Maximum stiffness topology optimization and dynamic response of a lightweight sandwich arch under impact load
-
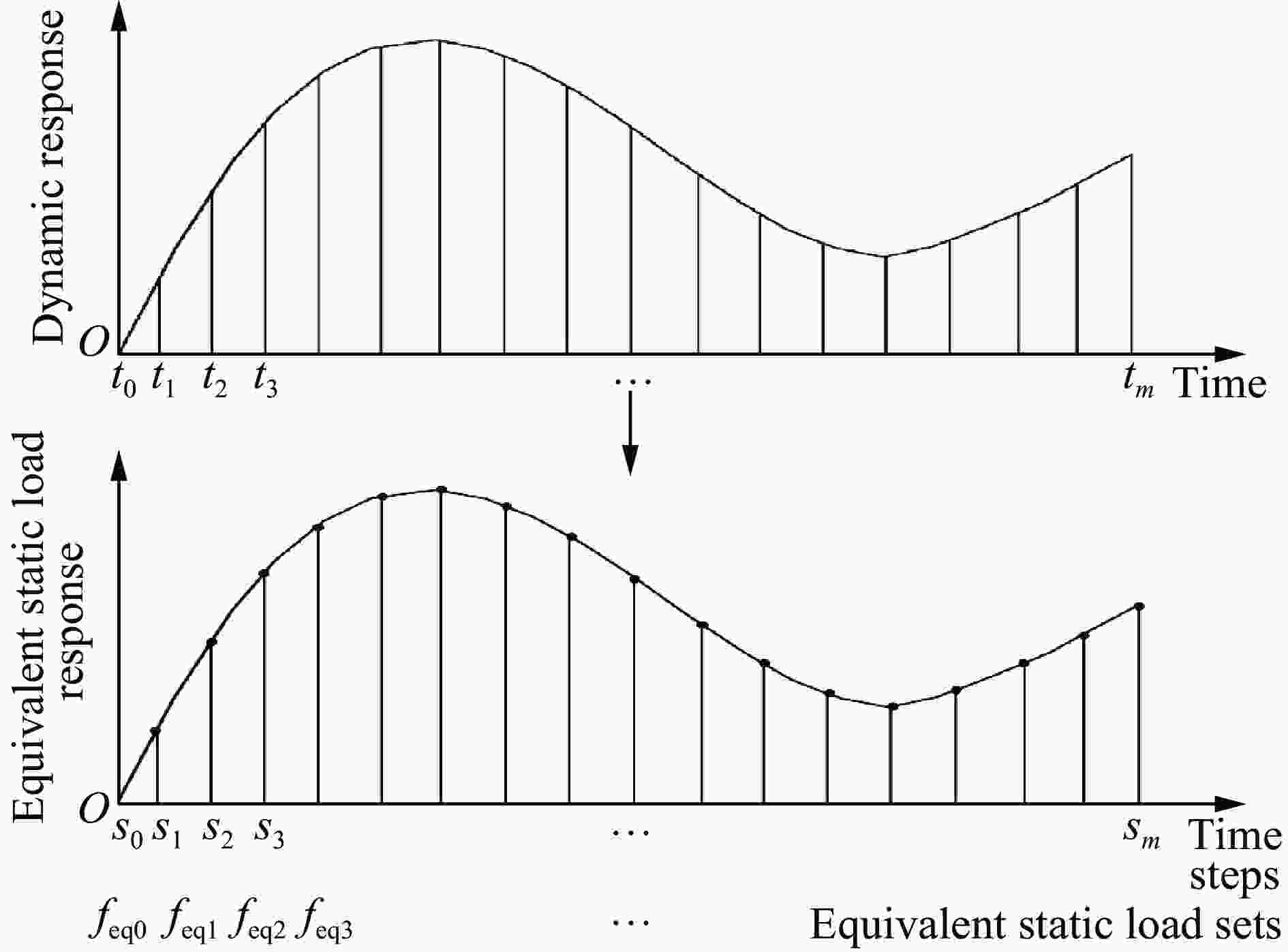
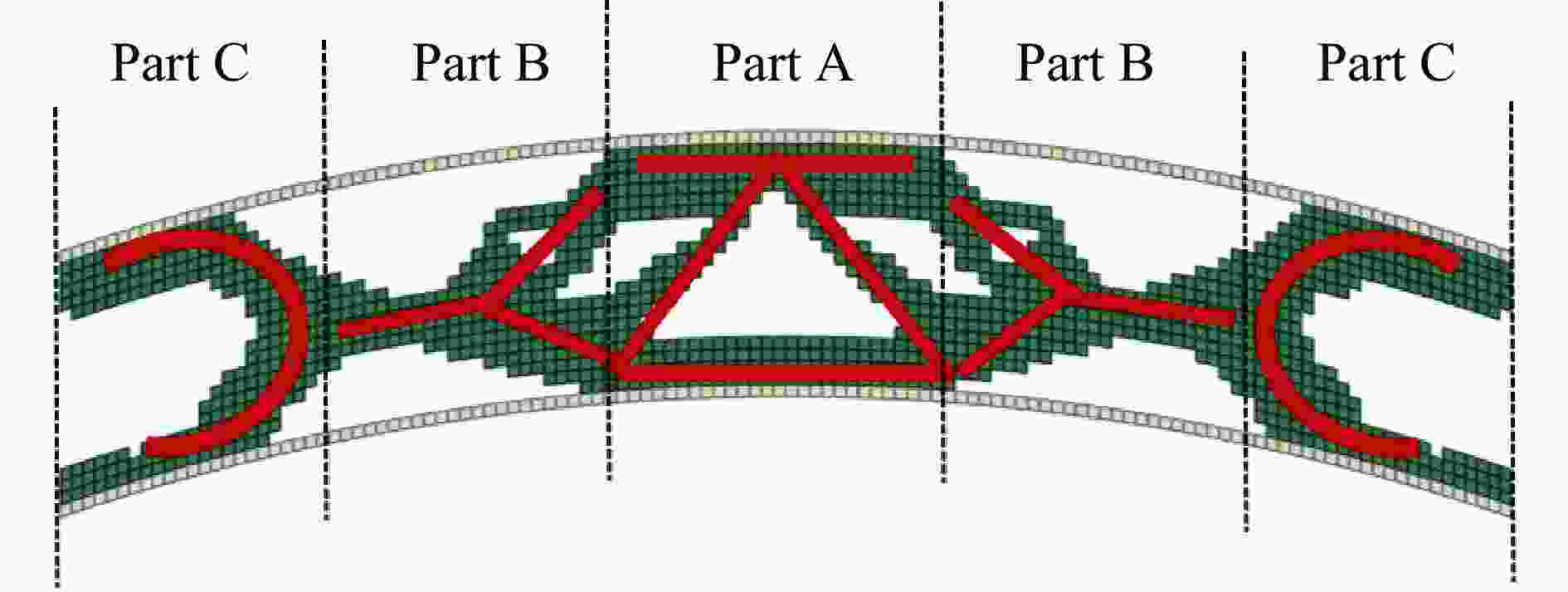
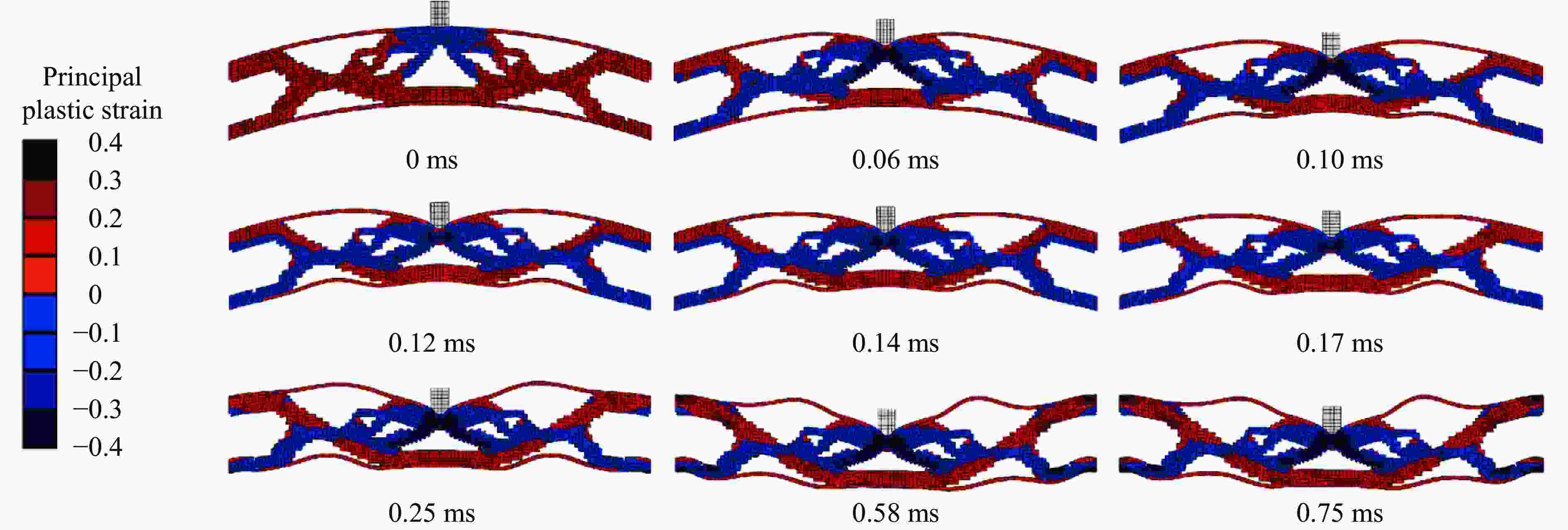
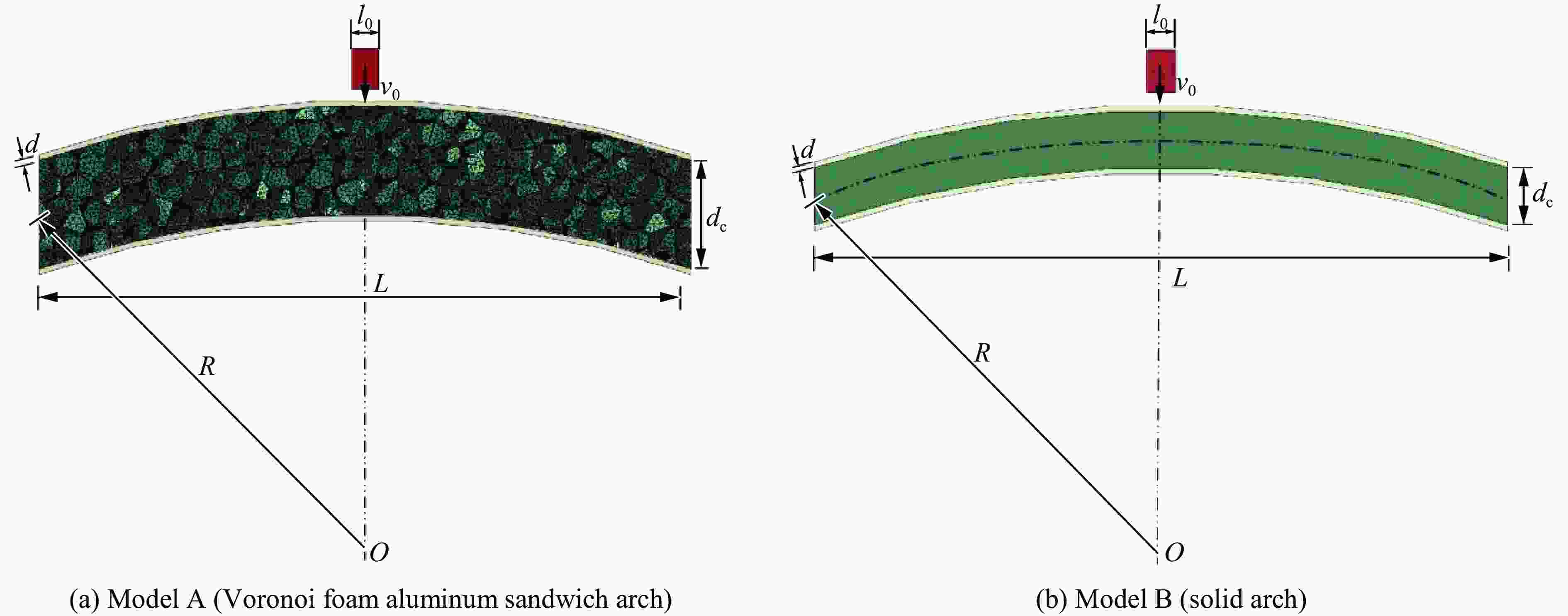
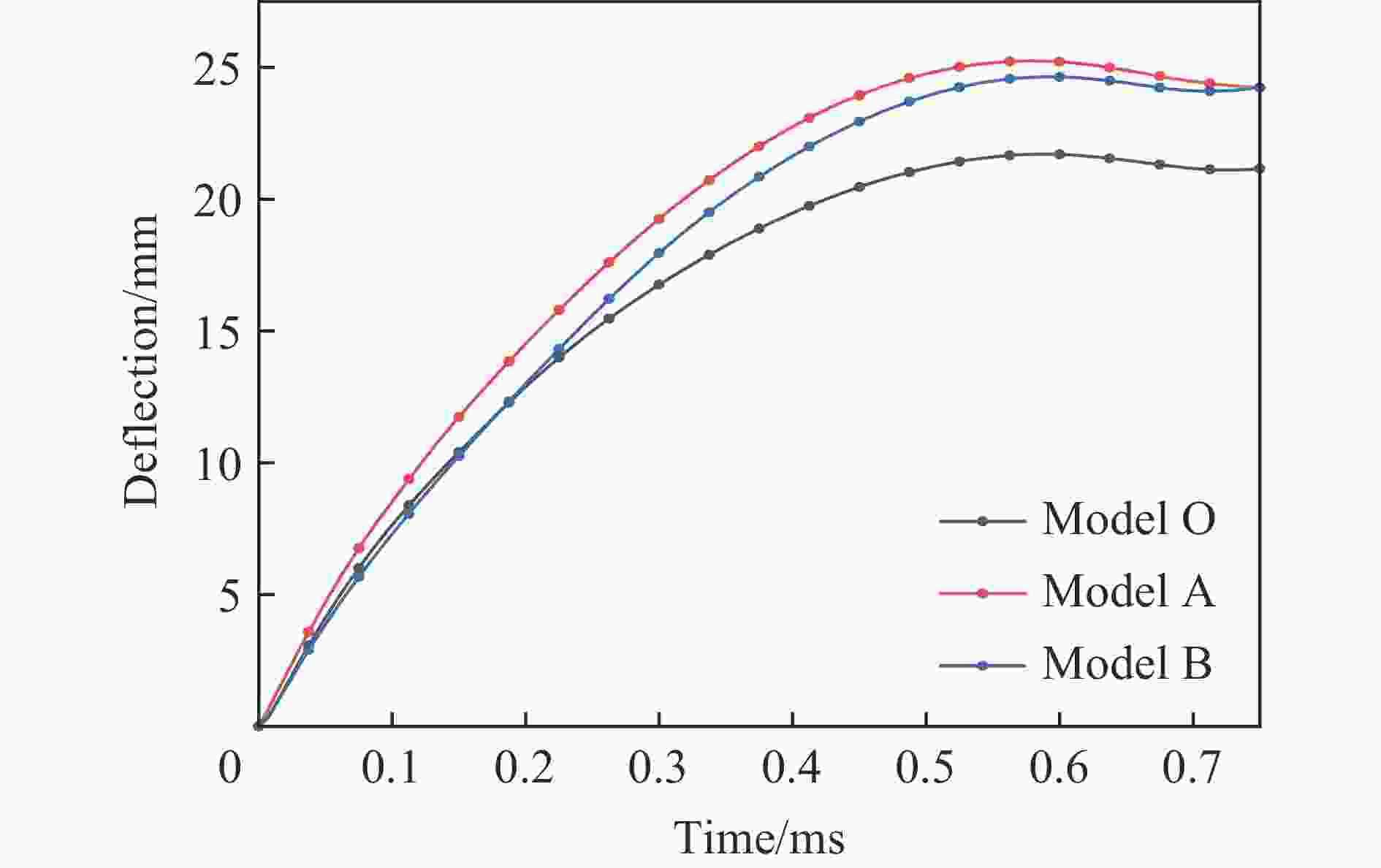
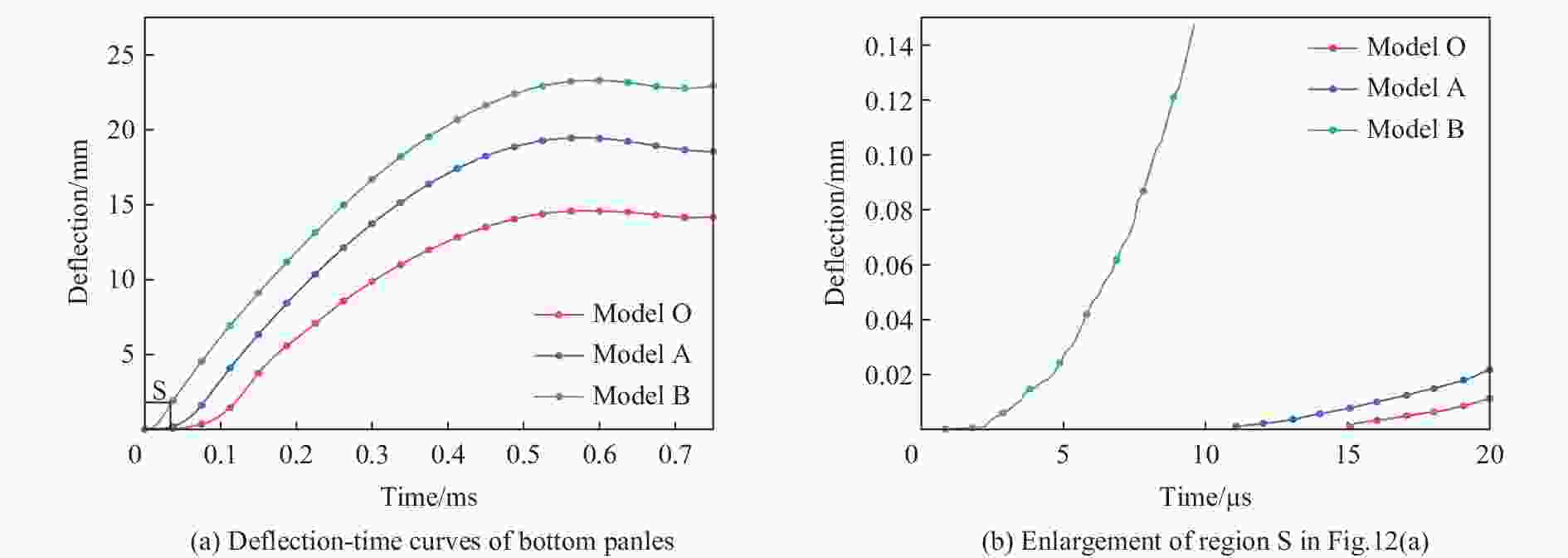
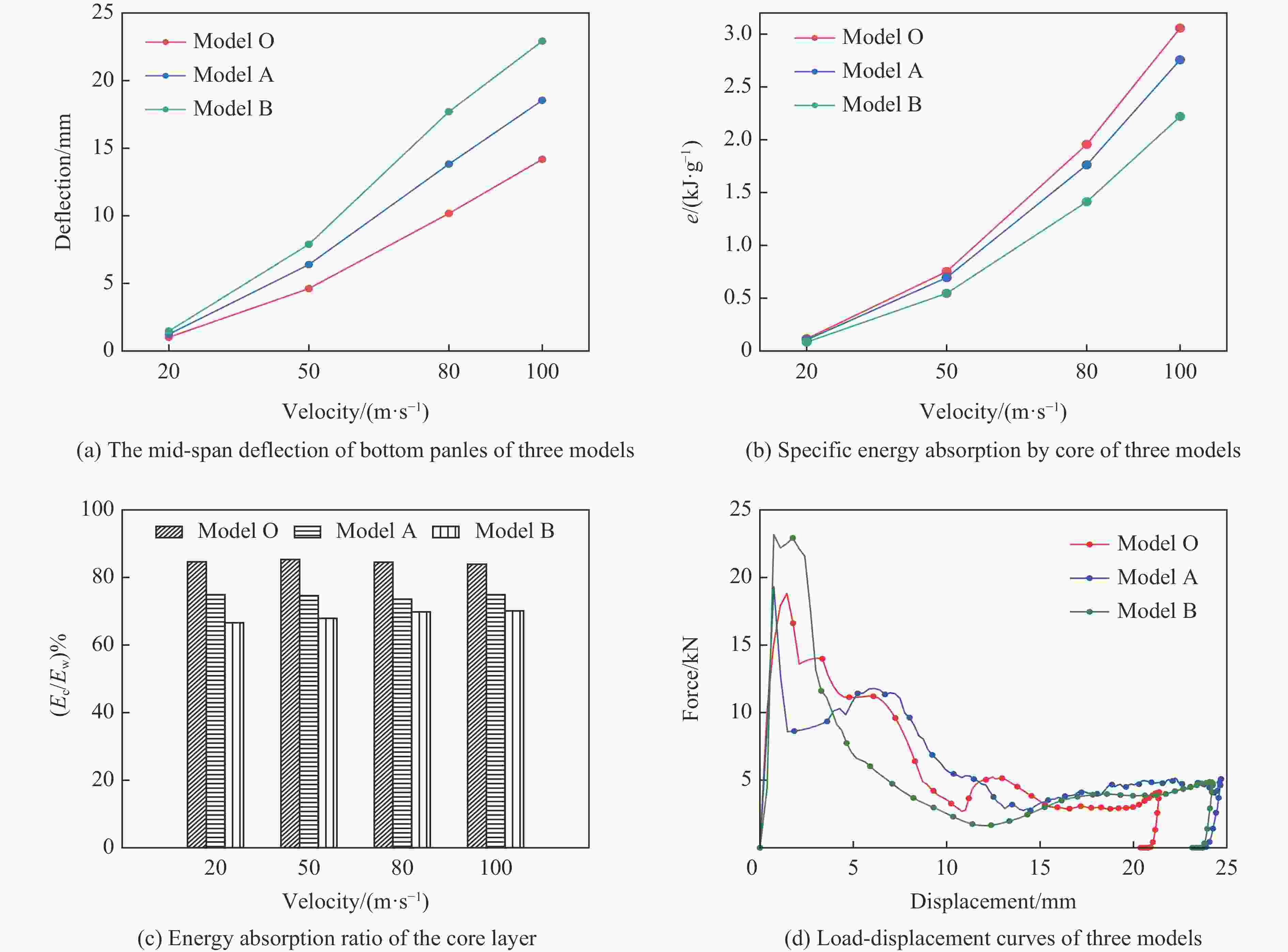
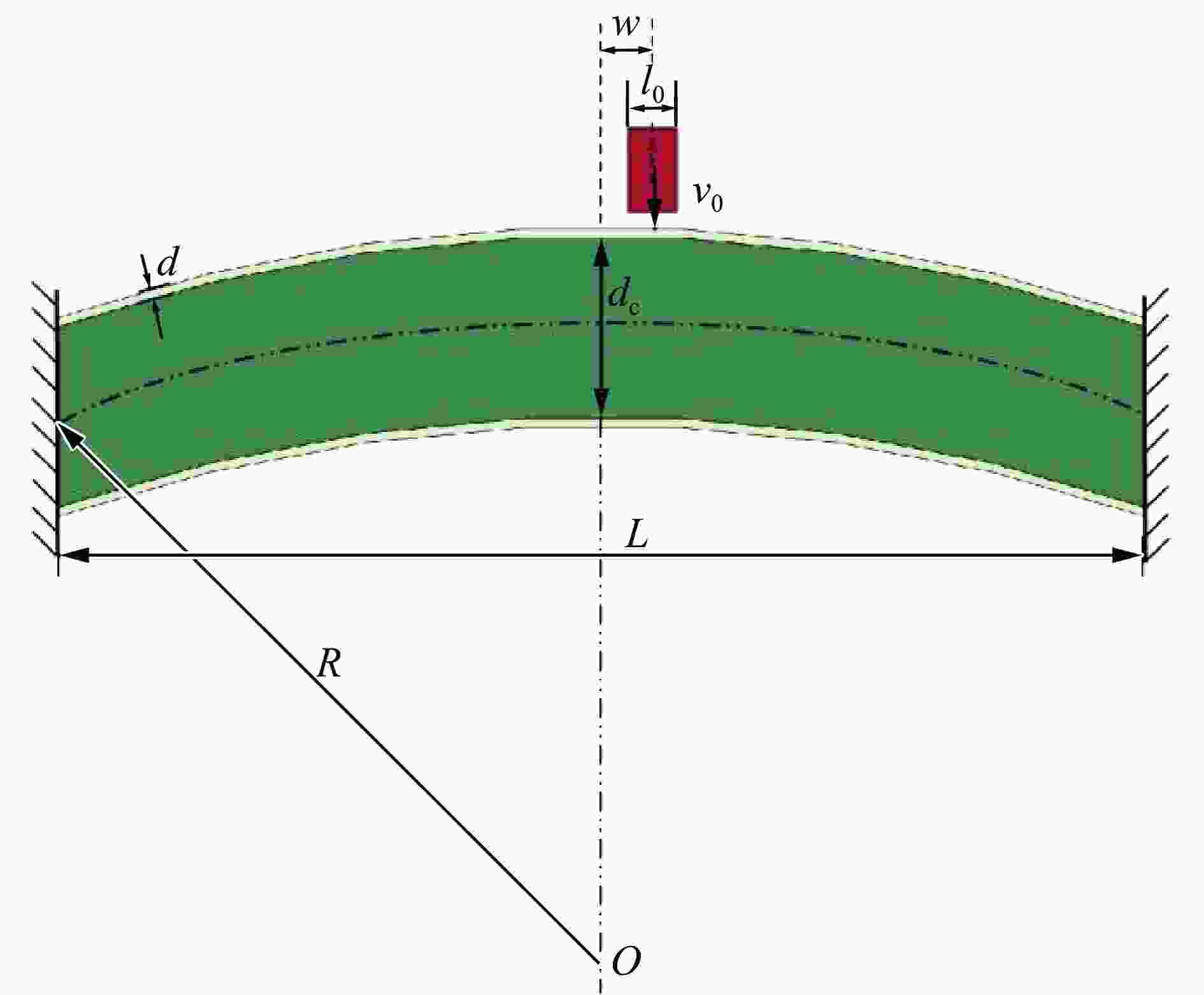
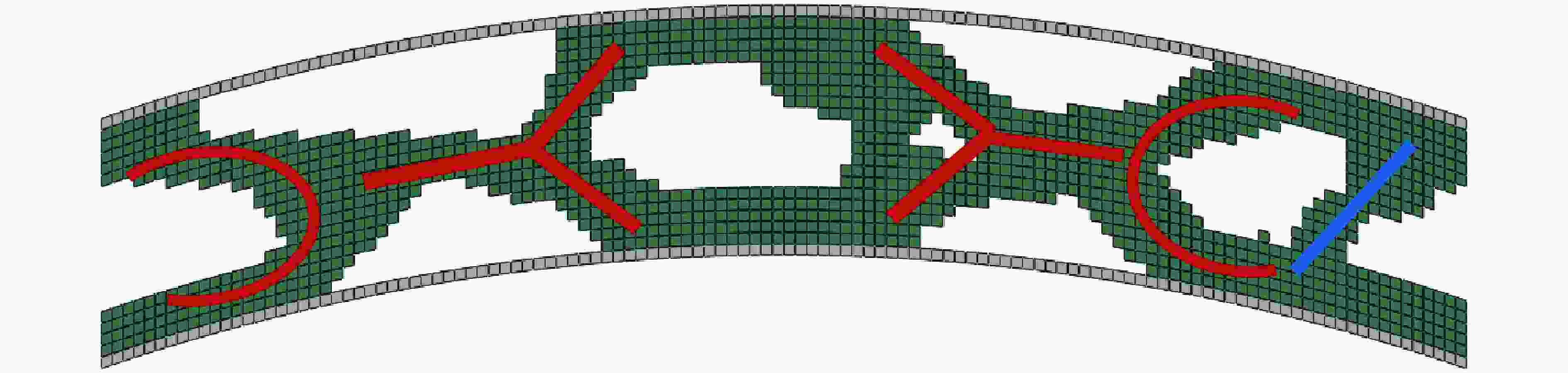
摘要: 基于双向渐进结构优化方法(bi-directional evolutionary structural optimization,BESO)框架,将传统动态载荷优化法中的内外层迭代引入到ABAQUS-MATLAB平台集成优化中,改进动态载荷拓扑优化流程。对初速度为100 m/s的子弹冲击下的夹芯拱结构进行拓扑优化设计和动力学响应分析。优化后夹芯拱芯层的变形模式可分为3个对称的部分,跨中区域的中部和上部主要发生压缩变形,呈现类三角点阵桁架结构,边界区域上部发生拉伸变形,下部发生压缩变形,呈现C形型结构,跨中和边界之间的过渡区域以拉弯联合变形为主,呈现Y形结构。通过与两种等质量的拱结构对比,分析了3种结构在不同初速度的子弹冲击下结构的挠度以及芯层的能量吸收情况。结果表明:在相同的冲击速度下,优化后的结构挠度最小,芯层比吸能最高;当冲击速度较低时,优化后的结构的抗冲击性能优势并不明显;在所研究的冲击速度范围内,冲击速度越高,优化后结构的抗冲击性能越好。对比对称载荷与非对称载荷(冲击点偏移量为100%)下2种优化结构在不同载荷工况下的动态响应,结果表明:载荷工况不同,得到的最终优化结果也略有所不同,但在相同载荷下结构的响应相差较小,每种工况下得到的优化结果在相应工况下所展现的力学性能略优,但均明显优于传统结构。因此,在对称冲击载荷下优化所得的结构具有一定的普遍性。Abstract: Based on the bi-directional evolutionary structural optimization method (BESO), the nested loop structure of the traditional dynamic load optimization method was introduced into the ABAQUS-MATLAB platform integrated optimization to improve the dynamic load topology optimization process. Topological optimization design and dynamic response analysis of sandwich arch structure under the impact of projectile with initial velocity of 100 m/s were carried out. After optimization, the deformation mode of the core for sandwich arch can be divided into three symmetrical part: the compression dominated deformation occurs in the middle and the upper part of the mid-span region, which like the triangular lattice truss structure; the tensile and compression dominated deformation occurs in the upper and the lower part of the boundary region respectively, which presents the C-shaped structure; and the transition region, which presents the Y-shaped structure, between the mid-span and the boundary is dominated by the combination of tension and bending deformation. The dynamic response of the optimization results under the impact load was analyzed. The deflections of top and bottom sheets and energy absorption of core of two comparison models with equal mass (Voronoi aluminum foam sandwich arch and solid arch) and optimization arch structure under the impact load with the initial velocity of 100 m/s were compared. The deflection and specific energy absorption of the cores of the three models under the impact of the projectiles with the initial velocities of 100, 80, 50 and 20 m/s were compared. The results show that: under the same impact velocity, the optimization structure has the minimum deflection and the maximum specific energy absorption capability; while with the low impact velocity, the impact-resistance advantage of the optimization structure is not obvious. Furthermore, in the range of the impact velocity which has been studied, the optimization structure shows the better impact-resistance performance with the higher velocity. The dynamic responses of the two optimization structures with symmetric load and asymmetric load (the offset of impact point is 100%) under different load conditions were compared. The deflection of top and bottom sheets and the specific energy absorption of core of four models (symmetric optimization result, asymmetric optimization result, Voronoi aluminum foam sandwich arch and solid arch) were compared. The results show that: under different load conditions, the final optimization results are slightly different, and the different of structural responses under the same load is relatively small. The optimization results obtained under each working condition show slightly better mechanical properties under the corresponding condition, but optimization structures are significantly better than the traditional structures. Therefore, the structure optimized by symmetrical impact load has a certain universality.
-
Key words:
- topology optimization /
- impact load /
- sandwich arch /
- dynamic response /
- energy absorption
-
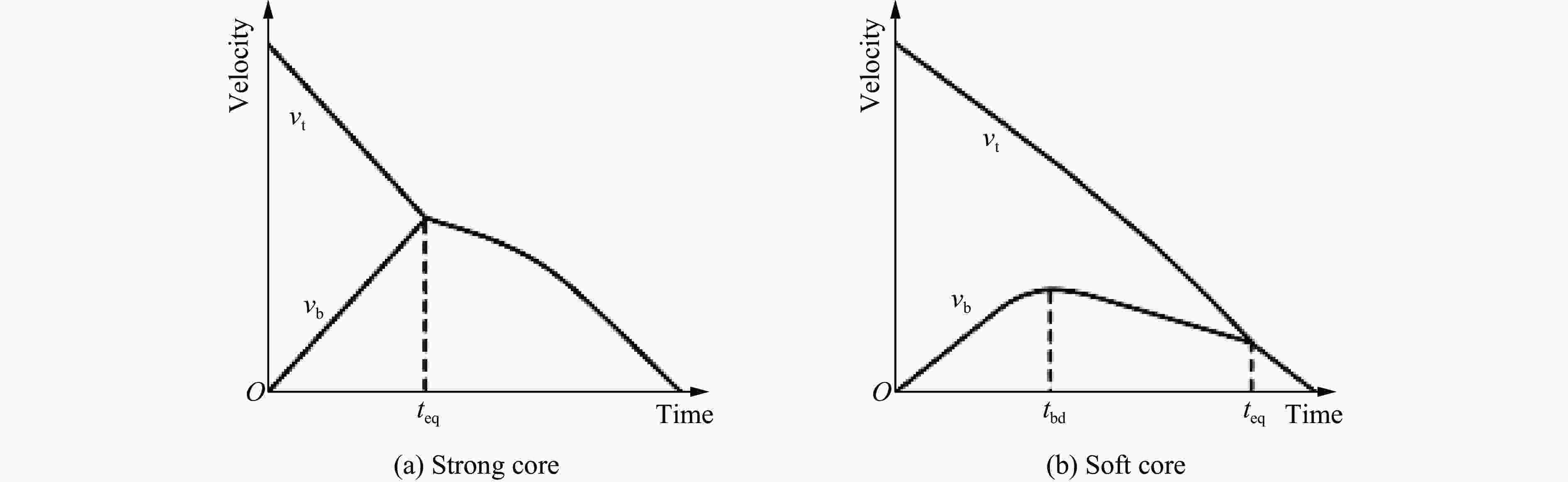
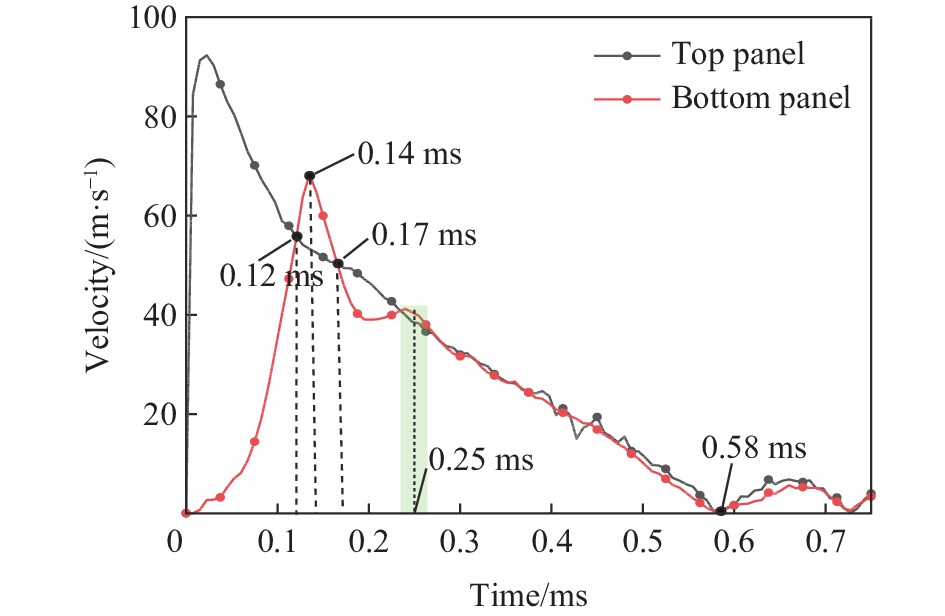
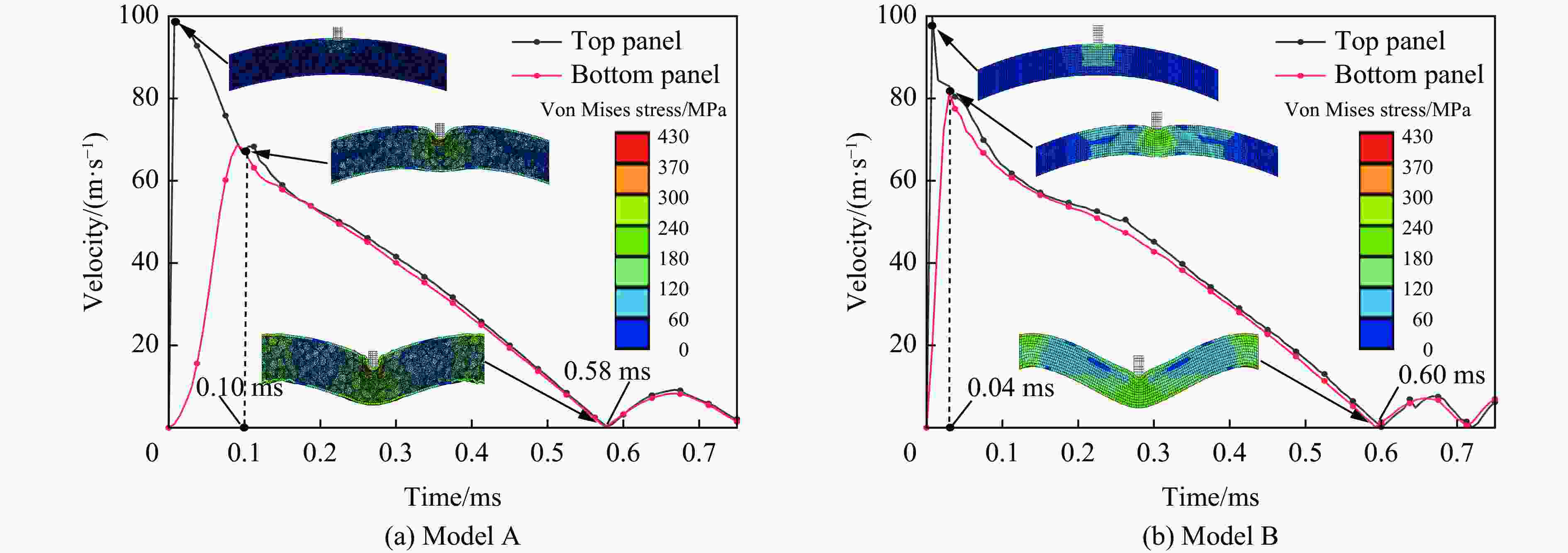
图 7 不同类型芯层夹芯结构上、下面板速度时程曲线
Figure 7. Velocity versus time histories of the mid-span of the top and bottom panels for two types of sandwich response[34]
-
[1] RIZOV V, SHIPSHA A, ZENKERT D. Indentation study of foam core sandwich composite panels [J]. Composite Structures, 2005, 69(1): 95–102. DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2004.05.013. [2] HOU W H, ZHU F, LU G X, et al. Ballistic impact experiments of metallic sandwich panels with aluminium foam core [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2010, 37(10): 1045–1055. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2010.03.006. [3] ZHU F, WANG Z H, LU G X, et al. Some theoretical considerations on the dynamic response of sandwich structures under impulsive loading [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2010, 37(6): 625–637. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2009.11.003. [4] CHANG W S, VENTSEL E, KRAUTHAMMER T, et al. Bending behavior of corrugated-core sandwich plates [J]. Composite Structures, 2005, 70(1): 81–89. DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2004.08.014. [5] SHU C F, ZHAO S Y, HOU S J. Crashworthiness analysis of two-layered corrugated sandwich panels under crushing loading [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2018, 133: 42–51. DOI: 10.1016/j.tws.2018.09.008. [6] ZHU F, ZHAO L M, LU G X, et al. A numerical simulation of the blast impact of square metallic sandwich panels [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2009, 36(5): 687–699. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2008.12.004. [7] 余同希, 朱凌, 许骏. 结构冲击动力学进展(2010—2020) [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2021, 41(12): 121401. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2021-0113.YU T X, ZHU L, XU J. Progress in structural impact dynamics during 2010—2020 [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2021, 41(12): 121401. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2021-0113. [8] 王海任, 李世强, 刘志芳, 等. 爆炸载荷下双向梯度仿生夹芯圆板的力学行为 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2021, 41(4): 043201. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0132.WANG H R, LI S Q, LIU Z F, et al. Mechanical behaviors of bi-directional gradient bio-inspired circular sandwich plates under blast loading [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2021, 41(4): 043201. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0132. [9] 彭克锋, 崔世堂, 潘昊, 等. 冲击载荷作用下柱壳链中的弹性波传播简化模型及其解析解 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2021, 41(1): 011403. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0246.PENG K F, CUI S T, PAN H, et al. Simplified model of elastic wave propagation in cylindrical shell chain under impact load and its analytical solution [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2021, 41(1): 011403. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0246. [10] 曾祥, 刘彦, 许泽建, 等. 爆炸载荷作用下玻璃钢/硬质聚氨酯泡沫夹层结构抗冲击性能实验研究 [J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2021, 41(11): 1145–1153. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2021.036.ZENG X, LIU Y, XU Z J, et al. Experimental study on impact resistance of glass fiber reinforced plastic/rigid polyurethane foam sandwich structures under air blast loading [J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2021, 41(11): 1145–1153. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2021.036. [11] 邢运, 杨嘉陵. 动物进化的抗冲击策略及其仿生机理研究 [J]. 力学进展, 2021, 51(2): 295–341. DOI: 10.6052/1000-0992-20-027.XING Y, YANG J L. Research progress of impact-resistance strategies and biomi-metic mechanism in animal evolution [J]. Advances in Mechanics, 2021, 51(2): 295–341. DOI: 10.6052/1000-0992-20-027. [12] 李肖成, 徐绯, 杨磊峰, 等. 薄板在冲击载荷下线弹性理想塑性响应的相似性研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2021, 41(11): 113103. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0374.LI X C, XU F, YANG L F, et al. Study on the similarity of elasticity and ideal plasticity response of thin plate under impact loading [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2021, 41(11): 113103. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0374. [13] NIKBAKT S, KAMARIAN S, SHAKERI M. A review on optimization of composite structures Part I: laminated composites [J]. Composite Structures, 2018, 195: 158–185. DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2018.03.063. [14] NIKBAKHT S, KAMARIAN S, SHAKERI M. A review on optimization of composite structures Part II: functionally graded materials [J]. Composite Structures, 2019, 214: 83–102. DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.01.105. [15] ROZVANY G I N, BENDSOE M P, KIRSCH U. Layout optimization of structures [J]. Applied Mechanics Reviews, 1995, 48(2): 41–119. DOI: 10.1115/1.3005097. [16] RIETZ A. Sufficiency of a finite exponent in SIMP (power law) methods [J]. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 2001, 21(2): 159–163. DOI: 10.1007/s001580050180. [17] BENDSØE M P, KIKUCHI N. Generating optimal topologies in structural design using a homogenization method [J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 1988, 71(2): 197–224. DOI: 10.1016/0045-7825(88)90086-2. [18] SUZUKI K, KIKUCHI N. A homogenization method for shape and topology optimization [J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 1991, 93(3): 291–318. DOI: 10.1016/0045-7825(91)90245-2. [19] XIE Y M, STEVEN G P. A simple evolutionary procedure for structural optimization [J]. Computers & Structures, 1993, 49(5): 885–896. DOI: 10.1016/0045-7949(93)90035-C. [20] QUERIN O M, STEVEN G P, XIE Y M. Evolutionary structural optimisation (ESO) using a bidirectional algorithm [J]. Engineering Computations, 1998, 15(8): 1031–1048. DOI: 10.1108/02644409810244129. [21] YOUNG V, QUERIN O M, STEVEN G P, et al. 3D and multiple load case bi-directional evolutionary structural optimization (BESO) [J]. Structural Optimization, 1999, 18(2): 183–192. DOI: 10.1007/BF01195993. [22] HUANG X, XIE Y M. Bi-directional evolutionary topology optimization of continuum structures with one or multiple materials [J]. Computational Mechanics, 2009, 43(3): 393–401. DOI: 10.1007/s00466-008-0312-0. [23] HUANG X, XIE Y M. Evolutionary topology optimization of continuum structures with an additional displacement constraint [J]. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 2010, 40(1): 409–416. DOI: 10.1007/s00158-009-0382-4. [24] CHOI W S, PARK G J. Structural optimization using equivalent static loads at all time intervals [J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2002, 191(19/20): 2105–2122. DOI: 10.1016/S0045-7825(01)00373-5. [25] PARK G J, KANG B S. Validation of a structural optimization algorithm transforming dynamic loads into equivalent static loads [J]. Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications, 2003, 118(1): 191–200. DOI: 10.1023/A:1024799727258. [26] PARK K J, LEE J N, PARK G J. Structural shape optimization using equivalent static loads transformed from dynamic loads [J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2005, 63(4): 589–602. DOI: 10.1002/nme.1295. [27] 蓝萌. 双向渐进结构优化法原理及其动力学优化研究 [J]. 机电技术, 2017(1): 17–22. DOI: 10.19508/j.cnki.1672-4801.2017.01.006.LAN M. Research of bi-directional evolutionary structural optimization method and dynamic response [J]. Mechanical & Electrical Technology, 2017(1): 17–22. DOI: 10.19508/j.cnki.1672-4801.2017.01.006. [28] 王宪杰. 基于改进BESO算法的多尺度多相材料并行优化设计 [D]. 西安: 西北工业大学, 2015. DOI: 10.7666/d.D689590.WANG X J. Multi-scale concurrent optimization of compositestructure and its periodic multiphase composite materialbased on improved BESO algorithm [D]. Xi'an, Shaanxi, China: Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2015. DOI: 10.7666/d.D689590. [29] 阎琨. 冲击荷载下结构优化设计研究 [D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2016.YAN K. Structural optimization method of structure subject to impact loads [D]. Dalian, Liaoning, China: Dalian University of Technology. [30] YAN K, CHENG G D, WANG B P. Adjoint methods of sensitivity analysis for Lyapunov equation [J]. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 2016, 53(2): 225–237. DOI: 10.1007/s00158-015-1323-z. [31] HUANG X, XIE Y M. Evolutionary topology optimization of continuum structures: methods and applications [M]. Chichester, UK: Wiley, 2010: 17–50. [32] ZHANG Y, JIN T, LI S Q, et al. Sample size effect on the mechanical behavior of aluminum foam [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2019, 151: 622–638. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2018.12.019. [33] TILBROOK M T, DESHPANDE V S, FLECK N A. The impulsive response of sandwich beams: Analytical and numerical investigation of regimes of behaviour [J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 2006, 54(11): 2242–2280. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmps.2006.07.001. [34] FLECK N A, DESHPANDE V S. The resistance of clamped sandwich beams to shock loading [J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2004, 71(3): 386–401. DOI: 10.1115/1.1629109. [35] XIE Q H, JING L, WANG Z H, et al. Deformation and failure of clamped shallow sandwich arches with foam core subjected to projectile impact [J]. Composites Part B:Engineering, 2013, 44(1): 330–338. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2012.04.070. [36] 张鹏飞, 刘志芳, 李世强. 内爆炸载荷下梯度泡沫铝夹芯管的动态响应 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2020, 40(7): 071402. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0418.ZHANG P F, LIU Z F, LI S Q. Dynamic response of sandwich tubes with graded foam aluminum cores under internal blast loading [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2020, 40(7): 071402. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0418. [37] 苏兴亚, 敬霖, 赵隆茂. 爆炸载荷下分层梯度泡沫铝夹芯板的失效模式与抗冲击性能 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2019, 39(6): 063103. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0198.SU X Y, JING L, ZHAO L M. Failure modes and shock resistance of sandwich panels with layered-gradient aluminum foam cores under air-blast loading [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2019, 39(6): 063103. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0198. [38] 叶楠, 张伟, 黄威, 等. PVC夹芯板在冲击载荷下的动态响应与失效模式 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2017, 37(1): 37–45. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2017)01-0037-09.YE N, ZHANG W, HUANG W, et al. Dynamic response and failure mode of PVC sandwich plates subjected to impact loading [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2017, 37(1): 37–45. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2017)01-0037-09. [39] 邹广平, 孙杭其, 唱忠良, 等. 聚氨酯/钢夹芯结构爆炸载荷下动力学响应的数值模拟 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2015, 35(6): 907–912. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2015)06-0907-06.ZOU G P, SUN H Q, CHANG Z L, et al. Numerical simulation on dynamic response of polyurethane/steel sandwich structure under blast loading [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2015, 35(6): 907–912. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2015)06-0907-06. -







 下载:
下载: