A novel technique for determining the dynamic Bauschinger effect by electromagnetic Hopkinson bar
-
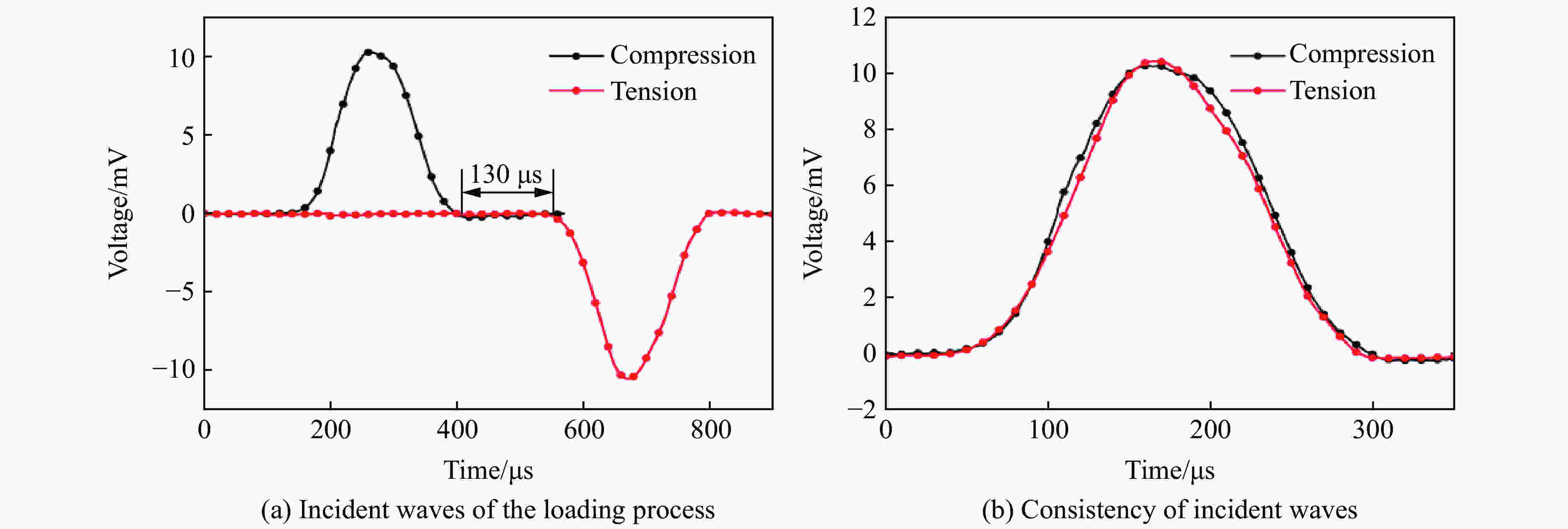
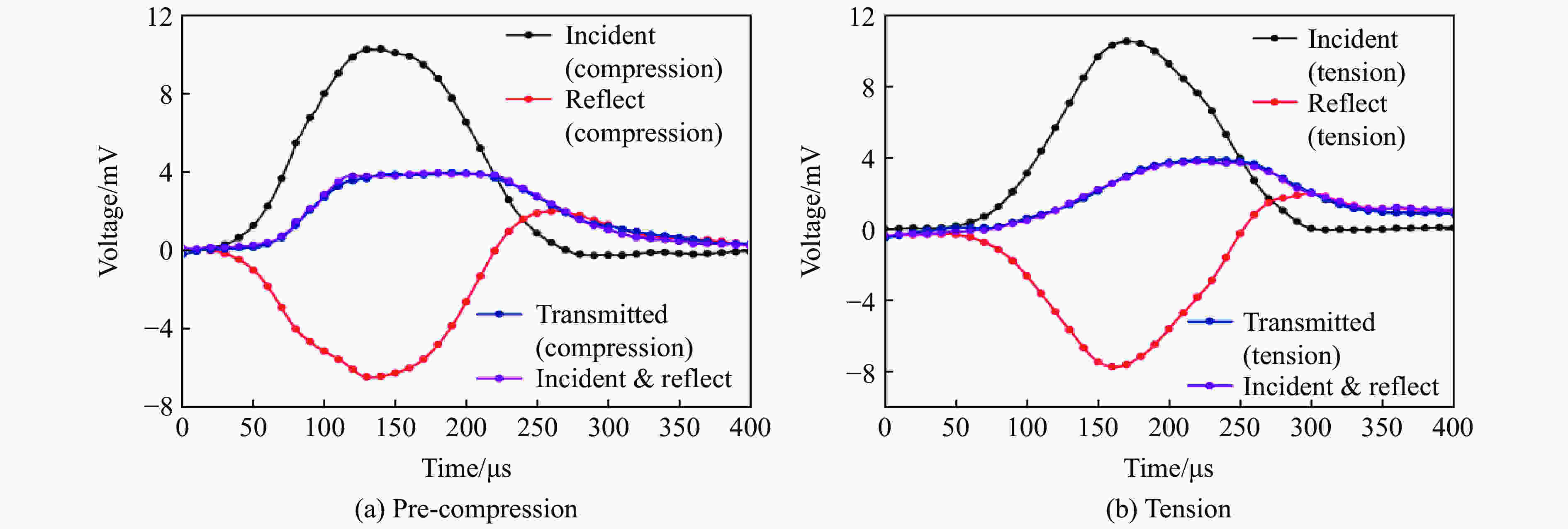
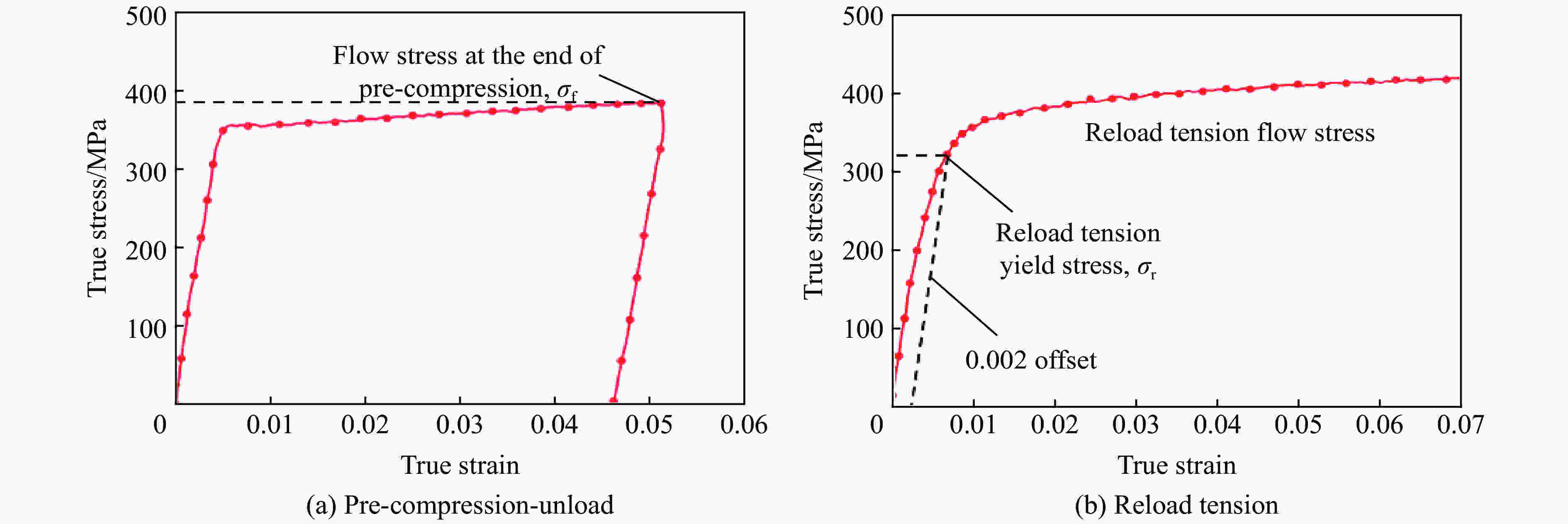
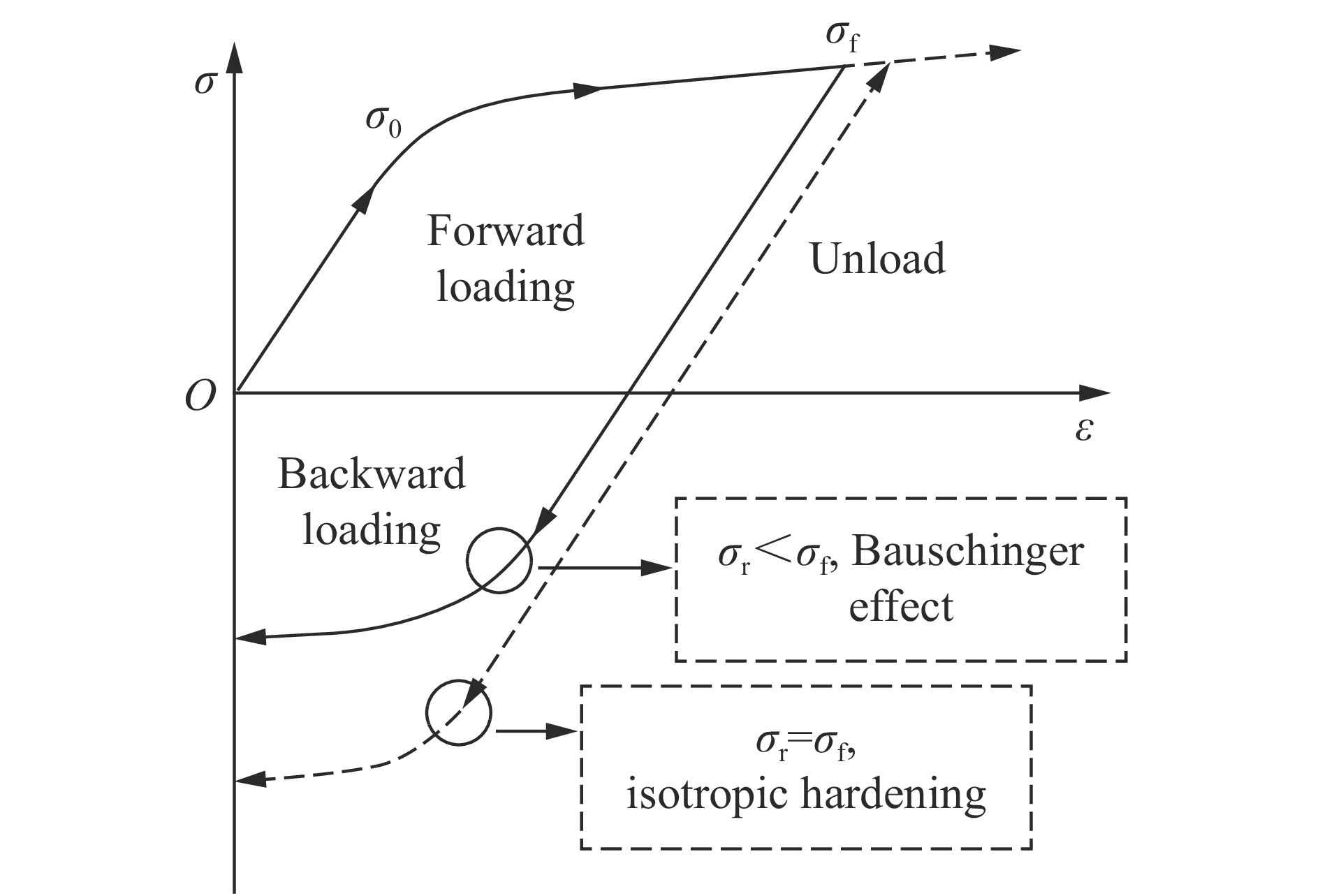
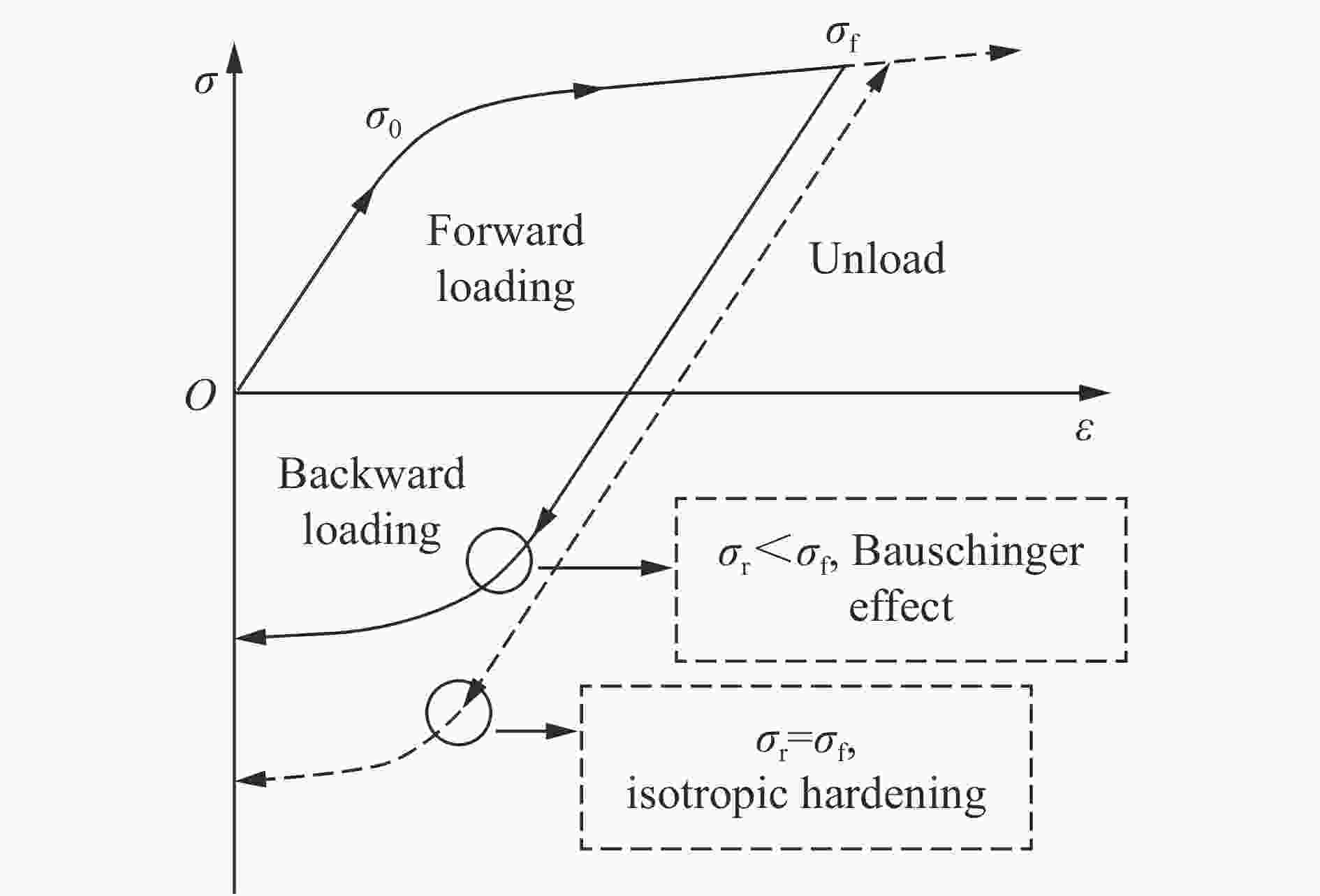
摘要: 金属材料在复杂载荷条件下的动态力学行为研究一直备受关注,但受限于实验设备,金属材料的动态包辛格效应响应一直都难以获得。为了探究金属材料的包辛格效应与应变率效应之间的关系,本文中提出一种基于电磁霍普金森杆(electromagnetic split Hopkinson bar,ESHB) 的非同步加载实验技术,为测试金属材料在高应变率加载下的包辛格效应提供了一种有效的实验方法。本文中,首先介绍了非同步加载装置的主要特点,即可以用两列由脉冲发生器产生的应力波对受载试样进行连续的一次动态拉-压循环加载,且加载过程保证了应力波的一致性。分析了应力波对试样加载过程中的波传播历程,确保了加载过程的连续性。随后介绍了动态加载过程,数据处理方法和波形分离手段,并对动态加载过程进行应力平衡性分析,论证了实验装置的可靠性。最后采用该方法测试了5%预应变下6061铝合金动态压缩-动态拉伸的包辛格效应,并与准静态下的实验结果进行对比。实验结果表明,该材料单轴压缩没有明显的应变率效应,但其包辛格效应具有应变率依赖性,高应变率下材料的包辛格应力影响因子由0.07增大至0.17,具有显著的提升,这对传统意义上铝合金材料应变率不敏感的结论提出了挑战。Abstract: Dynamic mechanical behavior of metallic materials under complicated loading conditions has attracted much attention. However, it is hard to obtain the dynamic Bauschinger effect of metallic materials due to the limitation of loading equipment. In order to investigate the relationship between the Bauschinger effect and strain rate effect of metallic materials, this paper proposes an asynchronous loading technique based on electromagnetic split Hopkinson bar system, which could provide an effective way to study the Bauschinger effect of metallic materials under high strain rate loading. We first introduce the main characteristics of the asynchronous loading device, that is, the specimen can be loaded by one cycle of continuous dynamic tension-compression loading pulse in which the two separate stress waves are created by electromagnetic pulse generators and prove to maintain their consistency. The propagation of stress waves was analyzed to ensure the continuity of the loading process. Then the dynamic loading process and the methods of data processing and stress wave separation are presented. Stress equilibrium was also analyzed in order to demonstrate the reliability of the equipment. Finally, the Bauschinger effect of 6061 aluminum alloy at 5% pre-strain during the process of dynamic compression to dynamic tension loading was studied using this method, and the corresponding quasi-static tests were also conducted for comparison. It was found that the material shows less strain-rate sensitivity under axial compression loading, while its Bauschinger stress parameter increases from 0.07 in quasi-static loading to 0.17 in dynamic loading. The results indicate that the Bauschinger effect of 6061 aluminum alloys depends on the strain rate and can be significantly enhanced under dynamic loading. This conclusion presents a challenge to the traditional conception that aluminum alloys are insensitive to strain rate.
-
表 1 采集点可采集到的应力波
Table 1. Stress waves collected at acquisition points
采集点 −1 250 mm −150 mm 1 800 mm 2 500 mm $ {\varepsilon }_{\mathrm{I}1} $ − $ {\varepsilon }_{\mathrm{I}2} $ $ {\varepsilon }_{\mathrm{I}2} $ 采集波形 $ {\varepsilon }_{\mathrm{R}1} $ $ {\varepsilon }_{\mathrm{T}2} $. $ {\varepsilon }_{\mathrm{T}1} $ $ {\varepsilon }_{\mathrm{T}1} $ − − $ {\varepsilon }_{\mathrm{R}2} $ − 注:(1) $ {\varepsilon }_{\mathrm{I}1} $为第1列波的入射波;(2) $ {\varepsilon }_{\mathrm{R}1} $为第1列波的反射波;(3) $ {\varepsilon }_{\mathrm{T}1} $为第1列波的透射波;(4) $ {\varepsilon }_{\mathrm{I}2} $为第2列波的入射波;(5) $ {\varepsilon }_{\mathrm{R}2} $为第2列波的反射波;(6) $ {\varepsilon }_{\mathrm{T}2} $为第2列波的透射波。 表 2 材料参数
Table 2. Material Parameters
密度/(kg·m−3) 弹性模量/GPa 屈服强度/MPa 泊松比 $ 2.7\times {10}^{3} $ 70 360 0.33 -
[1] BAUSCHINGER J. Changes of the elastic limit and the modulus of elasticity on various metals [J]. Zivilingenieur, 1881, 27: 289–348. [2] STOLTZ R E, PELLOUX R M. The Bauschinger effect in precipitation strengthened aluminum alloys [J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1976, 7(8): 1295–1306. DOI: 10.1007/BF02658814. [3] STOUT M G, ROLLETT A D. Large-strain Bauschinger effects in fcc metals and alloys [J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1990, 21(12): 3201. DOI: 10.1007/BF02647315. [4] FREDERICK C O, ARMSTRONG P J. A mathematical representation of the multiaxial Bauschinger effect [J]. Materials at High Temperatures, 2007, 24(1): 1–26. DOI: 10.3184/096034007X207589. [5] BUCKLEY S N, ENTWISTLE K M. The Bauschinger effect in super-pure aluminum single crystals and polycrystals [J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1956, 4(4): 352–361. DOI: 10.1016/0001-6160(56)90023-2. [6] ATKINSON J D, BROWN L M, STOBBS W M. The work-hardening of copper-silica: IV: the Bauschinger effect and plastic relaxation [J]. Philosophical Magazine, 1974, 30(6): 1247–1280. DOI: 10.1080/14786437408207280. [7] MOAN G D, EMBURY J D. Study of the Bauschinger effect in Al-Cu alloys [J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1979, 27(5): 903–914. DOI: 10.1016/0001-6160(79)90125-1. [8] HIDAYETOGLU T K, PICA P N, HAWORTH W L. Aging dependence of the Bauschinger effect in aluminum alloy 2024 [J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 1985, 73: 65–76. DOI: 10.1016/0025-5416(85)90296-4. [9] 唐长国, 朱金华, 周惠久. 金属材料屈服强度的应变率效应和热激活理论 [J]. 金属学报, 1995, 31(6): 248–253. DOI: 10.1007/BF02943514.TANG C G, ZHU J H, ZHOU H J. Correlation between yield stress and strain rate for metallic materials and thermal activation approach [J]. Acta Metallrugica Sinica, 1995, 31(6): 248–253. DOI: 10.1007/BF02943514. [10] HOPKINSON B. X A method of measuring the pressure produced in the detonation of high, explosives or by the impact of bullets [J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London: Series A: containing Papers of a Mathematical or Physical Character, 1914, 213(497-508): 437–456. DOI: 10.1098/rsta.1914.0010. [11] MIAO Y, DU B, SHEIKH M Z. On measuring the dynamic elastic modulus for metallic materials using stress wave loading techniques [J]. Archive of Applied Mechanics, 2018, 88(11): 1953–1964. DOI: 10.1007/s00419-018-1422-6. [12] MIAO Y, DU B, MA C, et al. Some fundamental problems concerning the measurement accuracy of the Hopkinson tension bar technique [J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2019, 30(5): 055009. DOI: 10.1088/1361-6501/ab01b5. [13] 胡时胜, 王礼立, 宋力, 等. Hopkinson压杆技术在中国的发展回顾 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2014, 34(6): 4–20. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2014)06-0641-17.HU S S, WANG L L, SONG L, et al. Review of the development of Hopkinson pressure bar technique in China [J]. Explosion and Shock Wave, 2014, 34(6): 4–20. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2014)06-0641-17. [14] 李玉龙, 索涛, 郭伟国, 等. 确定材料在高温高应变率下动态性能的Hopkinson杆系统 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2005, 25(6): 487–492. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2005)06-0487-06.LI Y L, SUO T, GUO W G, et al. Determination of dynamic behavior of materials at elevated temperatures and high strain rates using Hopkinson bar [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2005, 25(6): 487–492. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2005)06-0487-06. [15] 李玉龙, 郭伟国. 微型 Hopkinson 杆技术 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2006, 26(4): 303–308. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2006)04-0303-06.LI Y L, GUO W G. Miniature-Hopkinson bar technique [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2006, 26(4): 303–308. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2006)04-0303-06. [16] 果春焕, 周培俊, 陆子川, 等. 波形整形技术在Hopkinson杆实验中的应用 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2015, 35(6): 881–887. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2015)06-0881-07.GUO C H, ZHOU P J, LU Z C, et al. Application of pulse shaping technique in Hopkinson bar experiments [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2015, 35(6): 881–887. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2015)06-0881-07. [17] THAKUR A, NEMAT-NASSER S, VECCHIO K S. Dynamic Bauschinger effect [J]. Acta materialia, 1996, 44(7): 2797–2807. DOI: 10.1016/1359-6454(95)00385-1. [18] NIE H, SUO T, WU B, et al. A versatile split Hopkinson pressure bar using electromagnetic loading [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2018, 116: 94–104. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2018.02.002. [19] 苗应刚, 李玉龙, 邓琼, 等. Investigation on experimental method of low-impedance materials using modified Hopkinson pressure bar [J]. Journal of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2015, 24(2): 269–276. DOI: 10.15918/j.jbit1004-0579.201524.0220.MIAO Y G, LI Y L, DENG Q, et al. Investigation on experimental method of low-impedance materials using modified Hopkinson pressure bar [J]. Journal of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2015, 24(2): 269–276. DOI: 10.15918/j.jbit1004-0579.201524.0220. [20] NIE H, SUO T, SHI X, et al. Symmetric split Hopkinson compression and tension tests using synchronized electromagnetic stress pulse generators [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2018, 122: 73–82. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2018.08.004. [21] RAVICHANDRAN G, SUBHASH G. Critical appraisal of limiting strain rates for compression testing of ceramics in a split Hopkinson pressure bar [J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1994, 77(1): 263–267. DOI: 10.1111/j.1151-2916.1994.tb06987.x. [22] FAN X, SUO T, SUN Q, et al. Dynamic mechanical behavior of 6061 Al alloy at elevated temperatures and different strain rates [J]. Acta Mechanica Solida Sinica, 2013, 26(2): 111–120. DOI: 10.1016/S0894-9166(13)60011-7. -






 下载:
下载: