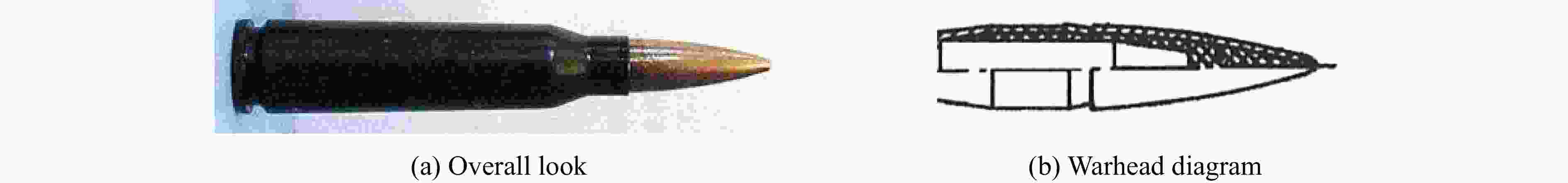
Optimal design of the head shape of a small-caliber supercavitating projectile
-
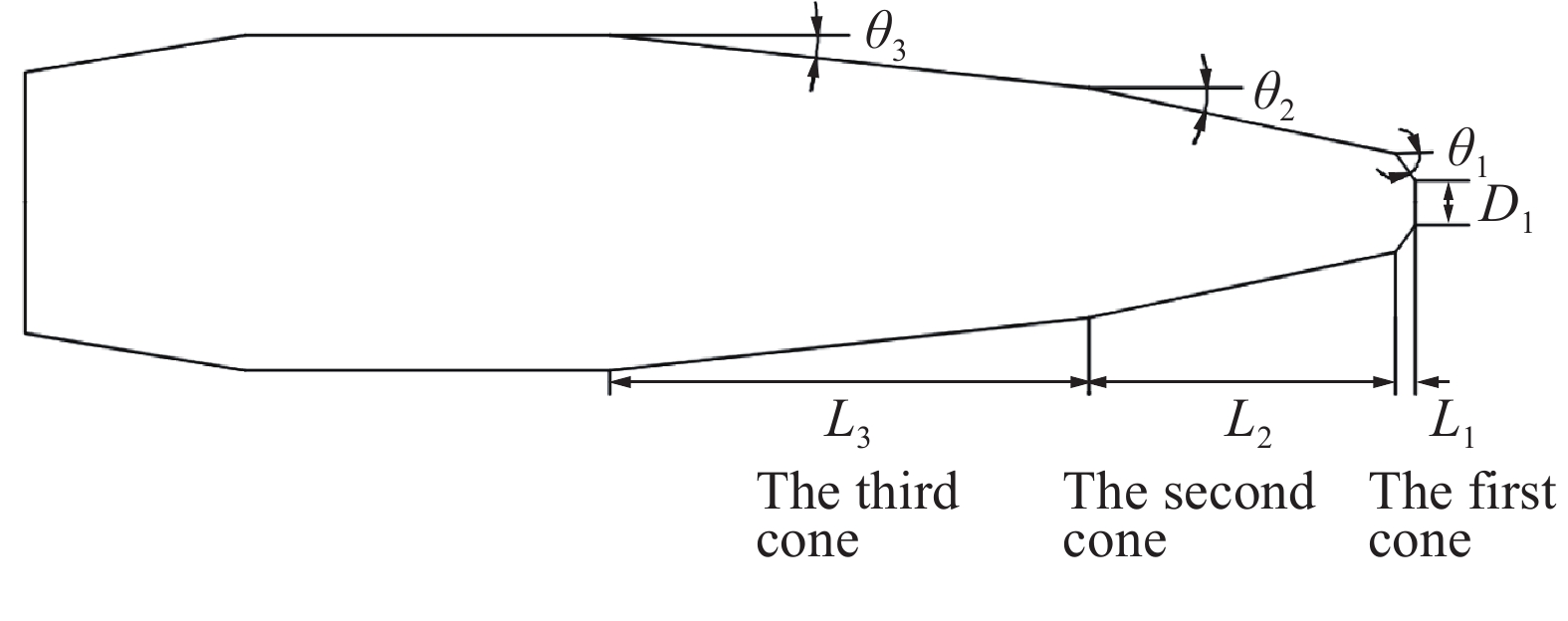
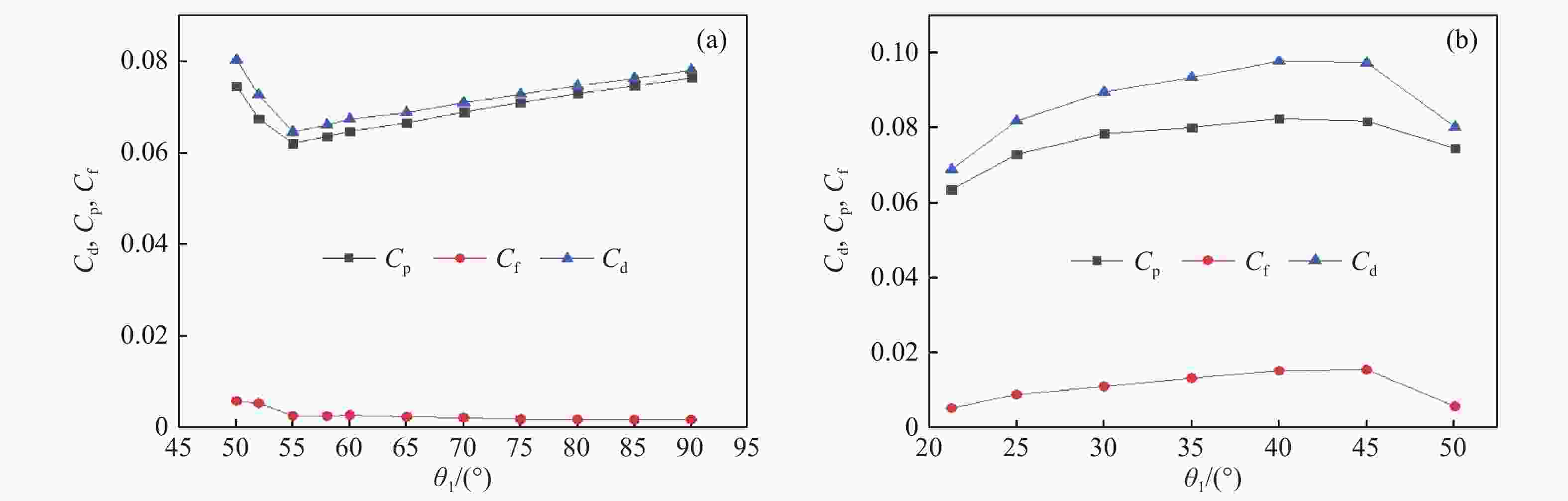
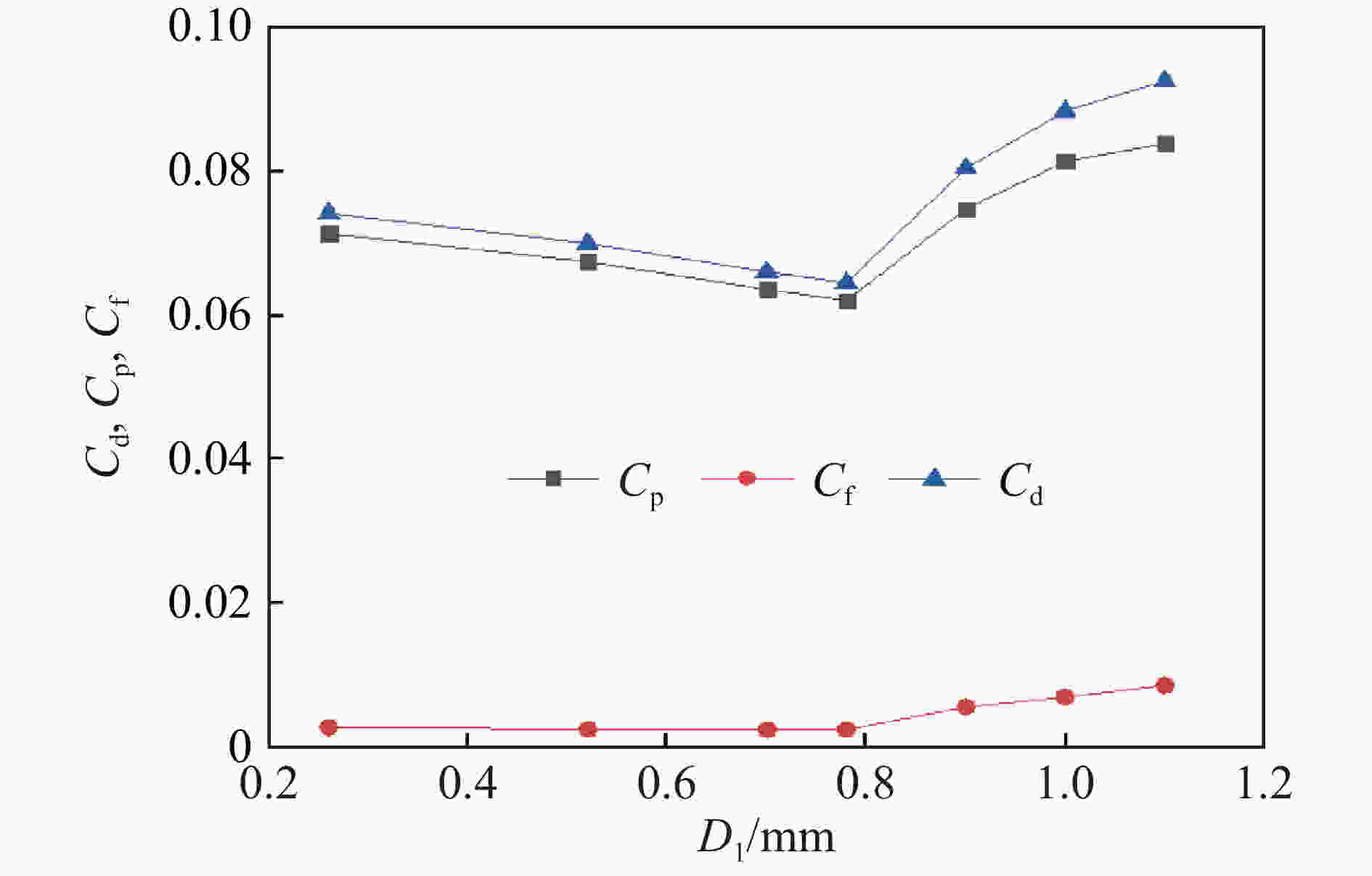
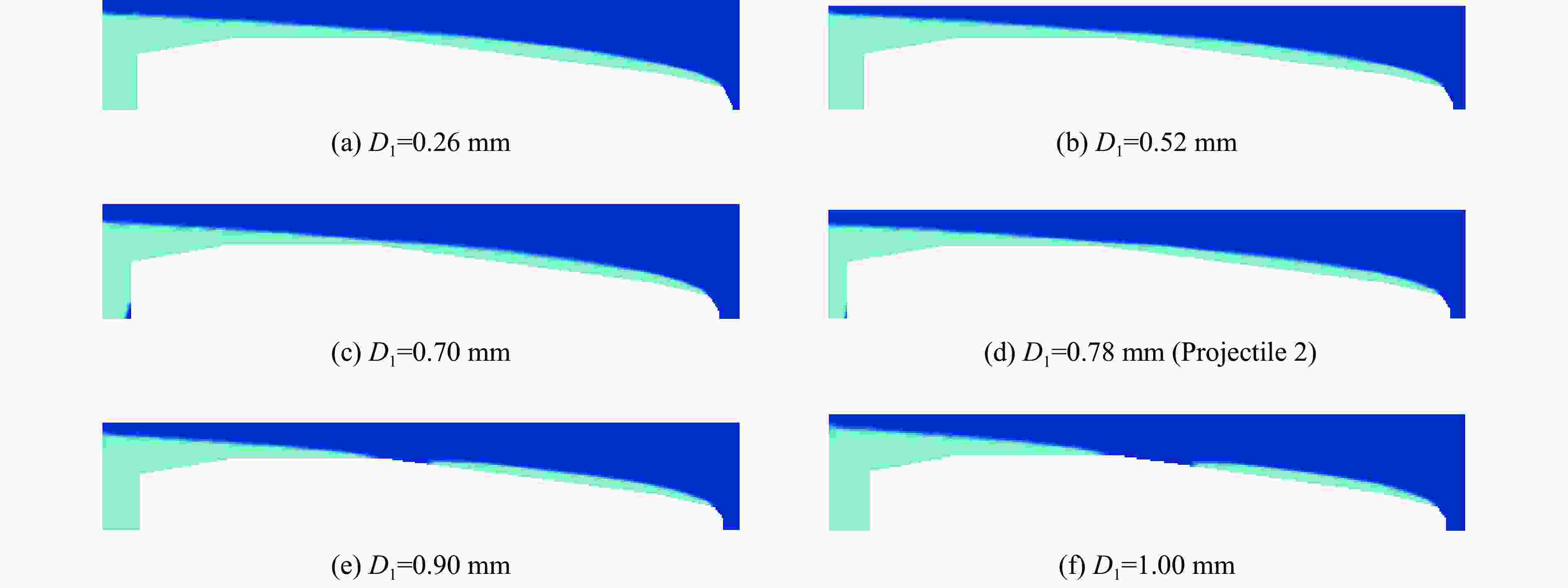
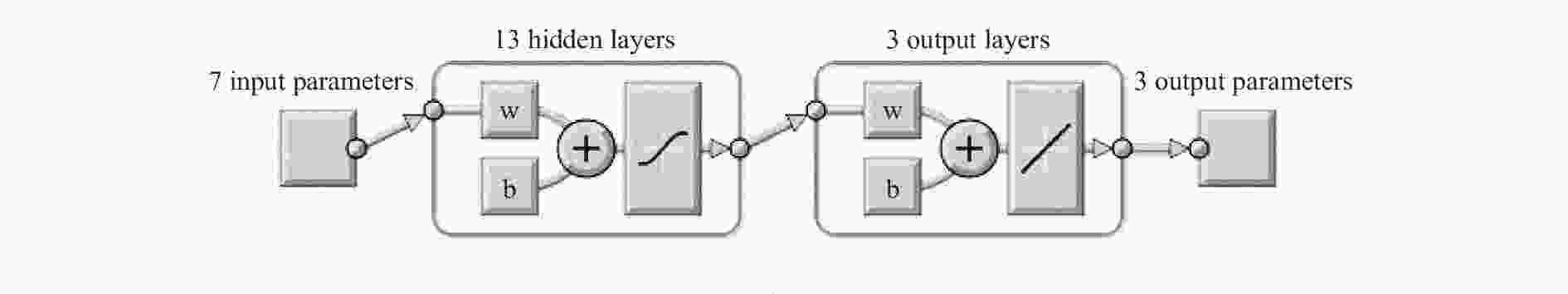
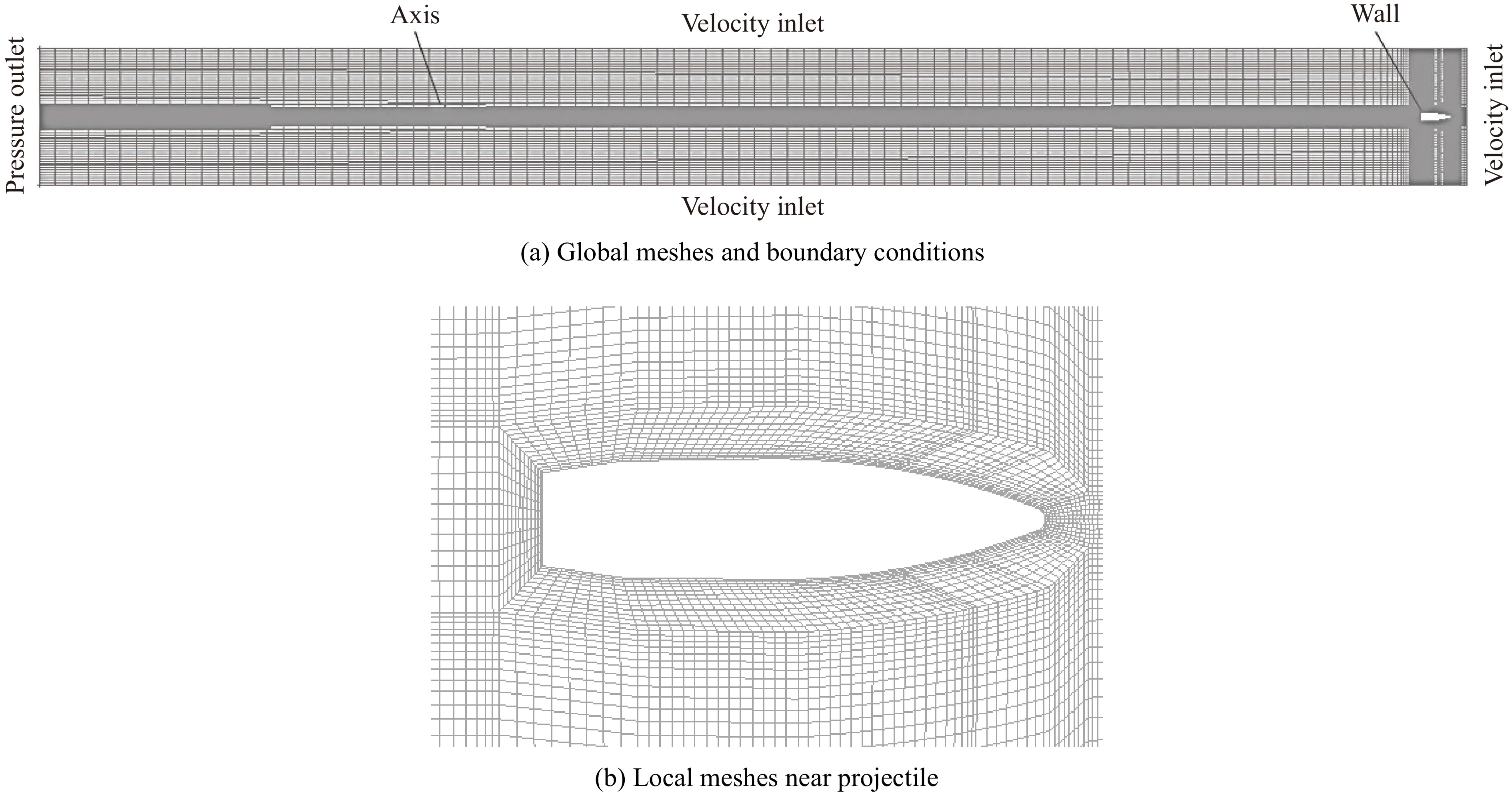
摘要: 在水下高速运动时,小口径射弹周围的水会发生空化现象,阻力系数最优的弹头几何外形对应着射弹被空泡全包裹的超空泡状态。针对一种小口径射弹,可以利用计算流体力学(CFD)数值方法模拟含空化现象的气液两相流动,探究空泡形态和阻力系数与射弹头部几何外形的关系。选取三段锥形为基本射弹头形,采用分步优化方式对射弹头部外形进行了优化。同时,结合神经网络与序列二次规划(SQP)算法减少优化过程中的计算量,缩短了优化工作所需的总时间。优化后的射弹阻力系数比优化前的减小约30%,且能够形成包裹全弹体的超空泡。Abstract: When a small-caliber projectile is moving underwater at a high speed, the water around the projectile will cavitate. The cavitation effect can greatly reduce the resistance of the moving vehicle, and the geometric shape of the warhead with the best drag coefficient corresponds to the supercavitating state where the projectile is completely enveloped by cavitation. Aiming at a small-caliber projectile, the computational fluid dynamics method is used to numerically simulate the gas-liquid two-phase flow with cavitation phenomenon, while the relationships of the cavitation shape and the drag coefficient with the geometry of the projectile’s head shape are explored. The three-segment cone type is selected as the basic projectile type, and the shape of the projectile is optimized by step optimization method. First, seven parameters are used to describe the three-segment cone shape of the projectile, and then the projectile is optimized in the order of the first section cone, the second and the third section cone. This method is used because the seven parameters are not independent of each other, and it is difficult to quantitatively determine the relationship between an individual parameter and the performance of the projectile. At the same time, the neural network is employed to perform nonlinear fitting with a large number of CFD numerical simulation results as learning samples, and the approximate calculation model of the shape parameters-drag coefficient of the projectile is established by neural network. Finally, the sequential quadratic programming (SQP) algorithm is introduced to find the optimal solution of the approximate calculation model. The use of neural network and SQP algorithm reduces the amount of calculation in the optimization process and the total time required for optimization work. After two rounds of optimization, the optimized projectile has a better ability to form supercavitation, and its drag coefficient has also been significantly improved compared to the original projectile, with a reduction about 30% compared to the projectile before optimization.
-
Key words:
- supercavitating projectile /
- drag coefficient /
- multi-step optimization /
- neural network /
- SQP algorithm
-
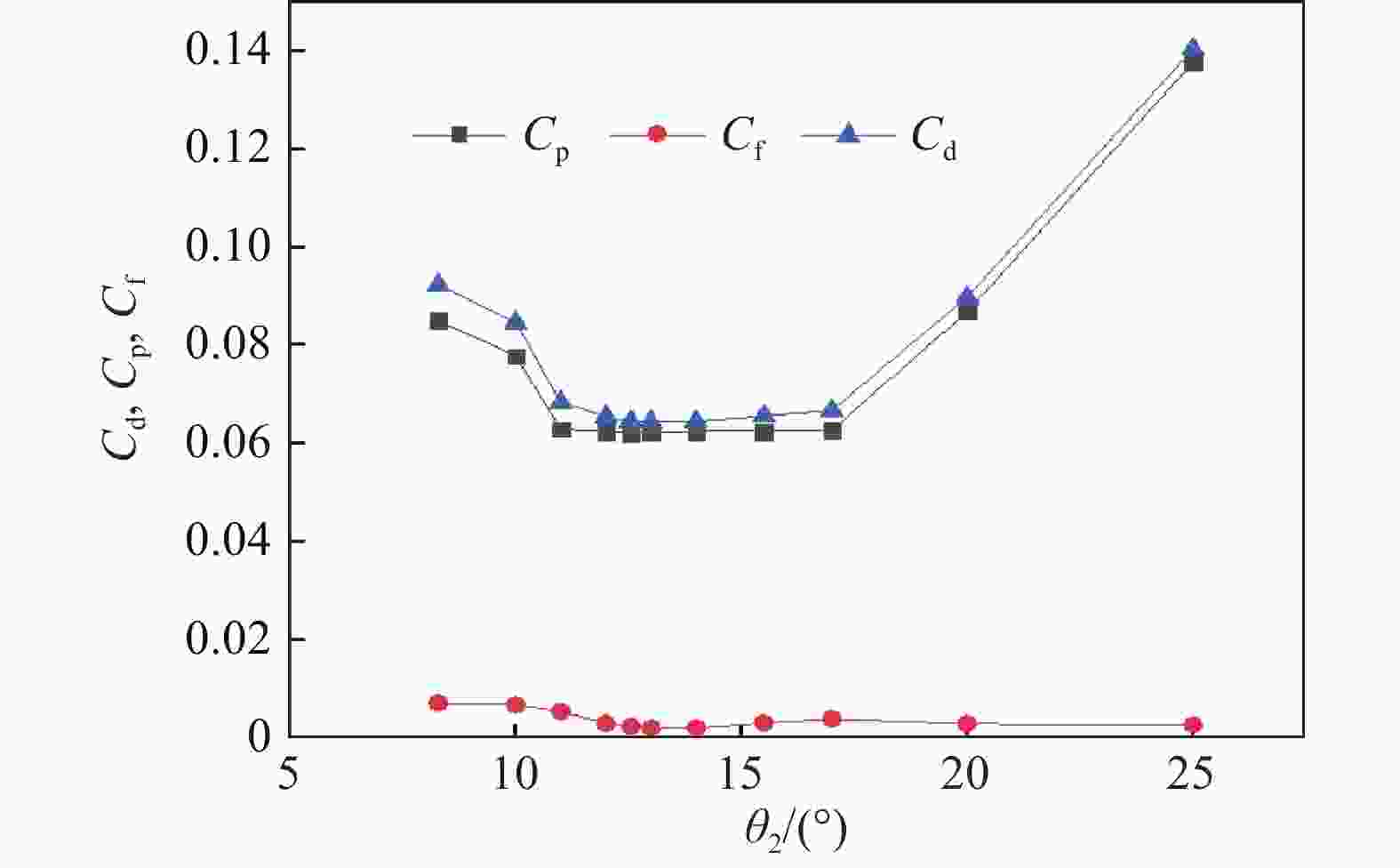
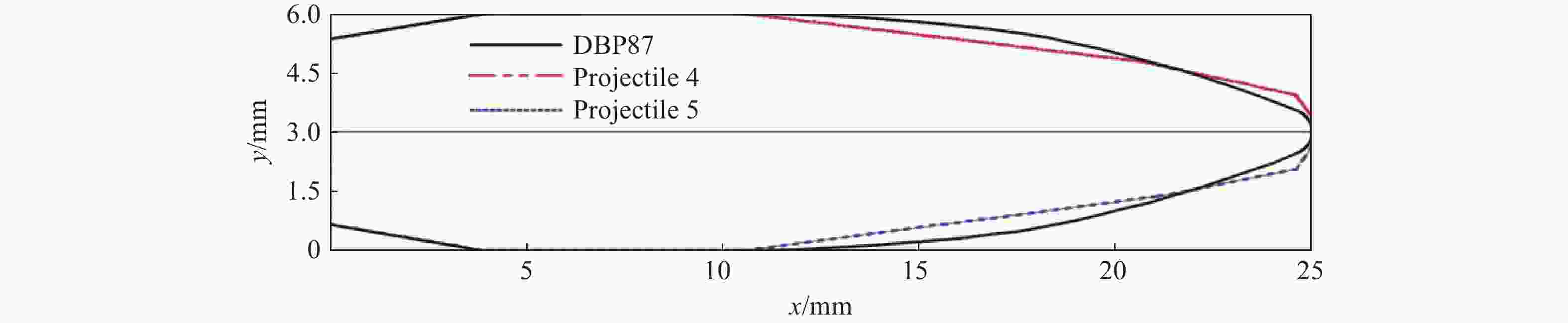
表 1 射弹1的参数
Table 1. Parameters of projectile 1
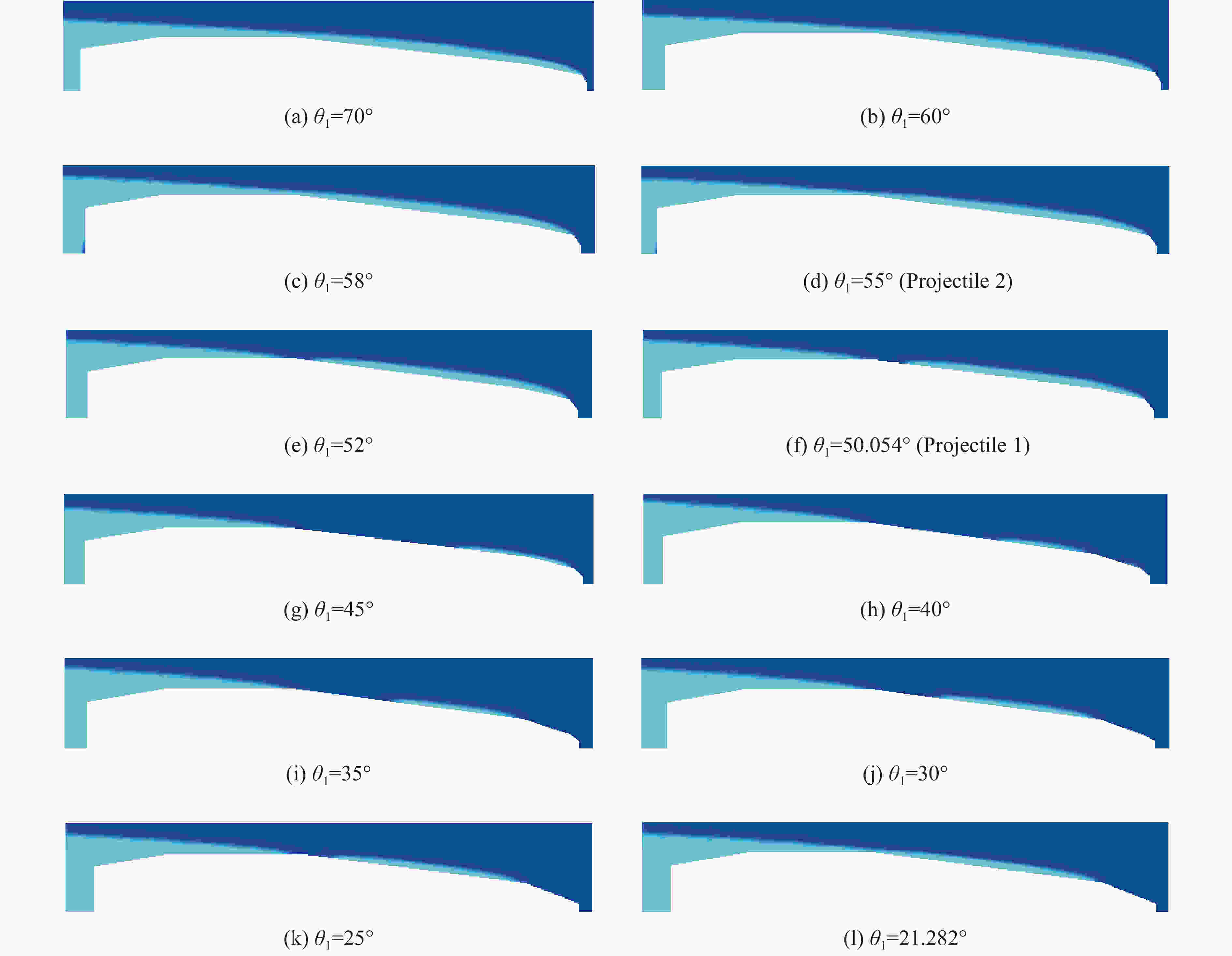
θ1/(°) L1/mm θ2/(°) L2/mm θ3/(°) L3/mm D1/mm 50.054 0.480 12.555 2.315 7.404 11.704 0.780 表 2 射弹2的参数
Table 2. Parameters of projectile 2
θ1/(°) L1/mm θ2/(°) L2/mm θ3/(°) L3/mm D1/mm 55.000 0.387 12.555 2.409 7.404 11.704 0.780 表 3 射弹3的参数
Table 3. Parameters of projectile 3
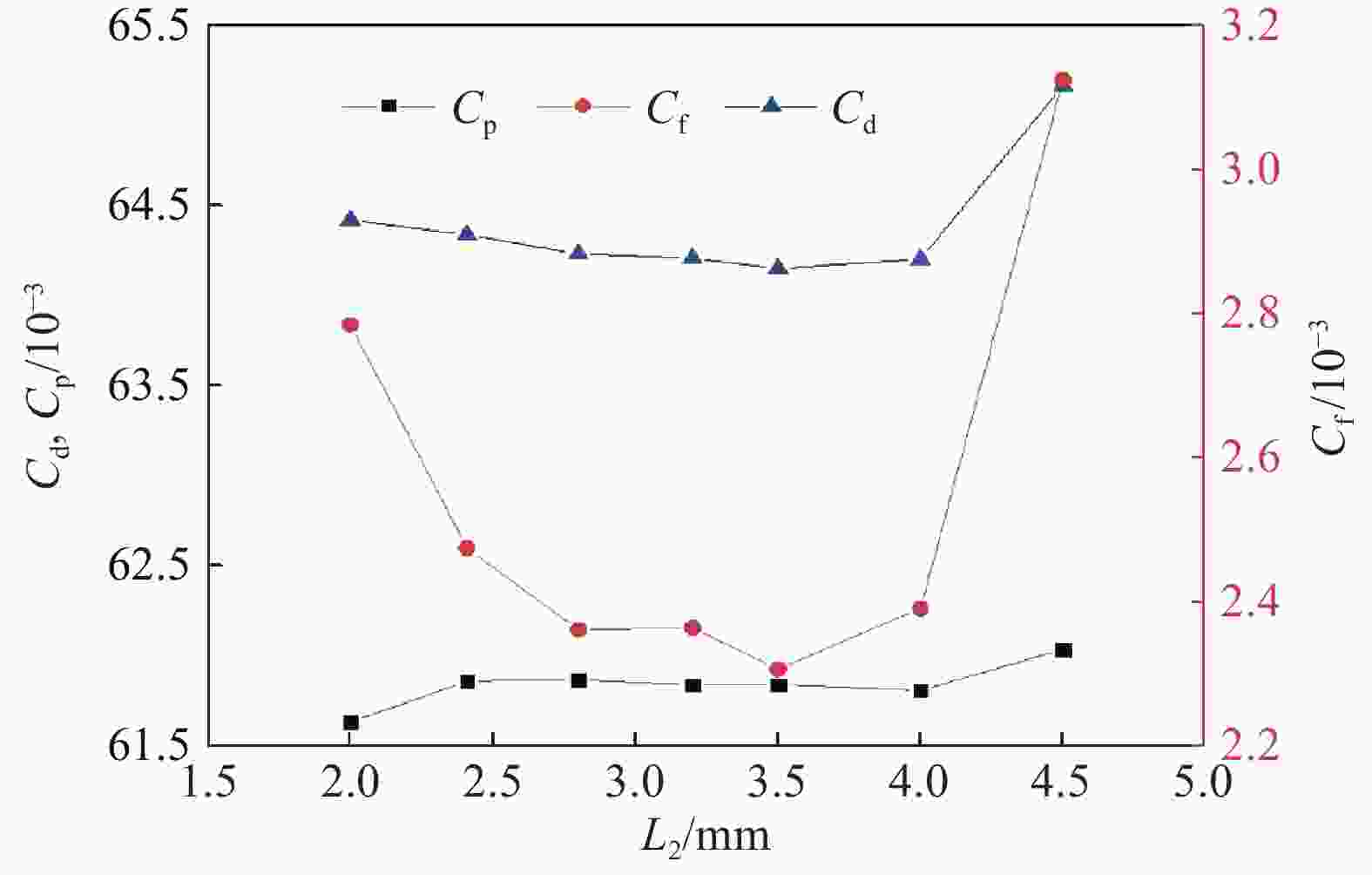
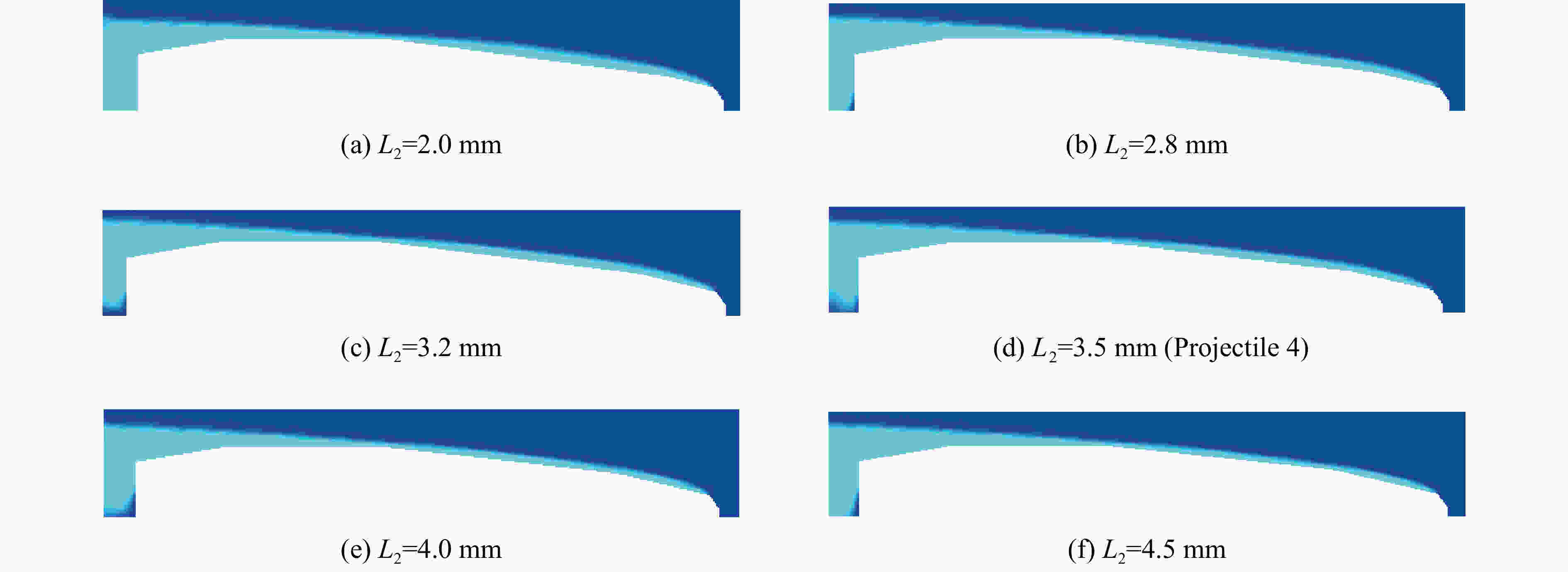
θ1/(°) L1/mm θ2/(°) L2/mm θ3/(°) L3/mm D1/mm 55.000 0.387 13.000 2.409 7.309 11.704 0.780 表 4 射弹4的参数
Table 4. Parameters of projectile 4
θ1/(°) L1/mm θ2/(°) L2/mm θ3/(°) L3/mm D1/mm 55.000 0.387 13.000 3.500 6.704 10.596 0.780 表 5 射弹5的参数
Table 5. Parameters of projectile 5
θ1/(°) L1/mm θ2/(°) L2/mm θ3/(°) L3/mm D1/mm 55.000 0.404 13.000 4.000 6.387 10.096 0.780 -
[1] 赵卫. 超空泡高速鱼雷技术综合分析 [D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2005: 51−59.ZHAO W. General analyse of superspeed supercavitating torpedo technique [D]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University, 2005: 51−59. [2] 牟晴, 赵潇雨, 周维. 超空泡技术在小口径炮弹上的应用 [J]. 四川兵工学报, 2010, 31(4): 31–33. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0707.2010.04.011. [3] 鲁林旺. 复杂结构体射弹出入水时超空泡流特性的研究 [D]. 杭州: 浙江理工大学, 2019: 31−35.LU L W. Research on supercavitation flows characteristics of projectiles with complex structure water exit and entry [D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, 2019: 31−35 [4] 罗格维诺维奇 T B. 自由边界流动的水动力学 [M]. 施红辉, 译. 上海: 上海交通大学出版社, 2012: 283−290. [5] SAVCHENKO Y N. Experimental investigation of supercavitating motion of bodies [Z] // VAN DEN BRAEMBUSSCHE. VKI Special Course on Supercavitating Flows. Brussels, Belgium, 2001. [6] SAVCHENKO Y N, VLASENKO Y D, SEMENENKO V N. Experimental studies of high-speed cavitated flows [J]. International Journal of Fluid Mechanics Research, 1999, 26(3): 365–374. DOI: 10.1615/InterJFluidMechRes.v26.i3.80. [7] 张学伟, 张亮, 王聪, 等. 基于Logvinovich独立膨胀原理的超空泡形态计算方法 [J]. 兵工学报, 2009, 30(3): 361–365. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1093.2009.03.021.ZHANG X W, ZHANG L, WANG C, et al. A calculation method for supercavity shape based on the Logvinovich independence principle of the cavity section expansion [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2009, 30(3): 361–365. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1093.2009.03.021. [8] 施红辉, 周素云, 张晓萍, 等. 水下超空泡流体机械的机理和技术研究综述 [C] // 第十五届全国激波与激波管学术会议论文集(下册). 杭州: 中国力学学会, 2012: 554−564. [9] 王云, 袁绪龙, 吕策. 弹体高速入水弯曲弹道实验研究 [J]. 兵工学报, 2014, 35(12): 1998–2002. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2014.12.010.WANG Y, YUAN X L, LYU C. Experimental research on curved trajectory of high-speed water-entry missile [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2014, 35(12): 1998–2002. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2014.12.010. [10] 孙士明, 颜开, 褚学森, 等. 射弹高速斜入水过程的数值仿真 [J]. 兵工学报, 2020, 41(S1): 122–127. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2020.S1.018.SUN S M, YAN K, CHU X S, et al. Numerical simulation of high-speed oblique water entry of a projectile [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2020, 41(S1): 122–127. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2020.S1.018. [11] 陈伟善, 郭则庆, 刘如石, 等. 空化器形状对超空泡射弹尾拍运动影响的数值研究 [J]. 工程力学, 2020, 37(4): 248–256. DOI: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2019.06.0328.CHEN W S, GUO Q Z, LIU R S, et al. Numerical simulation on the influence of cavitator shapes on the tail-slap of supercavitating projectiles [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2020, 37(4): 248–256. DOI: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2019.06.0328. [12] 郜冶, 刘乾坤, 陈宇翔. FBM湍流模型水翼空化绕流数值研究 [J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2013, 34(1): 92–97. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7043.201206013.GAO Y, LIU Q K, CHEN Y X. Numerical simulation on cavitating flow around hydrofoil with filter-based turbulence model [J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2013, 34(1): 92–97. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7043.201206013. [13] 卢炳举, 罗松, 朱珠, 等. 高速射弹入水空泡多相流场数值模拟 [J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2017, 38(12): 242–246. DOI: 10.11809/scbgxb2017.12.053.LU B J, LUO S, ZHU Z, et al. Numerical simulation of multiphase flow field of high velocity projectile entering water [J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2017, 38(12): 242–246. DOI: 10.11809/scbgxb2017.12.053. [14] 胡俊, 侯夏伊, 于勇. 基于当地流动特征的Schnerr-Sauer空化模型改进研究 [J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2021, 41(1): 9–15. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2019.272.HU J, HOU X Y, YU Y. A modified Schnerr-Sauer cavitation model with local flow properties [J]. Transaction of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2021, 41(1): 9–15. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2019.272. [15] HRUBES J D. High-speed imaging of supercavitating underwater projectiles [J]. Experiments in Fluids, 2001, 30(1): 57–64. DOI: 10.1007/s003480000135. [16] 范伟. 小口径弹药的“奇葩”: 中国DBP87式5.8毫米普通弹 [J]. 兵器知识, 2000(10): 30–32. [17] 三土, 明光. 让枪弹飞行于水陆间: 挪威DSG公司多环境弹药系统 [J]. 轻兵器, 2012(20): 35–39. [18] BRUNTON S L, NOACK B R, KOUMOUTSAKOS P. Machine learning for fluid mechanics [J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 2020, 52: 477–508. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-fluid-010719-060214. [19] BÖLCSKEI H, GROHS P, KUTYNIOK G, et al. Optimal approximation with sparsely connected deep neural networks [J]. SIAM Journal on Mathematics of Data Science, 2019, 1(1): 8–45. DOI: 10.1137/18M118709X. [20] HORNIK K, STINCHCOMBE M, WHITE H. Multilayer feedforward networks are universal approximators [J]. Neural Networks, 1989, 2(5): 359–366. DOI: 10.1016/0893-6080(89)90020-8. [21] 赵弘, 周瑞祥, 林廷圻. 基于Levenberg-Marquardt算法的神经网络监督控制 [J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2002, 36(5): 523–527. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-987X.2002.05.020.ZHAO H, ZHOU R X, LIN T Q. Neural network supervised control based on Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm [J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2002, 36(5): 523–527. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-987X.2002.05.020. [22] WECHSLER H. Learning from data: concepts, theory and methods, Vladimir Cherkassky and Filip Mulier, John Wiley, New York, 1998 [J]. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2000, 10(9): 747–748. DOI: 10.1002/1099-1239(20000730)10:9<747::AID-RNC507>3.0.CO;2-5. [23] 张菊亮, 章祥荪. 不等式约束最优化的非光滑精确罚函数的一个光滑近似 [J]. 系统科学与数学, 2000, 20(4): 499–505. DOI: 10.12341/jssms09839.ZHANG J L, ZHANG X S. A smoothing approximation to the exact penalty function for optimization with inequlity constraints [J]. Journal of Systems Science and Mathematical Sciences, 2000, 20(4): 499–505. DOI: 10.12341/jssms09839. -






 下载:
下载: