Damage of a multi-layer Q345 target under hypervelocity impact of a rod-shaped 93W projectile
-
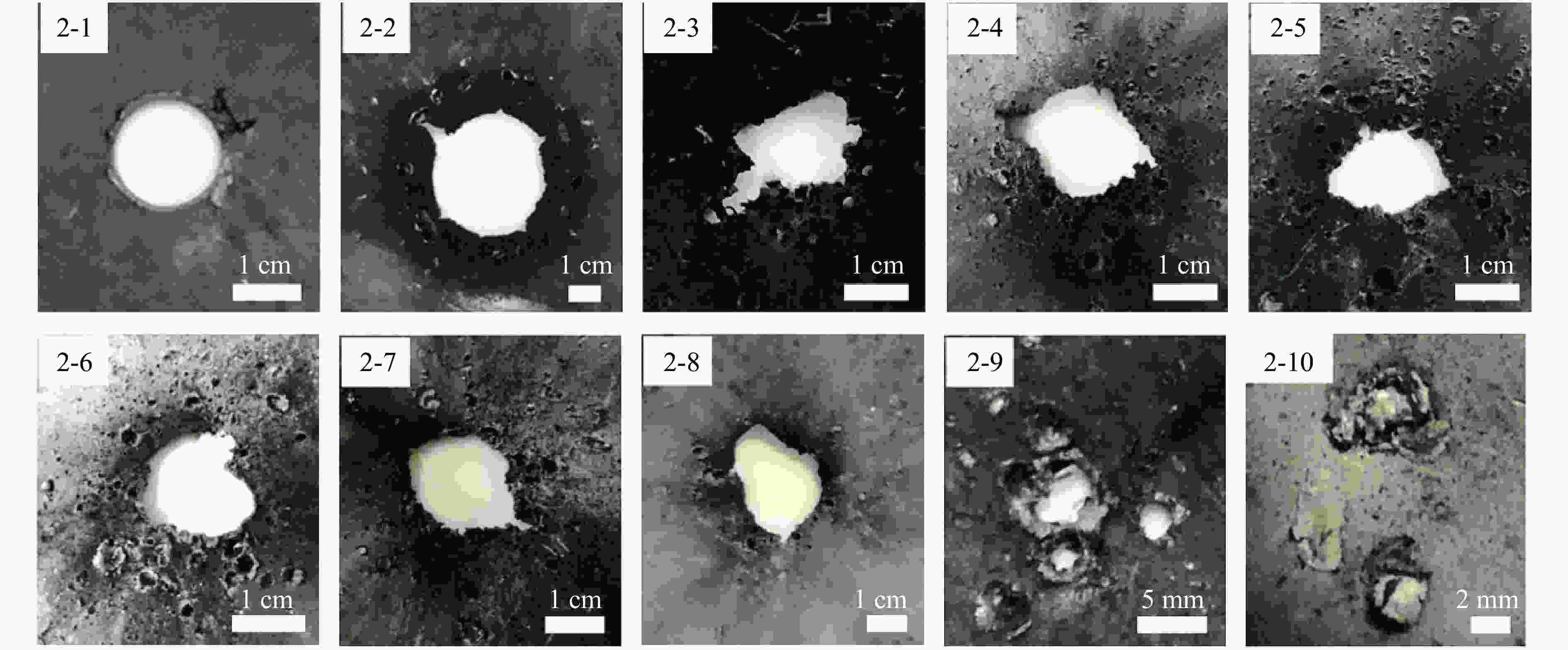
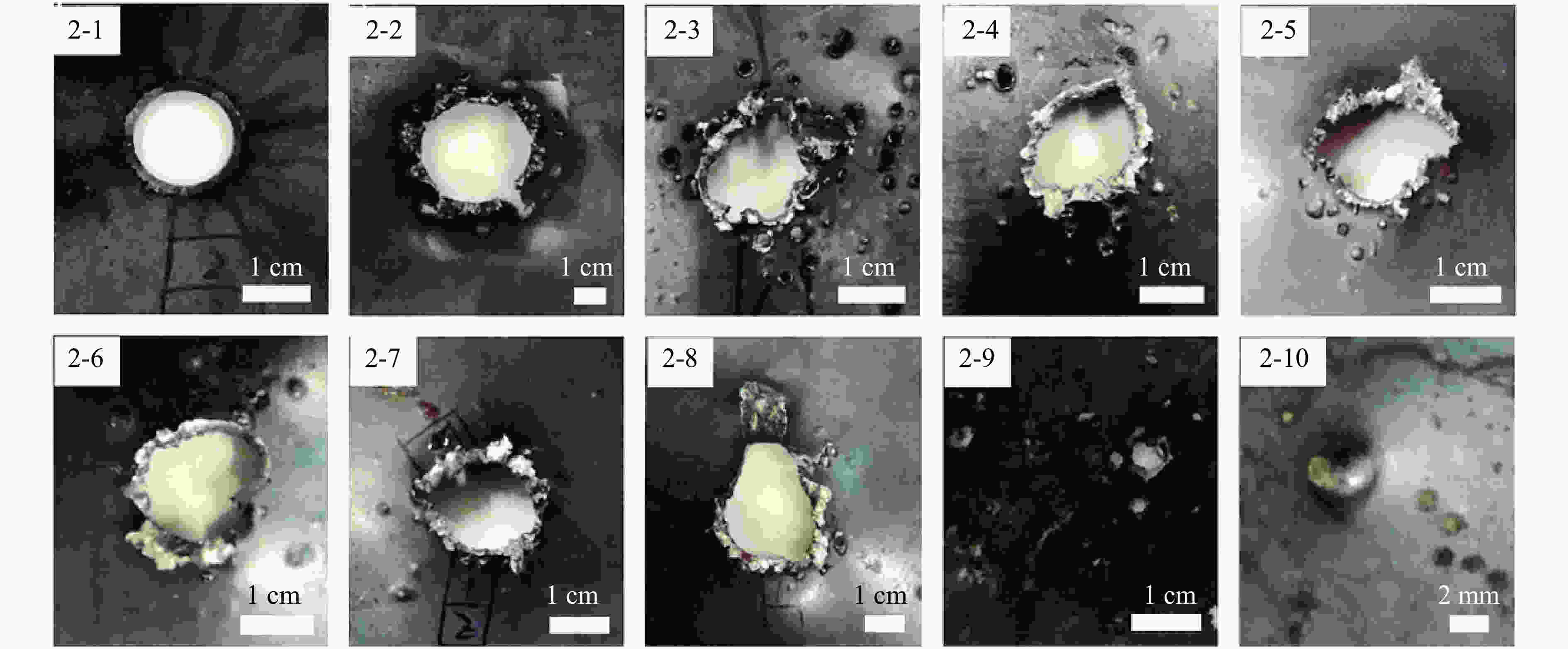
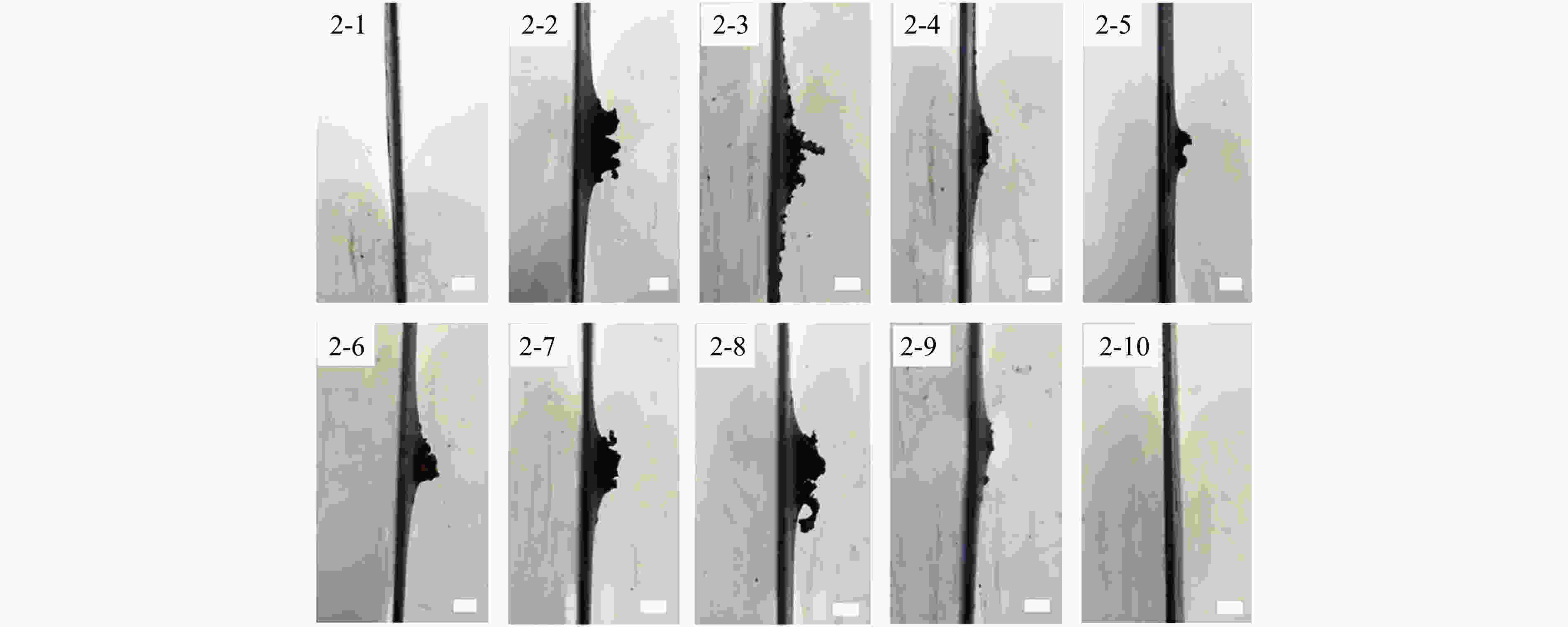
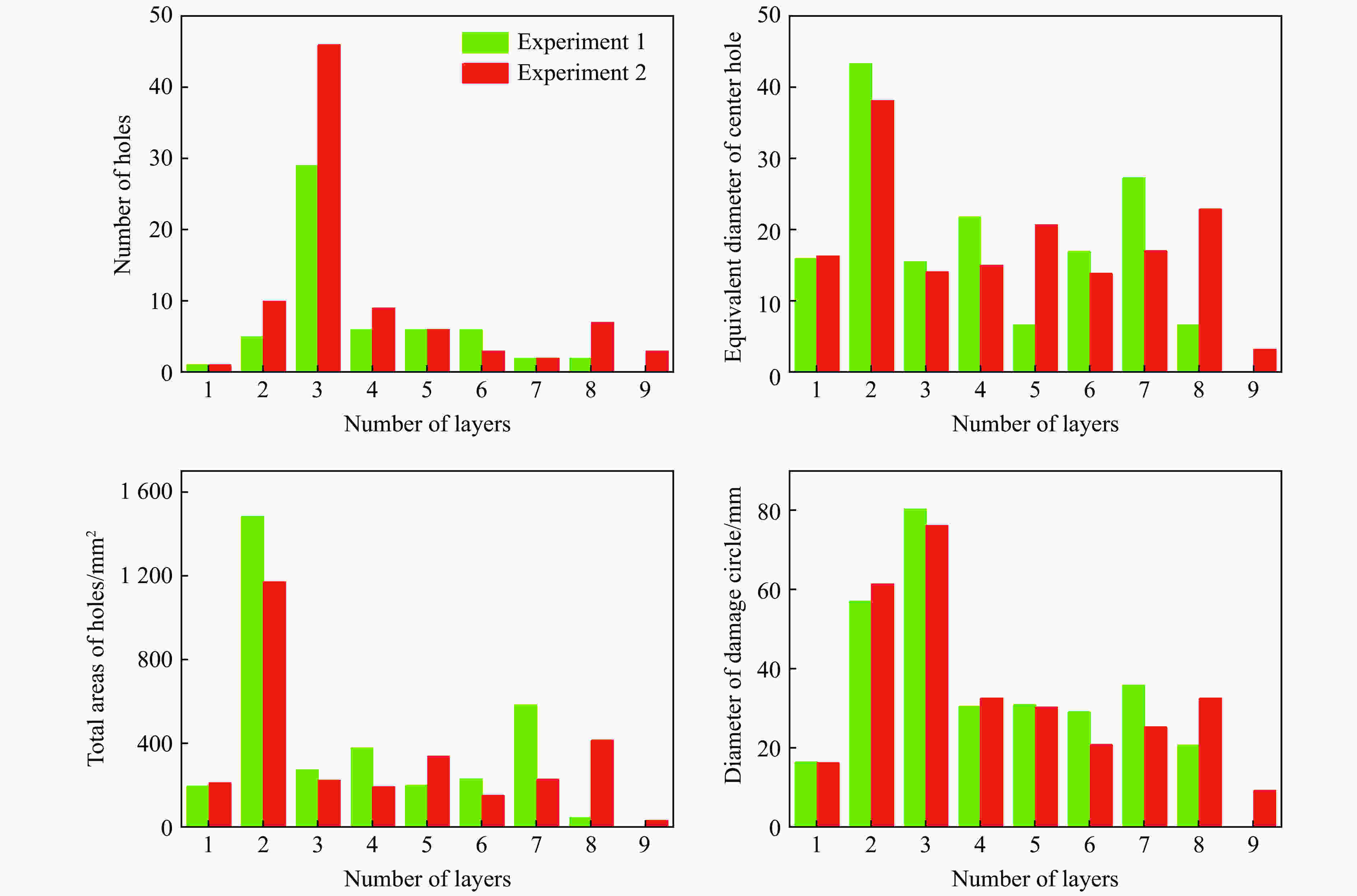
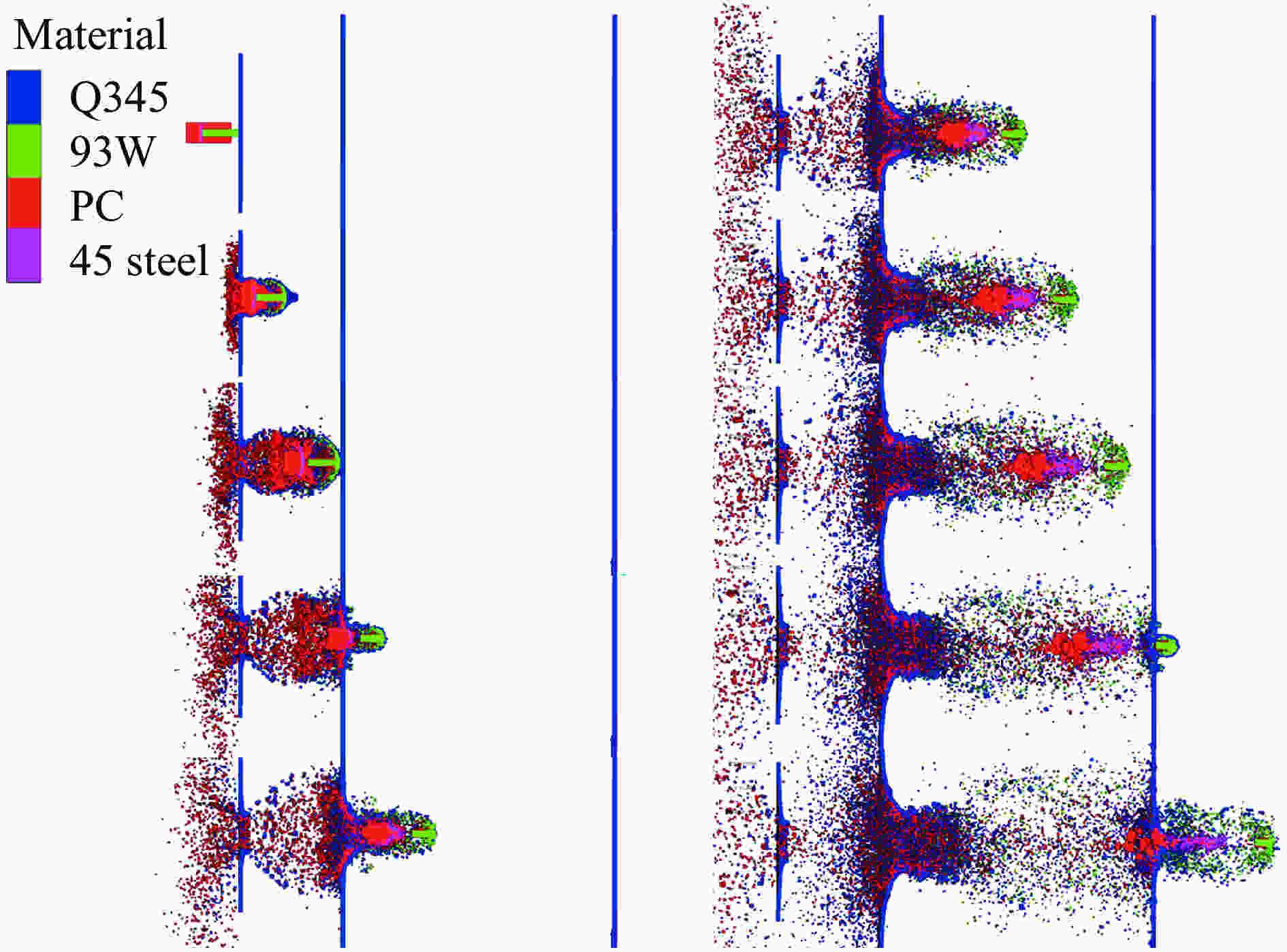
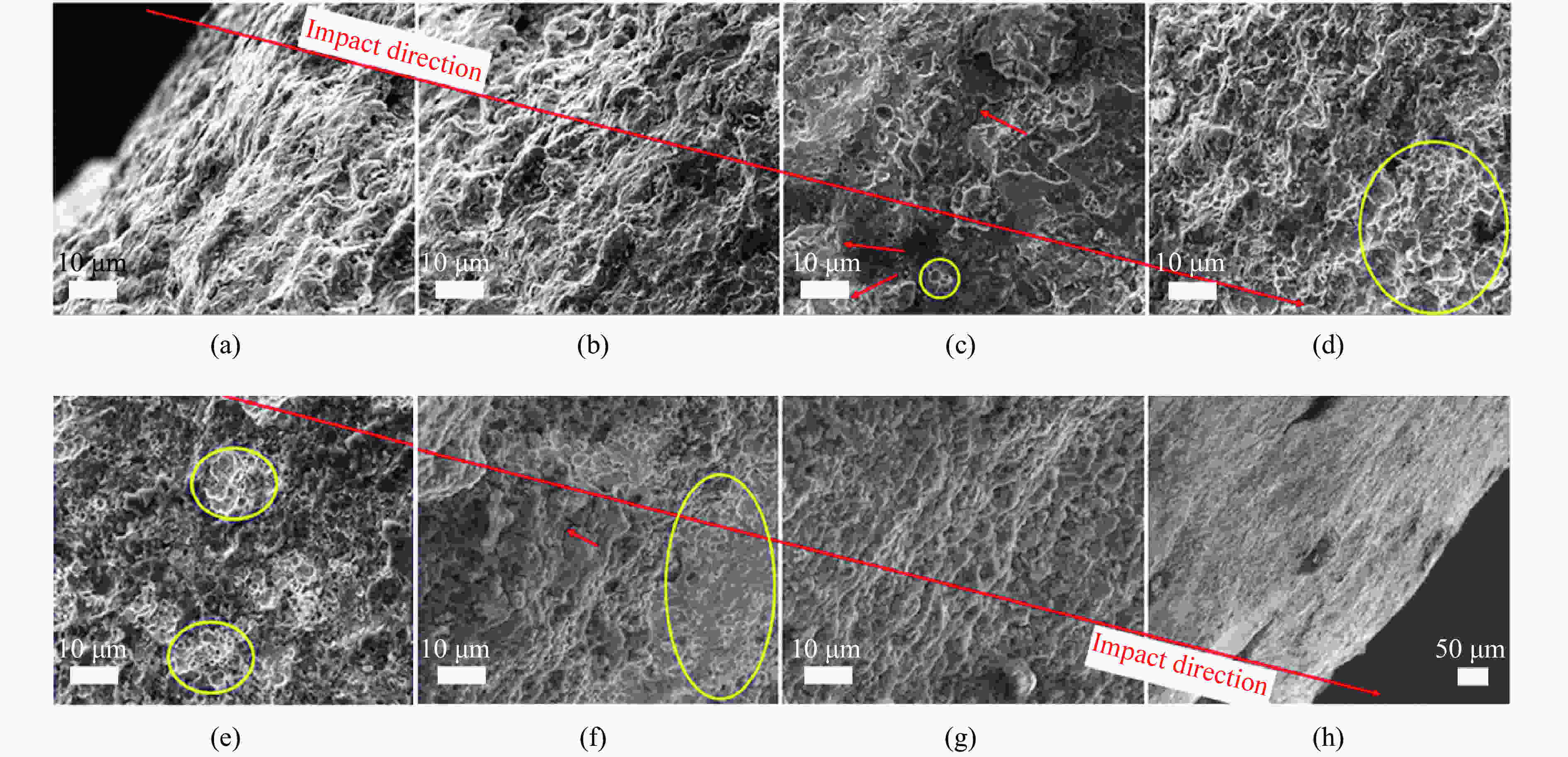
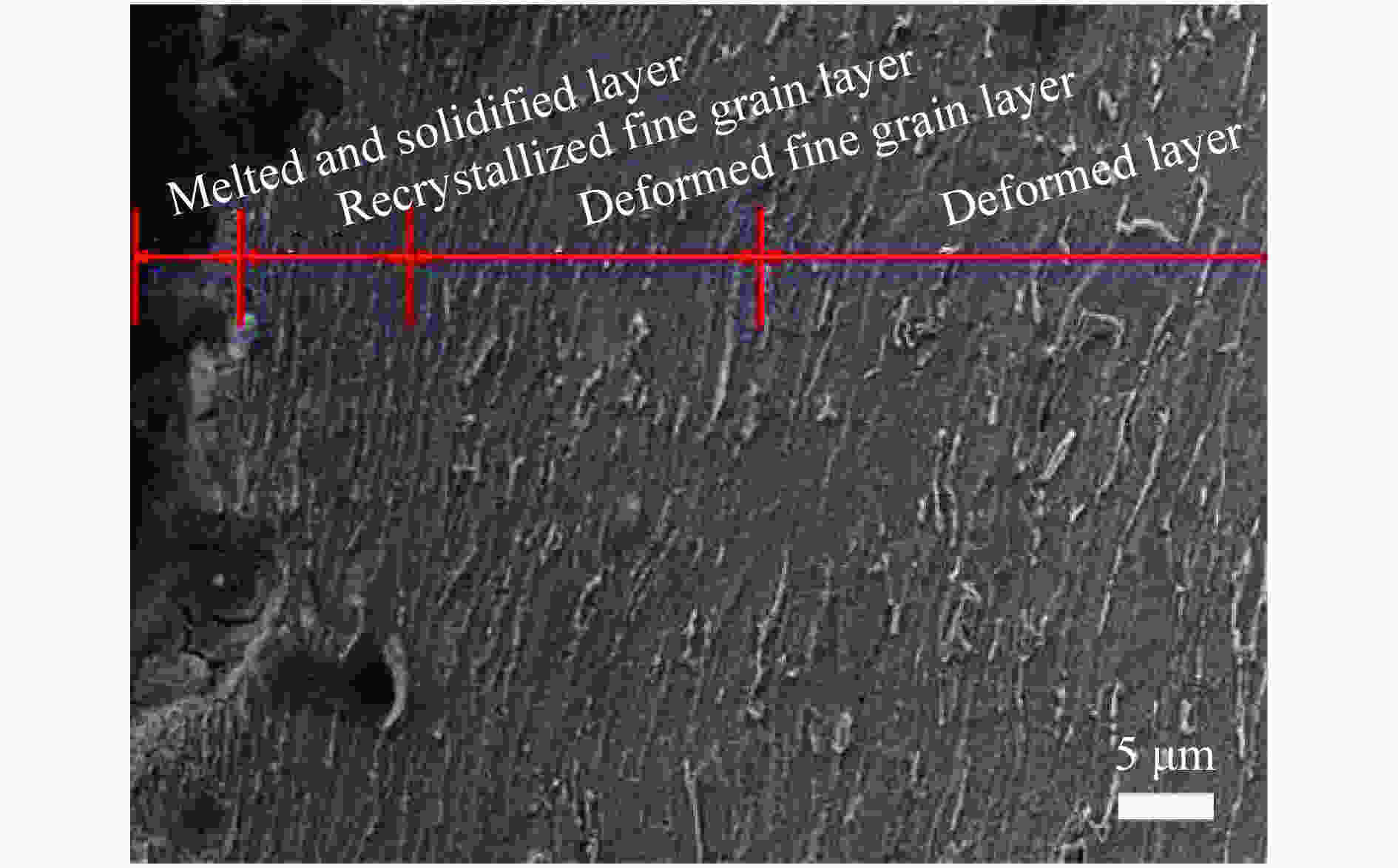
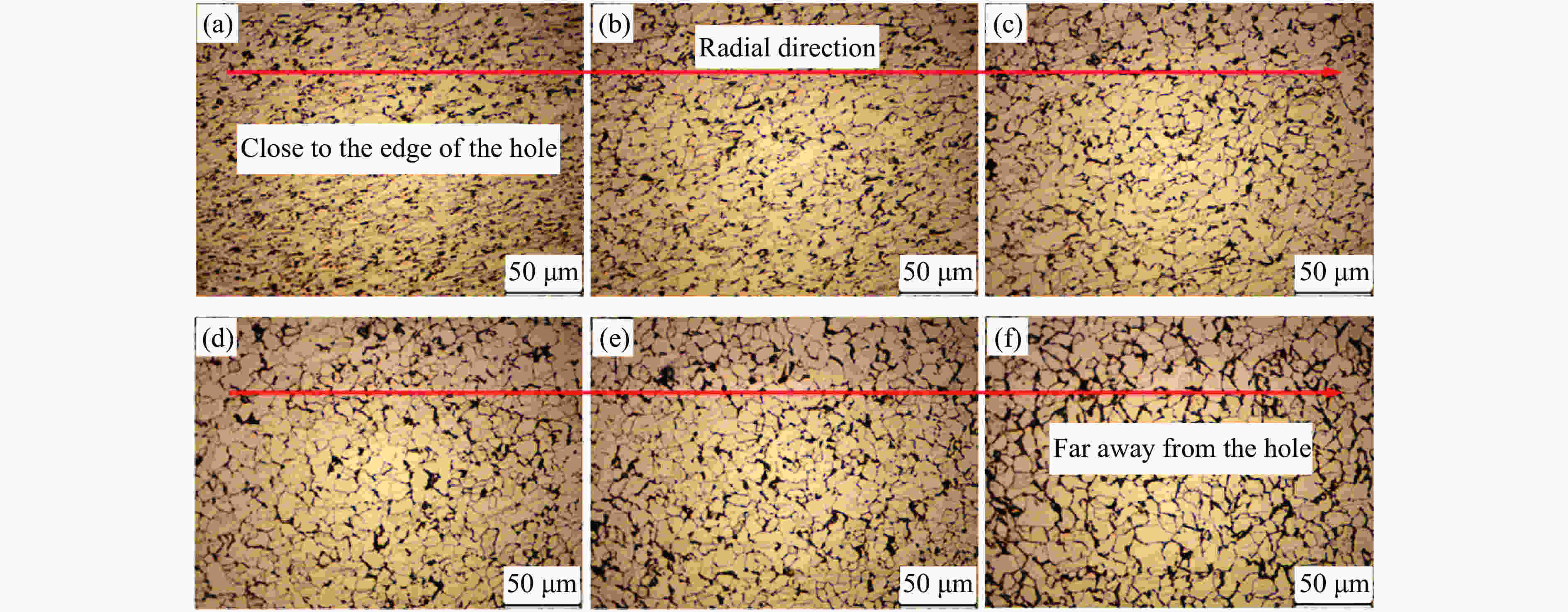
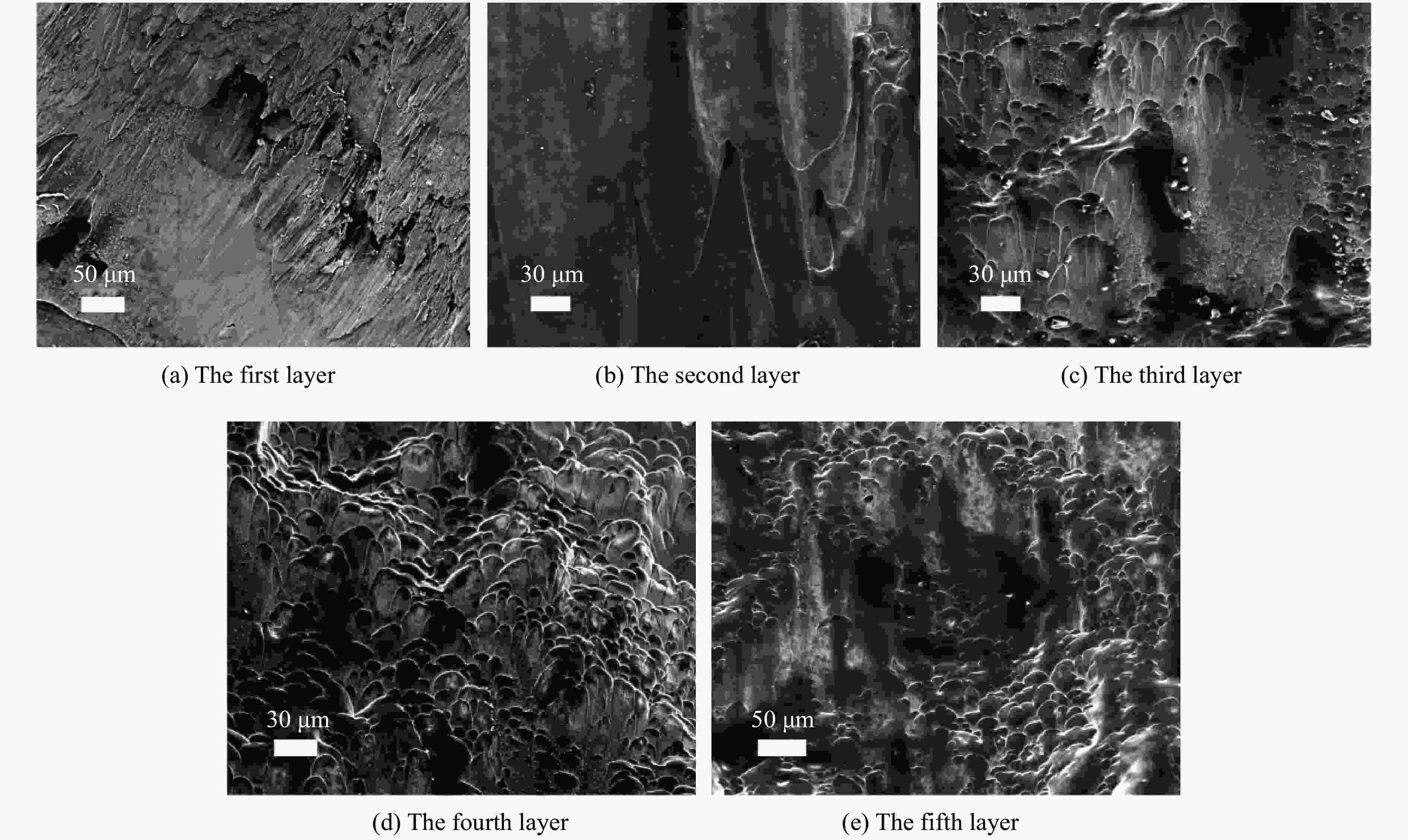
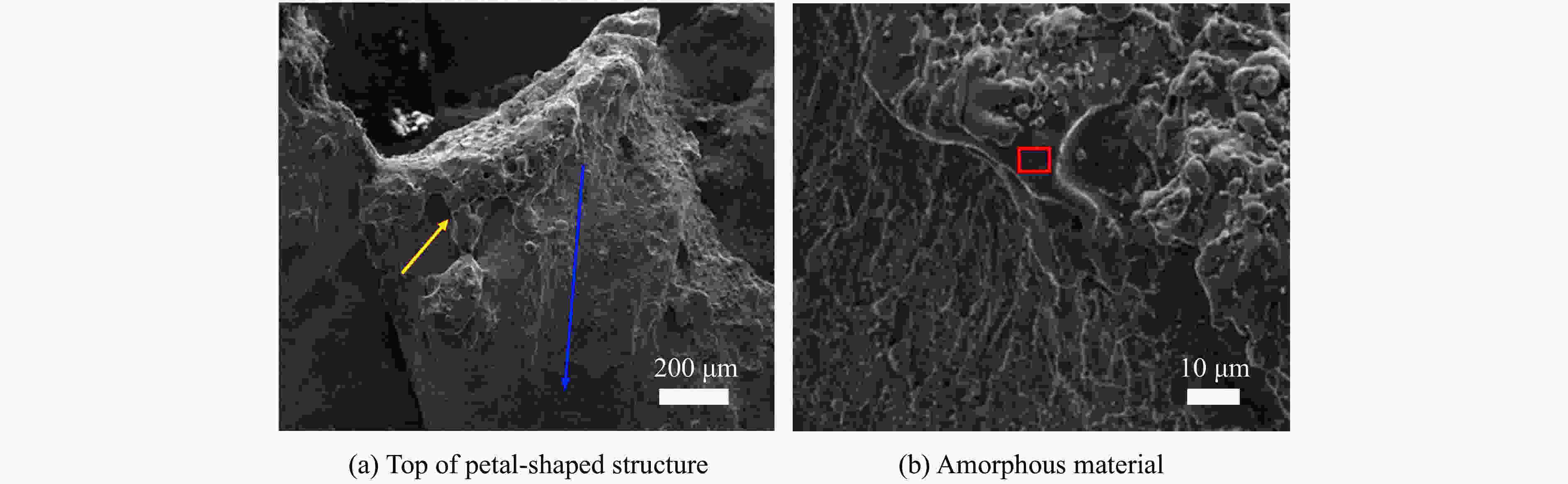
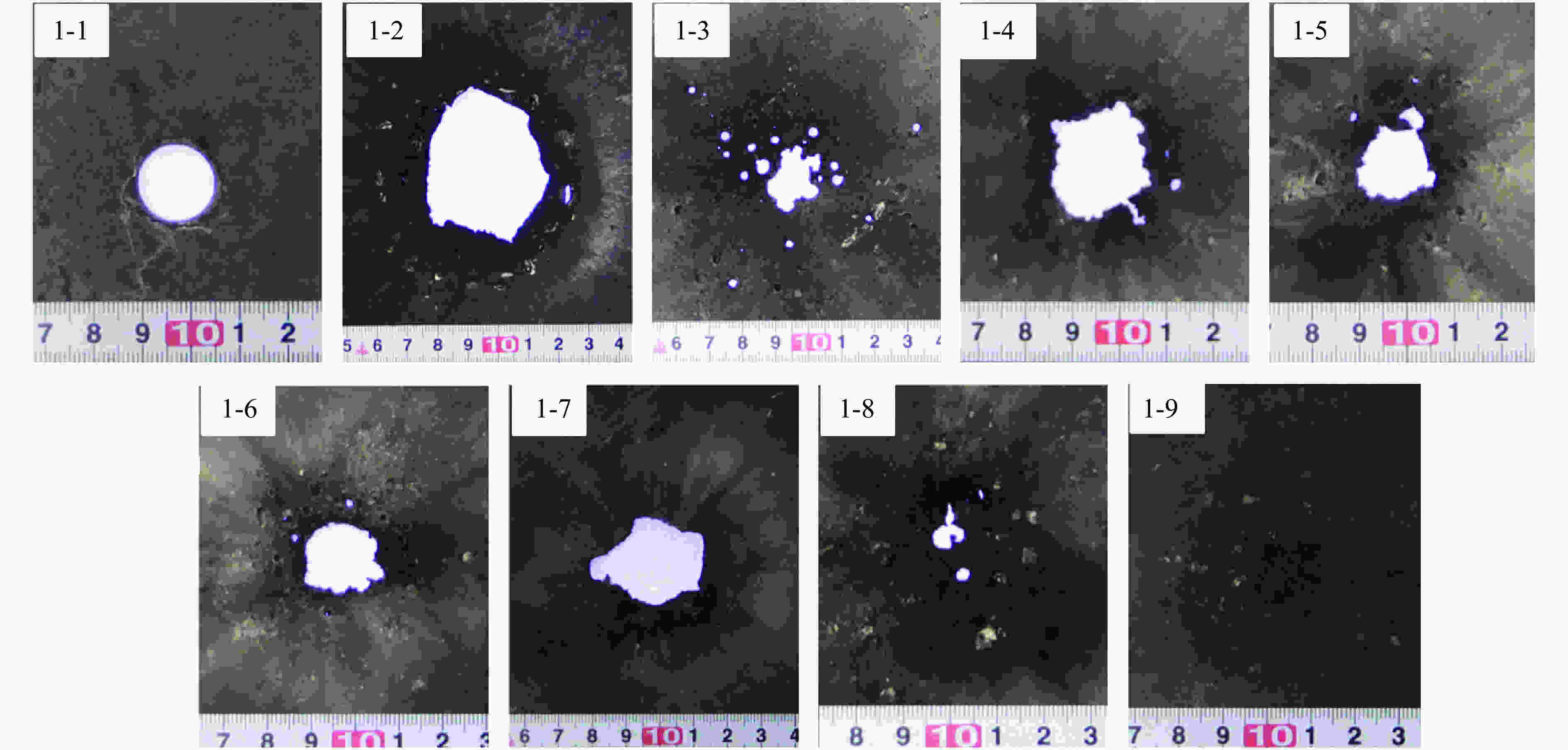
摘要: 为了解杆式弹超高速撞击多层薄钢靶的破坏过程及毁伤机理,开展了克级93W杆式弹正撞击多层Q345钢靶实验及数值模拟研究,通过扫描电子显微镜(scanning electron microscope,SEM)及金相显微镜,分析了超高速撞击实验后靶板材料的微观组织及成分。结果表明,超高速撞击作用下,靶板呈现出“翻唇”穿孔变形、花瓣状塑性变形、撕裂、撞击成坑及鼓包等破坏模式。靶板前3层毁伤以超高速穿孔为主,孔洞数目多但面积小,后几层靶板毁伤孔洞数目少且孔径呈先增大后减小趋势。微观分析表明靶材在强冲击压力下发生晶粒碎化、熔化及再结晶,撞击过程中会形成微孔聚集与微裂纹,可见靶板失效主要是熔融混合物冷却过程中产生的热应力与切应力下的剪切撕裂综合作用的结果。Abstract: In order to research the penetration characteristics and damage mechanism of multi-layer targets under hypervelocity impact, experiments and numerical simulations were carried out on a rod-shaped 93W projectile impacting a multi-layer Q345 steel target. A gram-order rod-shaped 93W projectile together with a sabot was launched by a 57/10 mm two-stage light gas gun to penetrate into a ten-layer Q345 target. The damage photos of the target after penetration were transformed into binary images by a Matlab processing software. The equivalent diameter of the center hole, the number and total areas of the holes, the diameters of damage circles of the ten-layer target were summed up and analyzed. The AUTODYN software was used to perform the smoothed particle hydrodynamics simulation. Then the microscopical data of the target plates were obtained by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and optical microscopy to analyze the microstructure and element composition. Results show that a rod-shaped 93W projectile could penetrate 8 or 9 layers of a ten-layer Q345 target under different initial impact velocities. Perforated lips, petal-shaped plastic deformation, tearing, cratering and bulging were formed in target plates. These failure modes are attributed to plastic expanding failure and shear tearing under shear stress. The damage mode of the first three layers of the target is dominated by hypervelocity perforation due to the high impact velocity, with many holes but small area, while the holes in the later layers are few, but the diameter increases first and then decreases as the masses and velocities of fragments decrease. The simulation results were verified by the experimental results. They are in good agreement with the experimental results. Micro analysis shows that the materials of the target and projectile are melt, while the grains are broken up, refined, melt and recrystallized in the target plates. There are aggregated micropores and microcracks formed during the penetration process. The micro analysis results show that the damage failure is mainly caused by the combined effects of thermal stress during the cooling process of the molten mixture and shear tearing under the shear stress, which is consistent with the macro-scopical results.
-
Key words:
- 93W /
- rod-shaped projectile /
- multi-layer Q345 target /
- micro analysis /
- damage mode
-
表 1 93钨合金的状态方程、强度模型材料参数
Table 1. Parameters of the equation of state and the strength model for 93W alloy
ρW0/(g·cm−3) cW0/(km·s−1) sW γW0 GW0/GPa YW0/GPa YW,max/GPa β n′ $\dfrac{{{\rm{d}}{G_{\rm{W}}}}}{{{\rm{d}}p}}$ $\dfrac{{{\rm{d}}{G_{\rm{W}}}}}{{{\rm{d}}T}}/{\rm{(MPa}}\cdot{{\rm{K}}^{{\rm{ - 1}}}}{\rm{)}}$ $\dfrac{ { {\rm{d} }Y} }{ { {\rm{d} }p} }$ 17.6 4.04 1.23 1.67 132 1.4 6 1.3 0.1 1.794 −40 0.019 027 表 2 Q345钢的状态方程、强度模型材料参数
Table 2. Parameters of the equation of state and the strength model for Q345 steel
ρs0/(g·cm−3) cs0/(m·s−1) ss γs0 A/MPa B/MPa n C m Tm/K ${\dot \varepsilon _{ {\rm{s0} } } }$/s−1 7.83 4 569 1.49 2.17 374 795.7 0.454 5 0.015 86 0.885 6 −1 795 0.001 表 3 聚碳酸酯的状态方程、强度方程材料参数
Table 3. Parameters of the equation of state and the strength model for polycarbonate
ρPC,0/(g·cm−3) cPC,0/(m·s−1) sPC γPC,0 E/GPa YPC,0 /MPa 1.2 1 933 2.65 0.61 1 80.6 表 4 3层靶各层毁伤面主孔等效直径实验及模拟结果比较
Table 4. Experimental and simulated results of the equivalent diameter of the center hole in each layer of the three-layer Q345 steel target
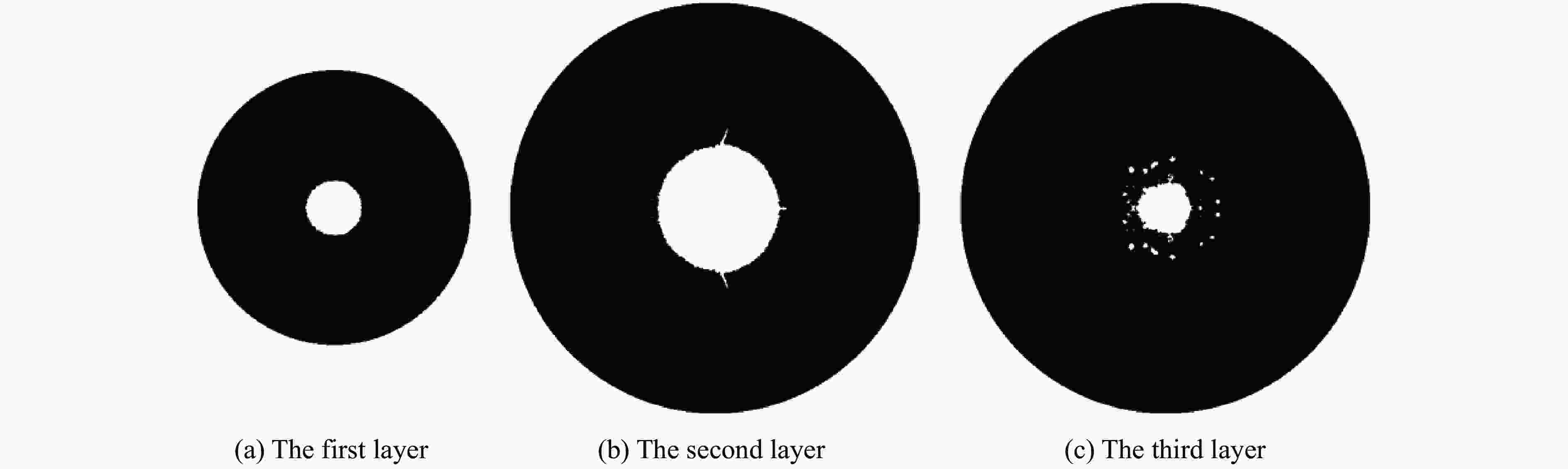
层别 等效直径/mm 误差/% 实验 模拟 第1层 16.34 16.15 1.162 第2层 38.11 36.29 4.773 第3层 14.06 15.44 9.809 表 5 第7层靶板中熔化后凝固的无定形态物质能量色散谱结果
Table 5. Energy dispersive spectrum analysis of amorphous material solidified after melting in the 7th layer
元素 质量分数/% 原子数分数/% 元素 质量分数/% 原子数分数/% C 2.45 13.14 Ni 2.18 2.39 Fe 63.38 73.23 W 32.00 11.23 表 6 撞击坑及孔洞熔化后凝固的无定形态物质EDS结果
Table 6. EDS analysis of amorphous material solidified after melting in impact crater and cavity
元素 质量分数/% 原子数分数/% 元素 质量分数/% 原子数分数/% C 4.67 17.12 K 12.67 3.01 O 15.75 43.37 Fe 30.03 23.70 Na 0.78 1.49 W 44.94 10.77 Mo 1.17 0.54 -
[1] 龙源, 岳小兵, 周翔, 等. 高速钢弹对多层大间隔金属靶的侵彻特性研究 [J]. 南京理工大学学报, 2004, 28(4): 369–374. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9830.2004.04.008.LONG Y, YUE X B, ZHOU X, et al. Characteristics of high-speed steel projectiles penetrating into multi-layer spaced metal plates [J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2004, 28(4): 369–374. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9830.2004.04.008. [2] 肖云凯, 吴昊, 方秦. 长杆弹超高速侵彻金属靶体的实验和模型分析 [J]. 兵工学报, 2017, 38(S1): 15–23.XIAO Y K, WU H, FANG Q. Experiment and theoretical model analysis of hypervelocity penetration of long-rod projectiles into metallic targets [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2017, 38(S1): 15–23. [3] 马坤, 李名锐, 陈春林, 等. 93钨合金弹体超高速撞击钢板破片群分布数值模拟 [J]. 兵工学报, 2019, 40(10): 2022–2031. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2019.10.007.MA K, LI M R, CHEN C L, et al. Simulation analysis of distribution of fragments of hypervelocity 93w projectile impacting on a steel plate target [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2019, 40(10): 2022–2031. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2019.10.007. [4] 赵汝岩, 卢洪义, 朱敏. 杆式动能体侵彻多层靶板数值仿真 [J]. 弹箭与制导学报, 2012, 32(6): 96–98, 116. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9728.2012.06.029.ZHAO R Y, LU H Y, ZHU M. Numerical analysis of rod kinetic energy projectile penetrating into multilayer spaced metal plates [J]. Journal of Projectiles, Rockets, Missiles and Guidance, 2012, 32(6): 96–98, 116. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9728.2012.06.029. [5] 刘洋, 姚江涛, 李国林, 等. 用数值模拟法研究战斗部侵彻多层间隔靶 [J]. 海军航空工程学院学报, 2009, 24(2): 144–148. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1522.2009.02.007.LIU Y, YAO J T, LI G L, et al. Numerical simulation of warhead penetrating into multi-layer spaced target [J]. Journal of Naval Aeronautical and Astronautical University, 2009, 24(2): 144–148. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1522.2009.02.007. [6] 汪庆桃, 吴克刚, 陈志阳. 圆柱形长杆超高速正碰撞薄板结构破碎效应 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2017, 36(5): 54–60. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2017.05.009.WANG Q T, WU K G, CHEN Z Y. Fragmentation effect of a long cylindrical rod with a hypervelocity normally impacting a thin plate structure [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2017, 36(5): 54–60. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2017.05.009. [7] 李金泉. 穿甲侵彻机理及绝热剪切带特性研究[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2005: 22−42.LI J Q. Study of armor-piercing mechanism and adiabatic shear banding characteristic[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2005: 22−42. [8] 罗荣梅. 细晶钨合金穿甲弹靶作用机理研究[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2016: 19−55.LUO R M. Study on penetration mechanism of fine-grained tungsten heavy alloy penetrator[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2016: 19−55. [9] 高华, 熊超, 殷军辉. 弹丸侵彻多层异质复合靶板中装甲钢变形细观和微观机理研究 [J]. 兵工学报, 2018, 39(8): 1565–1575. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2018.08.013.GAO H, XIONG C, YIN J H. Research on macroscopic and microscopic mechanisms of deformation of armor steel in multilayer heterogeneous composite target subjected to projectile [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2018, 39(8): 1565–1575. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2018.08.013. [10] 李争, 刘元雪, 张裕. 动能弹侵彻机理及其防护研究进展 [J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2016, 37(3): 9–14. DOI: 10.11809/scbgxb2016.03.003.LI Z, LIU Y X, ZHANG Y. Research progress of kinetic energy projectile penetration mechanism and protection [J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2016, 37(3): 9–14. DOI: 10.11809/scbgxb2016.03.003. [11] 刘宗伟, 武海军, 张学伦, 等. 高超弹体侵蚀机理及抗侵蚀设计研究 [J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2017, 38(4): 46–49. DOI: 10.11809/scbgxb2017.04.010.LIU Z W, WU H J, ZHANG X L, et al. Eroding mechanism and anti-eroding design technique of high speed penetrator [J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2017, 38(4): 46–49. DOI: 10.11809/scbgxb2017.04.010. [12] 钱秉文, 周刚, 李进, 等. 钨合金弹体超高速撞击混凝土靶成坑特性研究 [J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2018, 38(10): 1012–1017. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2018.10.004.QIAN B W, ZHOU G, LI J, et al. Study of the crater produced by hypervelocity tungsten alloy projectile into concrete target [J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2018, 38(10): 1012–1017. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2018.10.004. [13] 蒋东, 李永池, 于少娟, 等. 钨合金长杆弹侵彻约束AD95陶瓷复合靶 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2010, 30(1): 91–95. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2010)01-0091-05.JIANG D, LI Y C, YU S J, et al. Penetration of confined AD95 ceramic composite targets by tungsten long rods [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2010, 30(1): 91–95. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2010)01-0091-05. [14] 李平, 李大红, 宁建国, 等. Al2O3陶瓷复合靶抗长杆弹侵彻性能和机理实验研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2003, 23(4): 289–294. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1455.2003.04.001.LI P, LI D H, NING J G, et al. Experimental study on the ballistic performance and mechanism of confined ceramic targets against long rod penetrators [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2003, 23(4): 289–294. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1455.2003.04.001. [15] 楼建锋. 侵彻半无限厚靶的理论模型和数值模拟研究[D]. 绵阳: 中国工程物理研究院, 2012: 25−41.LOU J F. Theoretical model and numerical study on penetrating into semi-infinite targets[D]. Mianyang: China Academy of Engineering Physics, 2012: 25−41. [16] 张庆明, 黄风雷. 超高速碰撞动力学引论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2000: 1−5. [17] 杨益, 李晓军, 朱大明, 等. 超高速碰撞材料毁伤效应研究进展 [J]. 兵器材料科学与工程, 2014, 37(5): 133–140. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-244X.2014.05.037.YANG Y, LI X J, ZHU D M, et al. Research development of materials damage effect under hypervelocity impact [J]. Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2014, 37(5): 133–140. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-244X.2014.05.037. [18] 牛瑞涛. 空间碎片铝网防护屏超高速撞击特性研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2010: 2−10.NIU R T. Hypervelocity impact characteristic investigation of space debris aluminum mesh bumper[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2010: 2−10. [19] 管公顺. 航天器空间碎片防护结构超高速撞击特性研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2006: 33−35.GUAN G S. Hypervelocity impact characteristic investigation of spacecraft space debris shield configuration[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2006: 33−35. [20] Century Dynamics, Inc. AUTODYN theory manual revision 4.3[M]. Concord, CA: Century Dynamics, Inc., 2003. [21] STEINBERG D J, COCHRAN S G, GUINAN M W. A constitutive model for metals for applicable at high-strain rate [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1980, 51: 1498–1504. DOI: 10.1063/1.327799. [22] JOHNSON G R, COOK W H. A constitutive model and data for metals subjected to large strains, high strain rates, and high temperatures[C]// Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Ballistics. The Hague, Netherlands 1983: 541−547. [23] 蔡宣明. PBX炸药动态力学行为及起爆特性研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2015: 83−84.CAI X M. Study on dynamic mechanical behavior and initiation characteristic of PBX[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2015: 83−84. -






 下载:
下载: