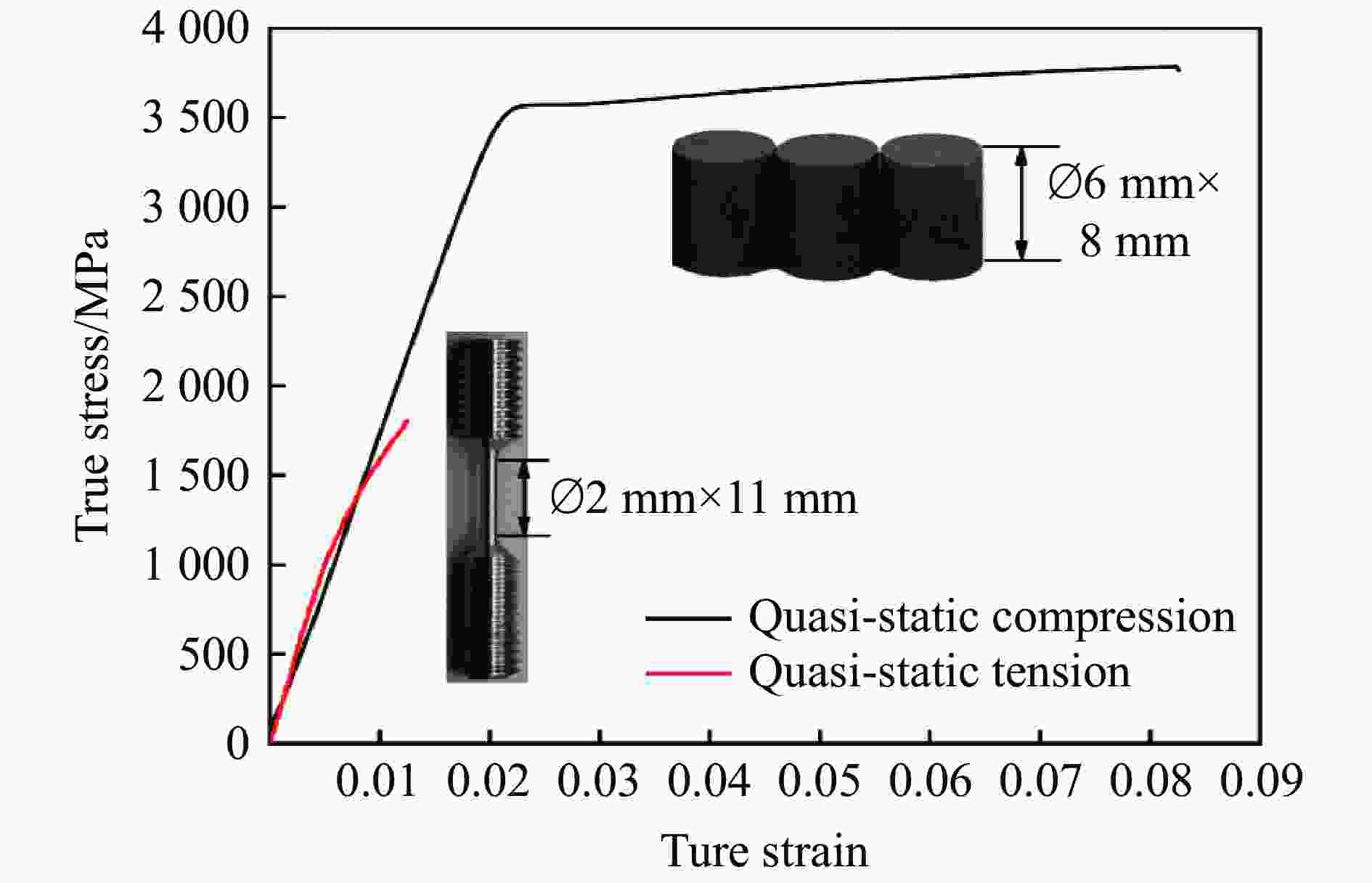
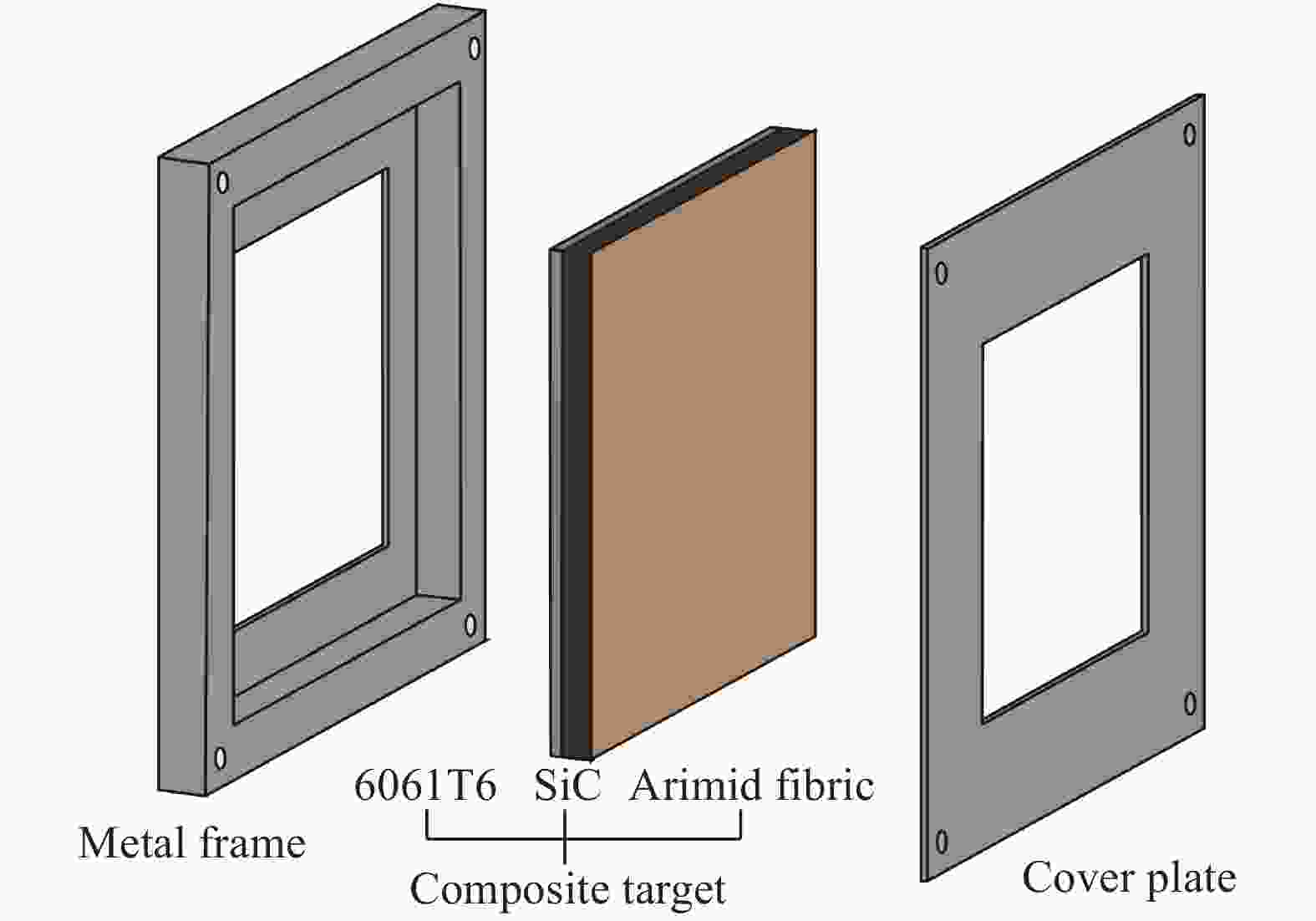
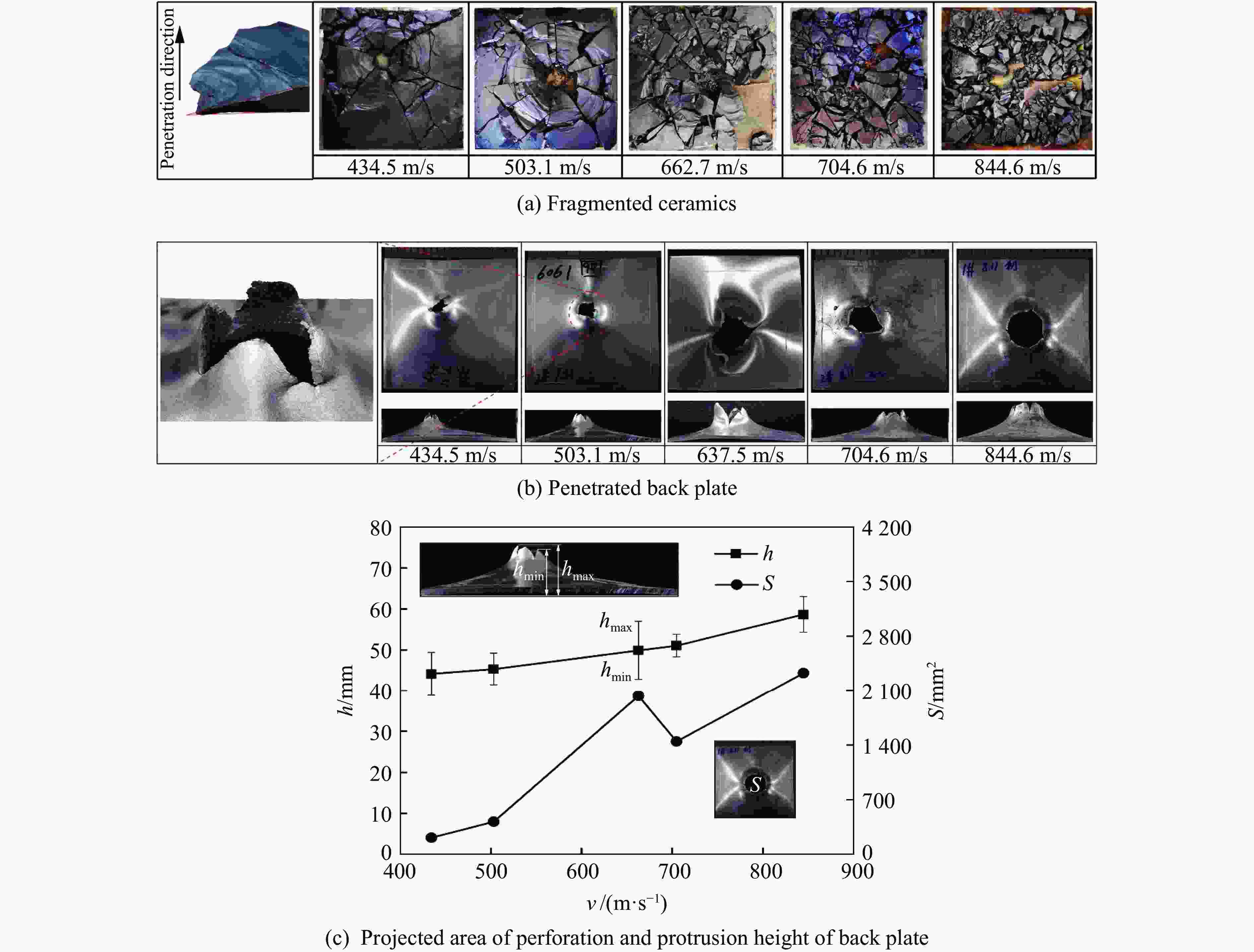
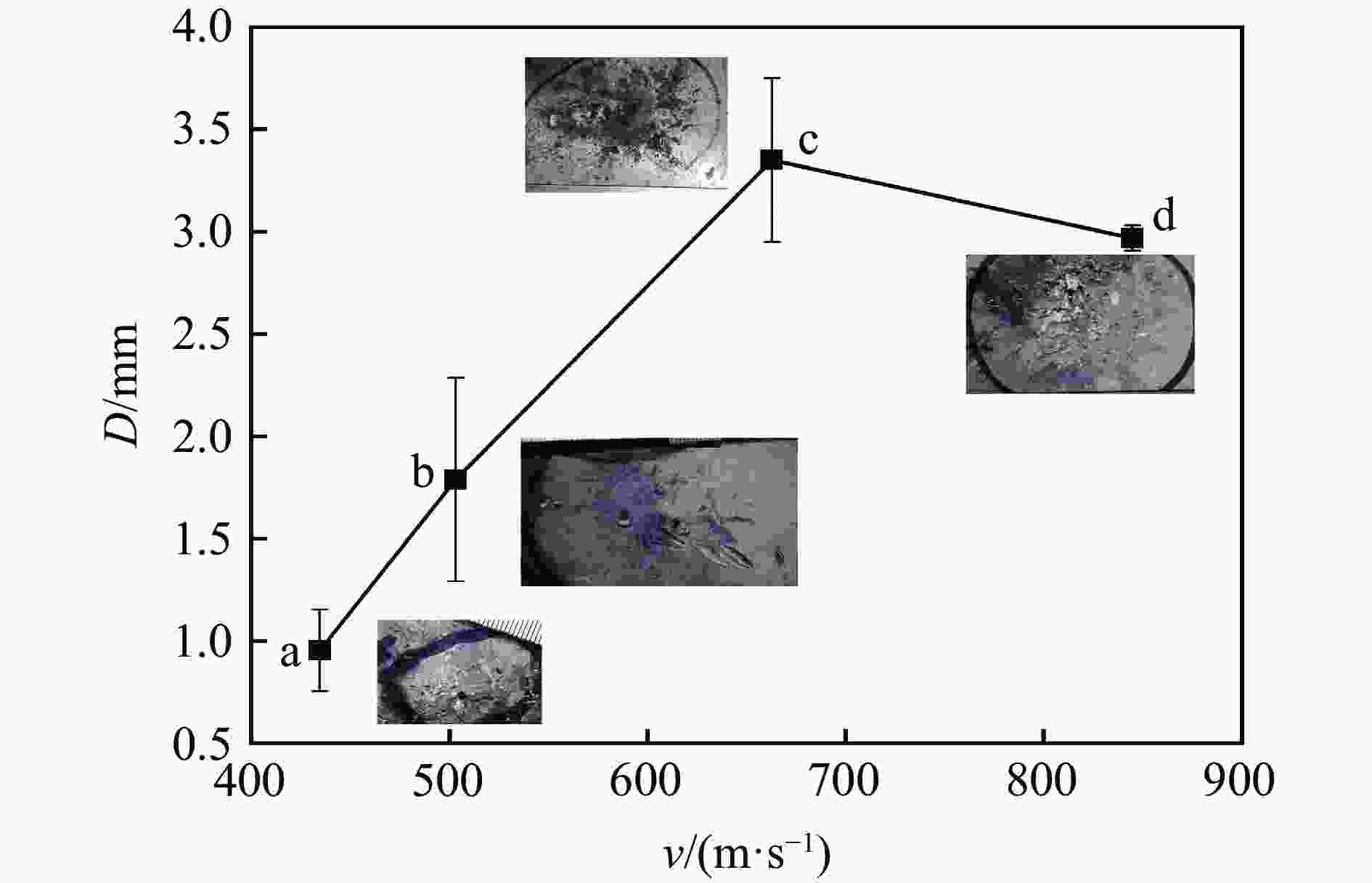
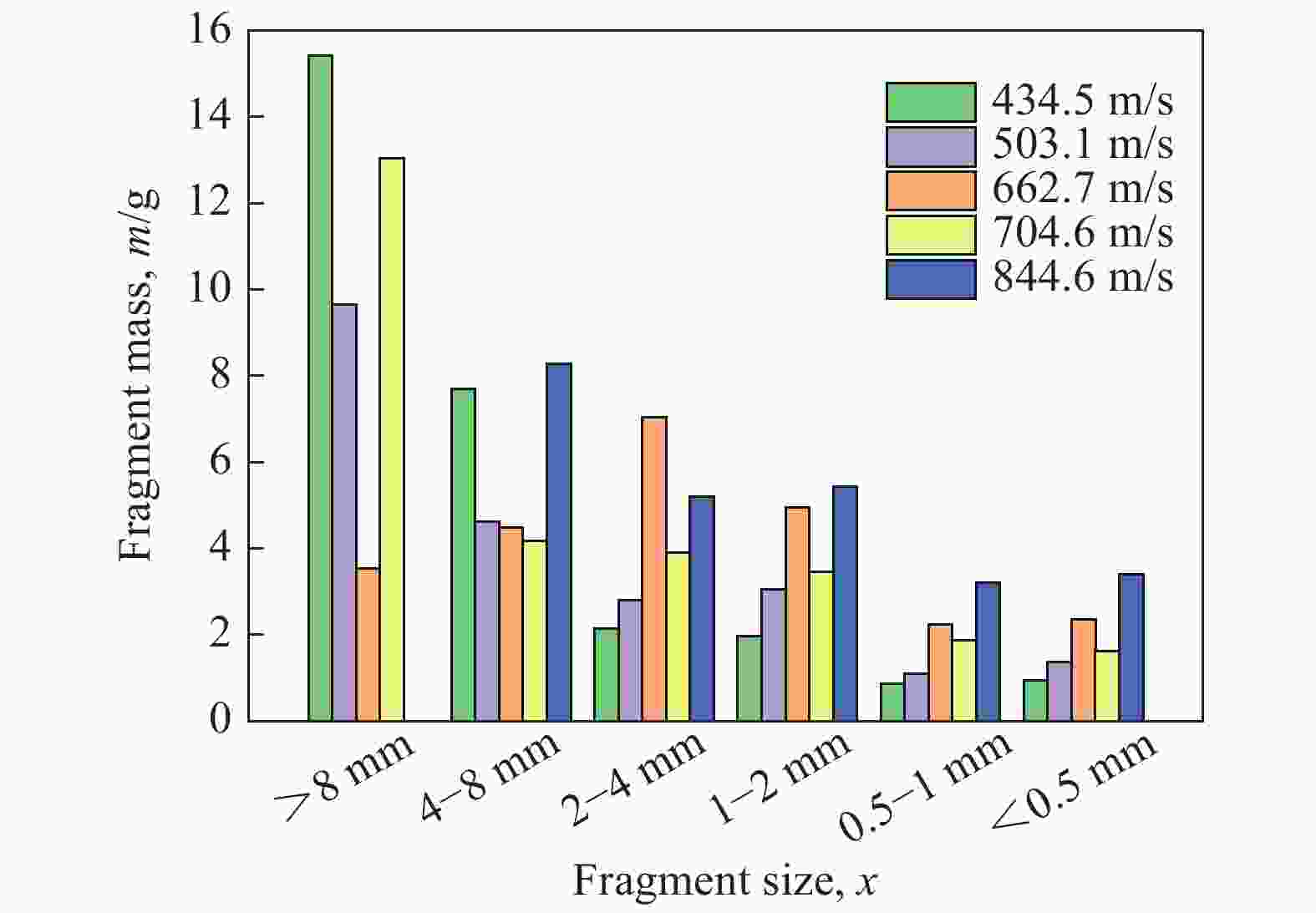
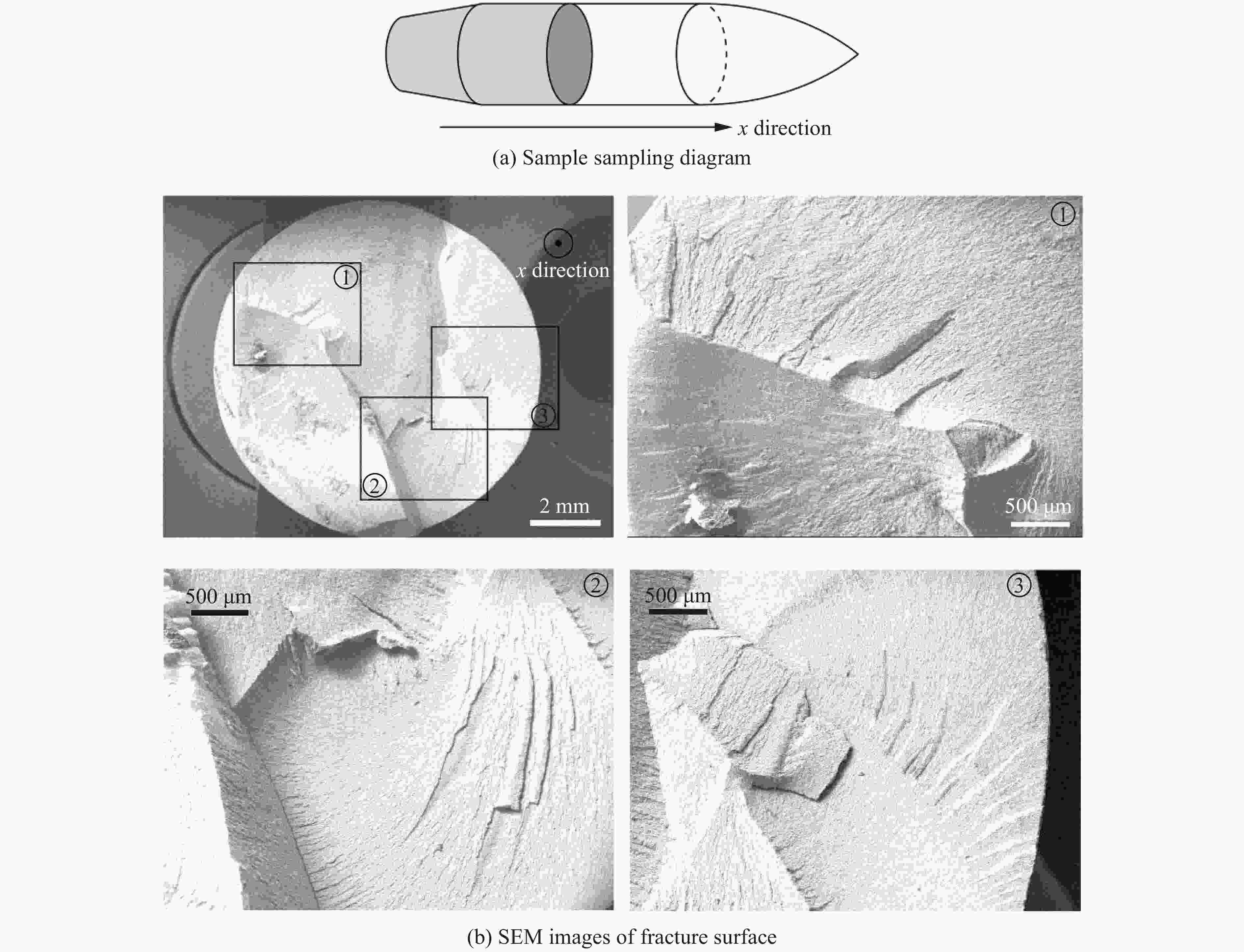
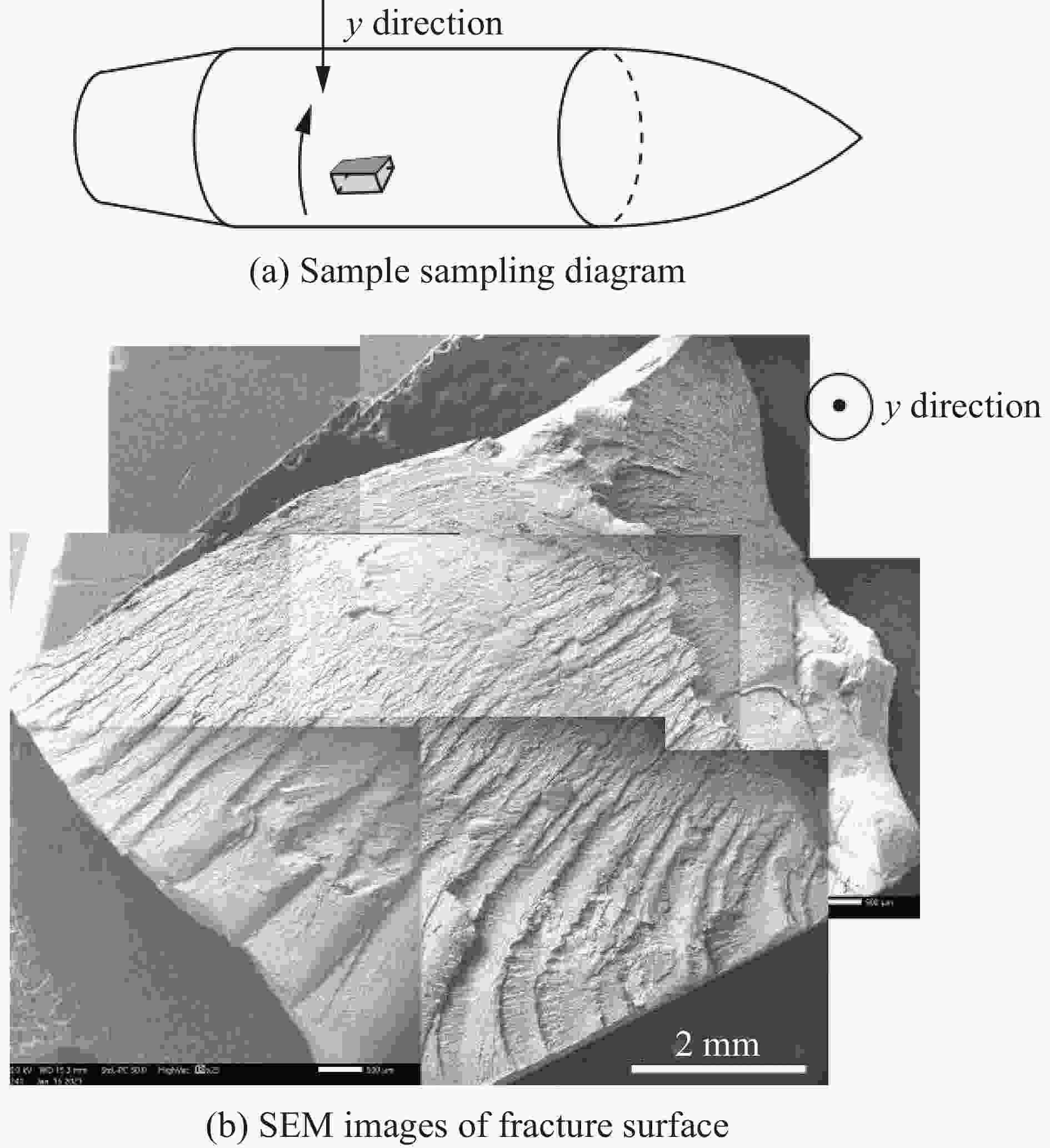
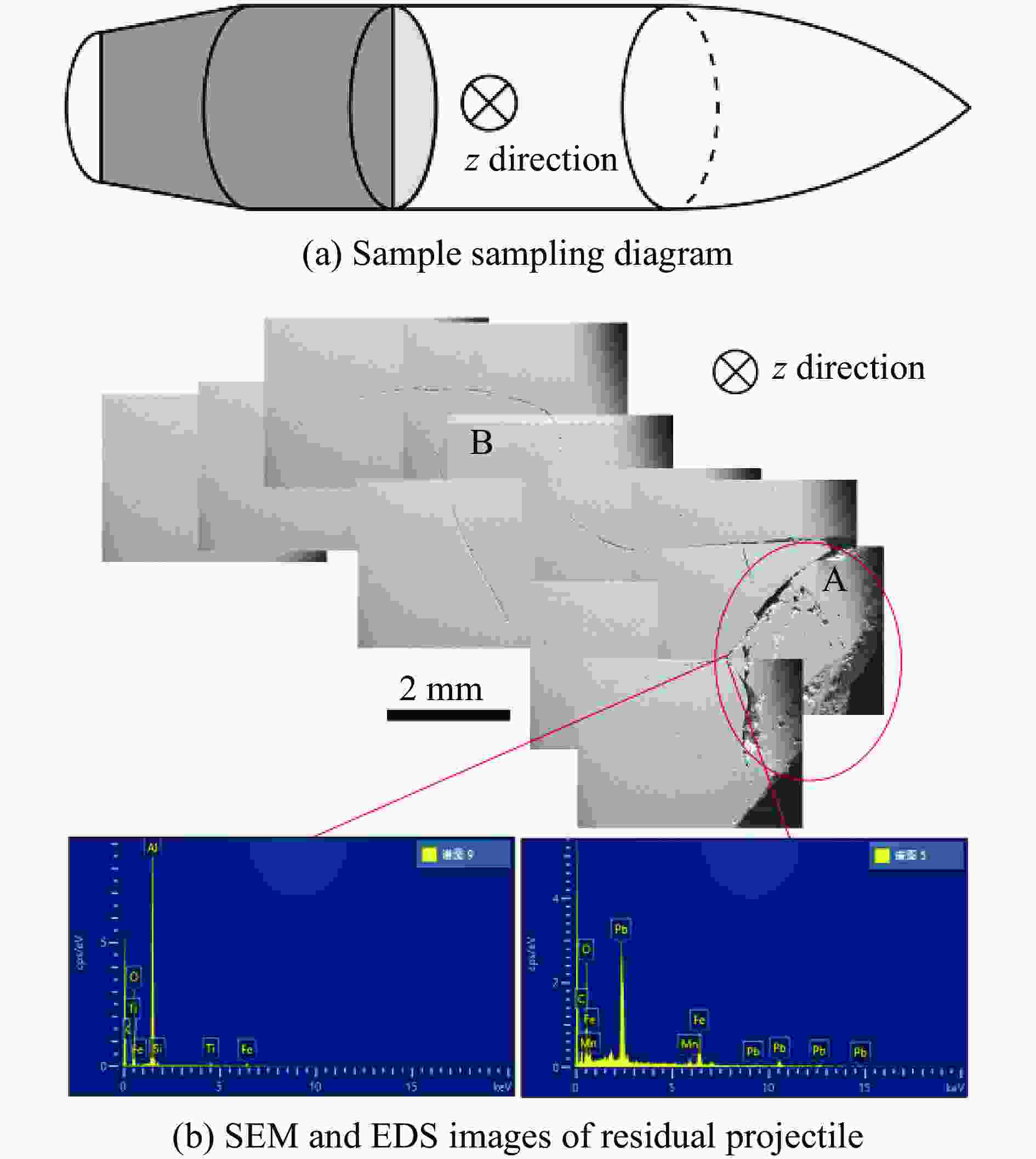
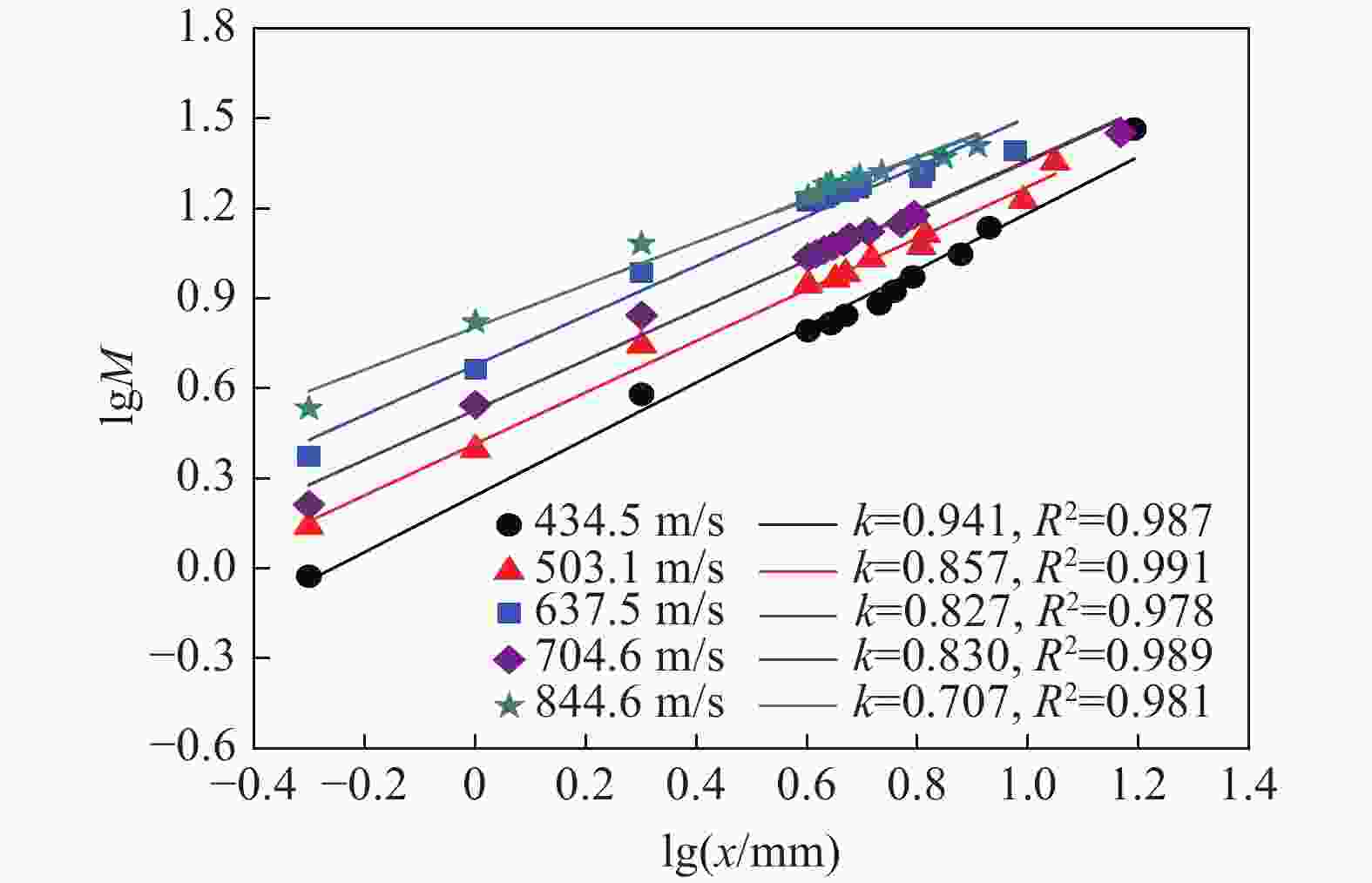
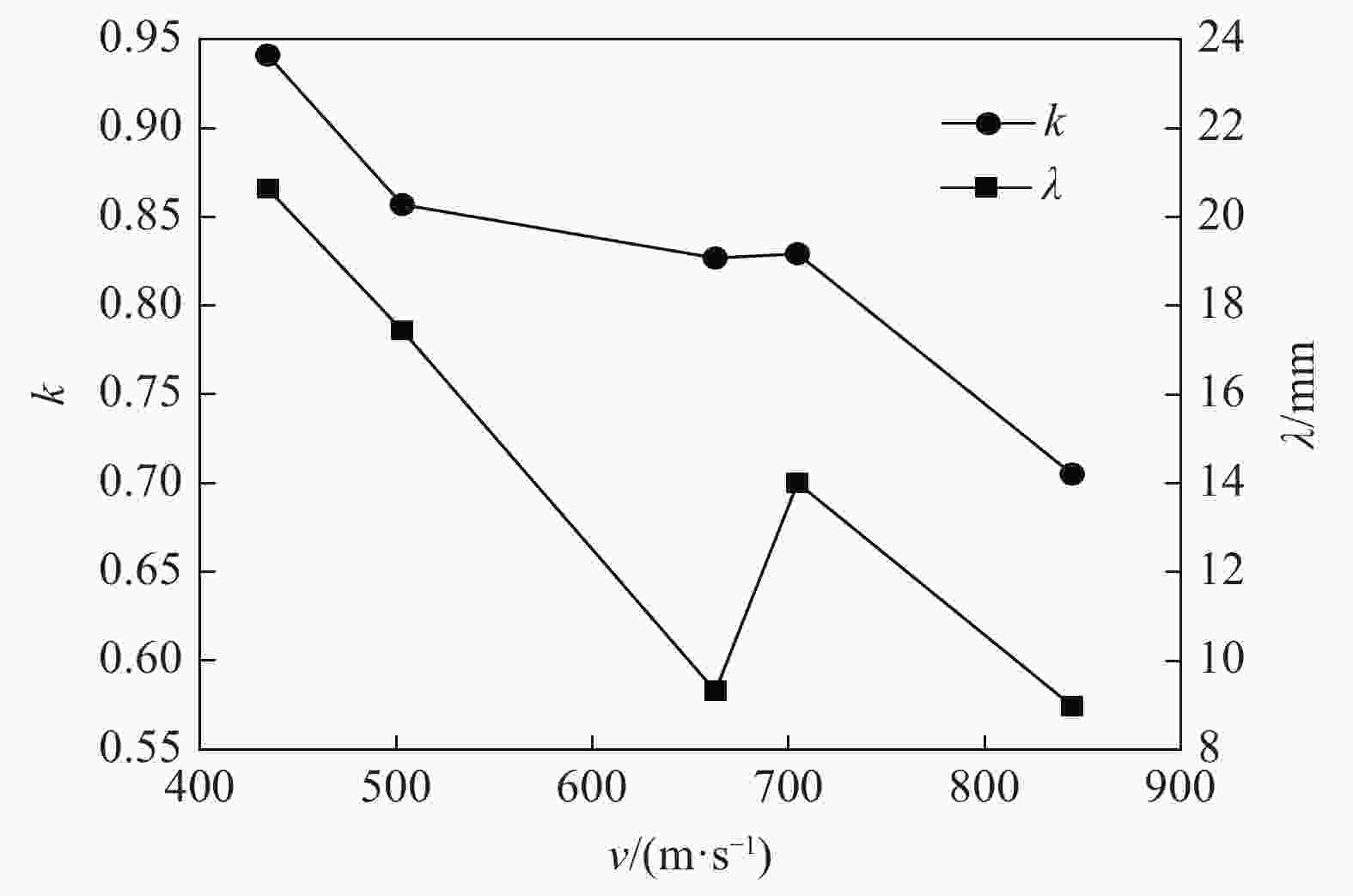
| [1] |
SAVIO S G, SENTHIL P, SINGH V, et al. An experimental study on the projectile defeat mechanism of hard steel projectile against boron carbide tiles [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2015, 86: 157–166. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2015.07.011.
|
| [2] |
DI BENEDETTO G, MATTEIS P, SCAVINO G. Impact behavior and ballistic efficiency of armor-piercing projectiles with tool steel cores [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2018, 115: 10–18. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2017.12.021.
|
| [3] |
RAHBEK D B, JOHNSEN B B. Fragmentation of an armour piercing projectile after impact on composite covered alumina tiles [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2019, 133: 103332. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2019.103332.
|
| [4] |
ASAHI KAWASHIMA, H K H K. Fracture toughness of Zr55Al10Ni5Cu30 bulk metallic glass by 3-point bend testing [J]. Materials Transactions, 2005(7): 1725–1732.
|
| [5] |
GRADY D E, KIPP M E. Impact failure and fragmentation properties of metals [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1997, 20(1): 293–308. DOI: 10.1016/S0734-743X(97)87502-1.
|
| [6] |
PIEKUTOWSKI A J. Effects of scale on debris cloud properties [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1997, 20(6): 639–650.
|
| [7] |
GRADY D E. Dissipation in adiabatic shear bands [J]. Mechanics of Materials, 1994, 17(2): 289–293.
|
| [8] |
MA G, ZHANG Y, ZHOU W, et al. The effect of different fracture mechanisms on impact fragmentation of brittle heterogeneous solid [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2018, 113: 132–143. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2017.11.016.
|
| [9] |
WANG C T, HE Y, JI C, et al. Dynamic fragmentation of a Zr-based metallic glass under various impact velocities [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2021, 56(4): 2900–2911. DOI: 10.1007/s10853-020-05495-5.
|
| [10] |
SHAN J, XU S, LIU Y, et al. Dynamic breakage of glass sphere subjected to impact loading [J]. Powder Technology, 2018, 330: 317–329. DOI: 10.1016/j.powtec.2018.02.009.
|
| [11] |
SARVA S, NEMAT-NASSER S, MCGEE J, et al. The effect of thin membrane restraint on the ballistic performance of armor grade ceramic tiles [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2007, 34(2): 277–302. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2005.07.006.
|
| [12] |
CHI R, SERJOUEI A, SRIDHAR I, et al. Pre-stress effect on confined ceramic armor ballistic performance [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2015, 84: 159–170. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2015.05.011.
|
| [13] |
LYNCH N J, BLESS S J, CULLIS I G, et al. The influence of confinement on the penetration of ceramic targets by KE projectiles at 1.8 and 2.6 km/s [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2006, 33(1): 390–401. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2006.09.029.
|
| [14] |
LUNDBERG P, RENSTRÖM R, LUNDBERG B. Impact of metallic projectiles on ceramic targets: transition between interface defeat and penetration [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2000, 24(3): 259–275. DOI: 10.1016/S0734-743X(99)00152-9.
|
| [15] |
SAVIO S G, RAMANJANEYULU K, MADHU V, et al. An experimental study on ballistic performance of boron carbide tiles [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2011, 38(7): 535–541. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2011.01.006.
|
| [16] |
GRADY D E. Fragmentation of rings and shells[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2006: 2−9.
|
| [17] |
GRADY D E. Fragment size distributions from the dynamic fragmentation of brittle solids [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2008, 35(12): 1557–1562. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2008.07.042.
|
| [18] |
张青艳. 脆性材料在准静态和冲击压缩载荷作用下的动态碎裂过程[D]. 宁波: 宁波大学, 2019: 26−46.ZHANG Q Y. Fragmentations of brittle materials under quasi-static and dynamic compression[D]. Ningbo: Ningbo University, 2019: 26−46.
|






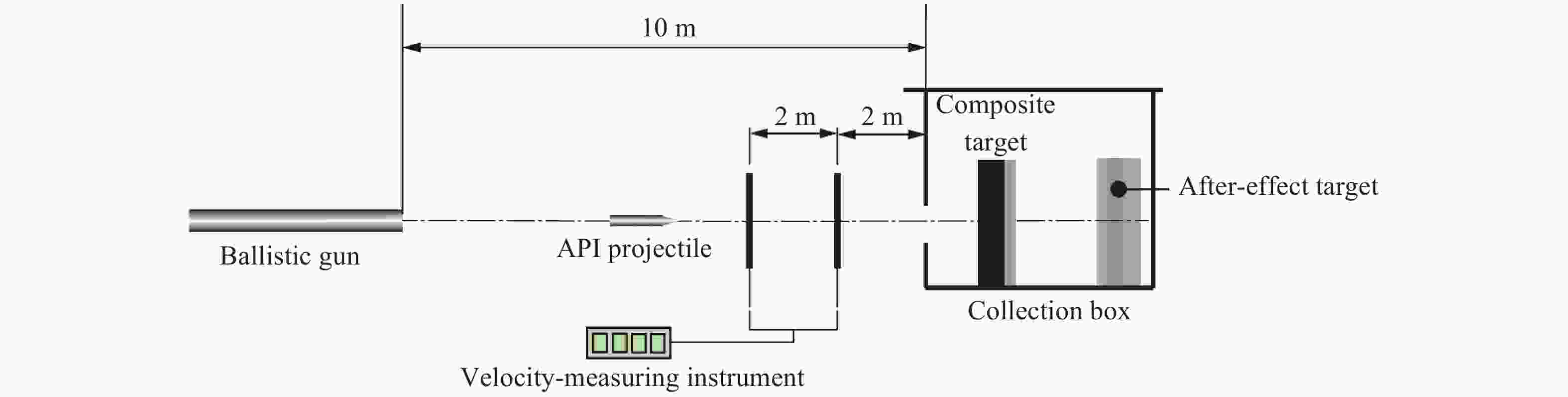
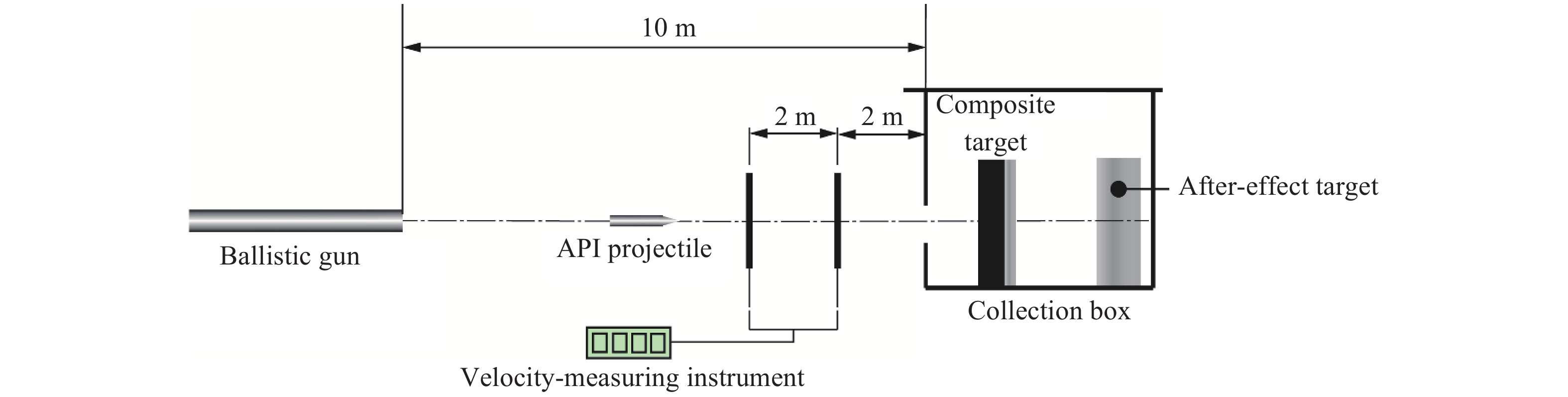
 下载:
下载: