Investigation on the technology of soft recovery of fragment produced by metal cylindrical shell subjected to explosive loading
-
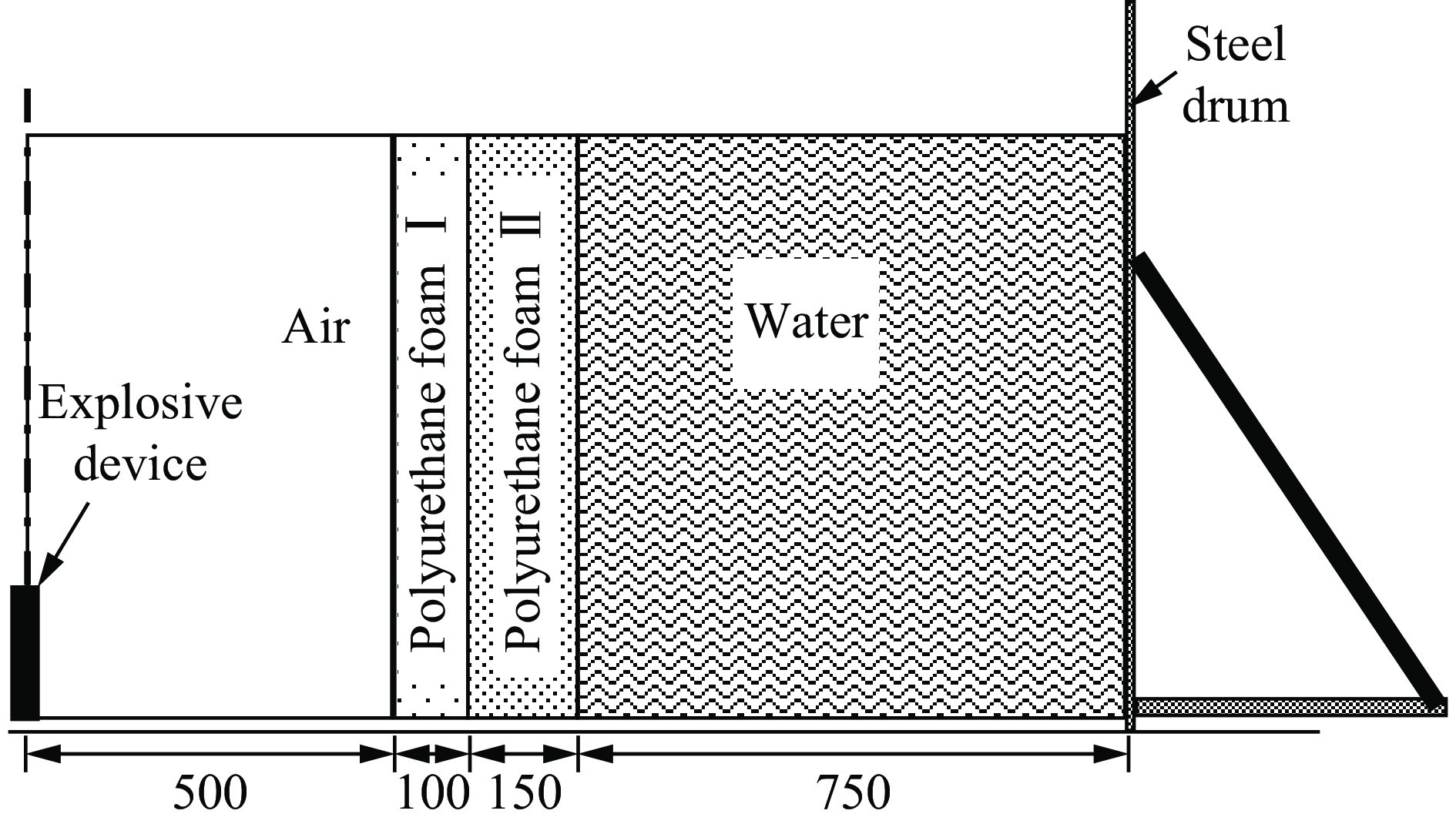
摘要: 针对爆炸加载下金属柱壳膨胀断裂破片软回收的研究需求,本文通过理论分析和初步的数值模拟设计了由低密度聚氨酯泡沫与水介质为主体的回收装置。与传统单一材料为主的回收装置相比,该回收装置既能在破片高速阶段将低阻抗聚氨酯泡沫对破片的冲击压力减小到约为水对破片冲击压力的1/3,又使破片速度全程持续地较大幅度衰减,还能在破片低速阶段又能充分利用水介质密度大的优势,减小以聚氨酯泡沫单一材料为主的回收装置尺寸。依托该装置开展了炸药加载下304不锈钢柱壳膨胀断裂回收实验。通过测量回收池外壁速度、检查实验后的回收池外观,发现回收池池壁和底部完好,可以重复使用;通过对回收破片称重统计,破片回收率超过85%,破片内外界面辨识度高,破片表面车刀纹清晰可见,内部可见多条未贯穿的裂纹。表明该回收装置对破片的冲击损伤显著降低。根据破片断口和表面信息,推测了破片在金属柱壳的大致位置。本文最后初步给出了回收破片的平均厚度及质量分布等相关信息的统计结果。Abstract: According to the requirements on the soft recovery of fragments of expanding cylindrical metal shells under explosion loading, this paper presents a recovery device combining low density polyurethane foam and water medium through theoretical analysis and numerical simulation. Compared to traditional recovery device designed with a single material, the combined recovery device can reduce the amplitude of impact pressure, which is produced by the initial interaction of low impedance polyurethane foam with high speed fragments, by about 1/3 compared to the impact pressure produced by water, and maintain the high decay rate of fragment speed. It can also make full use of the advantages of high density of water medium when the fragment speed is less than 0.5 km/s, which can reduce the decay thickness of the recovery device based on single polyurethane foam. Based on the device, the recovery experiment of expansion and fracture of 304 stainless steel cylindrical shell under explosive loading is carried out. Through the measurement of the wall velocity of the recovery tank and the appearance inspection after the experiment, it is implied that the wall and bottom of the recovery tank are in good condition and can be reused. According to the statistics of the recovered fragments, the recovery rate of the fragments is more than 85%, and the internal and external interfaces of fragments are highly recognizable, the turning blade lines on the surface of the fragments are clearly visible, and several non-penetrating cracks are visible, which verified that the impact damage of the recovery device to the fragments is significantly reduced. Acording to the fracture and surface information of the fragments, the approximate position of the fragments in the metal cylindrical shell is inferred. Finally, the statistical results of the average thickness and mass distribution of the recovered fragments are given.
-
Key words:
- impact dynamics /
- expansion fracture /
- soft-recovery /
- secondary damage
-
表 1 不同材料的冲击雨贡纽参数
Table 1. Shock Hugoniot parameters of different materials
表 2 水、石蜡等软材料对不同速度不锈钢破片产生的冲击压力
Table 2. Impact pressure of water, paraffin and other soft materials on stainless steel fragments
材料 ρ/(g·cm−3) 冲击压力/GPa v=1.8 km/s v=2.0 km/s 石蜡 0.918 6.76 7.74 水 1.0 5.21 6.09 泡沫碳 0.48 1.69 2.05 聚氨酯泡沫Ⅰ 0.16 0.60 0.73 聚氨酯泡沫Ⅱ 0.321 1.39 1.66 -
[1] 卢秋虹, 王宁, 范诚, 等. 壁厚对HR2钢柱壳爆轰加载下膨胀断裂行为的影响 [J]. 材料研究学报, 2020, 34(4): 241–246. DOI: 10.11901/1005.3093.2019.177.LU Q H, WANG N, FAN C, et al. Effect of shell thickness on expanding fracture behavior of HR2 steel cylinders under explosive loading [J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 2020, 34(4): 241–246. DOI: 10.11901/1005.3093.2019.177. [2] 禹富有, 董新龙, 俞鑫炉, 等. 不同填塞装药下金属柱壳断裂特性的实验研究 [J]. 兵工学报, 2019, 40(7): 1418–1424. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2019.07.011.YU F Y, DONG X L, YU X L, et al. Fracture characteristics of metal cylinder shells with different charges [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2019, 40(7): 1418–1424. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2019.07.011. [3] HIROE T, FUJIWARA K, HATA H, et al. Deformation and fragmentation behaviour of exploded metal cylinders and the effects of wall materials, configuration, explosive energy and initiated locations [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2008, 35(12): 1578–1586. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2008.07.002. [4] HIROE T, FUJIWARA K, HATA H, et al. Explosively driven expansion and fragmentation behavior for cylinders, spheres and rings of 304 stainless steel [J]. Materials Science Forum, 2010, 638−642: 1035–1040. DOI: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.638-642.1035. [5] 马利, 胡洋, 辛健, 等. 圆柱形爆炸容器绝热剪切瞬态失效过程 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2012, 32(2): 136–142. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2012)02-0136-07.MA L, HU Y, XIN J, et al. Transient failure process of explosion containment vessels subjected to adiabatic shear [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2012, 32(2): 136–142. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2012)02-0136-07. [6] 朱文辉, 薛鸿陆, 刘仓理, 等. 爆炸容器承受内部加载的实验研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 1995, 15(4): 374–381.ZHU W H, XUE H L, LIU C L, et al. Experimental study on the explosive chambers under internal blast loading [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 1995, 15(4): 374–381. [7] 张绍兴, 李翔宇, 丁亮亮, 等. 聚焦式战斗部破片轴向飞散控制技术 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2018, 32(1): 015103. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.20170512.ZHANG S X, LI X Y, DING L L, et al. Axial dispersion control of focusing fragment warhead [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2018, 32(1): 015103. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.20170512. [8] 史志鑫, 尹建平, 王志军, 等. 预制破片的形状对破片飞散性能影响的数值模拟研究 [J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2017, 38(12): 31–35. DOI: 10.11809/scbgxb2017.12.008.SHI Z X, YIN J P, WANG Z J, et al. Numerical simulation of the influence of prefabricated fragments shape on fragment scattering performance [J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2017, 38(12): 31–35. DOI: 10.11809/scbgxb2017.12.008. [9] 李翔宇, 卢芳云, 王志兵, 等. 可变形定向破片战斗部模型试验和数值模拟研究 [J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2006, 28(1): 121–124. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2006.01.027.LI X Y, LU F Y, WANG Z B, et al. A study of simulation and experiment of target-directed deformable warhead model [J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2006, 28(1): 121–124. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2006.01.027. [10] 胡八一, 董庆东, 韩长生, 等. TC4钛合金自然破片的引燃机理 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 1995, 15(3): 254–258.HU B Y, DONG Q D, HAN C S, et al. Analysis of the firing mechanics for Ti-6AL-4V natural fragments [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 1995, 15(3): 254–258. [11] 汤铁钢, 李庆忠, 孙学林, 等. 45钢柱壳膨胀断裂的应变率效应 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2006, 26(2): 129–133. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2006)02-0129-05.TANG T G, LI Q Z, SUN X L, et al. Strain-rate effects of expanding fracture of 45 steel cylinder shells driven by detonation [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2006, 26(2): 129–133. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2006)02-0129-05. [12] 汤铁钢, 谷岩, 李庆忠, 等. 爆轰加载下金属柱壳膨胀破裂过程研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2003, 23(6): 529–533.TANG T G, GU Y, LI Q Z, et al. Expanding fracture of steel cylinder shell by detonation driving [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2003, 23(6): 529–533. [13] 宋桂飞, 李成国, 夏福君, 等. 回收战斗部破片的新型爆炸容器及应用 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2008, 28(4): 372–377. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2008)04-0372-06.SONG G F, LI C G, XIA F J, et al. A new explosion vessel used to recover warhead fragments and its application [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2008, 28(4): 372–377. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2008)04-0372-06. [14] 陈志闯, 李伟兵, 朱建军, 等. 40CrMnSiB钢圆柱壳体膨胀断裂中间状态回收试验研究 [J]. 兵工学报, 2018, 39(11): 2137–2144. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2018.11.007.CHEN Z C, LI W B, ZHU J J, et al. Recovery experiment study of cylindrical 40CrMnSiB steel shell in intermediate phase of expanding fracture processes [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2018, 39(11): 2137–2144. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2018.11.007. [15] GOTO D M, BECKER R, ORZECHOWSKI T J, et al. Investigation of the fracture and fragmentation of explosively driven rings and cylinders [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2008, 35(12): 1547–1556. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2008.07.081. [16] AUTODYN matsum_v6. 1_review [Z]. Concord: Century Dynamics Inc, 2010. [17] MARSH S P. Los Alamos series on dynamic material properties [M]. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1980. -







 下载:
下载: