An improvement of the wall-pressure theory and numerical method for shock waves in underwater explosion
-
摘要: 水下爆炸冲击波是舰船抗冲击评估中重要的载荷成分,也是水中结构物毁伤程度快速预报的关键和依据。通过小当量实验发现,由于传统 Taylor 平板理论公式忽略了冲击波波速的非线性变化 ,导致其在预报近距离水下爆炸冲击波壁压脉宽时出现偏差。为此,给出了比例爆距R/W1/3为0.11~5.30 m/kg1/3 (R为爆距,W为炸药质量)下的冲击波速度拟合公式,对传统Taylor理论公式进行修正。修正后,在R/W1/3=0.11 m/kg1/3下,壁压脉宽及冲量偏差大幅减小;在R/W1/3≥0.21 m/kg1/3下,两者偏差均小于12%。此外,在处理水下近场和中远场爆炸问题时,发现数值耗散会导致壁压峰值被明显削弱,于是提出了一种可行的数值策略消除计算中数值耗散导致的削弱效应,结果与修正的Taylor平板理论公式吻合良好,峰值偏差均小于9%。改进后的冲击波壁压理论公式及数值计算方法可为舰船抗爆抗冲击领域提供理论和技术支撑。
-
关键词:
- 水下爆炸 /
- 壁压 /
- 冲击波 /
- Taylor平板理论
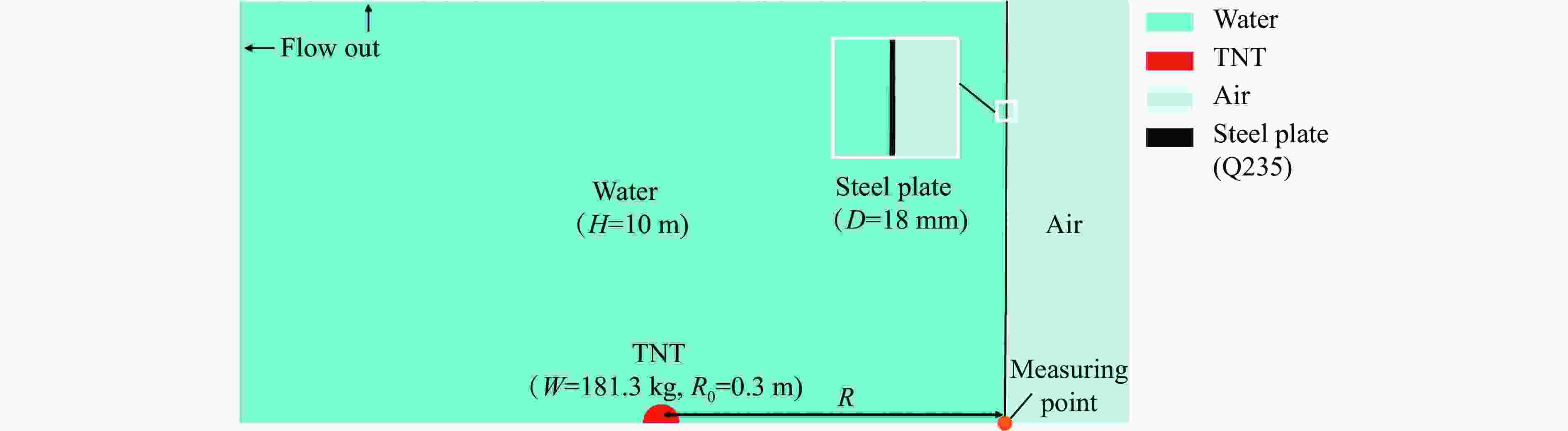
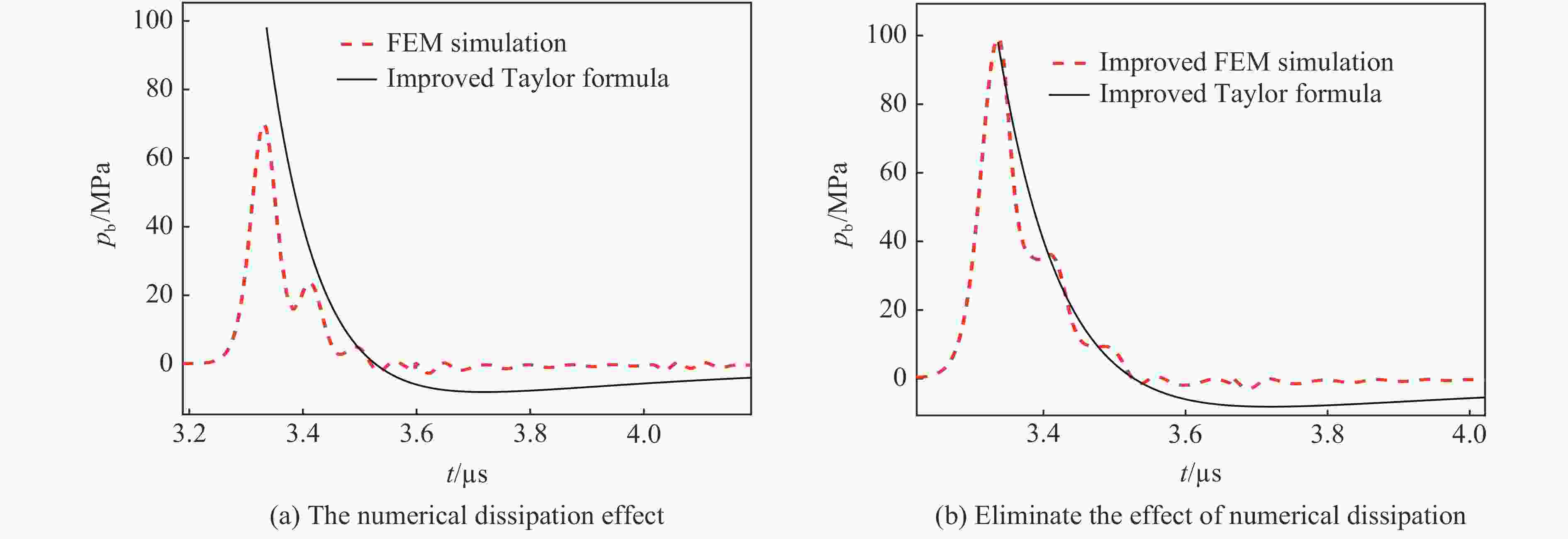
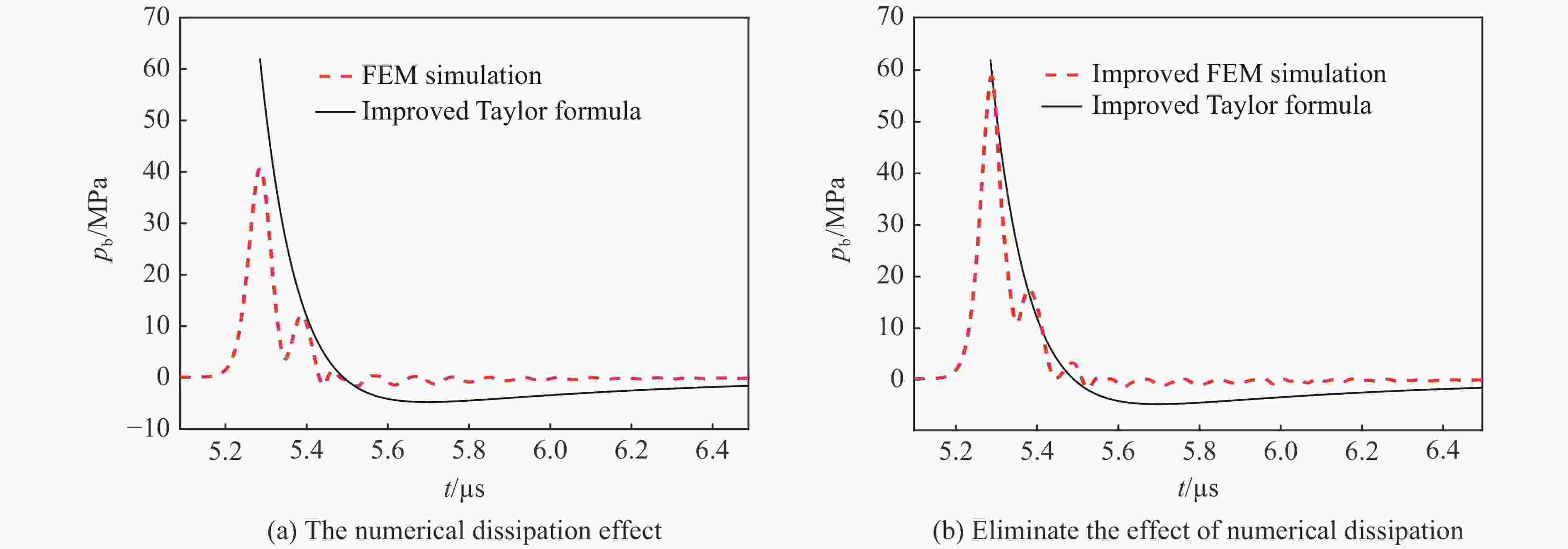
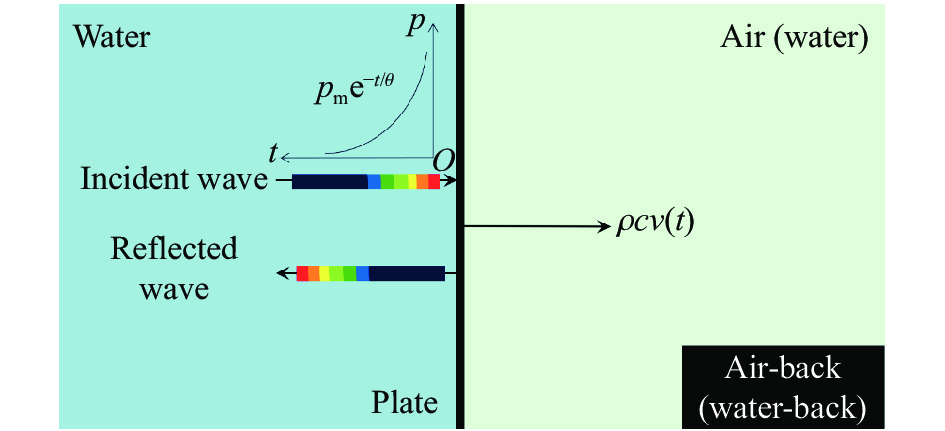
Abstract: Underwater blast shock wave is an important load in the evaluation of the impact resistance of ships, and it is also the key and basis for the fast prediction of the structure damage in underwater explosions. In the present study, a series of small equivalent underwater explosion experiments were carried out in the explosion tank. By comparing the theoretical predicted and experimental measured wall pressure characteristics, the applicability of the traditional Taylor formula in predicting the wall pressure of the underwater explosion shock wave was explored. It is found that the deviation of the Taylor plate theory in predicting the pulse width of the wall-pressure is mainly because the nonlinear variation of the shock wave velocity is not considered. Given this, a fitting formula of the shock wave velocity for 0.11 m/kg1/3≤R/W1/3≤5.30 m/kg1/3, where R is the detonation distance and W is the charge weight, is given to improve the traditional Taylor theoretical formula. The corrected theoretical values are in good agreement with the experimental values. For R/W1/3=0.11 m/kg1/3, the pulse-width deviation of the wall-pressure of the shock wave between the improved Taylor formula and the experimental result is reduced from 79.6% to 26.6%, and the deviation of the impulse is reduced from 119.3% to 58.4%. For R/W1/3≥0.21 m/kg1/3, the deviations of the pulse-width and the impulse of wall-pressure are both less than 12%. Moreover, in the simulation of the wall-pressure change at different distances by numerical method (e.g., finite element method), it is found that the numerical dissipation causes the plate to move in advance (before the arrival of the shock wave front), leading to a significant decrease in the peak of the wall-pressure when dealing with the near-field and far-field underwater explosion problems. Therefore, a feasible numerical strategy was proposed to eliminate the weakening effect caused by numerical dissipation. The improved numerical results are in great agreement with the improved Taylor plate theory, and the deviation of the wall-pressure peak is less than 9%. The improved theoretical formula and numerical method for the shock wave wall pressure can provide theoretical and technical supports for the field of explosion protection of ships.-
Key words:
- underwater explosion /
- wall pressure /
- shock wave /
- Taylor plate theory
-
表 1 冲击波壁压峰值实验值与传统Taylor理论公式结果对比
Table 1. Comparison of the experimental and theoretical Taylor formula results of wall pressure
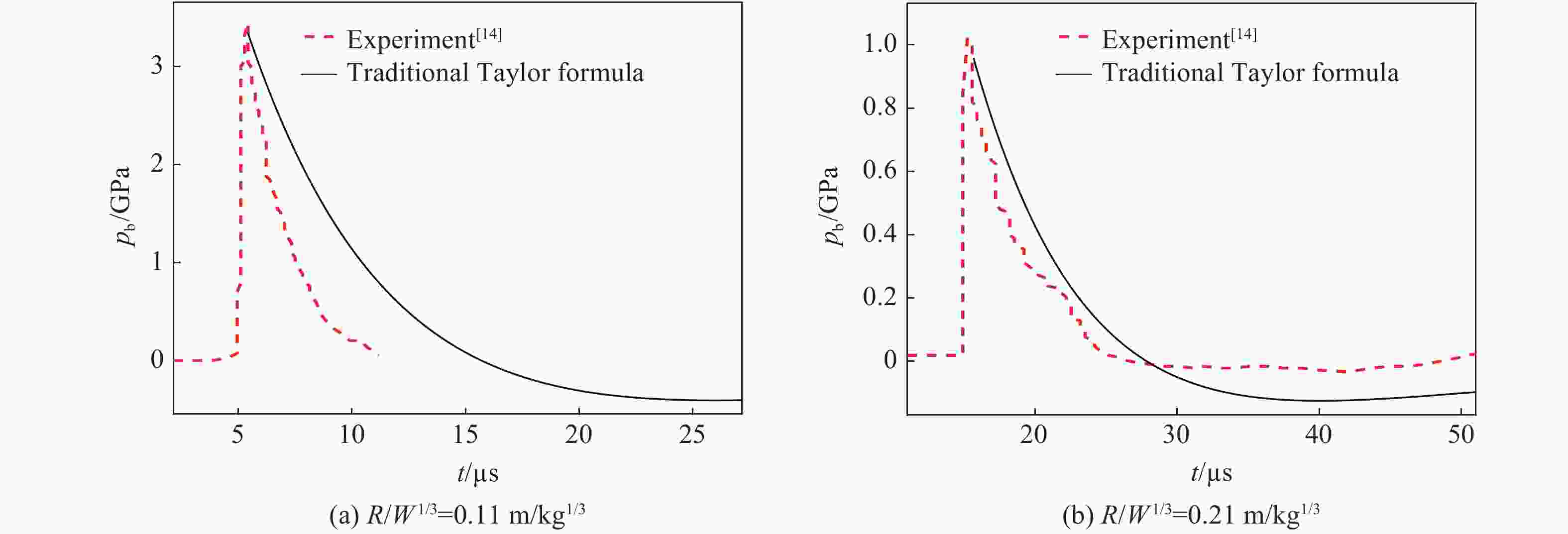
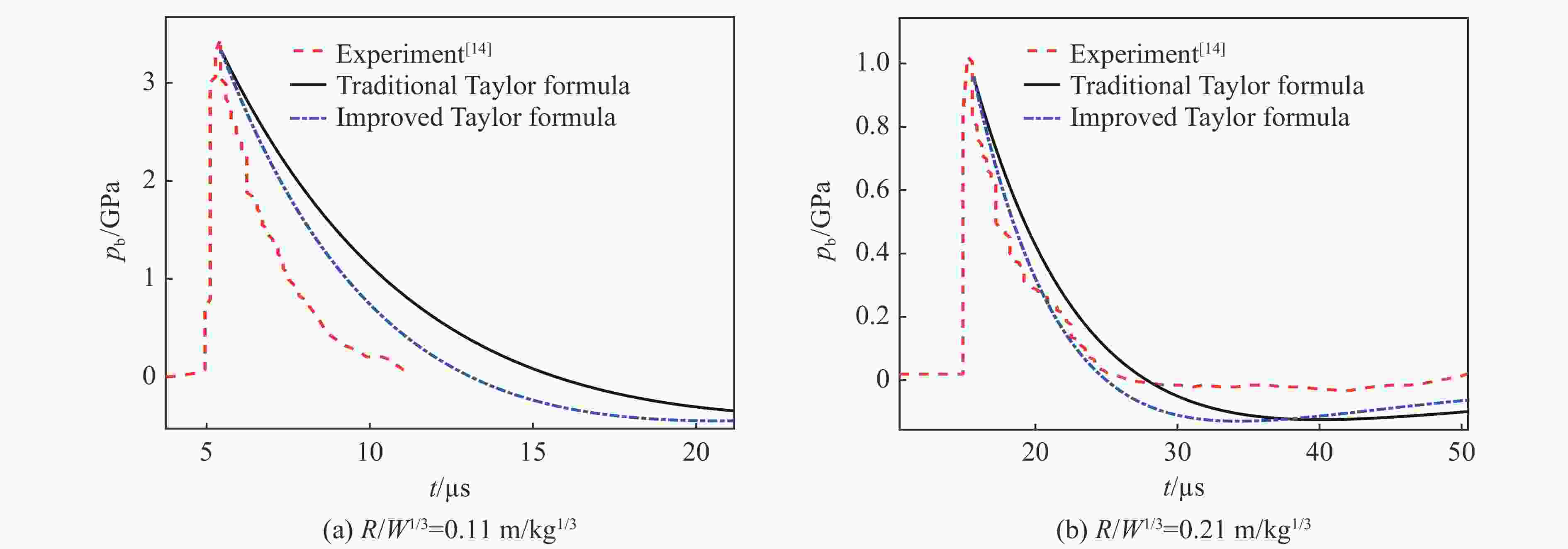
工况 钢板材料 D/mm W/g (R·W−1/3)/(m·kg−1/3) R/R0 壁压峰值 pb,th/MPa pb,exp/MPa δp/% 1 Q235 3 9.9 0.11 2.0 3340.0 3460.0 3.6 2 Q235 3 9.9 0.21 4.0 960.0 1020.0 6.3 3 1 5.0 0.88 16.6 107.0 81.2 −24.1 4 A3 16 1.0 1.63 30.7 61.0 58.0 −4.9 5 Q235 20 13.0 1.86 35.1 57.4 48.1 −16.2 6 Q235 20 13.0 2.62 49.5 38.8 33.8 −12.9 7 Q235 20 13.0 2.79 52.6 36.4 32.3 −11.3 8 Q235 20 13.0 3.34 63.1 29.6 27.7 −6.4 9 Q235 20 13.0 3.72 70.2 26.3 26.2 −0.4 10 Q235 20 13.0 4.16 78.4 23.2 22.9 −1.3 11 Q235 20 13.0 4.65 87.7 20.4 19.2 −5.9 表 2 冲击波壁压脉宽、冲量实验值与传统Taylor理论公式结果对比
Table 2. Comparison of the experimental and theoretical Taylor formula results of wall pressure pulse width and impulse
工况 (R·W−1/3)/(m·kg−1/3) R/R0 脉宽 冲量 tb,exp/µs tb,th/µs δt/% Iexp/(Pa·s) Ith/(Pa·s) δI/% 1 0.11 2.0 5.7 10.3 79.6 5585.9 12253.0 119.3 2 0.21 4.0 11.5 12.6 10.2 3402.4 4255.4 25.1 3 0.88 16.6 7.7 8.4 9.1 262.4 304.7 16.1 4 1.63 30.7 24.6 25.6 4.1 449.2 492.7 9.7 5 1.86 35.1 55.7 58.5 5.0 880.7 946.2 7.4 6 2.62 49.5 63.6 66.4 4.4 665.3 708.6 6.5 7 2.79 52.6 64.9 68.2 5.1 644.1 673.9 4.6 8 3.34 63.1 70.5 72.3 2.6 550.9 578.4 5.0 9 3.72 70.2 72.2 75.1 4.0 524.7 528.7 0.8 10 4.16 78.4 75.7 78.5 3.7 470.0 480.1 2.1 11 4.65 87.7 80.5 82.1 2.0 411.1 435.2 5.9 表 3 不同比例爆距处的冲击波速度
Table 3. The shock wave velocities at different values of
$R/W^{1/3} $ (R·W−1/3)/(m·kg−1/3) R/R0 c/(m·s−1) (R·W−1/3)/(m·kg−1/3) R/R0 c/(m·s−1) (R·W−1/3)/(m·kg−1/3) R/R0 c/(m·s−1) 0.11 2.00 2835 0.32 6.00 1773 0.90 17.00 1563 0.12 2.25 2612 0.34 6.50 1745 0.95 18.00 1558 0.13 2.50 2471 0.37 7.00 1721 1.01 19.00 1553 0.15 2.75 2338 0.40 7.50 1700 1.06 20.00 1550 0.16 3.00 2244 0.42 8.00 1683 1.33 25.00 1536 0.17 3.25 2154 0.45 8.50 1667 1.59 30.00 1526 0.19 3.50 2098 0.48 9.00 1653 1.86 35.00 1520 0.20 3.75 2034 0.50 9.50 1641 2.12 40.00 1515 0.21 4.00 1984 0.53 10.00 1631 2.39 45.00 1511 0.23 4.25 1949 0.58 11.00 1612 2.65 50.00 1508 0.24 4.50 1913 0.64 12.00 1598 3.18 60.00 1503 0.25 4.75 1882 0.69 13.00 1586 3.71 70.00 1500 0.27 5.00 1856 0.74 14.00 1581 4.24 80.00 1498 0.28 5.25 1830 0.80 15.00 1574 4.77 90.00 1496 0.29 5.50 1810 0.85 16.00 1568 5.30 100.00 1494 表 4 冲击波速度修正前后脉宽和壁压冲量及偏差对比
Table 4. Comparisons of the pulse width and impulse of the wall pressure and their deviations before and after the shock wave velocity correction
(R·W−1/3)/(m·kg−1/3) 脉宽 冲量 tb,exp/µs tb,th/µs δt/% tb,th1/µs δt1/% Iexp/(Pa·s) Ith/(Pa·s) δI/% Ith1/(Pa·s) δI1/% 0.11 5.7 10.3 79.6 7.2 26.6 5585.9 12253.0 119.3 8850.4 58.4 0.21 11.5 12.6 10.2 10.9 2.7 3402.4 4255.4 25.1 3678.3 8.1 0.88 7.7 8.4 9.1 8.1 4.9 262.4 304.7 16.1 293.1 11.7 表 5 冲击波波头耗散对壁压峰值的影响
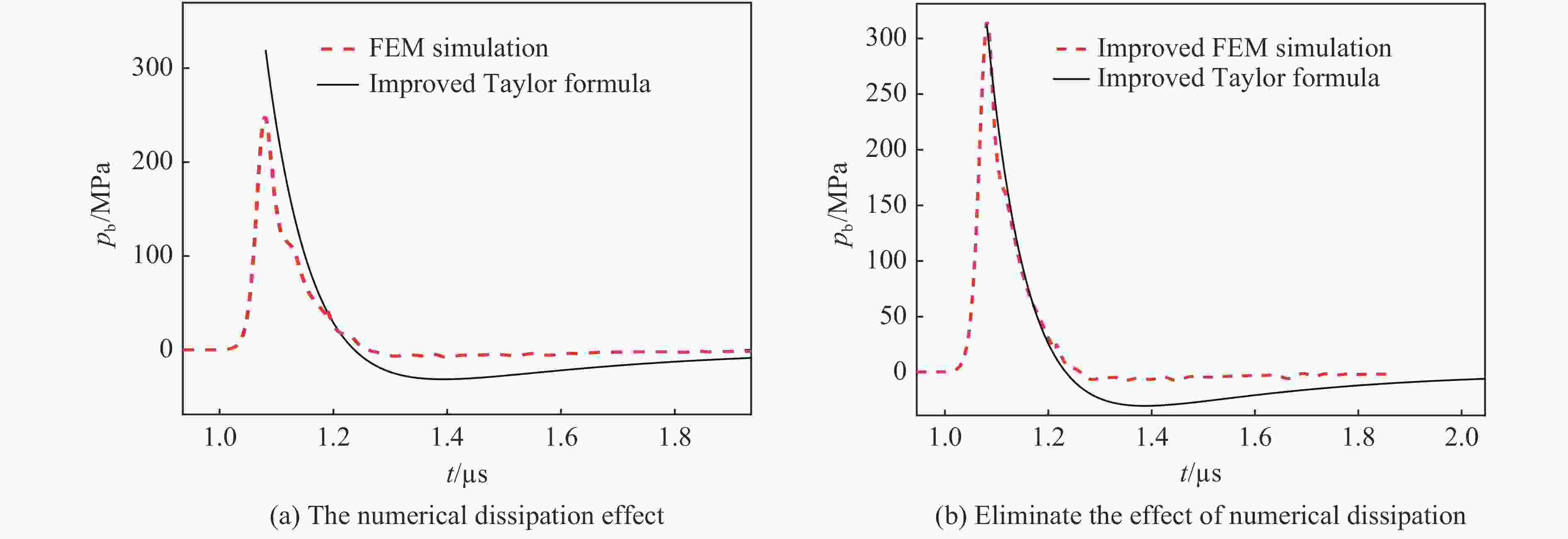
Table 5. Influence of shock wave head dissipation on wall pressure peak
R/R0 (R·W−1/3)/(m·kg−1/3) v/(m·s−1) 壁压峰值 pb,th/MPa pb,sim1/MPa δp,s1/% pb,sim2/MPa δp,s2/% 6 0.32 49.8 491.8 407.3 −17.1 533.2 8.4 7 0.37 43.2 390.2 312.0 −18.6 412.2 5.6 8 0.42 37.6 319.4 247.6 −23.1 324.7 1.7 9 0.48 33.7 267.7 202.2 −22.4 270.8 1.2 10 0.53 30.4 228.6 168.8 −24.0 229.6 0.4 11 0.58 27.4 198.1 143.5 −25.4 197.4 −0.4 12 0.64 25.0 174.8 130.5 −23.1 179.6 2.8 14 0.74 22.6 146.8 100.5 −25.9 142.4 −3.0 16 0.85 18.5 126.2 95.1 −24.6 128.3 1.7 18 0.95 15.5 110.5 82.7 −25.2 104.5 −5.4 20 1.06 14.2 98.1 69.7 −29.0 99.1 1.0 25 1.33 12.7 76.2 54.0 −29.1 76.0 −0.3 30 1.59 10.1 62.0 40.7 −34.4 58.6 −5.5 40 2.12 7.3 44.8 28.5 −36.4 41.4 −7.6 表 6 冲击波波头耗散对壁压冲量的影响
Table 6. Influence of shock wave head dissipation on wall pressure impulse
R/R0 (R·W−1/3)/(m·kg−1/3) v/(m·s−1) 冲量 Ith /(kPa·s) Isim1 /(kPa·s) δIs1/% Isim2 /(kPa·s) δIs2/% 6 0.32 49.8 24.2 18.7 −22.7 22.7 −6.2 7 0.37 43.2 20.0 15.2 −24.0 19.2 −4.0 8 0.42 37.6 16.9 12.8 −24.3 16.2 −4.1 9 0.48 33.7 14.6 10.1 −30.8 13.7 −6.2 10 0.53 30.4 12.7 9.3 −26.8 12.1 −4.7 11 0.58 27.4 11.3 8.3 −26.5 11.0 −2.7 12 0.64 25.0 10.1 7.2 −28.7 9.7 −3.4 14 0.74 22.6 8.7 5.7 −34.5 8.0 −8.1 16 0.85 18.5 7.7 4.8 −37.7 6.9 −10.4 18 0.95 15.5 6.8 4.1 −39.7 6.0 −11.8 20 1.06 14.2 6.1 3.6 −41.0 5.4 −11.5 25 1.33 12.7 4.9 2.7 −44.9 4.0 −18.4 30 1.59 10.1 4.1 2.0 −51.2 3.1 −24.4 40 2.12 7.3 3.1 1.4 −54.8 2.3 −25.8 -
[1] 金键, 朱锡, 侯海量, 等. 大型舰船在水下接触爆炸下的毁伤与防护研究综述 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2020, 40(11): 111401. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0105.JIN J, ZHU X, HOU H L, et al. Review on the damage and protection of large naval warships subjected to underwater contact explosions [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2020, 40(11): 111401. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0105. [2] PENG Y X, ZHANG A M, MING F R. Numerical simulation of structural damage subjected to the near-field underwater explosion based on SPH and RKPM [J]. Ocean Engineering, 2021, 222: 108576. DOI: 10.1016/J.OCEANENG.2021.108576. [3] 张阿漫, 王诗平, 彭玉祥, 等. 水下爆炸与舰船毁伤研究进展 [J]. 中国舰船研究, 2019, 14(3): 1–13. DOI: 10.19693/j.issn.1673-3185.01608.ZHANG A M, WANG S P, PENG Y X, et al. Research progress in underwater explosion and its damage to ship structures [J]. Chinese Journal of Ship Research, 2019, 14(3): 1–13. DOI: 10.19693/j.issn.1673-3185.01608. [4] JAVIER C, GALUSKA M, PAPA M, et al. Underwater explosive bubble interaction with an adjacent submerged structure [J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2021, 100: 103189. DOI: 10.1016/J.JFLUIDSTRUCTS.2020.103189. [5] JAVIER C, LEBLANC J, SHUKLA A. Hydrothermally degraded carbon fiber/epoxy plates subjected to underwater explosive loading in a fully submerged environment [J]. Marine Structures, 2020, 72: 102761. DOI: 10.1016/j.marstruc.2020.102761. [6] 刘靖晗, 唐廷, 韦灼彬, 等. 浅水爆炸冲击波在柱体附近荷载规律研究 [J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2021, 42(1): 168–173. DOI: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2021.01.031.LIU J H, TANG T, WEI Z B, et al. Research on explosive shock wave around column in shallow water [J]. Journal of Sichuan Ordnance, 2021, 42(1): 168–173. DOI: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2021.01.031. [7] 李海涛, 朱石坚, 陈志坚, 等. 全入射角度下平板冲击波的壁压载荷及局部空化特性 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2014, 34(3): 354–360. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2014)03-0354-07.LI H T, ZHU S J, CHEN Z J, et al. Characteristics of wall pressure and cavitation on the plate subjected to underwater explosion shock waves at any angle of incidence [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2014, 34(3): 354–360. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2014)03-0354-07. [8] 罗泽立, 周章涛, 毛海斌, 等. 水下爆炸强冲击波与平板结构相互作用的理论分析方法 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2017, 31(4): 443–452. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.2017.04.013.LUO Z L, ZHOU Z T, MAO H B, et al. Theoretical analysis of the interaction between the plate structure and strong shock wave in underwater explosion [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2017, 31(4): 443–452. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.2017.04.013. [9] 陈莹玉. 水下近场爆炸时不同结构形式的壁压与毁伤特性试验研究 [D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2019: 20−26.CHEN Y Y. Experimental study on wall pressure and damage of different structures to near-field underwater explosion [D]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University, 2019: 20−26. [10] 崔雄伟, 陈莹玉, 苏标, 等. 水下爆炸中气泡射流壁压特性实验研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2020, 40(11): 111404. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0106.CUI X W, CHEN Y Y, SU B, et al. Characteristics of wall pressure generated by bubble jets in an underwater explosion [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2020, 40(11): 111404. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0106. [11] 张显丕, 刘建湖, 潘建强, 等. 水下爆炸压力传感器技术研究综述 [J]. 计算机测量与控制, 2011, 19(11): 2600–2602. DOI: 10.16526/j.cnki.11-4762/tp.2011.11.082.ZHANG X P, LIU J H, PAN J Q, et al. Overview on techniques of underwater explosion pressure sensors [J]. Computer Measurement and Control, 2011, 19(11): 2600–2602. DOI: 10.16526/j.cnki.11-4762/tp.2011.11.082. [12] 屈子悦. 水下爆炸作用下圆柱壳绕射特性及压力分布特征研究 [D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2019: 5−36.QU Z Y. Study on diffraction characteristics and pressure distribution of cylindrical shell under underwater shock wave [D]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University, 2019: 5−36. [13] 王海坤, 刘建湖, 毛海斌, 等. 水下爆炸气泡及其射流的光电联合测量研究 [J]. 防护工程, 2015, 37(4): 36–42.WANG H K, LIU J H, MAO H B, et al. Photoelectric combined measurements of underwater explosion bubble and jet [J]. Protective Engineering, 2015, 37(4): 36–42. [14] 周章涛, 刘建湖, 裴红波, 等. 水下近距和接触爆炸流固耦合作用机理及加载效应研究 [J]. 兵工学报, 2017, 38(S1): 136–145.ZHOU Z T, LIU J H, PEI H B, et al. Fluid-structure interaction mechanism and loading effect in close-in and contact underwater explosions [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2017, 38(S1): 136–145. [15] 张臣, 金辉. 实船爆炸试验中近水面压力测量与分析 [J]. 水雷战与舰船防护, 2012, 20(4): 39–43.ZHANG C, JIN H. Measurement and analysis of near surface pressure in ship explosion test [J]. Mine Warfare and Ship Self-Defence, 2012, 20(4): 39–43. [16] 张振华, 王乘, 黄玉盈, 等. 舰船底部液舱结构在水下爆炸作用下的动态响应实验研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2007, 27(5): 431–437. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2007)05-0431-07.ZHANG Z H, WANG C, HUANG Y Y, et al. Experiment research of the dynamic response of fluid cabin in the bottom of warship subjected to underwater explosion [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2007, 27(5): 431–437. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2007)05-0431-07. [17] 赵章泳, 王明洋, 邱艳宇, 等. 爆炸波在非饱和钙质砂中的传播规律 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2020, 40(8): 083201. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0389.ZHAO Z Y, WANG M Y, QIU Y Y, et al. The propagation laws of blast wave in unsaturated calcareous sand [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2020, 40(8): 083201. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0389. [18] 庄铁栓, 王明洋, 伍俊, 等. 浅水爆炸下高桩钢管柱表面作用荷载实验研究 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2020, 39(1): 70–78; 108. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2020.01.011.ZHUANG T S, WANG M Y, WU J, et al. Tests for surface loading of high pile steel pipe column under shallow water explosion [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2020, 39(1): 70–78; 108. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2020.01.011. [19] TAYLOR G I. The pressure and impulse of submarine explosion waves on plates [C]//The Scientific Papers of Sir Geoffrey Ingram Taylor. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1963: 287−303. [20] 明付仁. 水下近场爆炸对舰船结构瞬态流固耦合毁伤特性研究 [D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2014: 123−125.MING F R. Damage characteristics of transient fluid-structure interaction of warship structures subjected to near-field underwater explosion [D]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University, 2014: 123−125. [21] ZAMYSHLYAEV B V, YAKOVLEV Y S. Dynamic loads in underwater explosion [M]. Washington, DC, USA: Intelligence Support Center, 1973. [22] 赵继波, 谭多望, 李金河, 等. 柱形装药水中爆炸近场径向压力测试初探 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2008, 22(3): 323–328. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.2008.03.018.ZHAO J B, TAN D W, LI J H, et al. Primary research on side pressure of cylindrical TNT at underwater explosive close-field [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2008, 22(3): 323–328. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.2008.03.018. [23] 畅里华, 何徽, 温伟峰, 等. 炸药水中爆炸冲击波超高速同时分幅/扫描摄影技术 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2018, 38(2): 437–442. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2016-0241.CHANG L H, HE H, WEN W F, et al. Study of underwater-explosion shock wave using ultrahigh-speed simultaneous framing and streak photography technology [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2018, 38(2): 437–442. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2016-0241. [24] ZHANG J X, WANG S S, JIA X Y, et al. An improved Kirkwood-Bethe model for calculating near-field shockwave propagation of underwater explosions [J]. AIP Advances, 2021, 11(3): 035123. DOI: 10.1063/5.0040224. -






 下载:
下载: