Study on the scaling law of geometrically-distorted thin-walled cylindrical shells subjected to axial impact
-
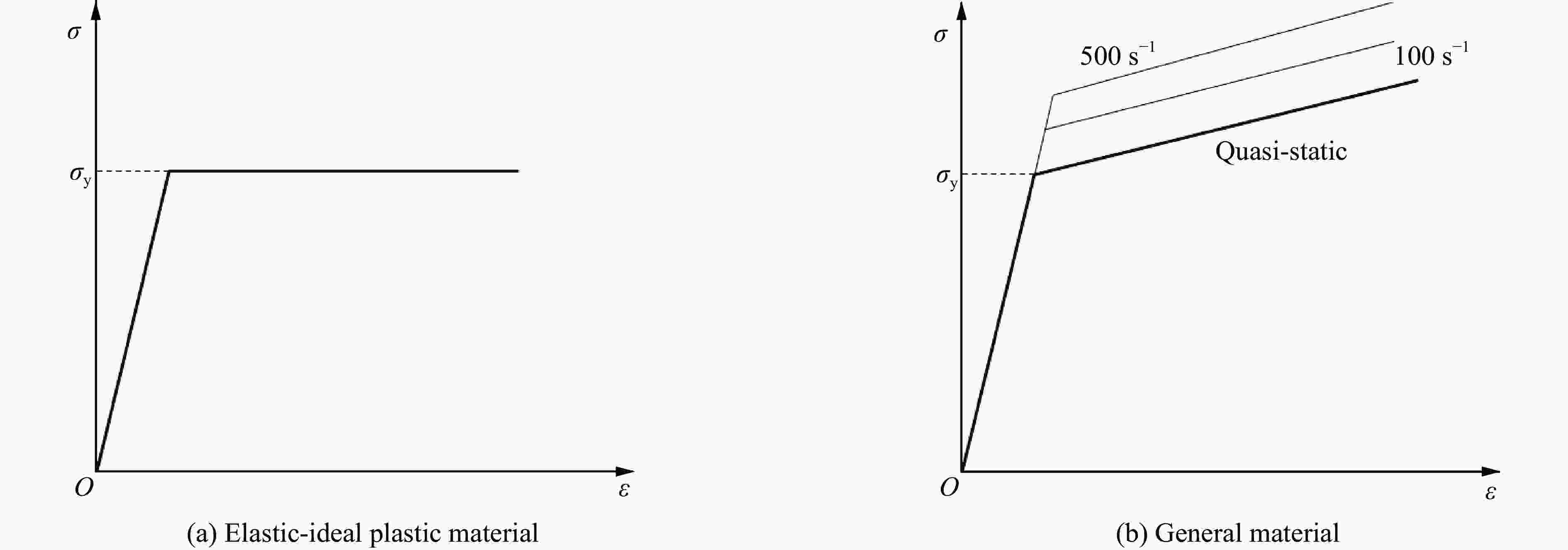
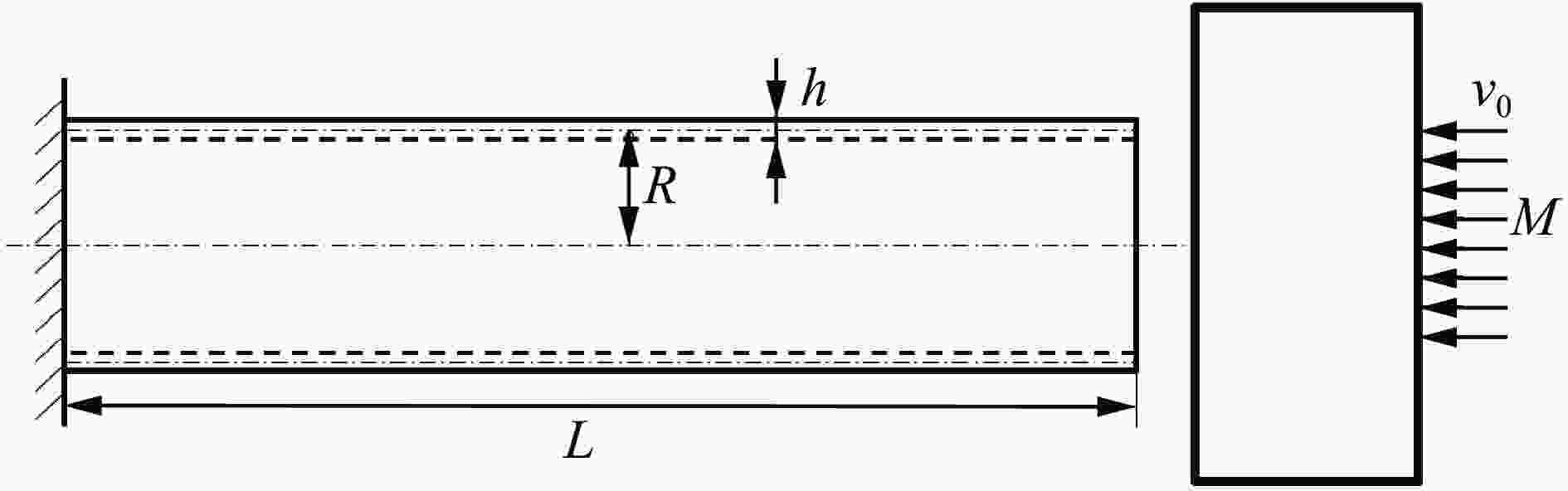
摘要: 对于受轴向冲击载荷作用的薄壁圆管动态响应的相似律问题,由于圆管的薄壁特性导致厚度无法与高度和半径按相同的比例进行结构缩放,从而产生模型的几何畸变,此时传统的相似律已无法描述原型与畸变模型之间的动态响应规律。基于薄壁圆管轴向冲击问题的控制方程,通过能量守恒和量纲分析,推导了考虑几何畸变条件下轴向冲击载荷作用的理想弹塑性薄壁圆管动态响应的相似律。通过在给定应变与应变率区间上建立比例模型预测的流动屈服应力与原型流动屈服应力的最佳逼近关系,将几何畸变相似律进一步推广至包含应变率和应变硬化的材料。通过数值方法验证了提出的几何畸变模型相似律的适用性。分析结果表明,提出的考虑厚度畸变的受轴向冲击薄壁圆管的相似律可用于预测原型结构的冲击动态响应,并显著降低比例模型与原型结构平均载荷和能量的偏差。Abstract: In scaling the dynamic responses of thin-walled cylindrical shells subjected to axial impact loading, the thickness cannot be adjusted according to the same scale as the radius and height due to the thin wall characteristics. Hence, geometrically-distorted models would be used, and the traditional scaling law cannot describe the relationship between the dynamic responses of the prototype and the geometrically-distorted model. In this paper, the scaling law for this case was derived for elastic-ideal plastic thin-walled cylindrical shells under axial impact loading. For strain hardening and strain-rate hardening material, based on the average load, deformation energy, and displacement of the shell in the axisymmetric deformation mode, the dimensionless numbers of three key design parameters, namely the stress, mass, and displacement, were obtained through the law of energy conservation. Then, the optimal approximation of the flow stress predicted by the distorted scaled model to the flow stress of the prototype was established on a given strain and strain rate interval. In this way, the derived scaling law can be applied to the case considering the coupling effects of geometric distortion, strain-rate sensitivity, and strain hardening. Finally, several finite element models of thin-walled cylindrical shell models subject to axial mass impact were established. These models use the elastic-ideal plastic material model and the general material model with strain-rate hardening and strain hardening effects. The modified impact velocity and impact mass were obtained by the present method using the geometrically-distorted model, which verified the effectiveness and correctness of the proposed scaling law. The results show that the geometrically distorted model corrected by the method proposed in this article can quite accurately predict the dynamic responses of the prototype, and significantly reduce the errors in the dynamic responses of the thin-walled cylindrical shell subjected to axial impact loading, especially the average load and deformation energy.
-
变量 比例因子 变量 比例因子 长度L[10] $\ \beta = {L_{\rm{m}}}/{L_{\rm{p}}}$ 位移δ[10] $\ {\beta _\delta } = \beta $ 密度ρ[10] $\ {\beta _\rho } = {\rho _{\rm{m}}}/{\rho _{\rm{p}}}$ 应力${\sigma _{\rm{d}}}$[10] $\ {\beta _{{\sigma _{\rm{d}}}}} = {\beta _\rho }\beta _v^2$ 速度v[10] $\ {\beta _v} = {v_{\rm{m}}}/{v_{\rm{p}}}$ 应变ε[10] $\ {\beta _\varepsilon } = 1$ 质量m[10] $\ {\beta _{{m} } } = {\beta _\rho }{\beta ^3}$ 应变率$\dot \varepsilon $[10] $\ {\beta _{\dot \varepsilon }} = {\beta _v}/\beta $ 时间t[10] $\ {\beta _{{t} } } = \beta /{\beta _v}$ 载荷P[11] $\ {\beta _{{P} } } = {\beta _\rho }{\beta ^2}\beta _v^2$ 加速度a[10] $\ {\beta _a} = \beta _v^2/\beta $ 动能Ek[11] $\ {\beta _{ {E_{\rm{k}}} } } = {\beta _\rho }{\beta ^3}\beta _v^2$ 表 2 受轴向冲击的理想弹塑性薄壁圆管比例因子
Table 2. Scaling factors of the elastic-ideal plastic thin-walled cylindrical shell under axial impact loading
变量 比例因子 变量 比例因子 长度L $\ \beta = {L_{\rm{m}}}/{L_{\rm{p}}}$ 位移δ $\ {\beta _\delta } = \beta $ 密度ρ $\ {\beta _\rho } = {\rho _{\rm{m}}}/{\rho _{\rm{p}}}$ 应力${\sigma _{\rm{d}}}$ $\ {\beta _{{\sigma _{\rm{d}}}}} = {\beta _\rho }\beta _v^2\sqrt {\beta /{\beta _{\rm{h}}}} $ 速度v $\ {\beta _v} = {v_{\rm{m}}}/{v_{\rm{p}}}$ 应变ε $\ {\beta _\varepsilon } = \sqrt {{\beta _h}/\beta } $ 质量m $\ {\beta _{{m} } } = {\beta _\rho }{\beta ^2}{\beta _h} $ 应变率$\dot \varepsilon $ $\ {\beta _{\dot \varepsilon }} = \left( {{\beta _v}/\beta } \right)\sqrt {{\beta _L}/{\beta _h}} $ 时间t $\ {\beta _{{t} } } = \beta /{\beta _v}$ 载荷P $\ {\beta _{{P} } } = {\beta _\rho }\beta {\beta _h}\beta _v^2$ 加速度 a $\ {\beta _a} = \beta _v^2/\beta $ 动能Ek $\ {\beta _{E_{\rm{k} } } } = {\beta _\rho }{\beta _h}{\beta ^2}\beta _v^2$ ρ/(g∙cm−3) E/GPa μ A/MPa B/MPa C n ${\dot \varepsilon _0}/\text{s}^{-1}$ 7.89 207 0.3 350 275 0.022 0.36 1 表 4 理想弹塑性模型几何畸变比例因子
Table 4. Scaling factors of geometrically-distorted models of elastic-ideal plastic material
$\ \beta $ η ${\ \beta _h}$ ${\ \beta _M}$ ${\ \beta _v}$ ${\ \beta _t}$ ${\ \beta _P}$ ${\ \beta _\delta }$ ${\ \beta _\varepsilon }$ 0.1 1.2 0.12 0.12 1.0466 0.0955 0.0131 0.1 1.0954 0.1 1.5 0.15 0.15 1.1067 0.0904 0.0184 0.1 1.2247 0.1 1.8 0.18 0.18 1.1583 0.0863 0.0241 0.1 1.3416 0.1 2.0 0.20 0.20 1.1892 0.0841 0.0283 0.1 1.4142 表 5 考虑应变率效应和应变硬化效应几何畸变模型比例因子
Table 5. Scaling factors of geometrically-distorted models considering strain-rate sensitivity and strain hardening
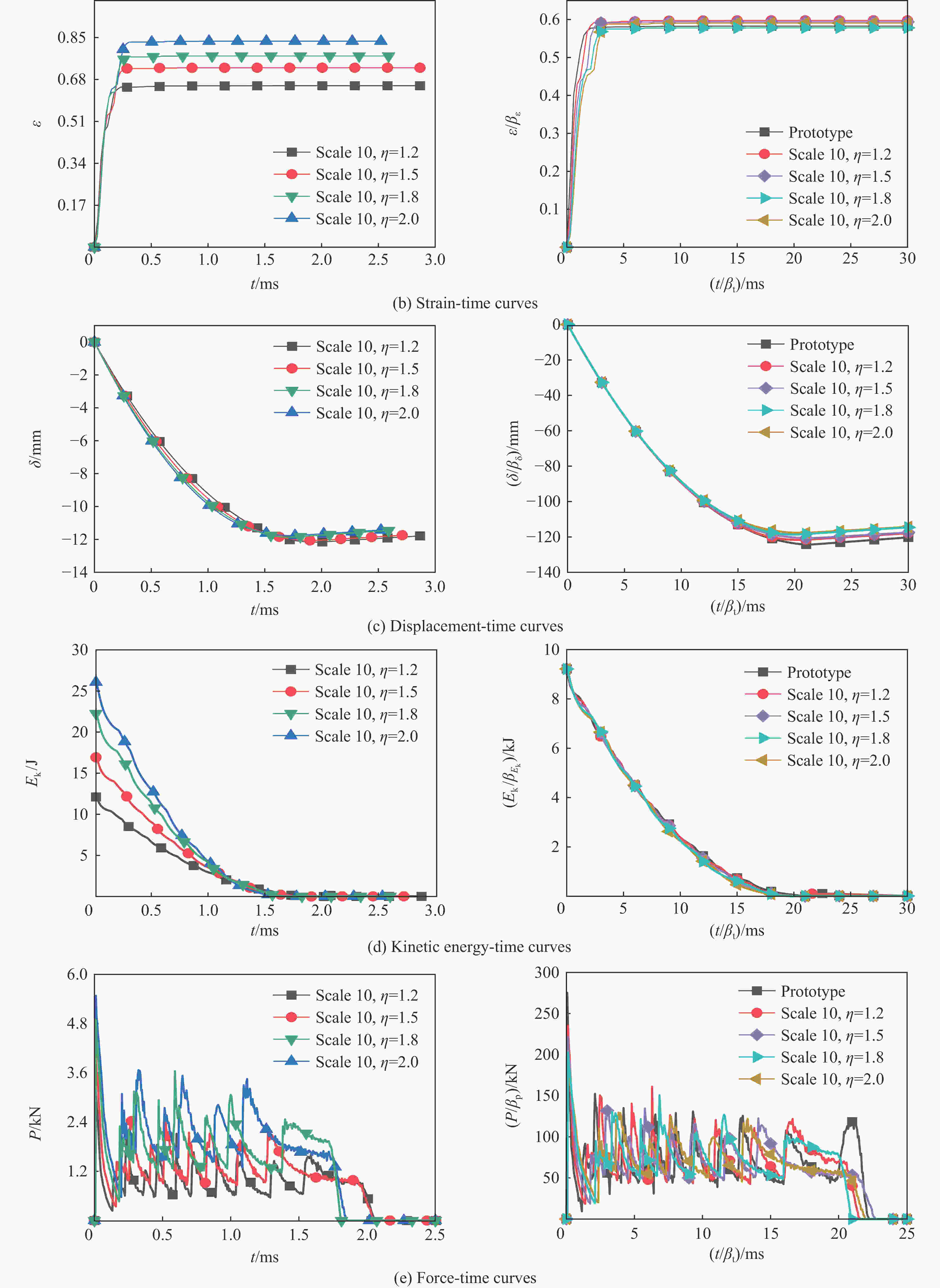
$\ \beta $ η ${\ \beta _h}$ ${\ \beta _M}$ ${\ \beta _v}$ ${\ \beta _t}$ ${\ \beta _P}$ ${\ \beta _\delta }$ ${\ \beta _\varepsilon }$ 0.1 1.2 0.12 0.12 1.0756 0.0930 0.0139 0.1 1.0954 0.1 1.5 0.15 0.15 1.1442 0.0874 0.0196 0.1 1.2247 0.1 1.8 0.18 0.18 1.2038 0.0831 0.0261 0.1 1.3416 0.1 2.0 0.20 0.20 1.2396 0.0807 0.0306 0.1 1.4142 表 6 比例模型与原型的峰值位移和平均载荷相对误差
Table 6. Relative errors in the peak displacement and average force between the scale models and prototype
模型 (δ/βδ)/mm 相对误差/% (P/βP)/kN 相对误差/% 原型 124.258 − 71.95 − β=1/10, η=1.2 121.669 2.084 73.43 2.057 β=1/10, η=1.5 120.651 2.903 69.48 3.433 β=1/10, η=1.8 118.642 4.520 75.85 5.420 β=1/10, η=2.0 117.678 5.295 72.25 0.417 表 7 考虑应变率与应变硬化效应的比例模型位移与平均载荷相对误差
Table 7. Relative errors in the peak displacement and average force of the scaled models considering strain-rate sensitivity and strain hardening
模型 (δ/βδ) /mm 相对误差/% (P/βP)/kN 相对误差/% 原型 90.740 − 97.79 − β=1/10, η=1.2 89.619 1.235 98.42 0.644 β=1/10, η=1.5 89.222 1.673 99.47 1.718 β=1/10, η=1.8 86.201 5.002 101.06 3.344 β=1/10, η=2.0 86.232 4.968 105.14 7.516 -
[1] JONES N. Structural impact [M]. 2nd ed. New York: Cambridge University Press, 2012. [2] 徐海斌, 张德志, 谭书舜, 等. 轴向压缩的金属薄壁圆管相似律的实验研究 [C] // 第20届全国结构工程学术会议论文集. 浙江宁波: 中国力学学会工程力学编辑部, 2011: 554–559. [3] ALEXANDER J M. An approximate analysis of the collapse of thin cylindrical shells under axial loading [J]. The Quarterly Journal of Mechanics and Applied Mathematics, 1960, 13(1): 10–15. DOI: 10.1093/qjmam/13.1.10. [4] ABRAMOWICZ W, JONES N. Dynamic axial crushing of circular tubes [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1984, 2(3): 263–281. DOI: 10.1016/0734-743X(84)90010-1. [5] KARAGIOZOVA D, JONES N. Influence of stress waves on the dynamic progressive and dynamic plastic buckling of cylindrical shells [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2001, 38(38/39): 6723–6749. DOI: 10.1016/S0020-7683(01)00111-1. [6] KARAGIOZOVA D, NURICK G N, YUEN S C K. Energy absorption of aluminium alloy circular and square tubes under an axial explosive load [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2005, 43(6): 956–982. DOI: 10.1016/j.tws.2004.11.002. [7] LU G, YU J L, ZHANG J J, et al. Alexander revisited: upper- and lower-bound approaches for axial crushing of a circular tube [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2021, 206: 106610. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2021.106610. [8] CASABURO A, PETRONE G, FRANCO F, et al. A review of similitude methods for structural engineering [J]. Applied Mechanics Reviews, 2019, 71(3): 030802. DOI: 10.1115/1.4043787. [9] COUTINHO C P, BAPTISTA A J, RODRIGUES J D. Reduced scale models based on similitude theory: a review up to 2015 [J]. Engineering Structures, 2016, 119: 81–94. DOI: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2016.04.016. [10] OSHIRO R E, ALVES M. Scaling impacted structures [J]. Archive of Applied Mechanics, 2004, 74(1/2): 130–145. DOI: 10.1007/BF02637214. [11] OSHIRO R E, ALVES M. Scaling of cylindrical shells under axial impact [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2007, 34(1): 89–103. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2006.02.003. [12] 王帅, 徐绯, 代震, 等. 结构冲击畸变问题的直接相似方法研究 [J]. 力学学报, 2020, 52(3): 774–786. DOI: 10.6052/0459-1879-19-327.WANG S, XU F, DAI Z, et al. A direct scaling method for the distortion problems of structural impact [J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2020, 52(3): 774–786. DOI: 10.6052/0459-1879-19-327. [13] WANG S, XU F, ZHANG X Y, et al. Material similarity of scaled models [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2021, 156: 103951. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2021.103951. [14] 李肖成, 徐绯, 杨磊峰, 等. 薄板在冲击载荷下线弹性理想塑性响应的相似性研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2021, 41(11): 113103. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0374.LI X C, XU F, YANG L F, et al. Study on the similarity of elasticity and ideal plasticity response of thin plate under impact loading [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2021, 41(11): 113103. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0374. [15] 秦健, 张振华. 原型和模型不同材料时加筋板冲击动态响应的相似预报方法 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2010, 30(5): 511–516. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2010)05-0511-06.QIN J, ZHANG Z H. A scaling method for predicting dynamic responses of stiffened plates made of materials different from experimental models [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2010, 30(5): 511–516. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2010)05-0511-06. [16] ALVES M, OSHIRO R E, CALLE M A G, et al. Scaling and structural impact [J]. Procedia Engineering, 2017, 173: 391–396. DOI: 10.1016/j.proeng.2016.12.036. [17] MAZZARIOL L M, ALVES M. Similarity laws of structures under impact load: geometric and material distortion [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2019, 157/158: 633–647. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2019.05.011. [18] WANG S, XU F, DAI Z. Suggestion of the DLV dimensionless number system to represent the scaled behavior of structures under impact loads [J]. Archive of Applied Mechanics, 2020, 90(4): 707–719. DOI: 10.1007/s00419-019-01635-9. [19] WANG S, XU F, ZHANG X Y, et al. A directional framework of similarity laws for geometrically distorted structures subjected to impact loads [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2022, 161: 104092. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2021.104092. [20] 李志斌, 虞吉林, 郑志军, 等. 薄壁管及其泡沫金属填充结构耐撞性的实验研究 [J]. 实验力学, 2012, 27(1): 77–86.LI Z B, YU J L, ZHENG Z J, et al. An experimental study on the crashworthiness of thin-walled tubes and their metallic foam-filled structures [J]. Journal of Experimental Mechanics, 2012, 27(1): 77–86. [21] 朱文波, 杨黎明, 余同希. 薄壁圆管轴向冲击下的动态特性研究 [J]. 宁波大学学报(理工版), 2014, 27(2): 92–96.ZHU W B, YANG L M, YU T X. Study on dynamic properties of thin-walled circular tubes under axial compression [J]. Journal of Ningbo University (Natural Science & Engineering Edition), 2014, 27(2): 92–96. [22] 余同希, 卢国兴, 张雄. 能量吸收: 结构与材料的力学行为和塑性分析 [M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019. [23] 白以龙, 黄筑平, 虞吉林, 等. 材料和结构的动态响应 [M]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社, 2005. [24] JOHNSON G R, COOK W H. A constitutive model and data for metals subjected to large strains, high strain rates and high temperatures [C] // Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Ballistics. Hague, Netherlands, 1983: 541–547. -






 下载:
下载: