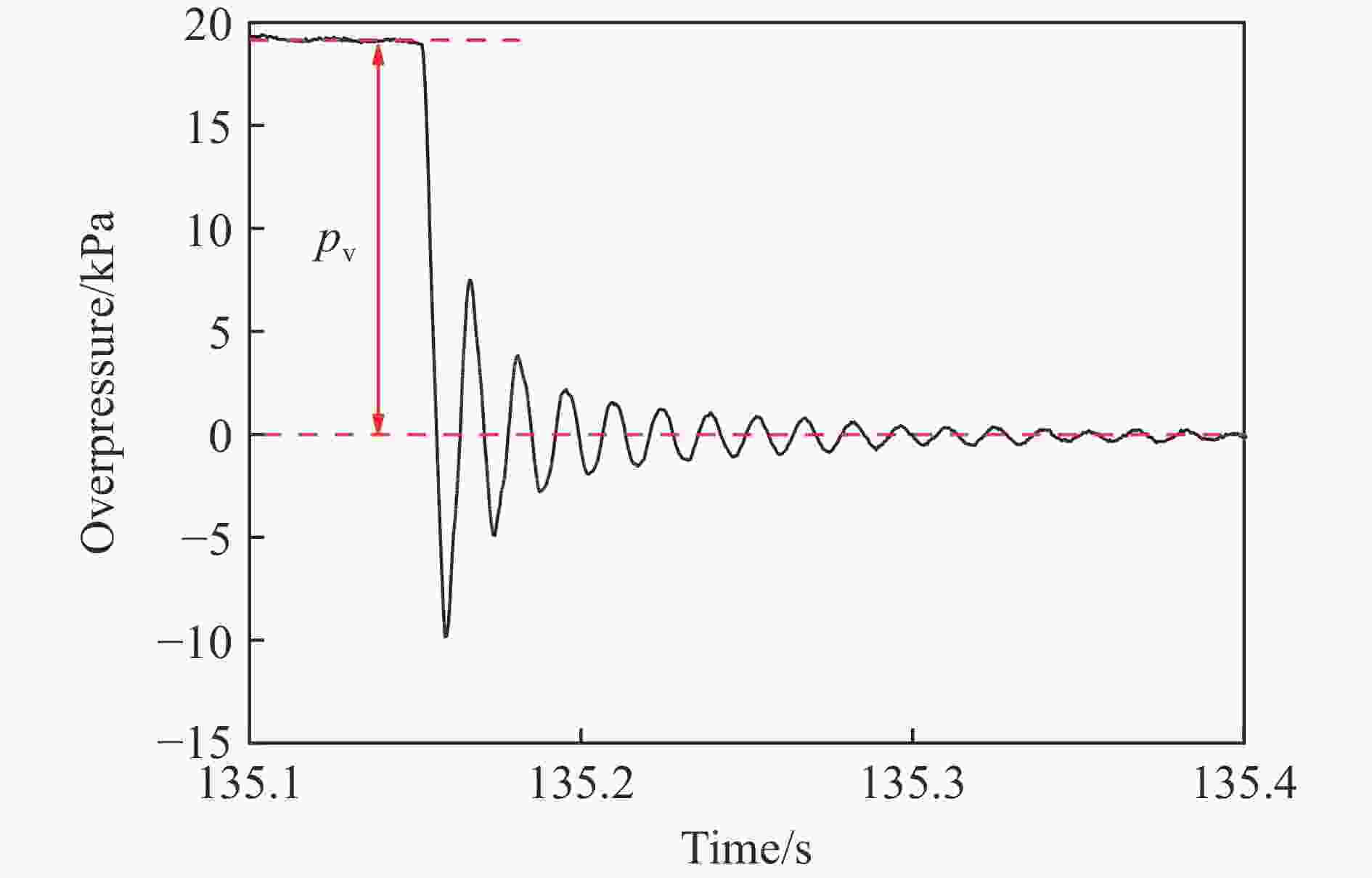
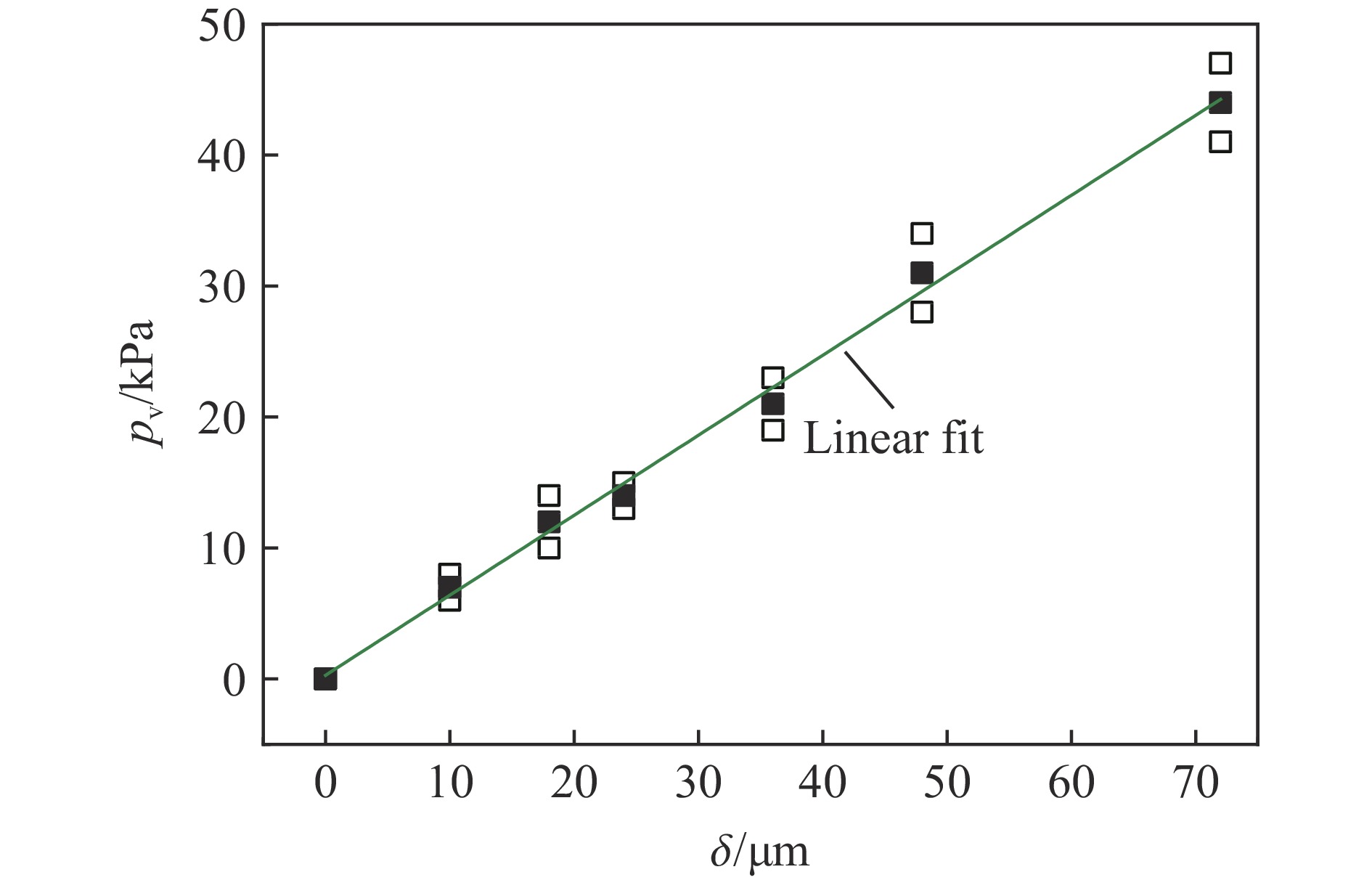
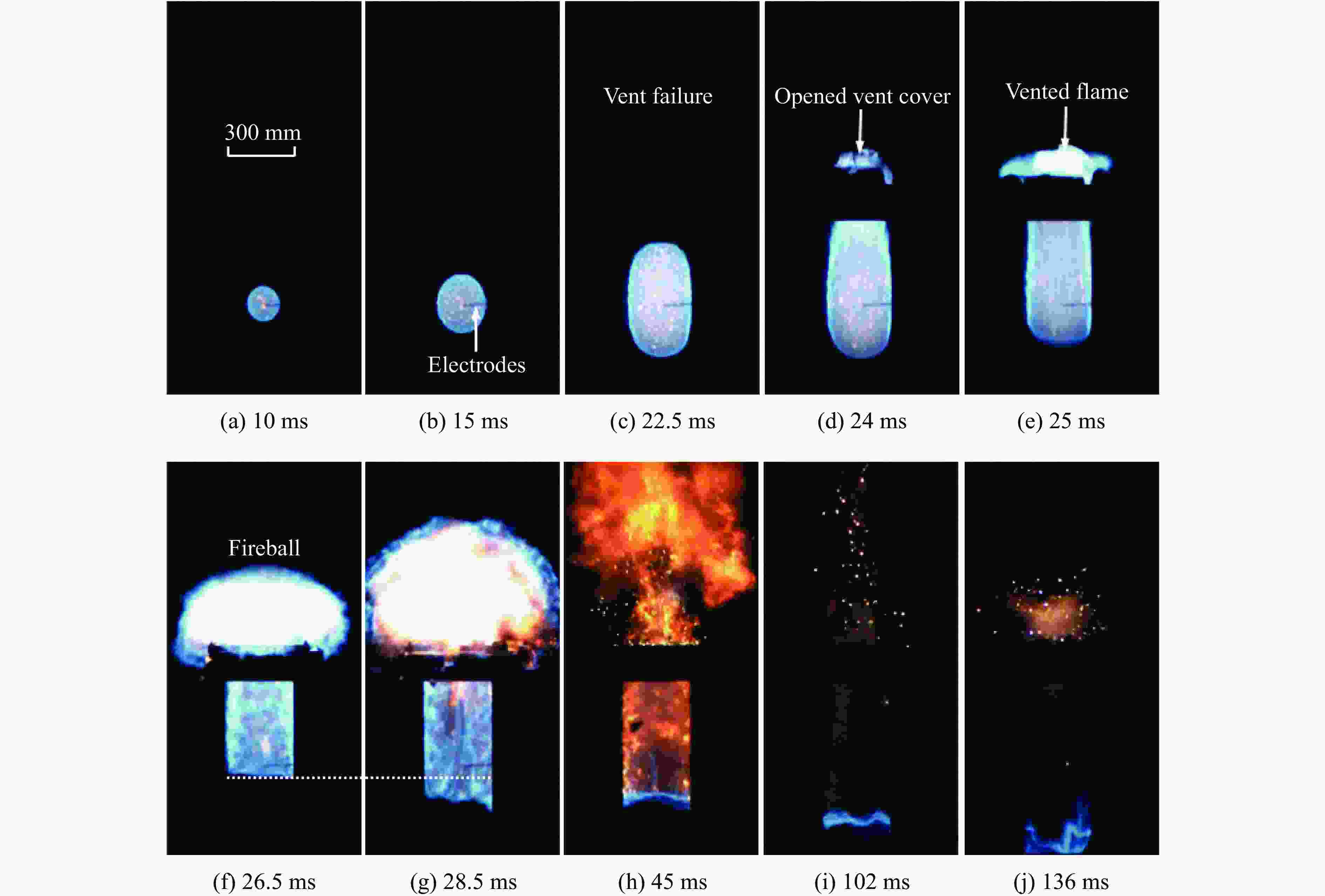
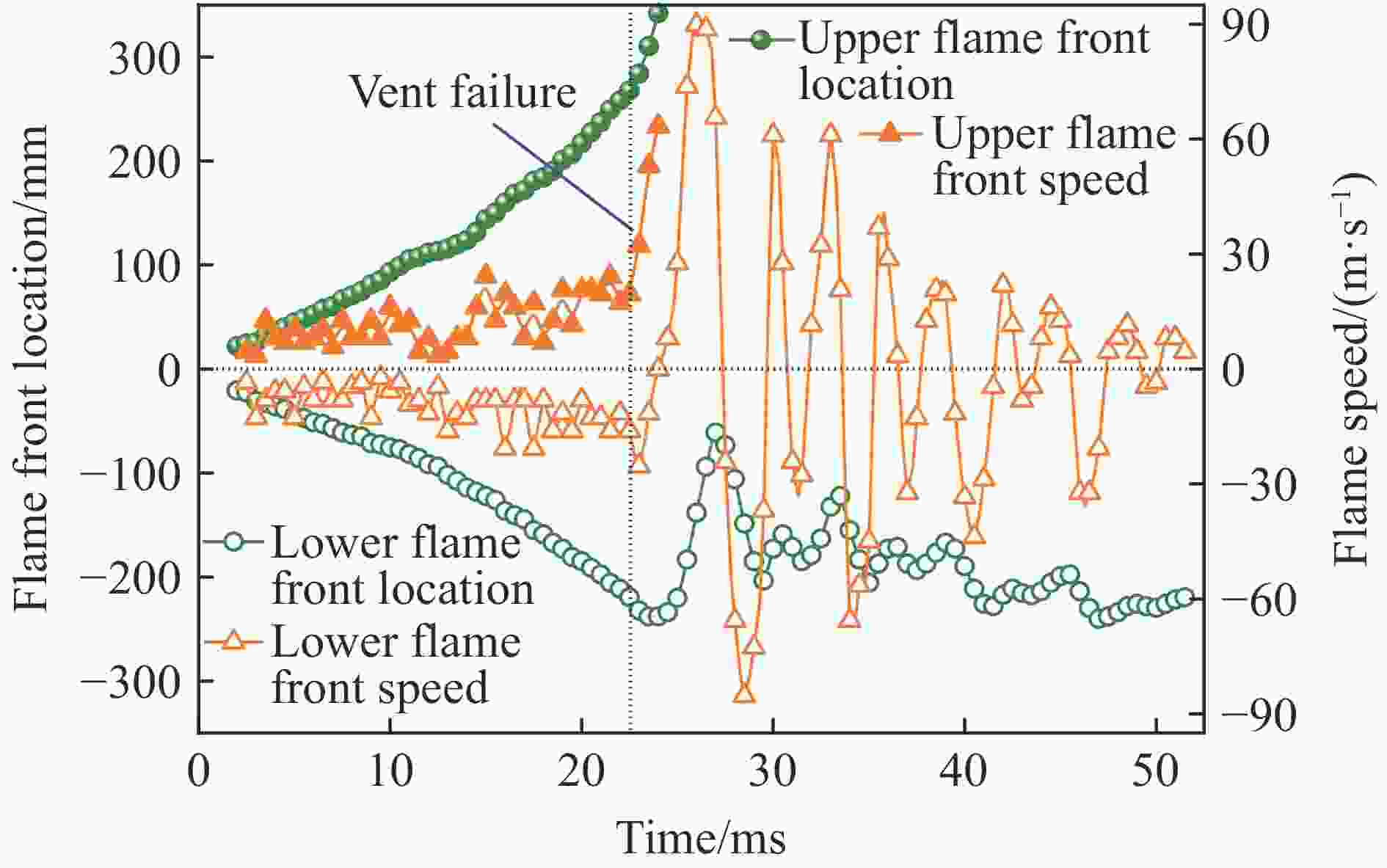
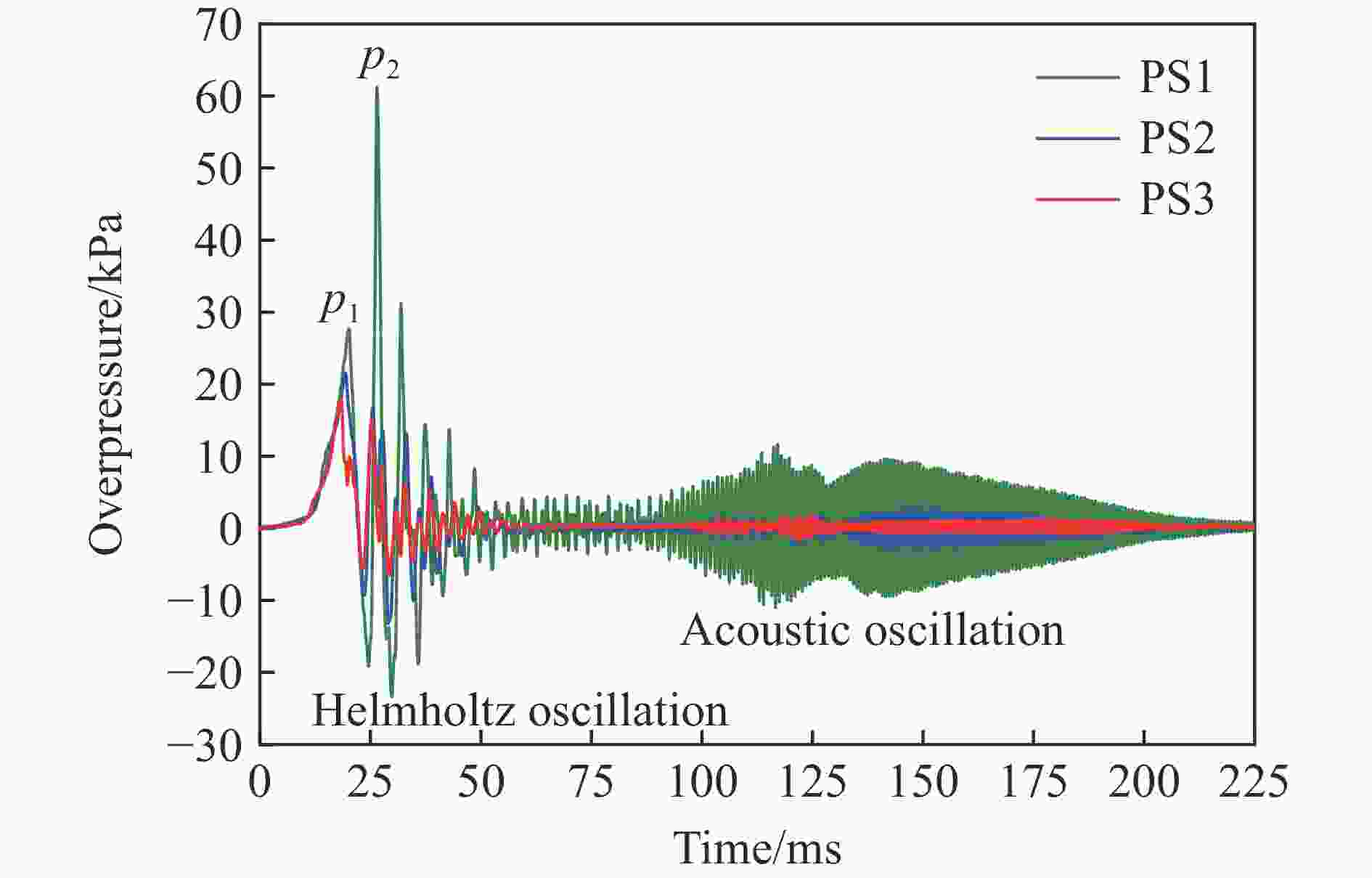
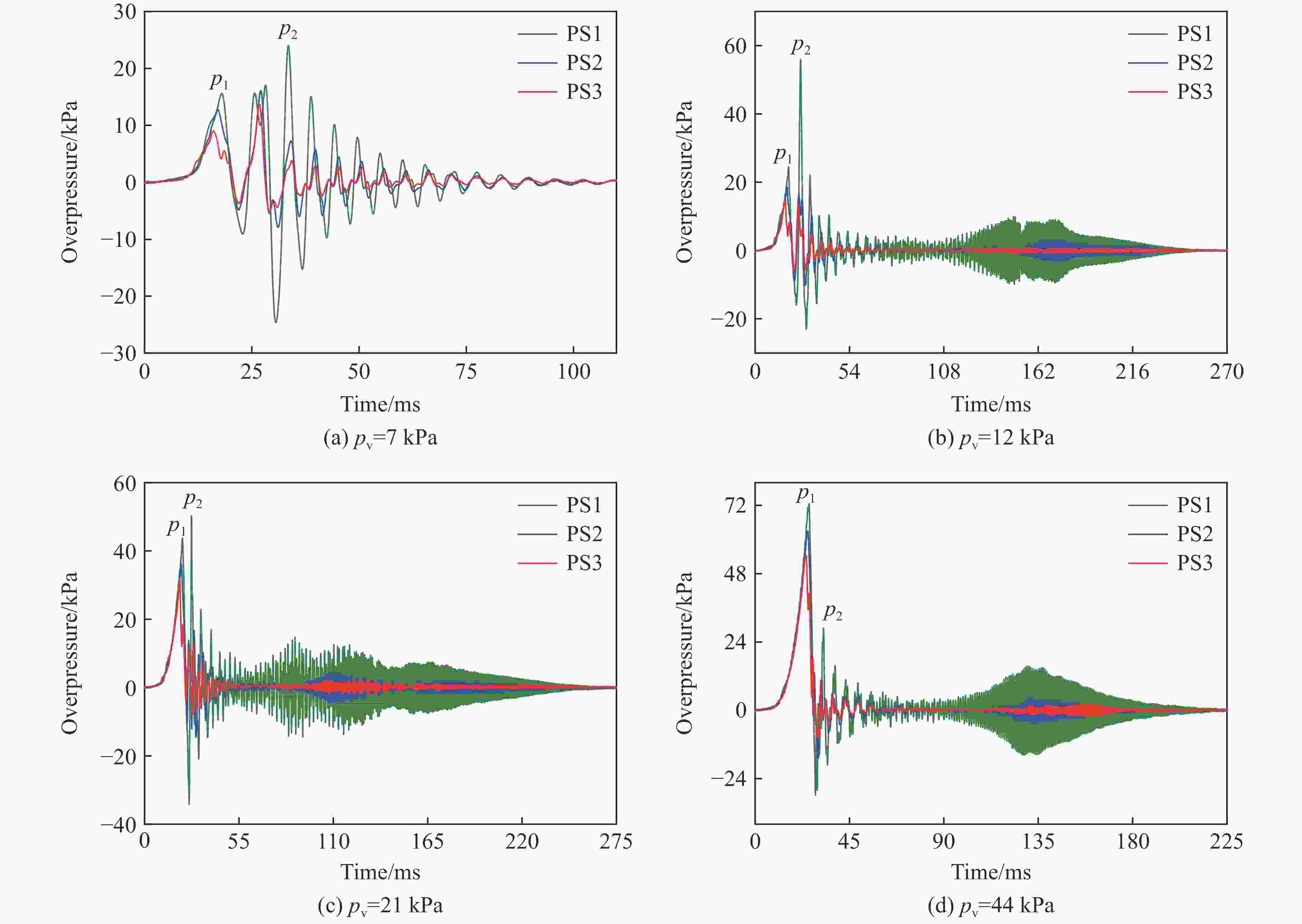
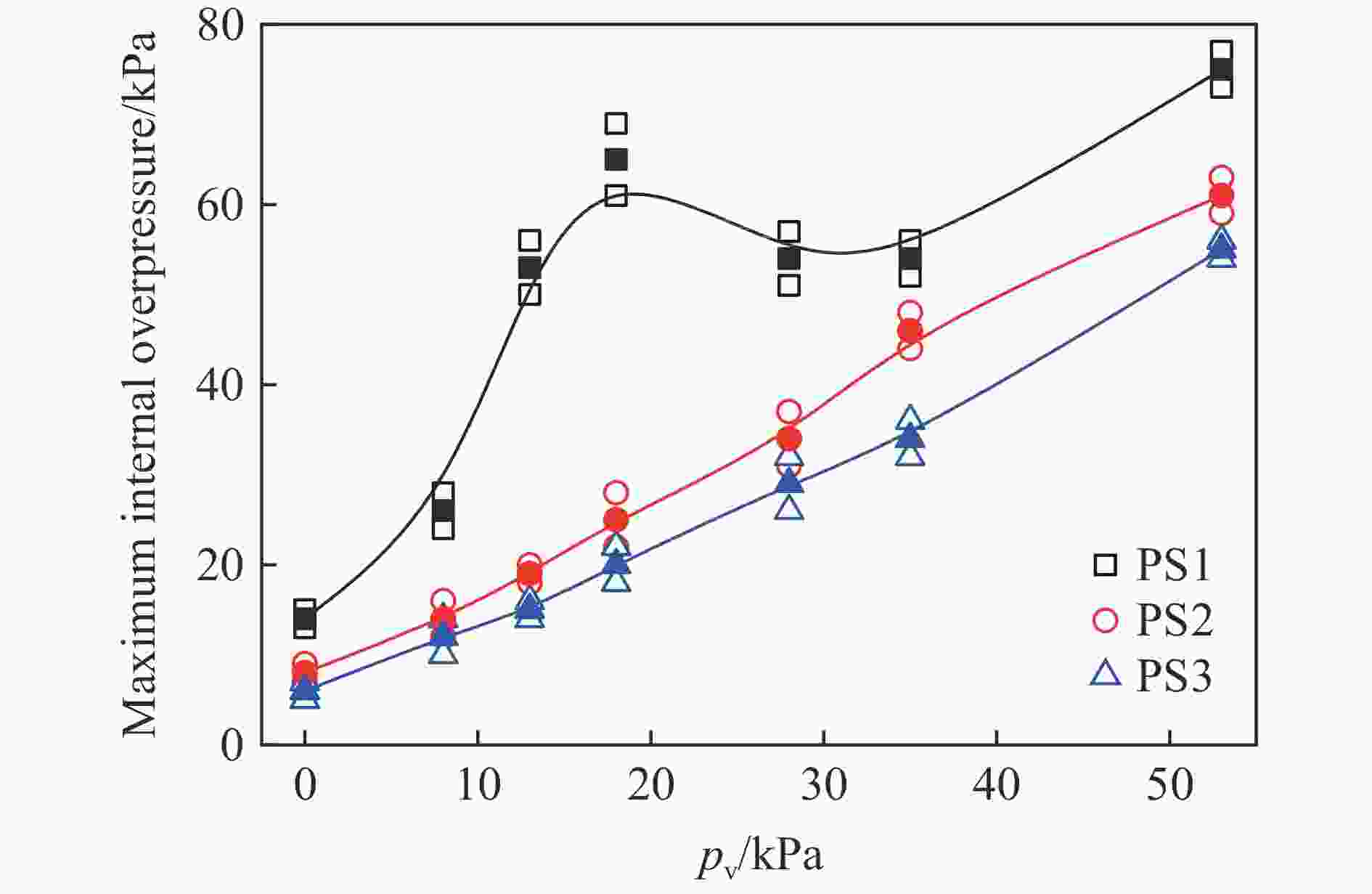
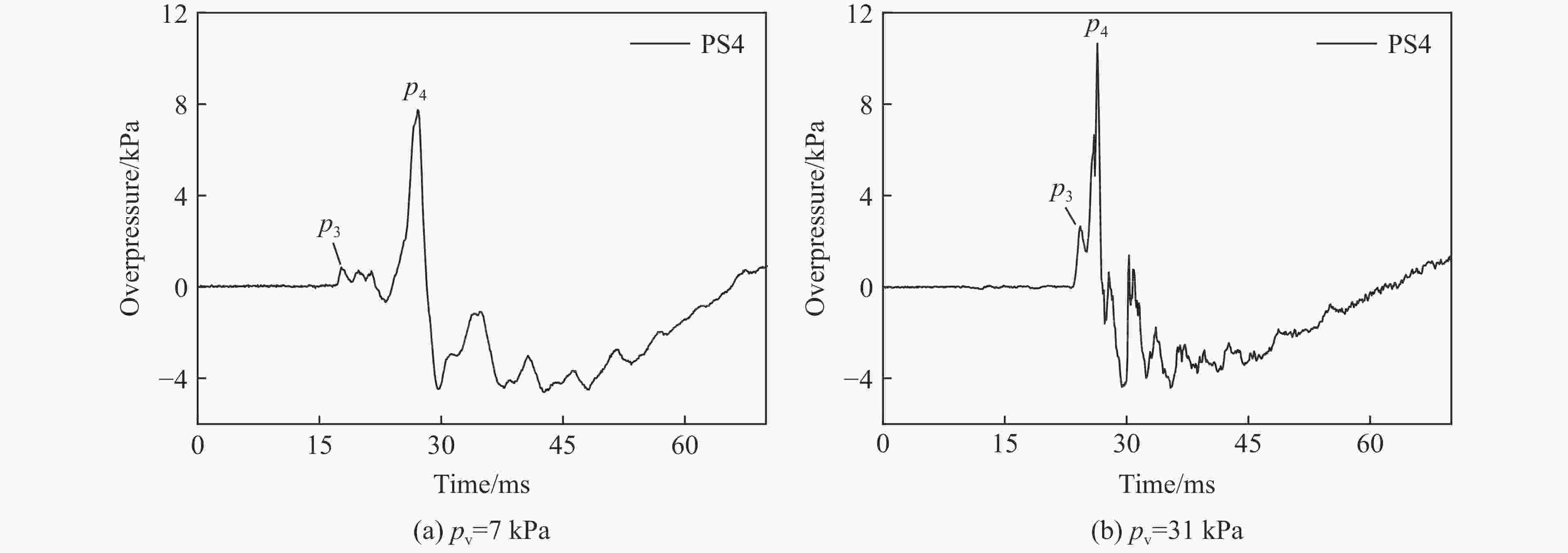
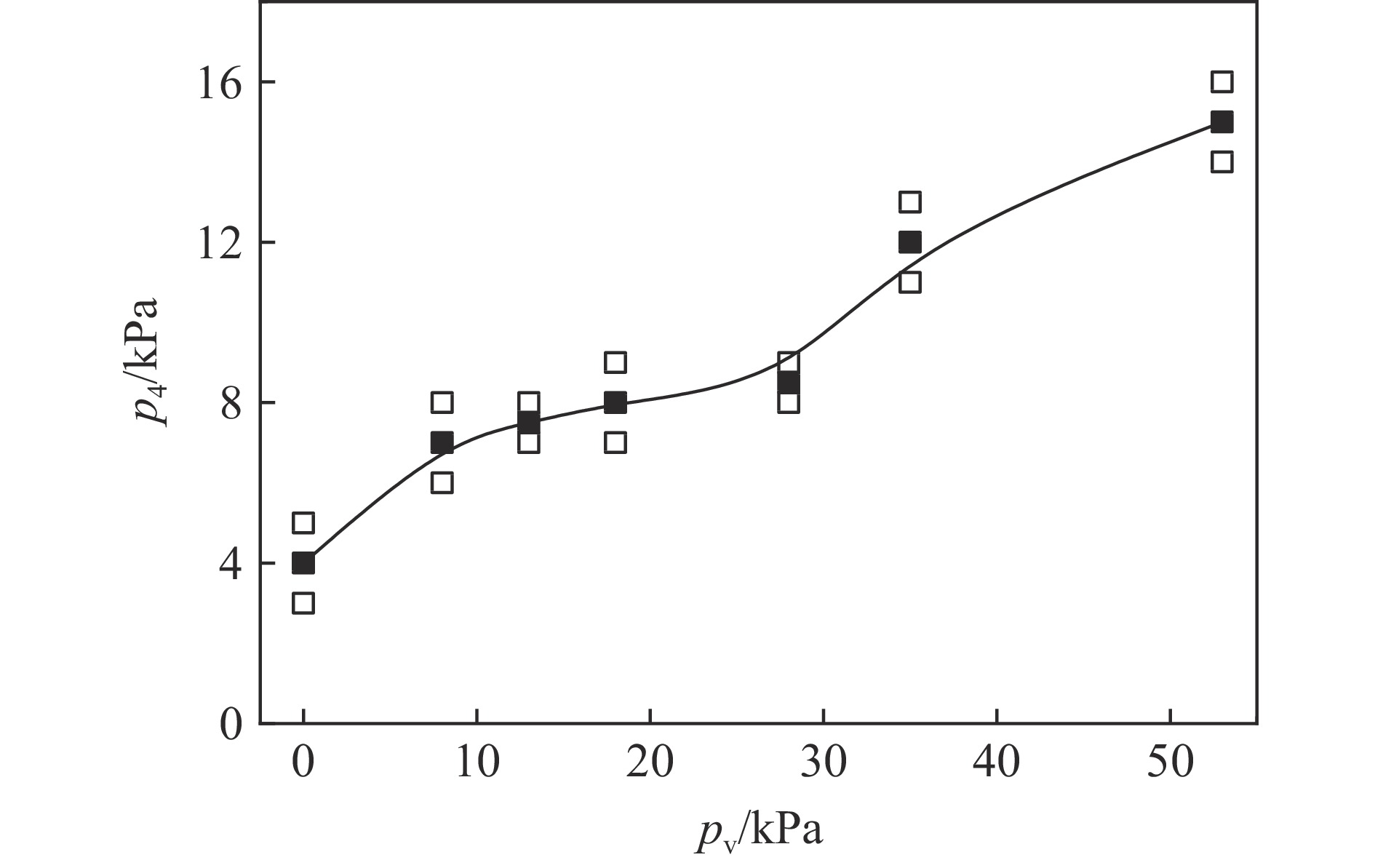
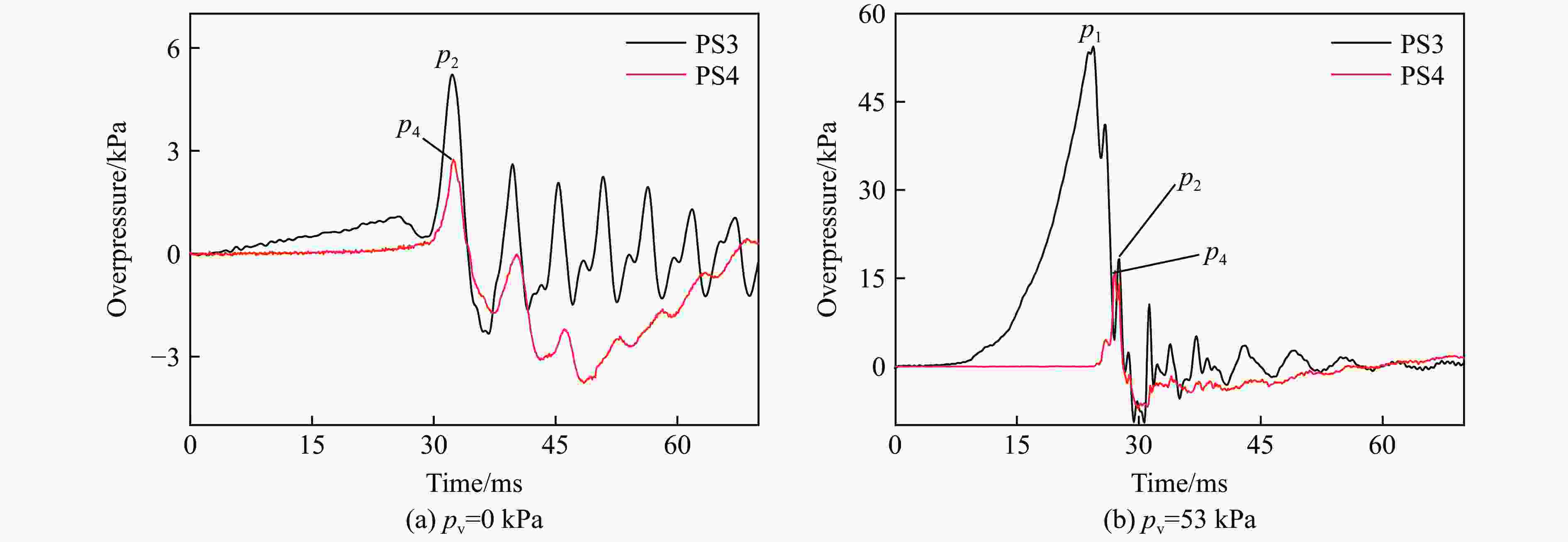
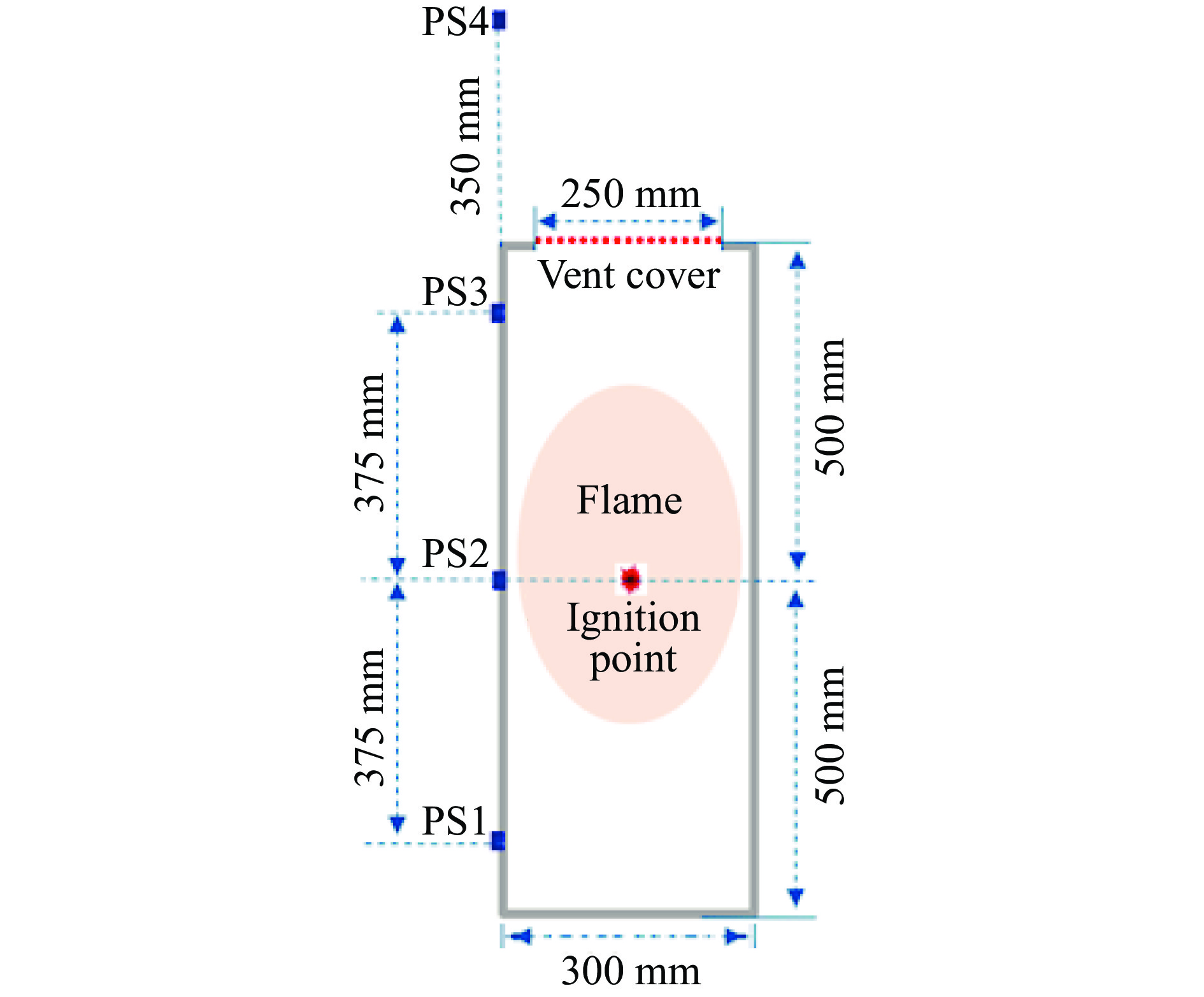
| [1] |
HUANG Z H, ZHANG Y, ZENG K, et al. Measurements of laminar burning velocities for natural gas–hydrogen–air mixtures [J]. Combustion and Flame, 2006, 146(1/2): 302–311. DOI: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2006.03.003.
|
| [2] |
HU E J, HUANG Z H, HE J J. et al. Experimental and numerical study on lean premixed methane-hydrogen-air flames at elevated pressures and temperatures [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2009, 34(16): 6951–6960. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2009.06.072.
|
| [3] |
LI Y C, BI M S, LI B, et al. Effects of hydrogen and initial pressure on flame characteristics and explosion pressure of methane/hydrogen fuels [J]. Fuel, 2018, 233: 269–282. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.06.042.
|
| [4] |
ZHENG K, YU M G, ZHENG L G, et al. Experimental study on premixed flame propagation of hydrogen/methane/air deflagration in closed ducts [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(8): 5426–5438. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.10.106.
|
| [5] |
王亚磊, 郑立刚, 于水军, 等. 约束端面对管内甲烷爆炸特性的影响 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2019, 39(9): 095401. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0249.WANG Y L, ZHENG L G, YU S J, et al. Effect of vented end faces on characteristics of methane explosion in duct [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2019, 39(9): 095401. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0249.
|
| [6] |
叶经方, 姜孝海, 贾正望, 等. 泄爆诱导二次爆炸的实验研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2004, 24(4): 356–362.YE J F, JIANG X H, JIA Z W, et al. Experimental investigations of external second-explosion induced by vented explosion [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2004, 24(4): 356–362.
|
| [7] |
MA Q J, ZHANG Q, CHEN J C, et al. Effects of hydrogen on combustion characteristics of methane in air [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39(21): 11291–11298. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2014.05.030.
|
| [8] |
胡俊, 万士昕, 浦以康, 等. 柱形容器开口泄爆过程中的火焰传播特性 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2004, 24(4): 330–336.HU J, WAN S X, PU Y K, et al. The characteristics of flame propagation during explosion venting from cylindrical vessel [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2004, 24(4): 330–336.
|
| [9] |
李乾, 冯梦梦, 马力, 等. 不同泄压条件对方管内爆炸压力特性的影响 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2019, 39(7): 072202. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0132.LI Q, FENG M M, MA L, et al. Influence of different pressure relief conditions on explosion pressure in square pipeline [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2019, 39(7): 072202. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0132.
|
| [10] |
孙玮, 王志荣, 马龙生, 等. 连通容器泄爆过程的影响因素 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2016, 36(4): 457–464. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2016)04-0457-08.SUN W, WANG Z R, MA L S, et al. Influence factors of gas explosion venting in linked vessels [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2016, 36(4): 457–464. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2016)04-0457-08.
|
| [11] |
YU M G, ZHENG K, ZHENG L G, et al. Effects of hydrogen addition on propagation characteristics of premixed methane/air flames [J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2015, 34: 1–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.jlp.2015.01.017.
|
| [12] |
YU M G, ZHENG K, ZHENG L G, et al. Scale effects on premixed flame propagation of hydrogen/methane deflagration [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40(38): 13121–13133. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.07.143.
|
| [13] |
WANG J, WU Y, SHAN W W, et al. Effect of variable cross-section duct on flame propagation characteristics of premixed hydrogen/methane/air combustible gas [J]. Combustion Science and Technology, 2021, 193(8): 1425–1443. DOI: 10.1080/00102202.2019.1697244.
|
| [14] |
ZHENG K, YU M G, ZHENG L G, et al. Effects of hydrogen addition on methane–air deflagration in obstructed chamber [J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2017, 80: 270–280. DOI: 10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2016.08.025.
|
| [15] |
LOWESMITH B J, MUMBY C, HANKINSON G, et al. Vented confined explosions involving methane/hydrogen mixtures [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2011, 36(3): 2337–2343. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2010.02.084.
|
| [16] |
SHIRVILL L C, ROBERTS T A, ROYLE M, et al. Experimental study of hydrogen explosion in repeated pipe congestion: Part 2: effects of increase in hydrogen concentration in hydrogen-methane-air mixture [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(5): 3264–3276. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.12.021.
|
| [17] |
YANG J, GUO J, WANG C H, et al. Effect of equivalence ratio on hydrogen-methane-air deflagration in a duct with an open end [J]. Fuel, 2020, 280: 118694. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.118694.
|
| [18] |
DUAN Z P, GUO J, WANG X B, et al. Experiments on vented deflagration of stoichiometric hydrogen-methane-air mixtures: effect of hydrogen fraction [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(46): 25615–25622. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.06.286.
|
| [19] |
RUDY W, ZBIKOWSKI M, TEODORCZYK A. Detonations in hydrogen-methane-air mixtures in semi confined flat channels [J]. Energy, 2016, 116: 1479–1483. DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2016.06.001.
|
| [20] |
曹勇, 郭进, 胡坤伦, 等. 点火位置对氢气-空气预混气体泄爆过程的影响 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2016, 36(6): 847–852. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2016)06-0847-06.CAO Y, GUO J, HU K L, et al. Effect of ignition locations on vented explosion of premixed hydrogen-air mixtures [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2016, 36(6): 847–852. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2016)06-0847-06.
|
| [21] |
GUO J, WANG C J, LI Q, et al. Effect of the vent burst pressure on explosion venting of rich methane–air mixtures in a cylindrical vessel [J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2016, 40: 82–88. DOI: 10.1016/j.jlp.2015.12.006.
|
| [22] |
RUI S C, GUO J, LI G, et al. The effect of vent burst pressure on a vented hydrogen–air deflagration in a 1 m3 vessel [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43(45): 21169–21176. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.09.124.
|
| [23] |
孙松, 王明洋, 高康华, 等. 大尺度泄爆构件对室内爆燃压力影响的实验研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2018, 38(2): 359–366. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2016-0211.SUN S, WANG M Y, GAO K H, et al. Experimental study on effect of large-scale explosion venting component on interior deglagration pressure [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2018, 38(2): 359–366. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2016-0211.
|
| [24] |
American National Standards Institute. NFPA 68 Standard on explosion protection by deflagration venting [S]. Quincy: National Fire Protection Association, 2007.
|
| [25] |
KUZNETSOV M, FRIEDRICH A, STERN G, et al. Medium-scale experiments on vented hydrogen deflagration [J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2015, 36: 416–428. DOI: 10.1016/j.jlp.2015.04.013.
|
| [26] |
GUO J, WANG C J, LIU X Y. Experimental study on duct-vented explosion of hydrogen–air mixtures in a wide range of equivalence ratio [J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2016, 55(35): 9518–9523. DOI: 10.1021/acs.iecr.6b02029.
|
| [27] |
PROUST C, LEPRETTE E. The dynamics of vented gas explosions [J]. Process Safety Progress, 2010, 29(3): 231–235. DOI: 10.1002/prs.10368.
|
| [28] |
WANG J G, GUO J, YANG F Q, et al. Effects of hydrogen concentration on the vented deflagration of hydrogen–air mixtures in a 1-m3 vessel [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43(45): 21161–21168. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.09.108.
|
| [29] |
BAUWENS C R L, CHAFFEE J, DOROFEEV S A. Experimental and numerical study of methane–air deflagrations in a vented enclosure [J]. Fire Safety Science, 2009, 9: 1043–1054. DOI: 10.3801/iafss.fss.9-1043.
|
| [30] |
LI Q Q, HU E J, CHENG Y, et al. Measurements of laminar flame speeds and flame instability analysis of 2-methyl-1-butanol-air mixtures [J]. Fuel, 2013, 112: 263–271. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2013.05.039.
|
| [31] |
BAUWENS C R, CHAFFEE J, DOROFEEV S. Effect of instabilities and acoustics on pressure generated in vented propane-air explosions [C]// Proceedings of the 22nd International Colloquium on the Dynamics of Explosions and Reactive Systems. Minsk, Belarus, 2009.
|
| [32] |
MCCANN D P J, THOMAS G O, EDWARDS D H. Gasdynamics of vented explosions Part I: experimental studies [J]. Combustion and Flame, 1985, 59(3): 233–250. DOI: 10.1016/0010-2180(85)90128-2.
|
| [33] |
COOPER M G, FAIRWEATHER M, TITE J P. On the mechanisms of pressure generation in vented explosions [J]. Combustion and Flame, 1986, 65(1): 1–14. DOI: 10.1016/0010-2180(86)90067-2.
|
| [34] |
BAO Q, FANG Q, ZHANG Y D, et al. Effects of gas concentration and venting pressure on overpressure transients during vented explosion of methane–air mixtures [J]. Fuel, 2016, 175: 40–48. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.01.084.
|
| [35] |
TOMLIN G, JOHNSON D M, CRONIN P, et al. The effect of vent size and congestion in large-scale vented natural gas/air explosions [J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2015, 35: 169–181. DOI: 10.1016/j.jlp.2015.04.014.
|
| [36] |
曹勇. 点火位置对氢气-空气泄爆特性影响的实验研究 [D]. 淮南: 安徽理工大学, 2016: 27–38.CAO Y. Effect of ignition locations on vented explosion characteristic of premixed hydrogen-air mixtures [D]. Huainan: Anhui University of Science & Technology, 2016: 27–38.
|










 下载:
下载: