A modified reaction model of aluminum dust detonation
-
摘要: 铝粉反应模型是对悬浮铝粉尘气-固两相爆轰进行数值模拟研究的关键。通过考虑铝粉燃烧产物氧化铝(Al2O3)在高温下的分解吸热反应,改进了铝粉的扩散燃烧模型。将该模型嵌入到三维的气-固两相爆轰数值计算程序中,分别对铝粉/空气混合物以及铝粉/氧气混合物的爆轰进行了数值模拟,计算得到的稳定爆轰波速度与实验结果、文献值均吻合较好,误差小于5.5%,表明改进的铝粉反应模型适用于不同氧化气体氛围中铝粉尘爆轰的模拟计算。此外,对两相爆轰参数及爆轰流场的物理量分布进行分析,获得了铝粉反应模型对爆轰波结构的影响规律。Abstract: The reaction model of aluminum particles is the key to successfully simulate the two-phase detonation of aluminum suspensions. In this study, by considering the endothermic decomposition reaction of the aluminum oxide (Al2O3) product at high temperature, a diffusion combustion model for the aluminum particles was improved and was incorporated into the homemade numerical code for 3D simulation of gas-solid two-phase detonation. The numerical program is based on the theory of two-phase flows, both gaseous and solid phases are assumed to be continuous media with inter-phase transfer of mass, momentum and energy. The system of 3D governing equations is solved in Cartesian x-y-z coordinates using an Eulerian grid, the numerical simulation code uses an explicit finite difference scheme based on the space-time conservation element and solution element (CE/SE) method, and the fourth order Runge-Kutta method is used to solve the source terms of the governing equations. In addition, the stability is assured by the Courant-Friedrichs-Lewy (CFL) criterion. Program parallelization is realized based on the message-passing-interface (MPI) technique, and the reliability of the program is demonstrated by simulating the shock tube problem successfully. Based on the program and the improved reaction model for the aluminum particles, numerical simulations for detonations of Al/air mixtures and Al/O2 mixtures were performed, respectively, the simulated results of the steady detonation wave speeds are in agreement with the experimental results or the literature value, with the error of less than 5.5%, which demonstrate the validity of the improved reaction model for Al suspensions detonation in different oxidizing atmosphere. Moreover, the detonation parameters and the distributions of the physical quantities around the detonation wave are analyzed, and the influence law of the reaction model on the detonation wave structure is obtained.
-
Key words:
- aluminum particles /
- reaction model /
- two-phase detonation /
- reverse reaction
-
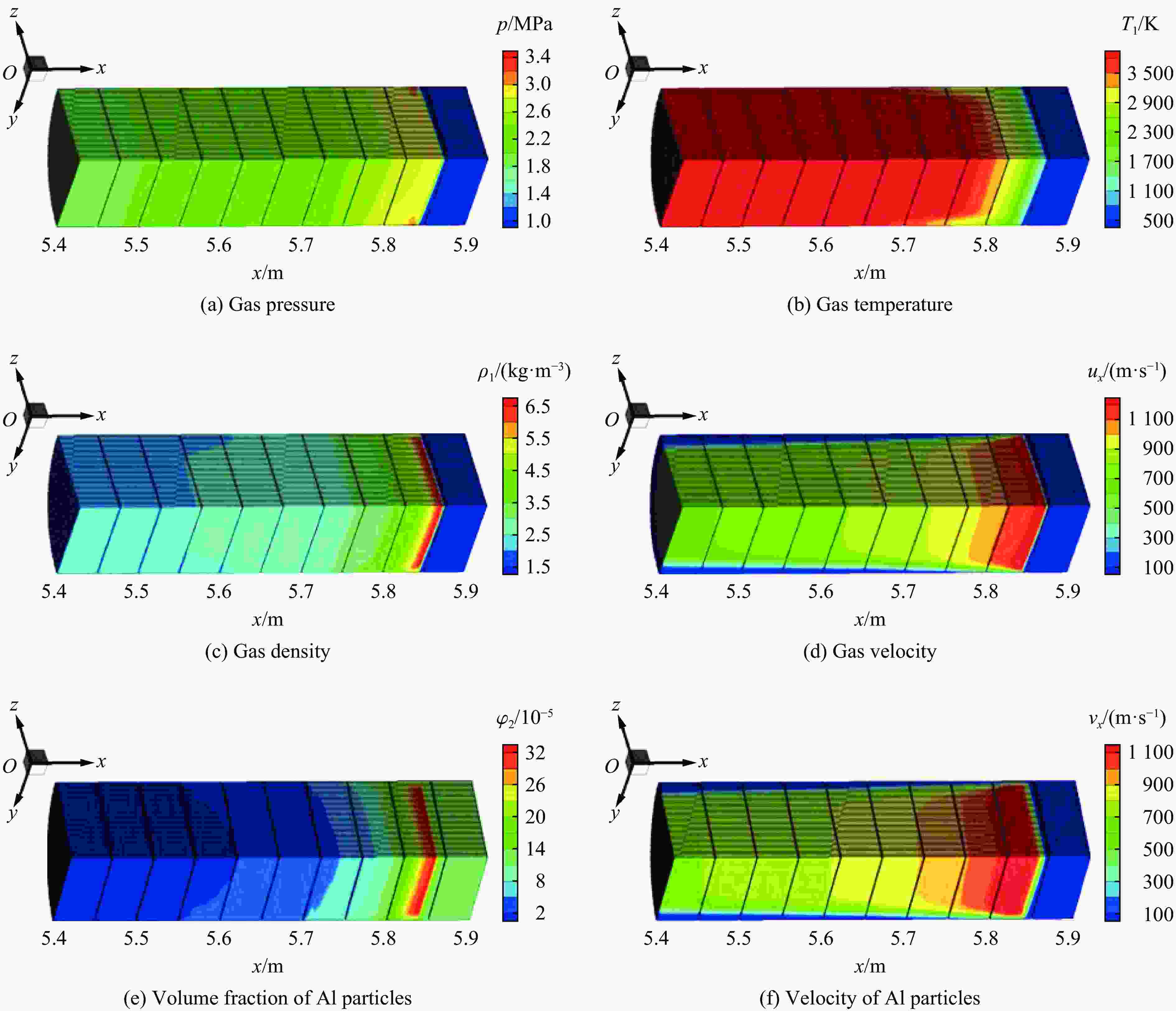
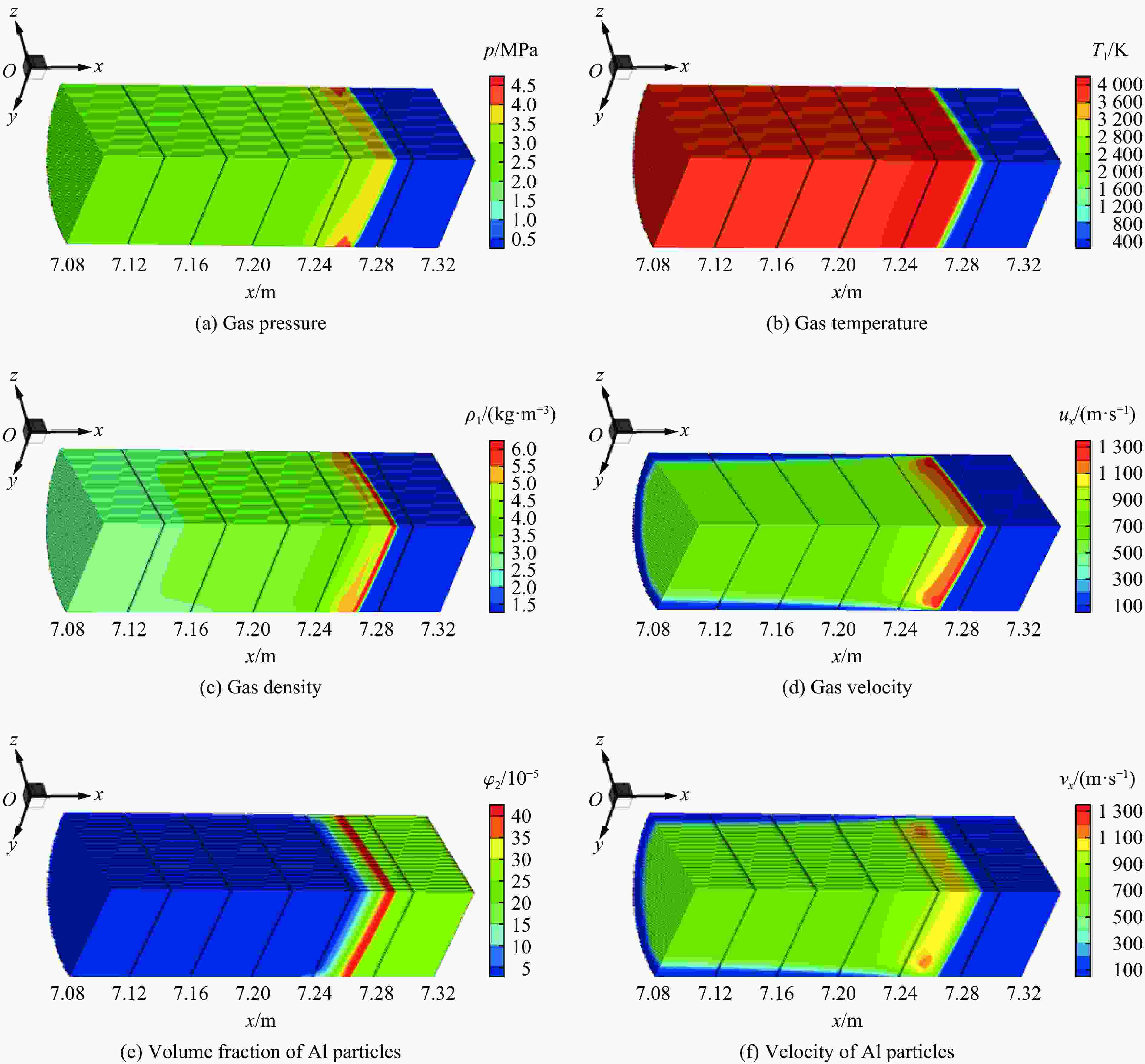
图 4 3.83 ms时刻铝粉/空气爆轰波阵面附近气体压力、气体温度、气体密度、气体轴向速度、铝粉体积分数以及铝粉轴向速度的分布
Figure 4. Distributions of gas pressure, gas temperature, gas density, gas velocity in the x direction, volume fraction of Al particles, and Al particles velocity in the x direction around the detonation wave for Al/air mixtures at t=3.83 ms
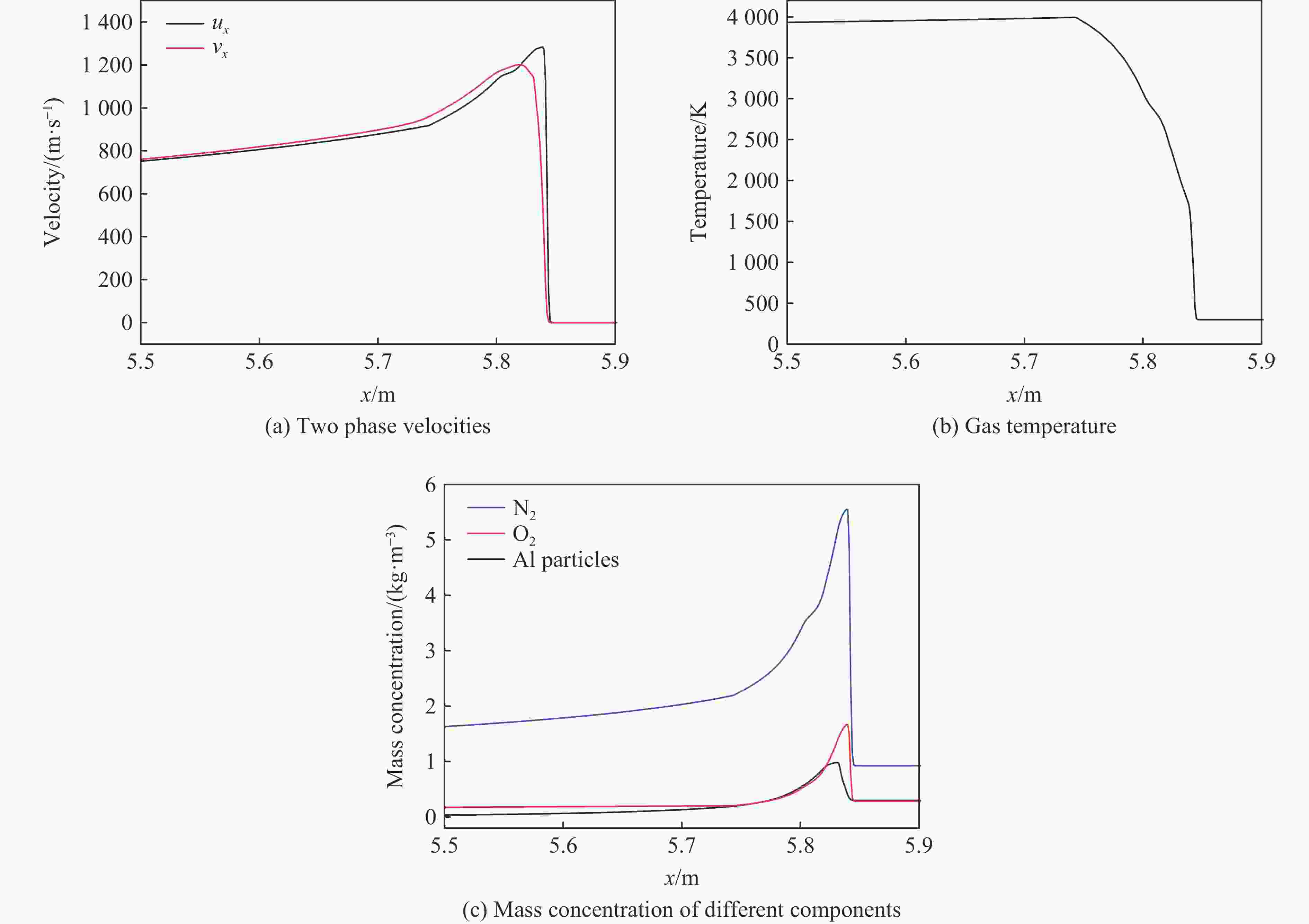
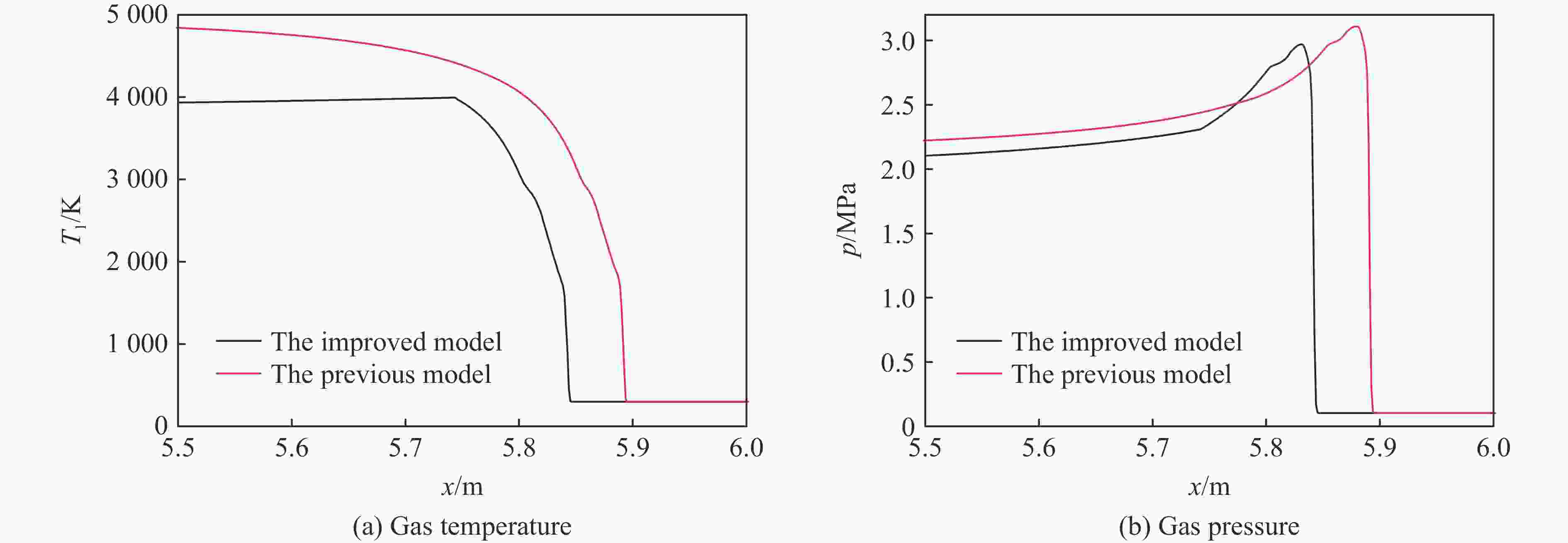
图 7 4.43 ms时刻铝粉/氧气爆轰波阵面附近气体压力、气体温度、气体密度、气体轴向速度、铝粉体积分数以及铝粉轴向速度的分布
Figure 7. Distributions of gas pressure, gas temperature, gas density, gas velocity in the x direction as well as volume fraction of Al particles, and Al particles velocity in the x direction around the detonation wave for Al/O2 mixtures at t=4.43 ms
-
[1] LIU X L, ZHANG Q. Influence of turbulent flow on the explosion parameters of micro- and nano-aluminum powder-air mixtures [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 299: 603–617. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.07.068. [2] VEYSSIERE B, KHASAINOV B A, BRIAND A. Investigation of detonation initiation in aluminium suspensions [J]. Shock Waves, 2008, 18(4): 307–315. DOI: 10.1007/s00193-008-0136-z. [3] FEDOROV A V, KHMEL T A. Numerical simulation of formation of cellular heterogeneous detonation of aluminum particles in oxygen [J]. Combustion, Explosion, and Shock Waves, 2005, 41(4): 435–448. DOI: 10.1007/s10573-005-0054-7. [4] BECKSTEAD M W. Correlating aluminum burning times [J]. Combustion, Explosion and Shock Waves, 2005, 41(5): 533–546. DOI: 10.1007/s10573-005-0067-2. [5] TANGUAY V, GOROSHIN S, HIGGINS A J, et al. Aluminum particle combustion in high-speed detonation products [J]. Combustion Science and Technology, 2009, 181(4): 670–693. DOI: 10.1080/00102200802643430. [6] BAZYN T, KRIER H, GLUMAC N. Evidence for the transition from the diffusion-limit in aluminum particle combustion [J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2007, 31(2): 2021–2028. DOI: 10.1016/j.proci.2006.07.161. [7] GLORIAN J, GALLIER S, CATOIRE L. On the role of heterogeneous reactions in aluminum combustion [J]. Combustion and Flame, 2016, 168: 378–392. DOI: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2016.01.022. [8] ZHANG F, GERRARD K, RIPLEY R C. Reaction mechanism of aluminum-particle-air detonation [J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 2009, 25(4): 845–858. DOI: 10.2514/1.41707. [9] BRIAND A, VEYSSIERE B, KHASAINOV B A. Modelling of detonation cellular structure in aluminium suspensions [J]. Shock Waves, 2010, 20(6): 521–529. DOI: 10.1007/s00193-010-0288-5. [10] BALAKRISHNAN K. Diffusion- and kinetics-limited combustion of an explosively dispersed aluminum particle [J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 2014, 30(2): 522–526. DOI: 10.2514/1.B35059. [11] KWON Y S, GROMOV A A, ILYIN A P, et al. The mechanism of combustion of superfine aluminum powders [J]. Combustion and Flame, 2003, 133(4): 385–391. DOI: 10.1016/S0010-2180(03)00024-5. [12] NIGMATULIN R I. Methods used in mechanics of continuous media for a description of multiphase mixtures [J]. Journal of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 1970, 34(6): 1097–1112. DOI: 10.1016/0021-8928(70)90174-7. [13] HAYNES W M. Handbook of chemistry and physics [M]. Florida: CRC Press, 2014. [14] LEVITAS V I, PANTOYA M L, CHAUHAN G, et al. Effect of the alumina shell on the melting temperature depression for aluminum nanoparticles [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2009, 113(32): 14088–14096. DOI: 10.1021/jp902317m. [15] 洪滔, 秦承森. 铝颗粒激波点火机制初探 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2003, 23(4): 295–299.HONG T, QIN C S. Mechanism of shock wave ignition of aluminum particle [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2003, 23(4): 295–299. [16] PRICE E W. Combustion of metalized propellants [M]// KUO K K. Fundamentals of Solid-Propellant Combustion. New York: American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 1984: 479−513. DOI: 10.2514/5.9781600865671.0479.0513. [17] STEINBERG T A, WILSON D B, BENZ F. The combustion phase of burning metals [J]. Combustion and Flame, 1992, 91(2): 200–208. DOI: 10.1016/0010-2180(92)90100-4. [18] GLASSMAN I. Combustion of metals revisited thermodynamically [C]// Proceedings of the Eastern States Section of the Combustion Institute. Princeton: The Combustion Institute, 1993: 17−26. [19] 沈维道, 童钧耕. 工程热力学[M]. 4版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2007.SHEN W D, TONG J G. Engineering thermodynamics [M]. 4th ed. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2007. [20] TORO E F. Riemann solvers and numerical methods for fluid dynamics: a practical introduction [M]. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer, 2009. DOI: 10.1007/b79761. [21] TULIS A J, SELMAN J R. Detonation tube studies of aluminum particles dispersed in air [J]. Symposium (International) on Combustion, 1982, 19(1): 655–663. DOI: 10.1016/s0082-0784(82)80240-3. [22] LIU L J, ZHANG Q, SHEN S L, et al. Evaluation of detonation characteristics of aluminum/JP-10/air mixtures at stoichiometric concentrations [J]. Fuel, 2016, 169: 41–49. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2015.11.090. [23] BENKIEWICZ K, HAYASHI K. Two-dimensional numerical simulations of multi-headed detonations in oxygen-aluminum mixtures using an adaptive mesh refinement [J]. Shock Waves, 2003, 12(5): 385–402. DOI: 10.1007/s00193-002-0169-7. -






 下载:
下载: