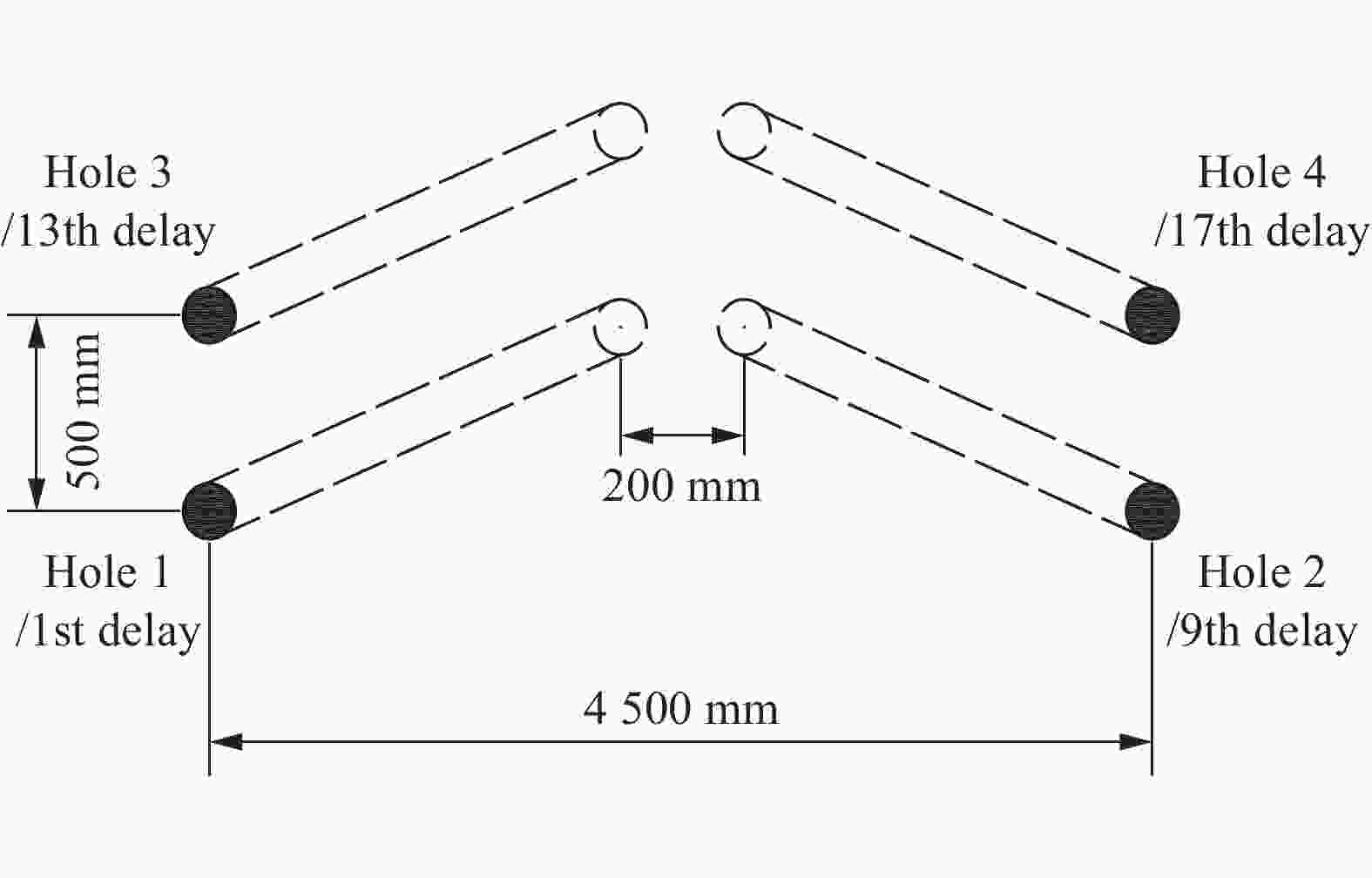
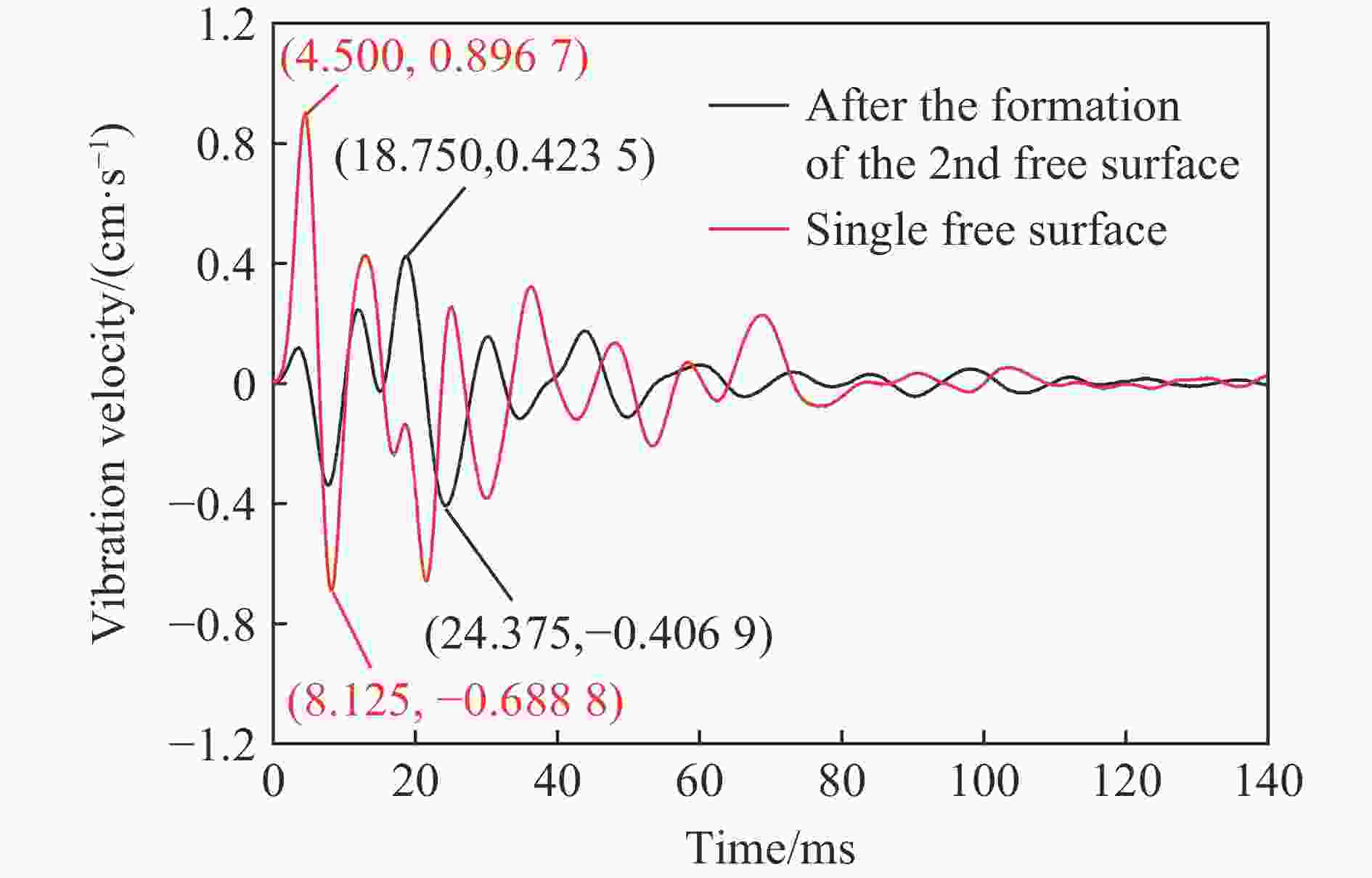
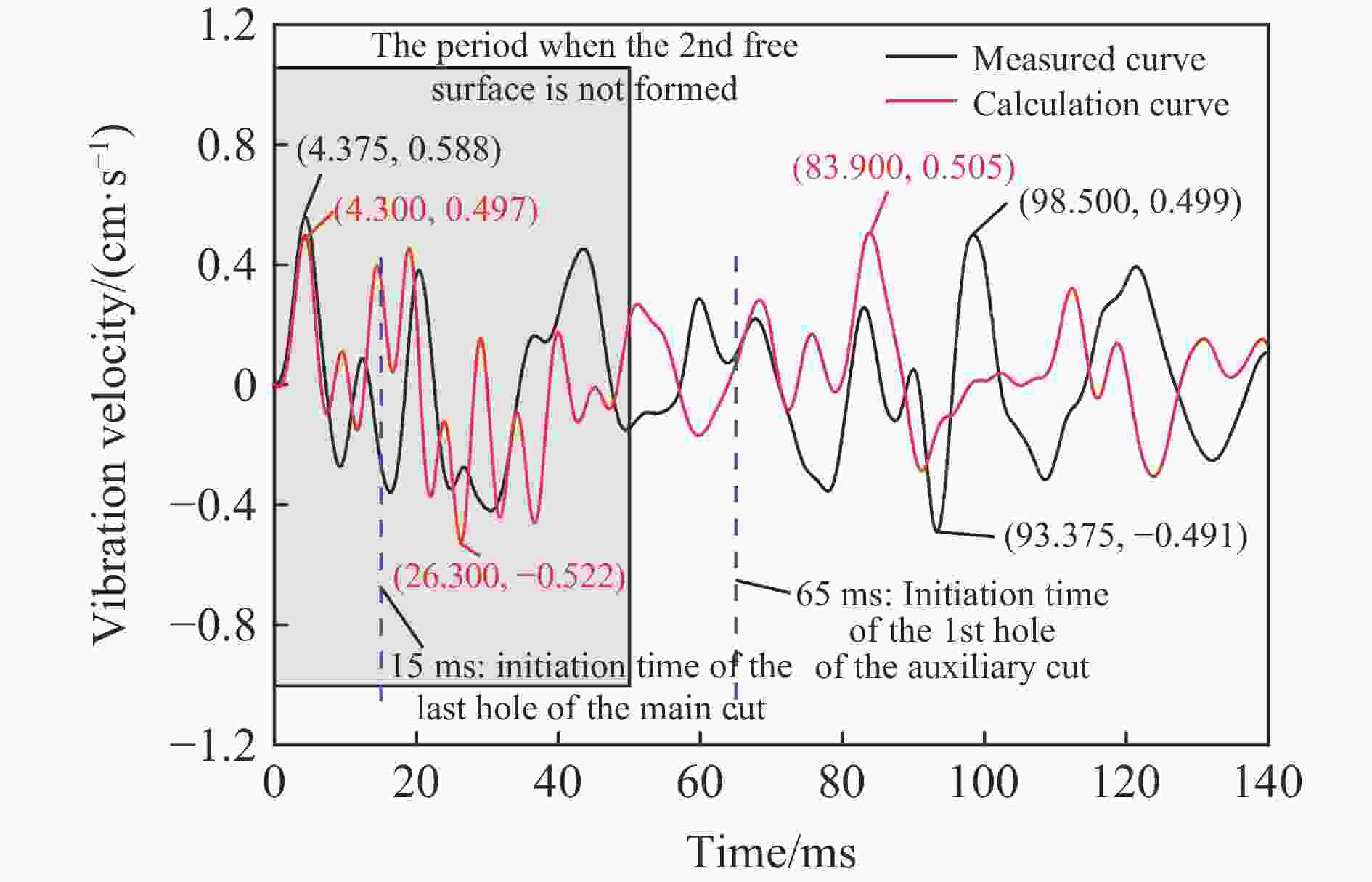
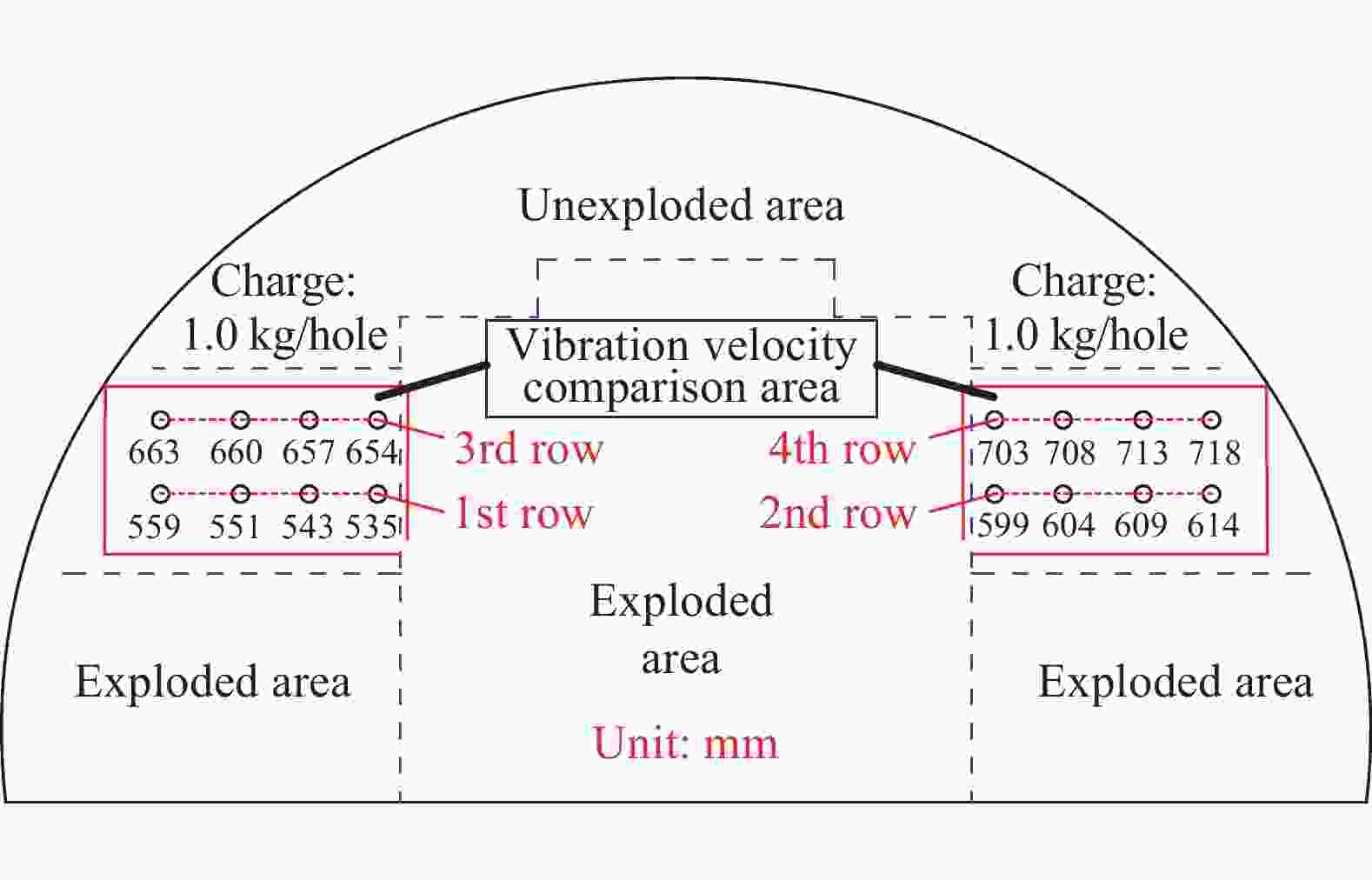
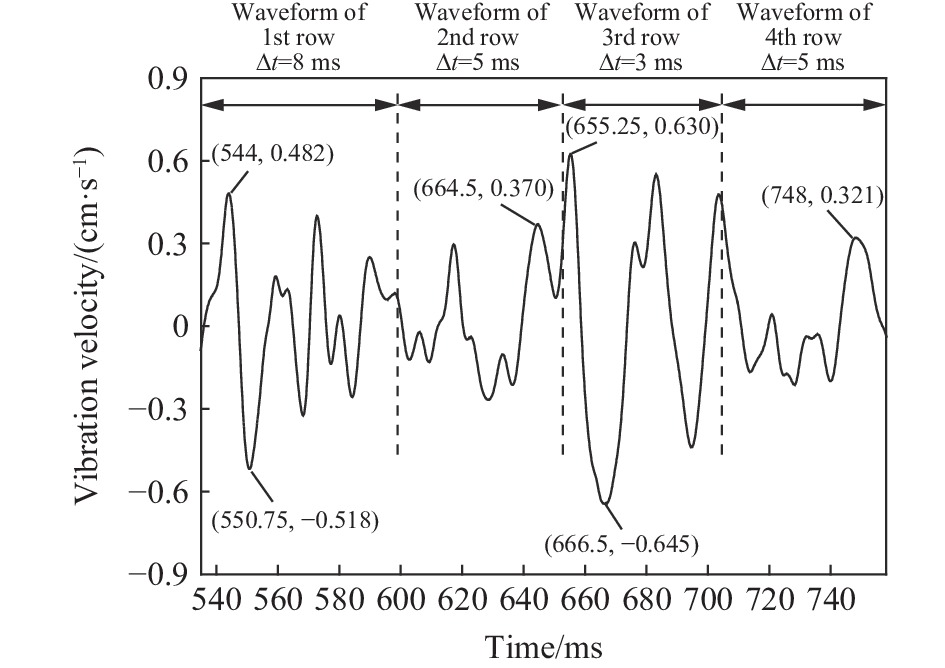
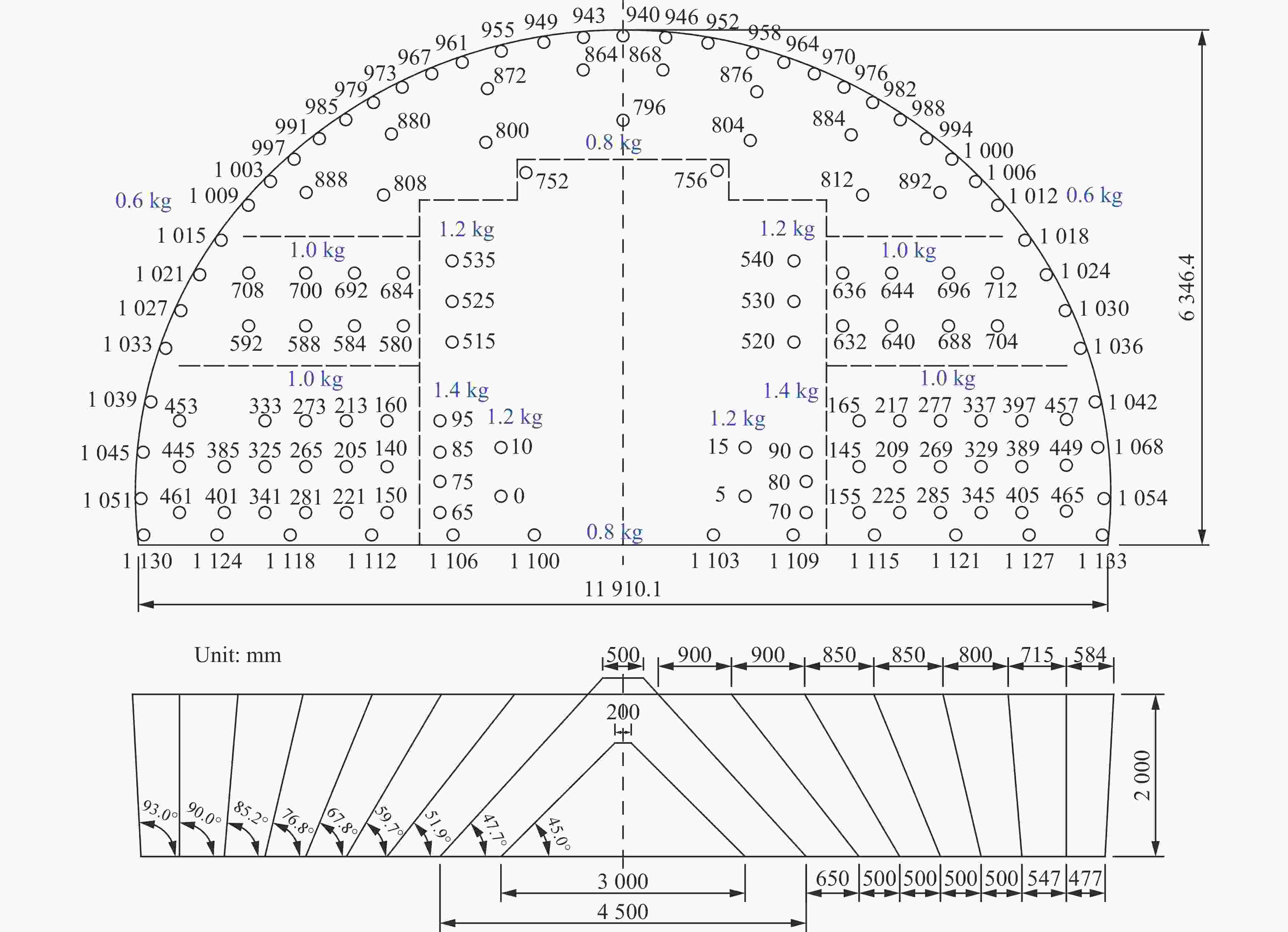
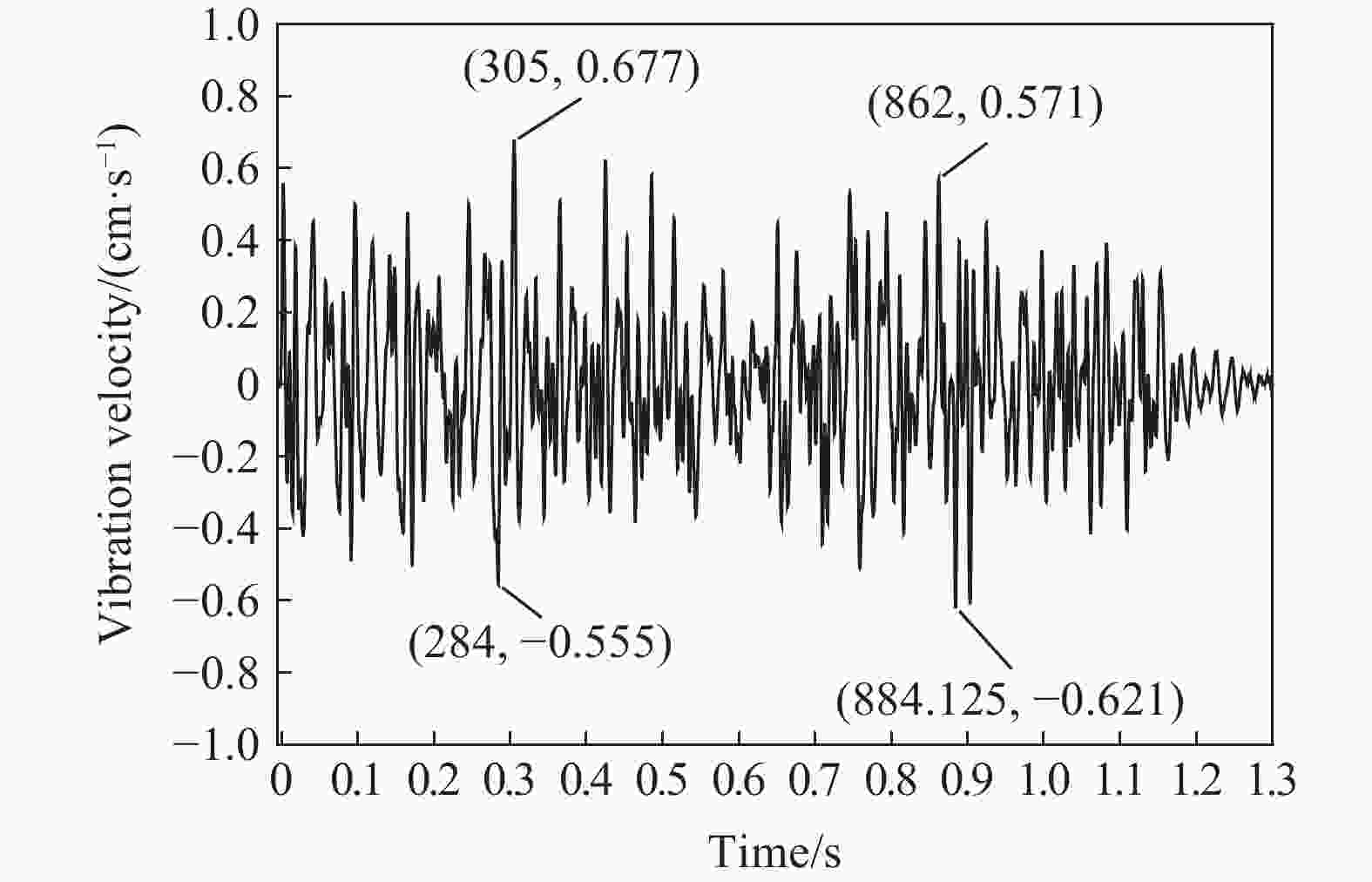
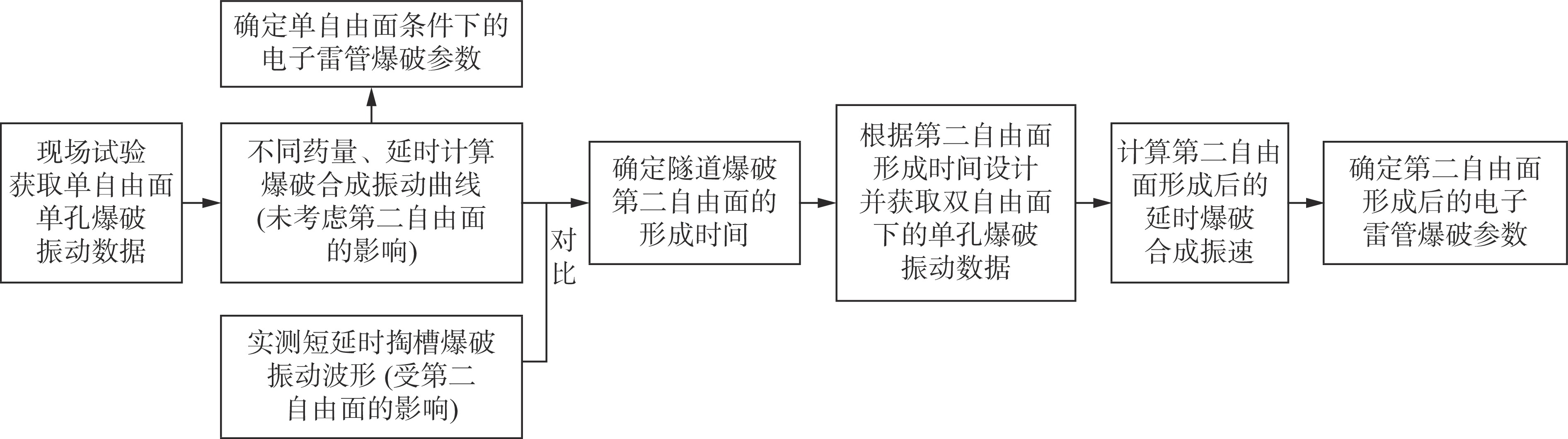
| [1] |
汪旭光, 沈立晋. 工业雷管技术的现状和发展 [J]. 工程爆破, 2003, 9(3): 52–57. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7051.2003.03.013.WANG X G, SHEN L J. The state-of-the-arts of industrial detonators [J]. Engineering Blasting, 2003, 9(3): 52–57. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7051.2003.03.013.
|
| [2] |
颜景龙. 中国电子雷管技术与应用 [J]. 中国工程科学, 2015, 17(1): 36–41. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2015.01.005.YAN J L. Technology and application of Chinese electronic detonator [J]. Engineering Sciences, 2015, 17(1): 36–41. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2015.01.005.
|
| [3] |
HASHEMI A S, KATSABANIS P. The effect of stress wave interaction and delay timing on blast-induced rock damage and fragmentation [J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2020, 53(5): 2327–2346. DOI: 10.1007/s00603-019-02043-9.
|
| [4] |
LENG Z D, SUN J S, LU W B, et al. Mechanism of the in-hole detonation wave interactions in dual initiation with electronic detonators in bench blasting operation [J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2021, 129: 103873. DOI: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2020.103873.
|
| [5] |
SINGH P K, ROY M P, PASWAN R K, et al. Blast vibration effects in an underground mine caused by open-pit mining [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2015, 80: 79–88. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2015.09.009.
|
| [6] |
FU H X, WONG L N Y, ZHAO Y, et al. Comparison of excavation damage zones resulting from blasting with nonel detonators and blasting with electronic detonators [J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2014, 47(2): 809–816. DOI: 10.1007/s00603-013-0419-2.
|
| [7] |
赵勇, 傅洪贤, 谢晋水, 等. 电子雷管在隧道钻爆法开挖中降振试验研究 [J]. 工程爆破, 2012, 18(1): 82–85. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7051.2012.01.022.ZHAO Y, FU H X, XIE J S, et al. Experimental research on decreasing blasting vibration velocity by digital detonator [J]. Engineering Blasting, 2012, 18(1): 82–85. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7051.2012.01.022.
|
| [8] |
曹杨, 王旭春, 余志伟, 等. 隧道近距下穿老旧建筑物爆破振动监测及减振技术研究 [J]. 施工技术, 2017, 46(11): 82–85. DOI: 10.7672/sgjs2017110082.CAO Y, WANG X C, YU Z W, et al. Blasting vibration monitoring and reduction technology of tunnel under-passing aging buildings in a short distance [J]. Construction Technology, 2017, 46(11): 82–85. DOI: 10.7672/sgjs2017110082.
|
| [9] |
傅洪贤, 沈周, 赵勇, 等. 隧道电子雷管爆破降振技术试验研究 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2012, 31(3): 597–603. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.03.018.FU H X, SHEN Z, ZHAO Y, et al. Experimental study of decreasing vibration technology of tunnel blasting with digital detonator [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2012, 31(3): 597–603. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.03.018.
|
| [10] |
管晓明, 傅洪贤, 王梦恕. 隧道近距下穿山坡楼房爆破振动测试研究 [J]. 岩土力学, 2014, 35(7): 1995–2003. DOI: 10.16285/j.rsm.2014.07.027.GUAN X M, FU H X, WANG M S. Blasting vibration characteristics monitoring of tunnel under-passing hillside buildings in short-distance [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2014, 35(7): 1995–2003. DOI: 10.16285/j.rsm.2014.07.027.
|
| [11] |
程围峰, 王振宇, 陈银鲁, 等. 引水隧洞电子雷管爆破震动特征研究 [J]. 铁道工程学报, 2014(5): 79–84. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2014.05.015.CHENG W F, WANG Z Y, CHEN Y L, et al. Research on the vibration characteristic of electronic detonator blasting for water diversion tunnel [J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2014(5): 79–84. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2014.05.015.
|
| [12] |
马晓明, 王振宇, 陈银鲁, 等. 精确微差爆破震动能量分布特征分析 [J]. 解放军理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 13(4): 449–454. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3443.2012.04.018.MA X M, WANG Z Y, CHEN Y L, et al. Analysis of energy distribution of accurate millisecond blasting vibration [J]. Journal of PLA University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2012, 13(4): 449–454. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3443.2012.04.018.
|
| [13] |
田振农, 孟祥栋, 王国欣. 城区隧道电子雷管起爆错相减震机理分析 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2012, 31(21): 108–111. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2012.21.022.TIAN Z N, MENG X D, WANG G X. Mechanism analysis of fault-phase vibration reduction for tunnel blasting initiated by electronic detonators in city area [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2012, 31(21): 108–111. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2012.21.022.
|
| [14] |
ANDERSON D A. A method site-specific prediction and control of ground vibration from blasting [C]// Proceedings of the First Mini-symposium on Explosives and Blasting Research, 1985: 28−42.
|
| [15] |
HINZEN K G. Modelling of blast vibrations [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 1988, 25(6): 439–445. DOI: 10.1016/0148-9062(88)90984-9.
|
| [16] |
AZIZABADI H R M, MANSOURI H, FOUCHÉ O. Coupling of two methods, waveform superposition and numerical, to model blast vibration effect on slope stability in jointed rock masses [J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2014, 61: 42–49. DOI: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2014.04.008.
|
| [17] |
龚敏, 吴昊骏, 孟祥栋, 等. 密集建筑物下隧道开挖微振控制爆破方法与振动分析 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2015, 35(3): 350–358. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2015)03-0350-09.GONG M, WU H J, MENG X D, et al. A precisely-controlled blasting method and vibration analysis for excavation under dense buildings [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2015, 35(3): 350–358. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2015)03-0350-09.
|
| [18] |
吴昊骏, 龚敏. 基于雷管实际延时范围的逐孔爆破振动合成计算与应用 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2019, 39(2): 151–161. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2017-0415.WU H J, GONG M. Calculation and application of hole by hole blasting vibration superposition based on measured delay times of detonators [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2019, 39(2): 151–161. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2017-0415.
|
| [19] |
IWANO K, HASHIBA K, NAGAE J, et al. Reduction of tunnel blasting induced ground vibrations using advanced electronic detonators [J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2020, 105: 103556. DOI: 10.1016/j.tust.2020.103556.
|
| [20] |
龚敏, 吴昊骏. 隧道爆破现场高速图像采集与精确控制爆破参数研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2019, 39(5): 3–12. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0319.GONG M, WU H J. High-speed photography image acquisition system in tunnel blasting and parameters study on precisely controlled blasting [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2019, 39(5): 3–12. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0319.
|







 下载:
下载: