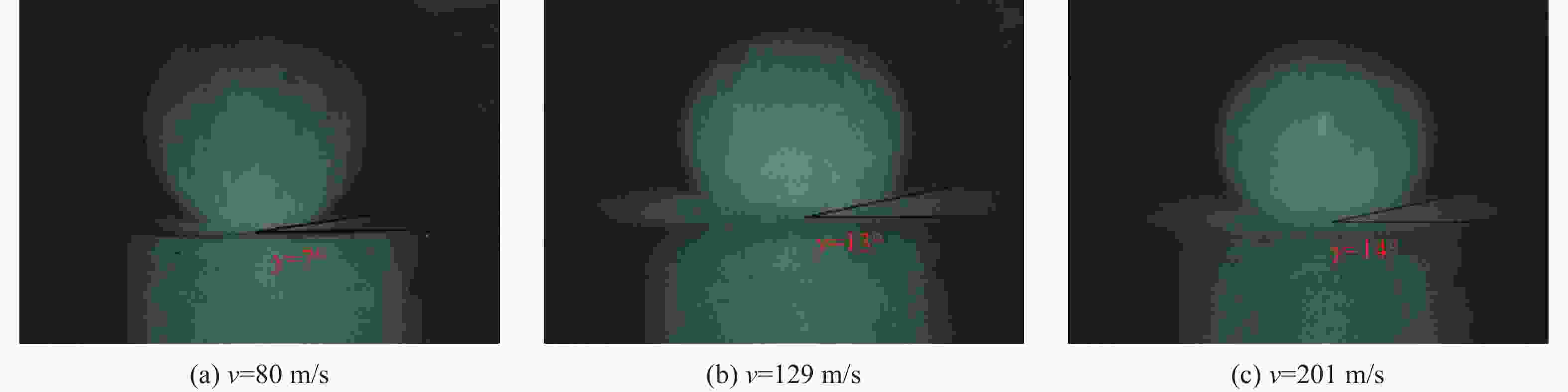
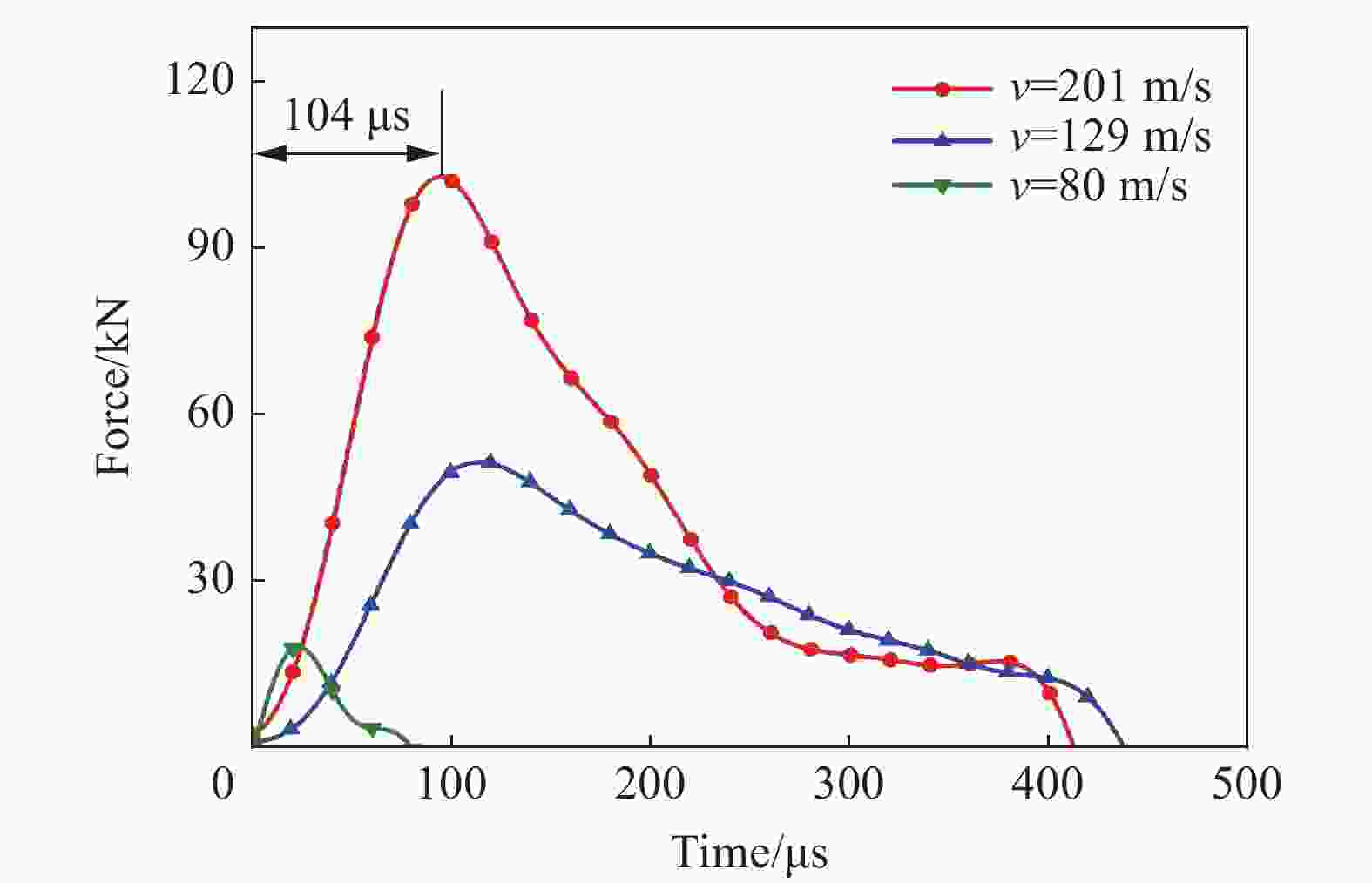
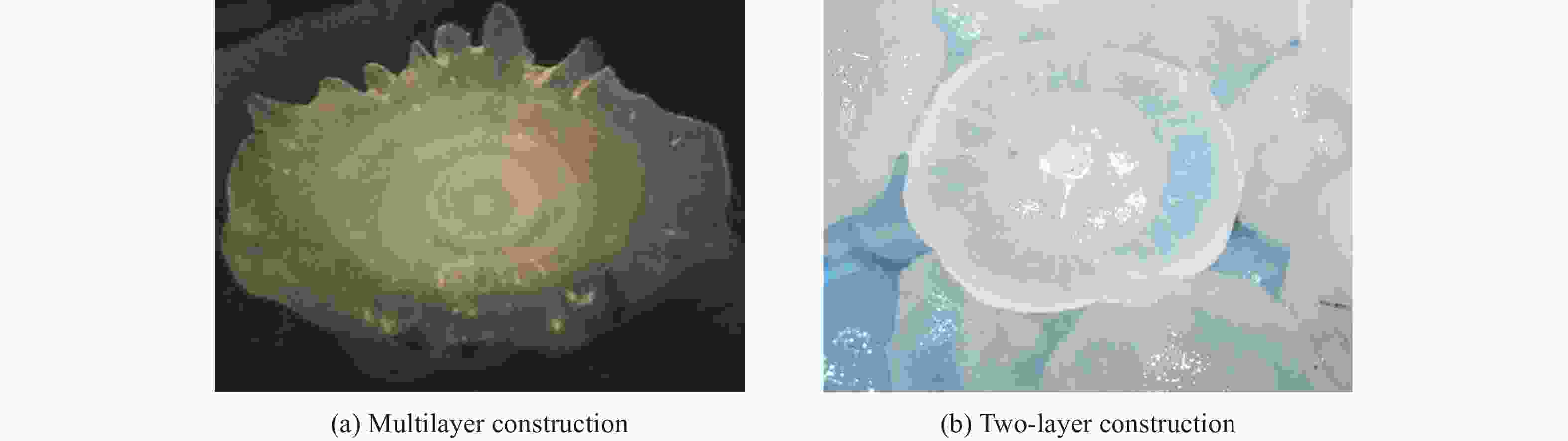
摘要: 为研究冰雹在不同撞击速度下的破碎特性及致损能力,通过空气炮加载技术,开展了单一性状冰球和层状结构冰球高速撞击刚性靶实验,利用测力杆记录了两种类型冰球在不同撞击速度下的撞击力时程曲线,并结合高速摄影技术研究了两类冰球的高速撞击破碎特性。实验结果表明:两类冰球高速撞击刚性靶的宏观破碎特性相似,在碰撞初始阶段冰球已完全破碎,形成微颗粒团簇体,反向溅射角呈随撞击动能增大而增大的趋势;与单一性状冰球撞击力曲线相比,层状结构冰球撞击力曲线中出现二次上升信号,推测是由于破碎界面在层间界面发生偏折,小球未完全破碎再次撞击测力杆所导致;高速撞击下层状结构冰球的撞击力高于单一性状冰球,推测是由于层间结构的存在延缓了冰球的破碎进程,提升了其在冲击方向传递动量的能力,进而产生了更高的撞击力。研究结果有助于深化对冰雹在高速撞击下的破坏力学行为的认识,同时可为飞行器结构防护、冰雹撞击安全设计研究等提供参考。Abstract: The hail impact has become a realistic threat for aerospace industries. Natural hail ice has a spherically-layered construction. In order to study the impact failure characteristics and damage ability of hail ice, spherically-layered ice spheres with two layers were created. A series of high- velocity impact experiments were conducted for the simulated hail ice spheres (both monolithic and spherically layered ice) through a smooth barrel gas gun. The dynamic failure properties of ice spheres were studied using high-speed video images during the impact event. Based on the experimental results, it is found that both the monolithic and layered ice spheres present the similar macroscopic crushing characteristics. The ice fragments are formed in the early impact stage. Fragments trajectories lie almost in the target plane. The angle between the fragment trajectories and the plane of the target increases with the increase of impact kinetic energy. A possible explanation for this phenomenon could be attributed to the release rate of projectile kinetic energy. The impact force histories of ice spheres under different velocities were recorded by a force measurement bar apparatus. The impact force curves of monolithic ice show a trend of a sudden increase of the force reaching a maximum, followed by a more gradually decreasing force versus time decay. However, the impact force curves of layered ice show a second rising signal at the last stage. The formation mechanism of the secondary rise signal is hypothesized that the internal small ball is not completely fragmented due to the deflection of failure front at the interlayer interface during impact process. The measured peak impact force is observed to increase with the increase of the projectile kinetic energy. The maximum peak force is reached at very early stage of the impact. Then the ice is actually fragmented, which can not transfer more momentum in the impact direction. In addition, there is a suggestion of higher impact forces for layered ice. This result is expected that the fragmentation process of layered-ice spheres is delayed by the interlayer interface, which is able to transfer much more momentum in the direction of the impact. The achievements of the study are helpful to better understand the dynamic mechanical behaviors of ice under impact loading, and can also provide reference for the safe design of aerocraft structure.
-
Key words:
- layered ice sphere /
- high velocity impact /
- impact force /
- dynamic failure /
- internal layer
-
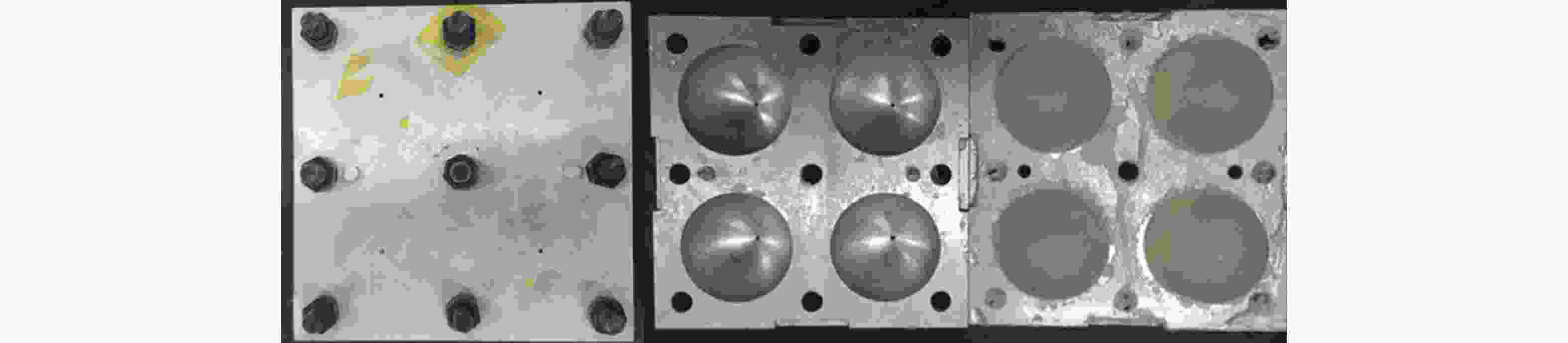
表 1 冰球高速撞击实验参数
Table 1. High-velocity impact test parameters of ice spheres
序号 类型 弹丸质量/g 撞击速度/(m·s−1) 1-1 层状结构冰球 98.0 162 1-2 层状结构冰球 97.8 87 1-3 层状结构冰球 97.9 102 2-1 单一性状冰球 100.3 129 2-2 单一性状冰球 97.1 80 2-3 单一性状冰球 97.1 201 表 2 层状结构冰球撞击力时程曲线二次升高信号时间
Table 2. Secondary rise signals in force-time histories of layered ice spheres
撞击速度/(m·s−1) 二次信号出现时刻/ms 小球撞击理论时刻/ms 162 197 185 102 201 294 87 243 345 -
[1] PEREIRA J, PADULA S, REVILOCK D, et al. Forces generated by high velocity impact of ice on a rigid structure: TM-2006-214263 [R]. NASA, 2006. [2] GUÉGAN P, OTHMAN R, LEBRETON D, et al. Experimental investigation of the kinematics of post-impact ice fragments [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2011, 38(10): 786–795. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2011.05.003. [3] COMBESCURE A, CHUZEL-MARMOT Y, FABIS J. Experimental study of high-velocity impact and fracture of ice [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2011, 48(20): 2779–2790. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2011.05.028. [4] TIPPMANN J D, KIM H, RHYMER J D. Experimentally validated strain rate dependent material model for spherical ice impact simulation [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2013, 57: 43–54. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2013.01.013. [5] PERNAS-SÁNCHEZ J, ARTERO-GUERRERO J A, VARAS D, et al. Analysis of ice impact process at high velocity [J]. Experimental Mechanics, 2015, 55: 1669–1679. DOI: 10.1007/s11340-015-0067-4. [6] KIM H, KEDWARD K T. Modeling hail ice and predicting impact damage initiation in composite structure [J]. AIAA Journal, 2000, 38(7): 1276–1286. DOI: 10.2514/2.1099. [7] KIM H, WELCH D, KEDWARD K T. Experimental investigation of high velocity ice impacts on woven carbon/epoxy composite panels [J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2003, 34(1): 25–41. DOI: 10.1016/S1359-835X(02)00258-0. [8] PARK H, KIM H. Damage resistance of single lap adhesive composite joints by transverse ice impact [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2010, 37(2): 177–184. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2009.08.005. [9] RHYMER J, KIM H. Prediction of delamination onset and critical force in carbon/epoxy panels impacted by ice spheres [J]. Computers, Materials and Continua, 2013, 35(2): 87–117. DOI: 10.1038/nmat3632. [10] DOLATI S, FEREIDOON A, SABET A R. Experimental investigation into glass fiber/epoxy composite laminates subjected to single and repeated high-velocity impacts of ice [J]. Iranian Polymer Journal, 2014, 23: 477–486. DOI: 10.1007/s13726-014-0242-y. [11] PERNAS-SÁNCHEZ J, ARTERO-GUERRERO J A, VARAS D, et al. Experimental analysis of ice sphere impacts on unidirectional carbon/epoxy laminates [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2016, 96: 1–10. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2016.05.010. [12] SONG Z H, LE J, WHISLER D, et al. Skin-stringer interface failure investigation of stringer-stiffened curved composite panels under hail ice impact [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2018, 122: 439–450. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2018.09.014. [13] JONES S J. High strain-rate compression tests on ice [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 1997, 101(32): 6099–6101. DOI: 10.1021/jp963162j. [14] DUTTA P K, COLE D M, SCHULSON E M, et al. A fracture study of ice under high strain rate loading [J]. International Offshore and Polar Engineering, 2004, 14: 182–188. DOI: 10.1109/TITS.2004.833767. [15] KIM H, KEUNE J N. Compressive strength of ice at impact strain rates [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2007, 42: 2802–2806. DOI: 10.1007/s10853-006-1376-x. [16] SHAZLY M, PRAKASH V, LERCH B A. High strain-rate behavior of ice under uniaxial compression [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2009, 46(6): 1499–1515. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2008.11.020. [17] 汪洋, 李玉龙, 刘传雄. 利用SHPB测定高应变率下冰的动态力学行为 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2011, 31(2): 215–219. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2011)02-0215-05.WANG Y, LI Y L, LIU C X. Dynamic mechanical behaviors of ice at high strain rates [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2011, 31(2): 215–219. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2011)02-0215-05. [18] WU X Q, PRAKASH V. Dynamic strength of distill water and lake water ice at high strain rates [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2015, 76: 155–165. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2014.09.013. [19] 李尚昆, 冯晓伟, 谢若泽, 等. 高应变率下纯水冰和杂质冰的动态力学行为研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2019, 39(9): 093103. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0270.LI S K, FENG X W, XIE R Z, et al. Dynamic compression property of distill-water ice and impurity-water ice at high strain rates [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2019, 39(9): 093103. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0270. [20] ANGHILERI M, INVEMIZZI F, MASCHERONI M. A survey of numerical models for hail impact analysis using explicit finite element codes [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2005, 31(8): 929–944. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2004.06.009. [21] CARNEY K S, BENSON D J, DUBOIS P, et al. A phenomenological high strain rate model with failure for ice [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2006, 43(25–26): 7820–7839. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2006.04.005. [22] SHERBUM J A, HORSTEMEYER M F. Hydrodynamic modeling of impact craters in ice [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2010, 37(1): 27–36. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2009.07.001. [23] SAIN T, NARASIMHAN R. Constitutive modeling of ice in the high strain rate regime [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2011, 48(5): 817–827. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2010.11.016. [24] PERNAS-SÁNCHEZ J, PEDROCHE D A, VARAS D, et al. Numerical modeling of ice behavior under high velocity impacts [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2012, 49: 1919–1927. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2012.03.038. [25] 刘洋, 王富生, 岳珠峰. 冰雹冲击复合材料层合板失效模式分析与数值模拟 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2011, 30(9): 150–154. DOI: 10.1631/jzus.A1000257.LIU Y, WANG F S, YUE Z F. Failure model analysis and simulation of laminated composite plate under hailstone impacting [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2011, 30(9): 150–154. DOI: 10.1631/jzus.A1000257. [26] TANG Z B, HANG C, SUO T, et al. Numerical and experimental investigation on hail impact on composite panels [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2017, 105: 102–108. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2016.05.016. [27] 张永康, 李玉龙, 汤忠斌, 等. 冰雹撞击下泡沫铝夹芯板的动态效应 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2018, 38(2): 373–380. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2016-0232.ZHANG Y K, LI Y L, TANG Z B, et al. Dynamic response of aluminum-foam-based sandwich panels under hailstone impact [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2018, 38(2): 373–380. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2016-0232. [28] 李光亮. 冰雹[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2002. -






 下载:
下载: