Measurement and calculation technology of temperature compensation of explosion flame based on infrared radiation
-
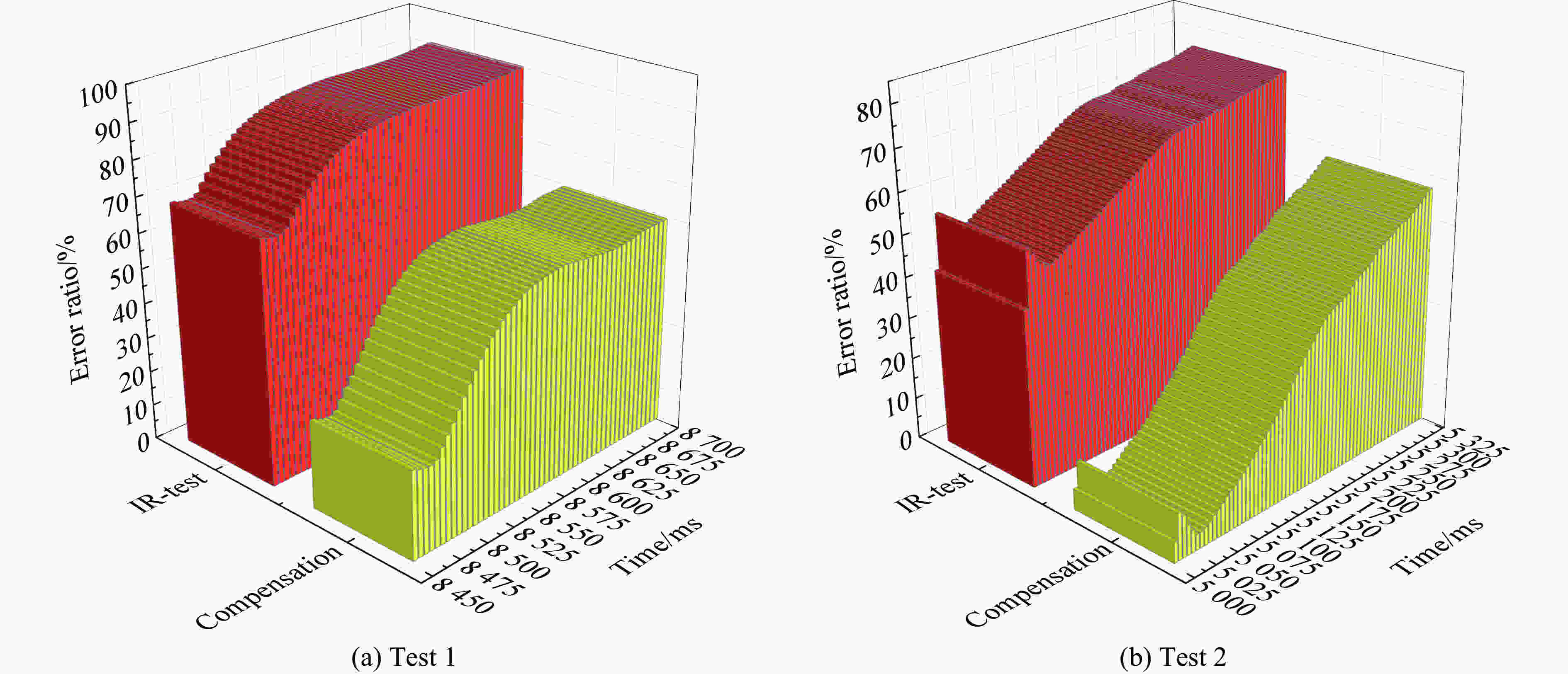
摘要: 应用辐射测温法进行爆炸火焰温度测试时,火焰发射率取经验定值的方法与火焰燃烧机理存在较大的偏差,同时测点距离与环境温湿度也会导致不同程度的热辐射衰减,从而影响爆炸火焰温度的测量精度。本文针对上述两个问题,基于大气辐射理论与光学传播规律,提出了辐射路径衰减补偿模型,结合由红外热像仪和比色测温仪测量的爆炸火焰动态发射率,对爆炸场火焰真温进行联合反演,并将测算结果与比色测温仪测得的火焰表面温度进行对比,得到了反演温度误差范围。试验结果表明,利用本文所提出的补偿模型测算得到的爆炸火焰温度,误差由补偿前的55.699%~89.847%降低到11.292%~59.077%,有效提高了外场爆炸瞬态火焰温度的测算精度。
-
关键词:
- 爆炸瞬态火焰 /
- 补偿温度估算 /
- 辐射路径衰减补偿模型 /
- 动态发射率测算
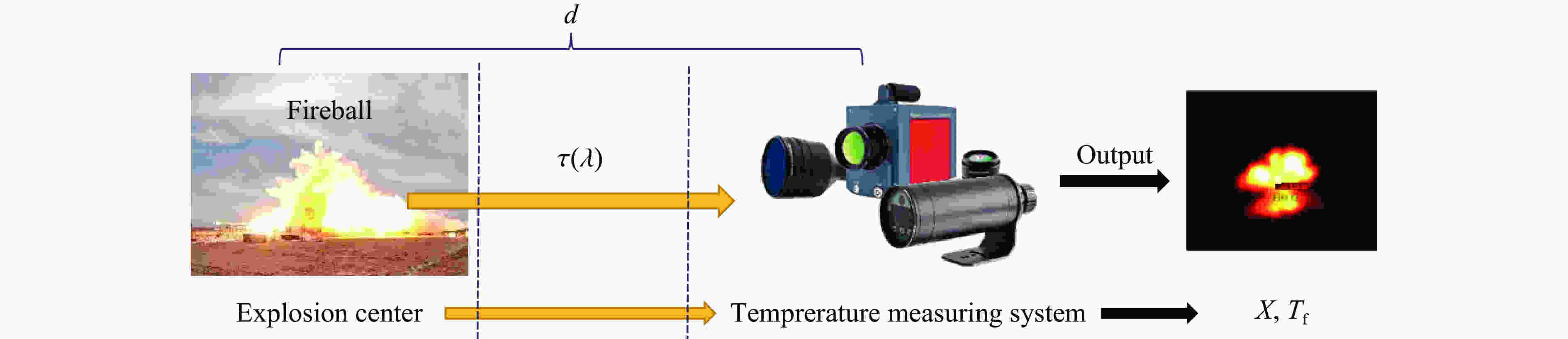
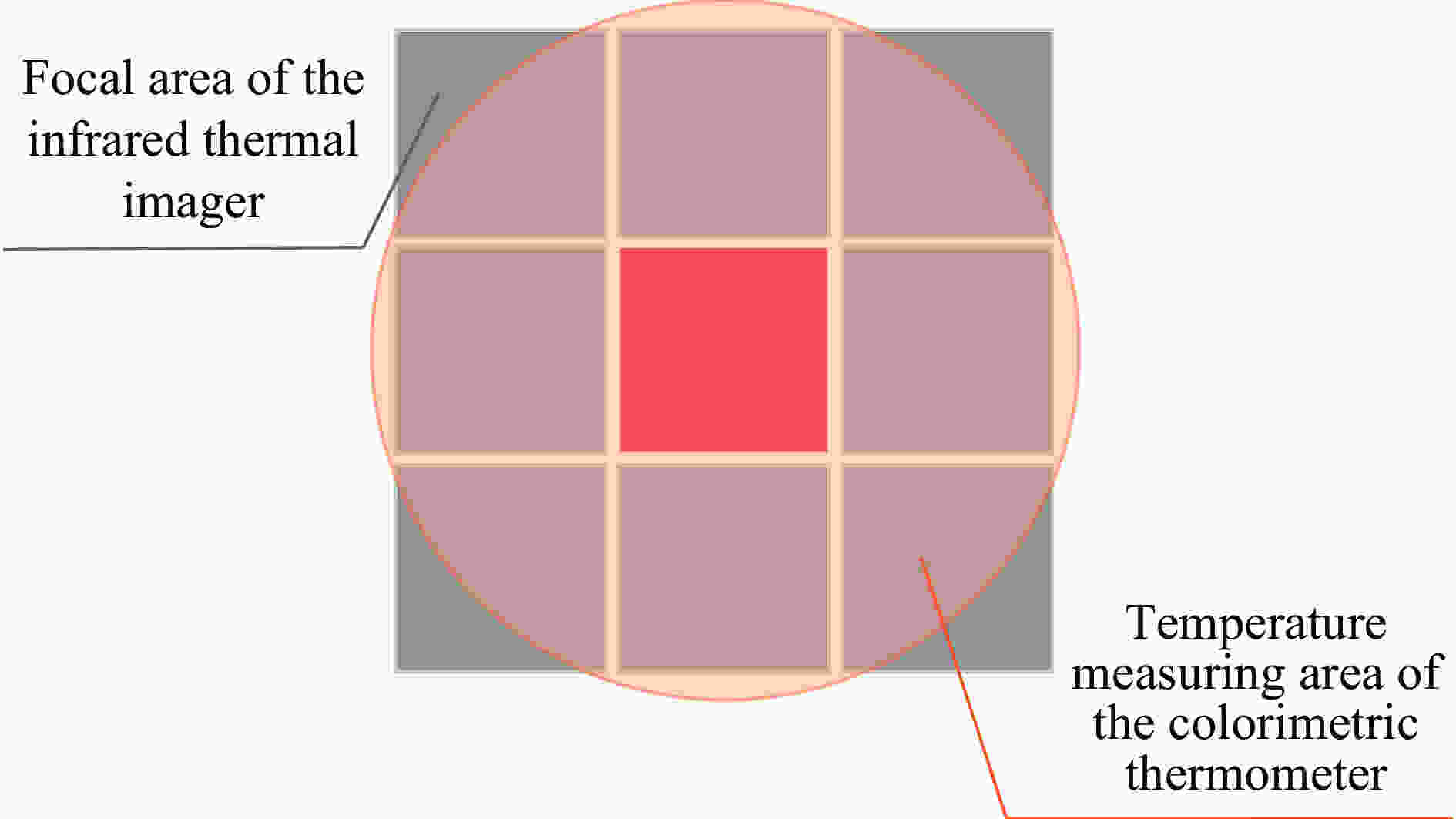
Abstract: In testing explosion flame temperature with radiation thermometry, there is relatively great deviation of empirical value of flame emissivity from flame combustion mechanism. Meanwhile, the distance of measure point from the flame and ambient temperature and humidity also cause attenuation of thermal radiation to different extent, affecting the accuracy of measurement of explosion flame’s temperature. With focuses on foregoing two problems and based on atmospheric radiation theory and the law of optics propagation, a model of radiation path attenuation compensation was deduced in accordance with the functional relation among explosion flame’s radiance, digital output value of thermal imager and explosion flame’s temperature, followed by obtainment of relevant parameters i.e. system responsivity in the model from radiometric calibration of thermal imager; then, the applicability of the gray body hypothesis of TNT explosion flame was confirmed by analyzing the composition of the products of TNT explosion flame. Therefore, a function model of explosion flame’s dynamic average emissivity was deduced concerning onsite atmospheric transmittance, digital output value of thermal imager and explosion flame’s temperature measured by the colorimetric thermometer in accordance with the expression of explosion flame’s radiance; finally, based on the receiver function of thermal imager’s effective radiation, a joint temperature compensation evaluation method, which combines radiation path compensation and dynamic emissivity, was proposed for joint inversion of explosion flame’s temperature at the explosion site and the range of temperature error of inversion was obtained through comparison of measured result with explosion flame’s surface temperature measured by colorimetric thermometer. The test result suggests the error of explosion flame’s temperature measured with the proposed compensation model is reduced to 11.292%−59.077% from previous 55.699%−89.847% before compensation, thus effectively improving the accuracy of measurement of transient flame temperature of explosion at external field and providing a means for accurate infrared thermography-based evaluation of thermal effect in explosion field. -
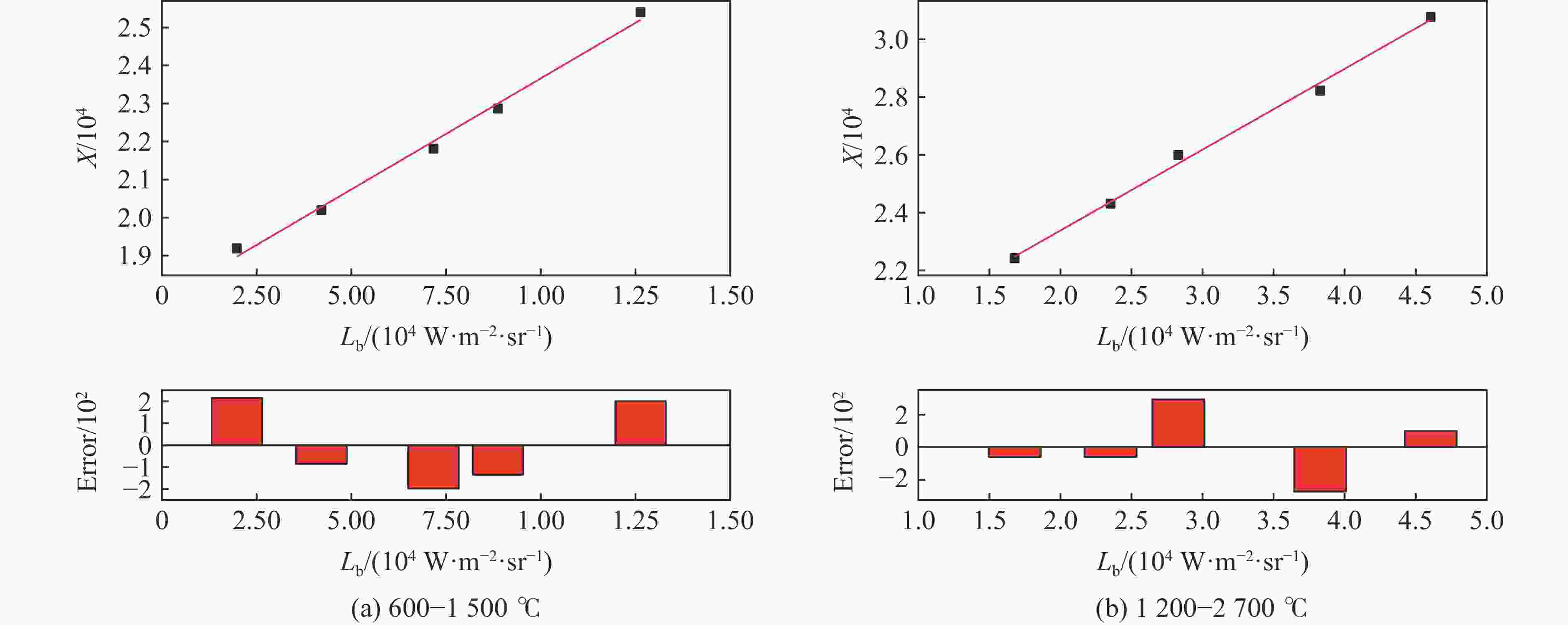
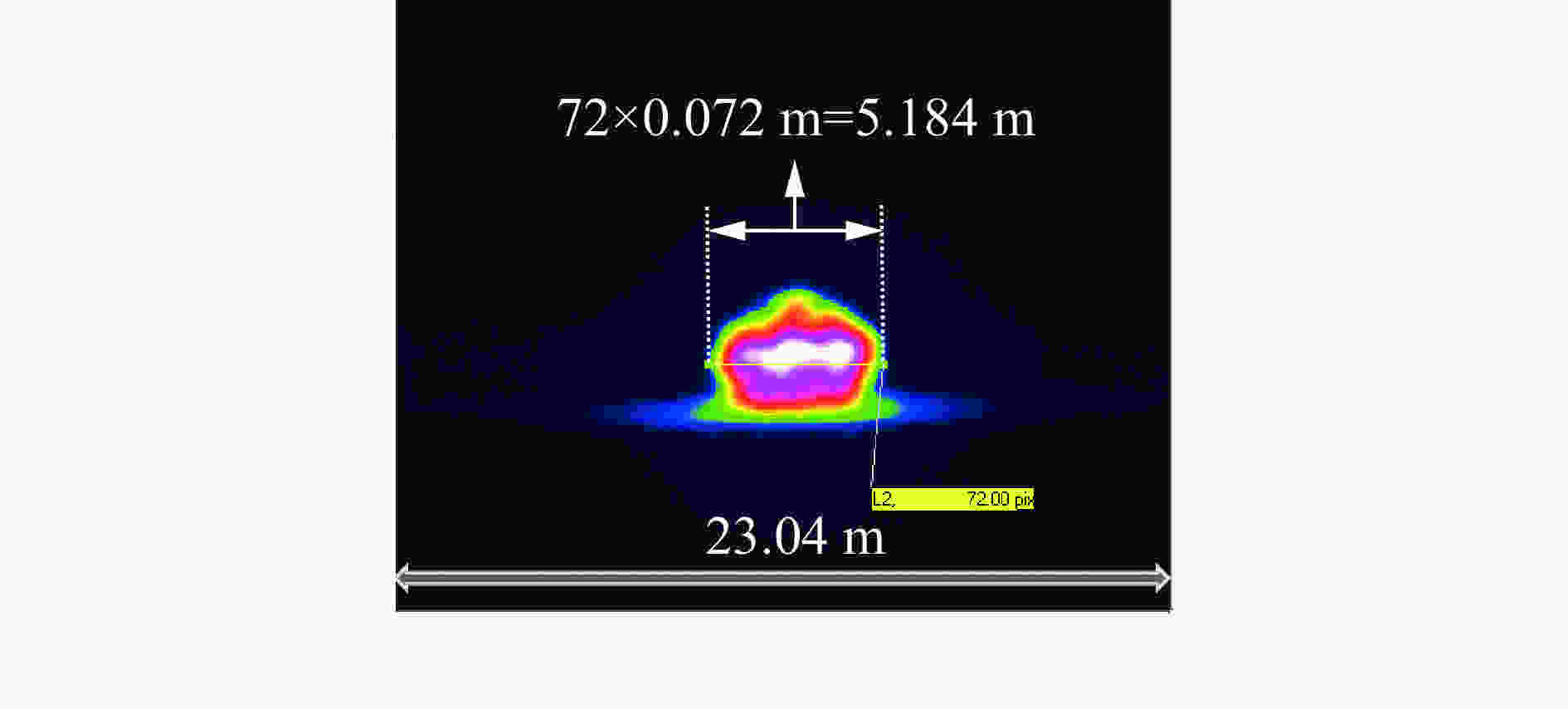
表 1 大气透射率计算表
Table 1. Atmospheric transmittance
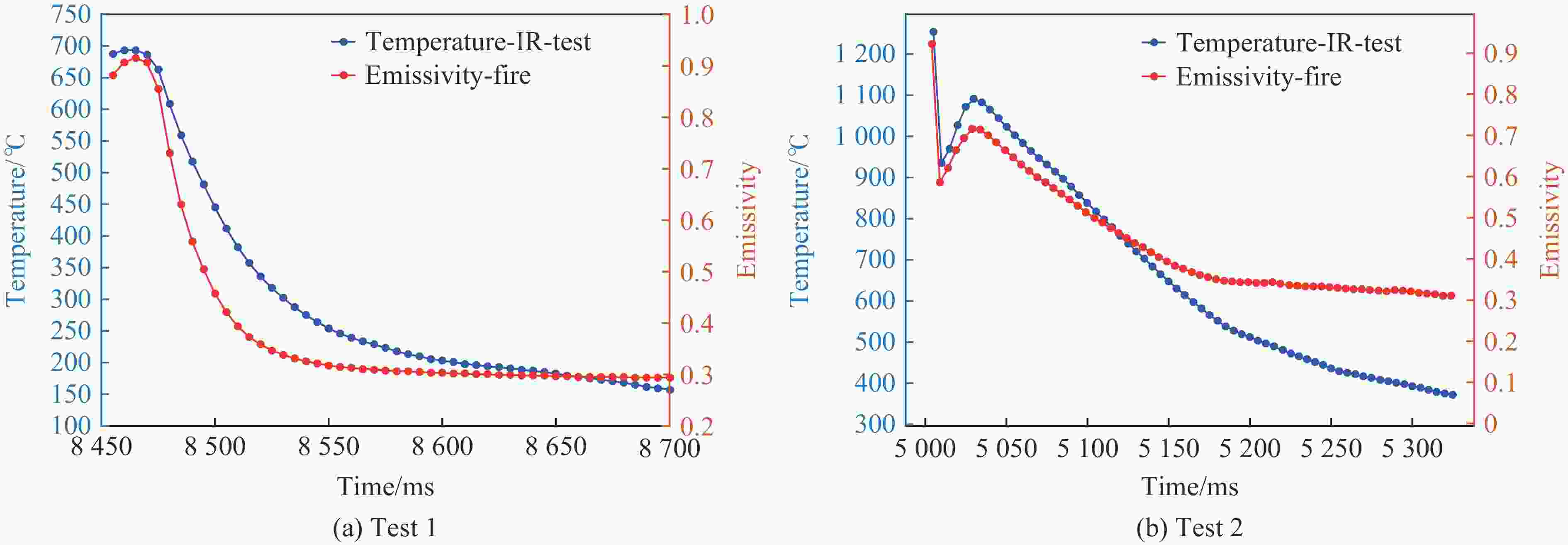
试验编号 d/m Tu/℃ w/% ${\tau _{{R_0}}}$ ${\tau '_{{R_0}}}$ ${\tau '_d}$ τ 1 36.0 1.70 51.0 0.682 0.783 0.749 0.651 2 60.0 27.0 79.9 0.634 0.747 0.622 0.527 表 2 试验中火焰动态发射率
Table 2. Flame dynamic emissivity in the tests
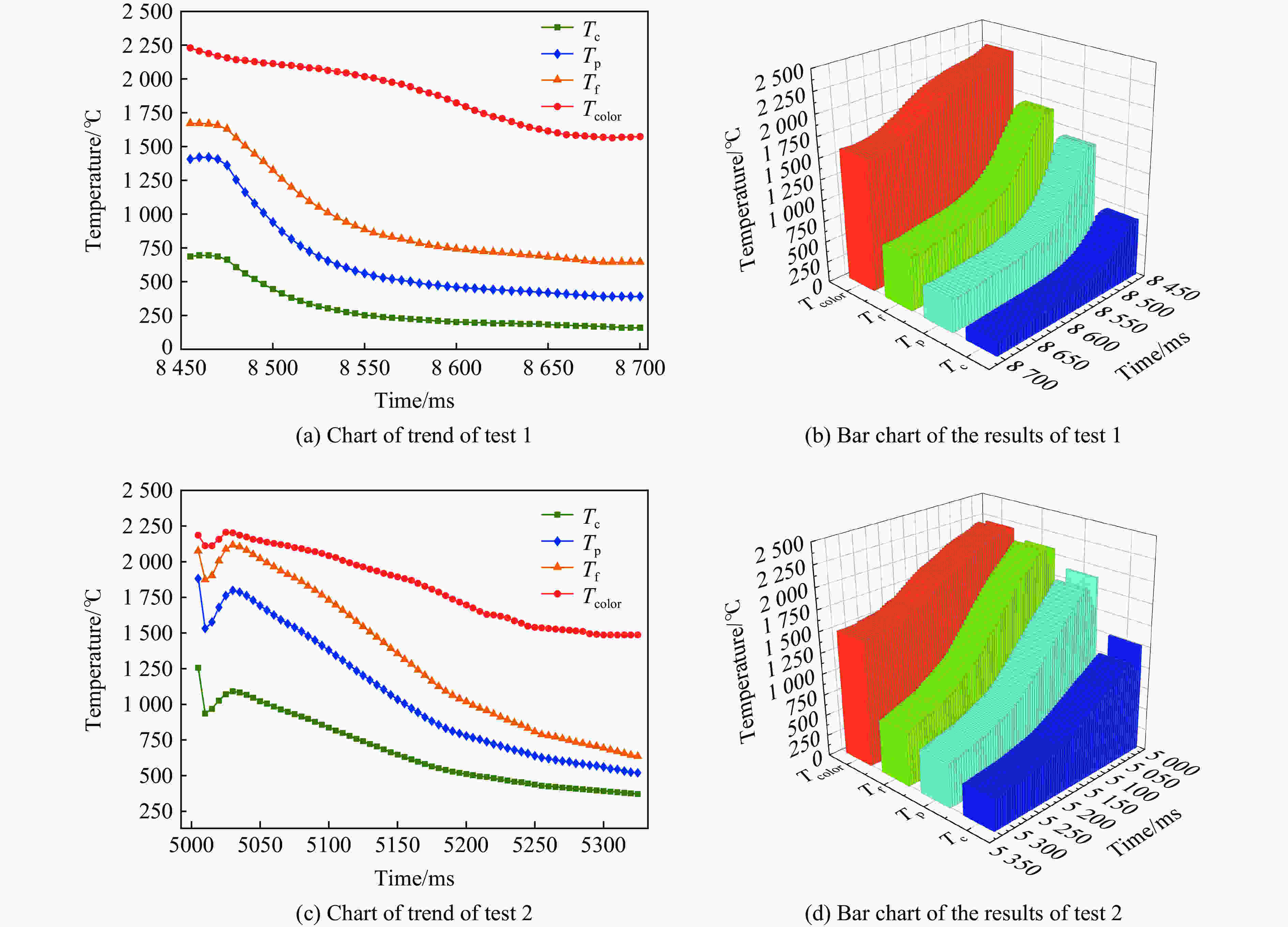
试验1 试验2 Time/ms εf Time/ms εf 8455 0.882 5005 0.922 8475 0.856 5030 0.716 8490 0.558 5050 0.664 8500 0.457 5065 0.613 8505 0.421 5080 0.573 8510 0.393 5100 0.514 … … … … 8570 0.309 5175 0.356 8585 0.306 5190 0.345 8620 0.299 5210 0.343 表 3 第1/2次试验中的爆炸火焰部分补偿反演温度及相对误差
Table 3. Compensation inversion temperature and relative error of explosion flame in two tests
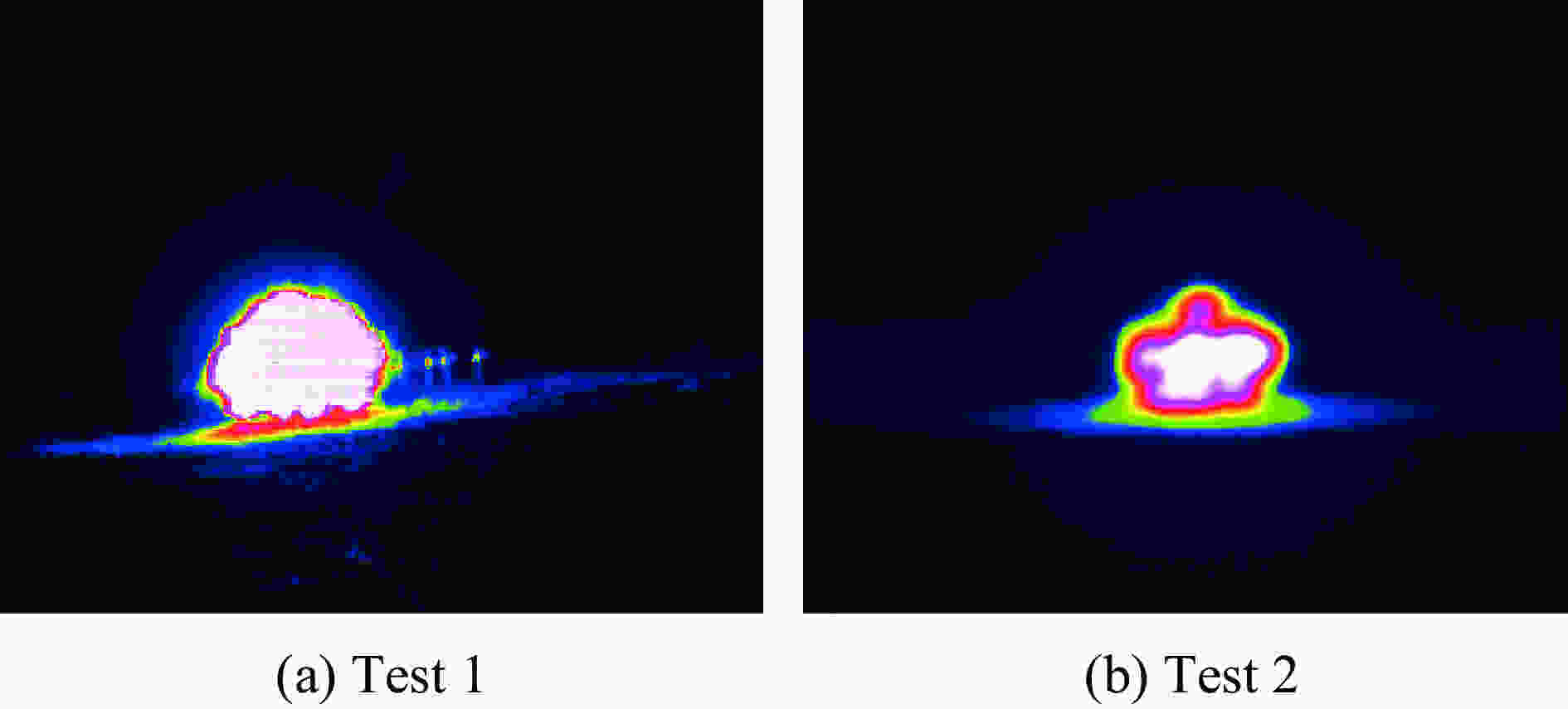
试验 Time/ms Tc/℃ Tp/℃ Tf/℃ Tcolor/℃ 误差/% IR-test Compensation 1 8460 693.611 1419.056 1672.052 2208.252 68.590 24.282 8480 608.342 1255.831 1565.070 2143.555 71.620 26.987 8495 481.107 1009.308 1386.643 2119.141 77.297 34.568 8500 444.863 938.477 1583.416 1323.390 78.947 37.370 8660 177.488 408.085 669.106 1588.001 88.824 57.865 8695 159.501 390.107 642.896 1570.997 89.847 59.077 2 5010 935.063 1530.082 1872.337 2110.685 55.699 11.292 5095 857.691 1413.376 1765.648 2057.991 58.324 14.205 5110 798.493 1309.191 1658.114 2010.002 60.274 17.507 5125 739.900 1204.139 1545.167 1963.005 62.308 21.286 5210 496.242 752.034 973.793 1651.999 69.961 41.054 5285 404.437 579.728 723.389 1510.000 73.217 52.093 -
[1] ZHANG Y C, WANG Z K, FU X B, et al. An experimental method for improving temperature measurement accuracy of infrared thermal imager [J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2019, 102: 103020. DOI: 10.1016/j.infrared.2019.103020. [2] SHAO L C, ZHOU Z J, CHEN L P, et al. Study of an improved two-colour method integrated with the emissivity ratio model and its application to air-and oxy-fuel flames in industrial furnaces [J]. Measurement, 2018, 123: 54–61. DOI: 10.1016/j.measurement.2018.03.024. [3] 杨词银, 张建萍, 曹立华. 基于大气透过率比例校正的目标辐射测量 [J]. 光学 精密工程, 2012, 20(7): 1626–1635. DOI: 10.3788/OPE.20122007.1626.YANG C Y, ZHANG J P, CAO L H. Infrared radiation measurement based on proportional corrected atmospheric transmittance [J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2012, 20(7): 1626–1635. DOI: 10.3788/OPE.20122007.1626. [4] 赵晨阳, 冯浩, 黄晓敏, 等. 红外测温技术在爆炸场温度测试中的精度研究 [J]. 红外技术, 2014, 36(8): 676–679. DOI: 10.11846/j.issn.1001_8891.201408015.ZHAO C Y, FENG H, HUANG X M, et al. Research on the precision of the infrared temperature-measuring technology in explosion fields temperature test [J]. Infrared Technology, 2014, 36(8): 676–679. DOI: 10.11846/j.issn.1001_8891.201408015. [5] MITROFANOV V V, PINAEV A V, ZHDAN S A. Calculations of detonation waves in gas-droplet systems [J]. Acta Astronautica, 1979, 6(3−4): 281–296. DOI: 10.1016/0094-5765(79)90099-7. [6] 李云红, 孙晓刚, 原桂彬. 红外热像仪精确测温技术 [J]. 光学 精密工程, 2007, 15(9): 1336–1341. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-924x.2007.09.005.LI Y H, SUN X G, YUAN G B. Accurate measuring temperature with infrared thermal imager [J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2007, 15(9): 1336–1341. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-924x.2007.09.005. [7] WANG L Y, DU H M, XU H. Compensation method for infrared temperature measurement of explosive fireball [J]. Thermochimica Acta, 2019, 680: 178342. DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2019.178342. [8] 安连生, 李林, 李全臣. 应用光学[M]. 3版. 北京: 北京理工大学出版社, 2002: 112−113. [9] ZHANG Z L, SUN W M, SHI L W, et al. Multi-wavelength pyrometry for temperature measurement in gas flames [C] // Proceedings of 2012 International Conference on Measurement, Information and Control. Harbin: IEEE, 2012: 198−201. DOI: 10.1109/MIC.2012.6273255. [10] DE RIS J. Fire radiation—A review [J]. Symposium (International) on Combustion, 1979, 17(1): 1003–1016. DOI: 10.1016/S0082-0784(79)80097-1. [11] SIEGEL R, HOWELL J R. Thermal radiation heat transfer [M]. 4th ed. Washington: Hemisphere Pub Corp, 1981. [12] GOROSHIN S, FROST D L, LEVINE J, et al. Optical pyrometry of fireballs of metalized explosives [J]. Propellants Explosives Pyrotechnics, 2006, 31(3): 169–181. DOI: 10.1002/prep.200600024. [13] LYNCH P, KRIER H, GLUMAC N. Emissivity of aluminum-oxide particle clouds: application to pyrometry of explosive fireballs [J]. Journal of Thermophysics and Heat Transfer, 2010, 24(2): 301–308. DOI: 10.2514/1.43853. [14] 刘丹丹, 黄印博, 魏合理, 等. 我国典型地区大气透过率的计算分析 [J]. 大气与环境光学学报, 2013, 8(4): 262–270. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6141.2013.04.003.LIU D D, HUANG Y B, WEI H L, et al. Atmospheric transmittance calculation in typical regions of China [J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Environmental Optics, 2013, 8(4): 262–270. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6141.2013.04.003. [15] 郭立红, 郭汉洲, 杨词银, 等. 利用大气修正因子提高目标红外辐射特性测量精度 [J]. 光学 精密工程, 2016, 24(8): 1871–1877. DOI: 10.3788/OPE.20162408.1871.GUO L H, GUO H Z, YANG C Y, et al. Improvement of radiation measurement precision for target by using atmosphere-corrected coefficients [J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2016, 24(8): 1871–1877. DOI: 10.3788/OPE.20162408.1871. [16] ORLOFF L, DE RIS J. Froude modeling of pool fires [J]. Symposium (International) on Combustion, 1982, 19(1): 885–895. DOI: 10.1016/S0082-0784(82)80264-6. [17] 齐文娟. 发射率对红外测温精度的影响[D]. 长春: 长春理工大学, 2006: 27−32. DOI: 10.7666/d.y930659. [18] WANG P F, LIU N A, HARTL K, et al. Measurement of the flow field of fire whirl [J]. Fire Technology, 2016, 52: 263–272. DOI: 10.1007/s10694-015-0511-0. -






 下载:
下载: