Numerical modeling on the launch process of a two-stage light gas gun using high-pressure gas as the driving source
-
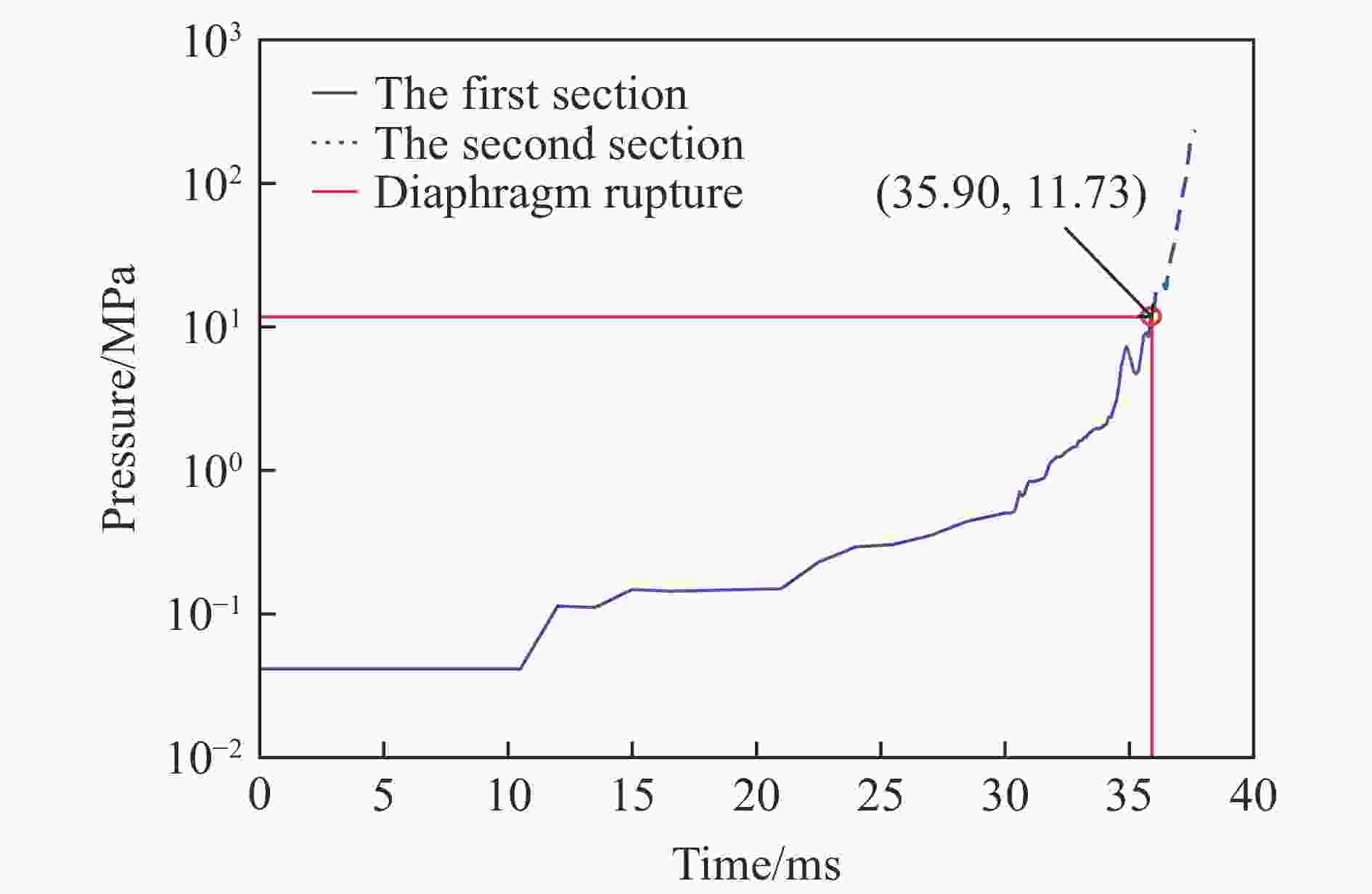
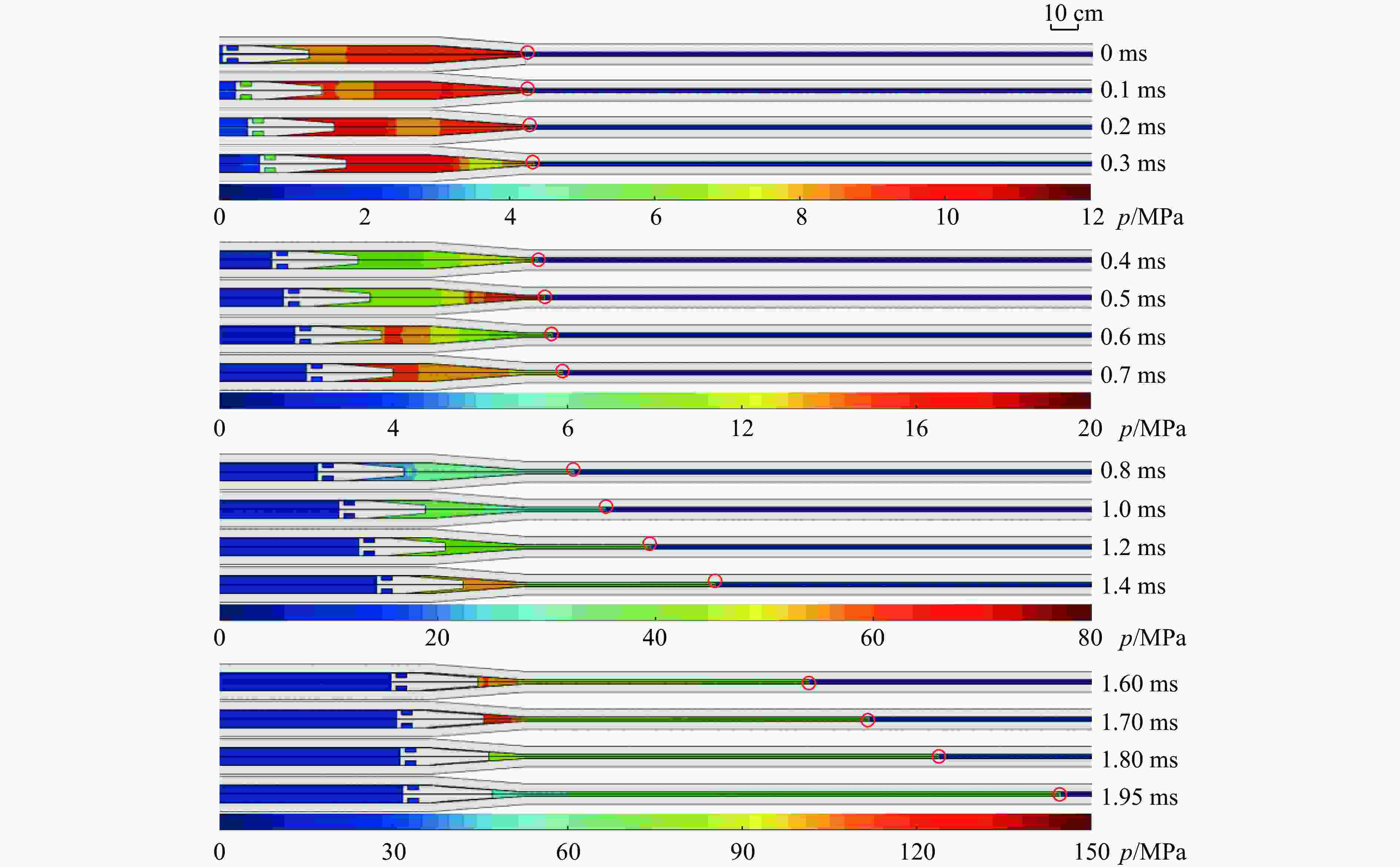
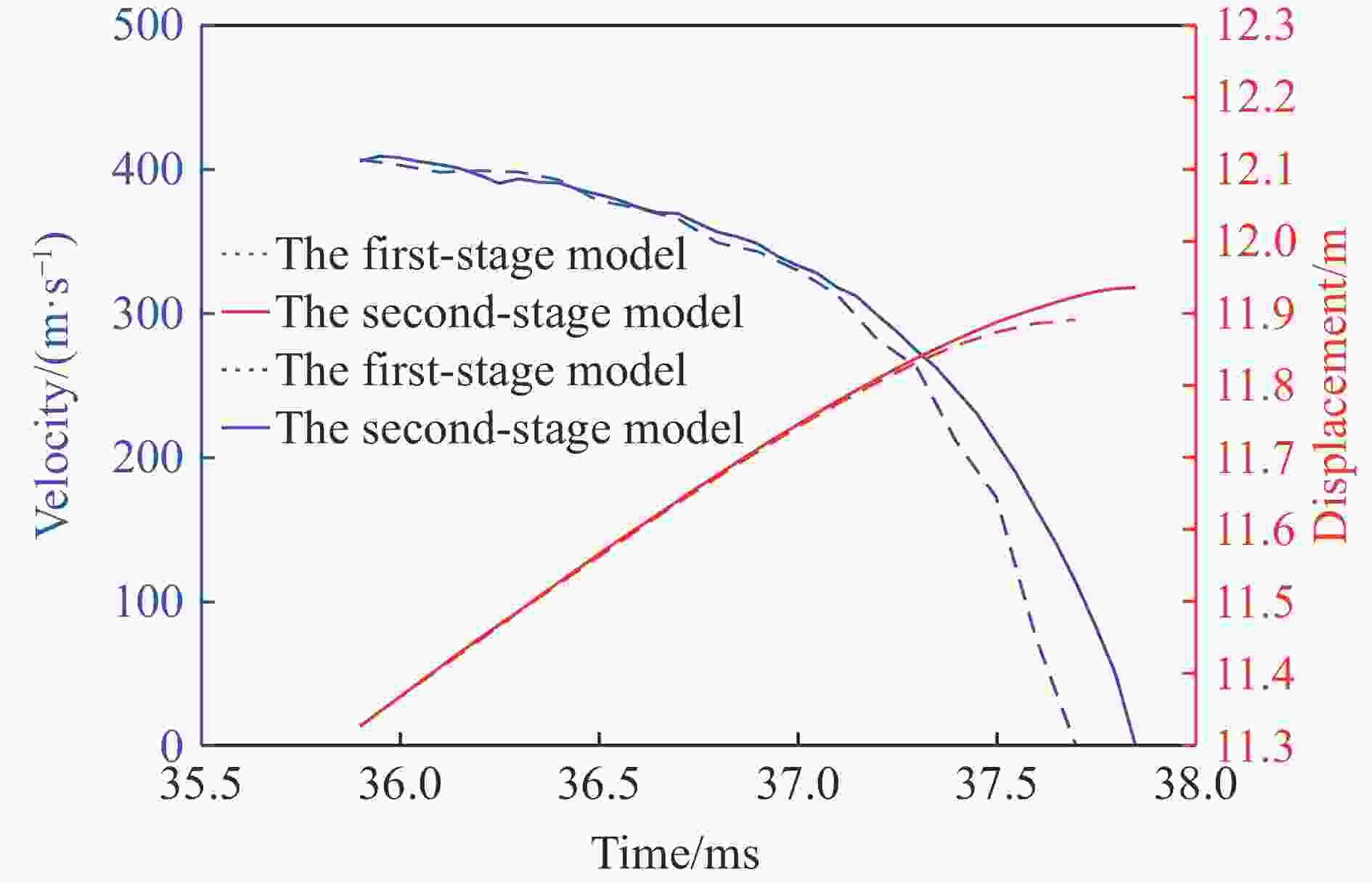
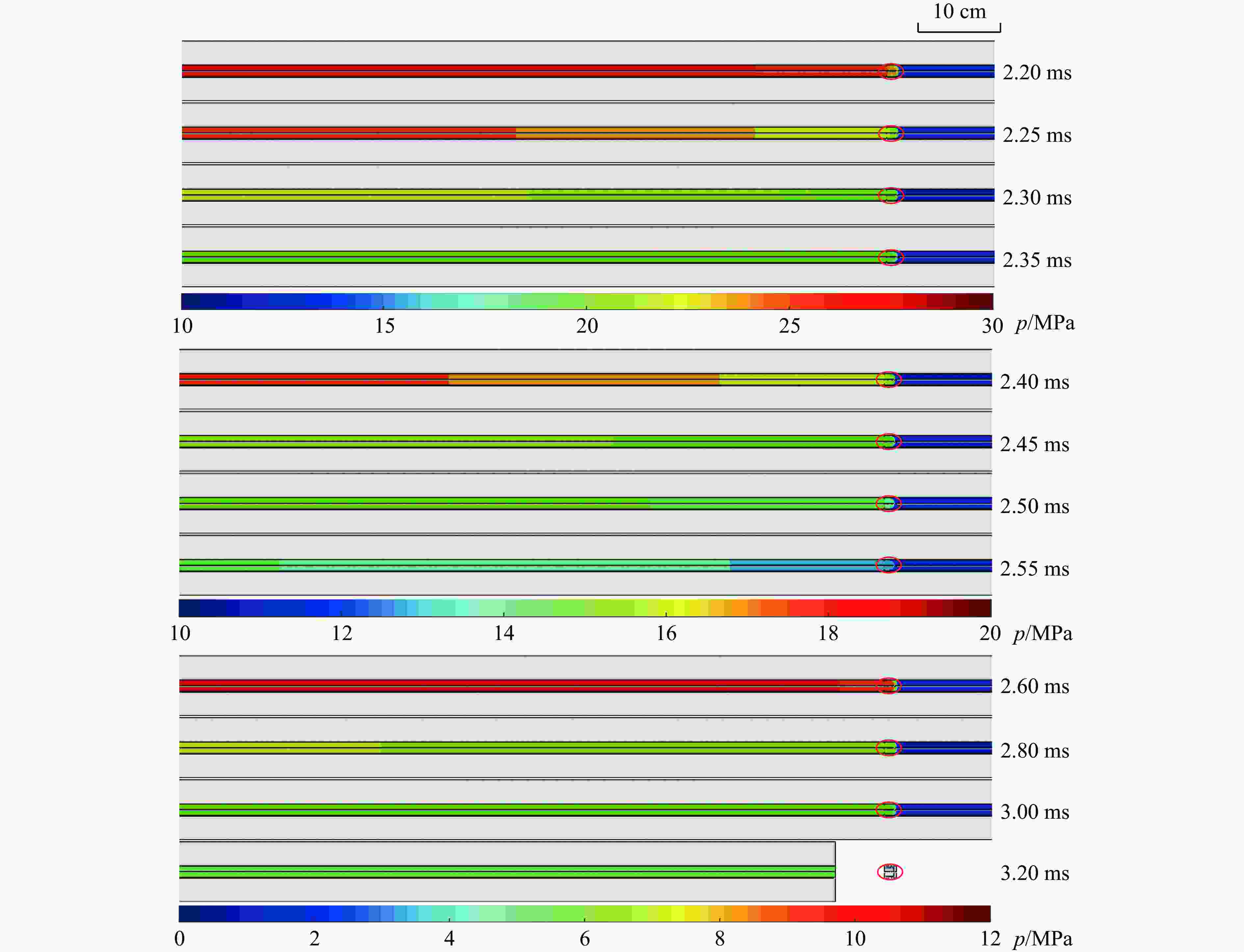
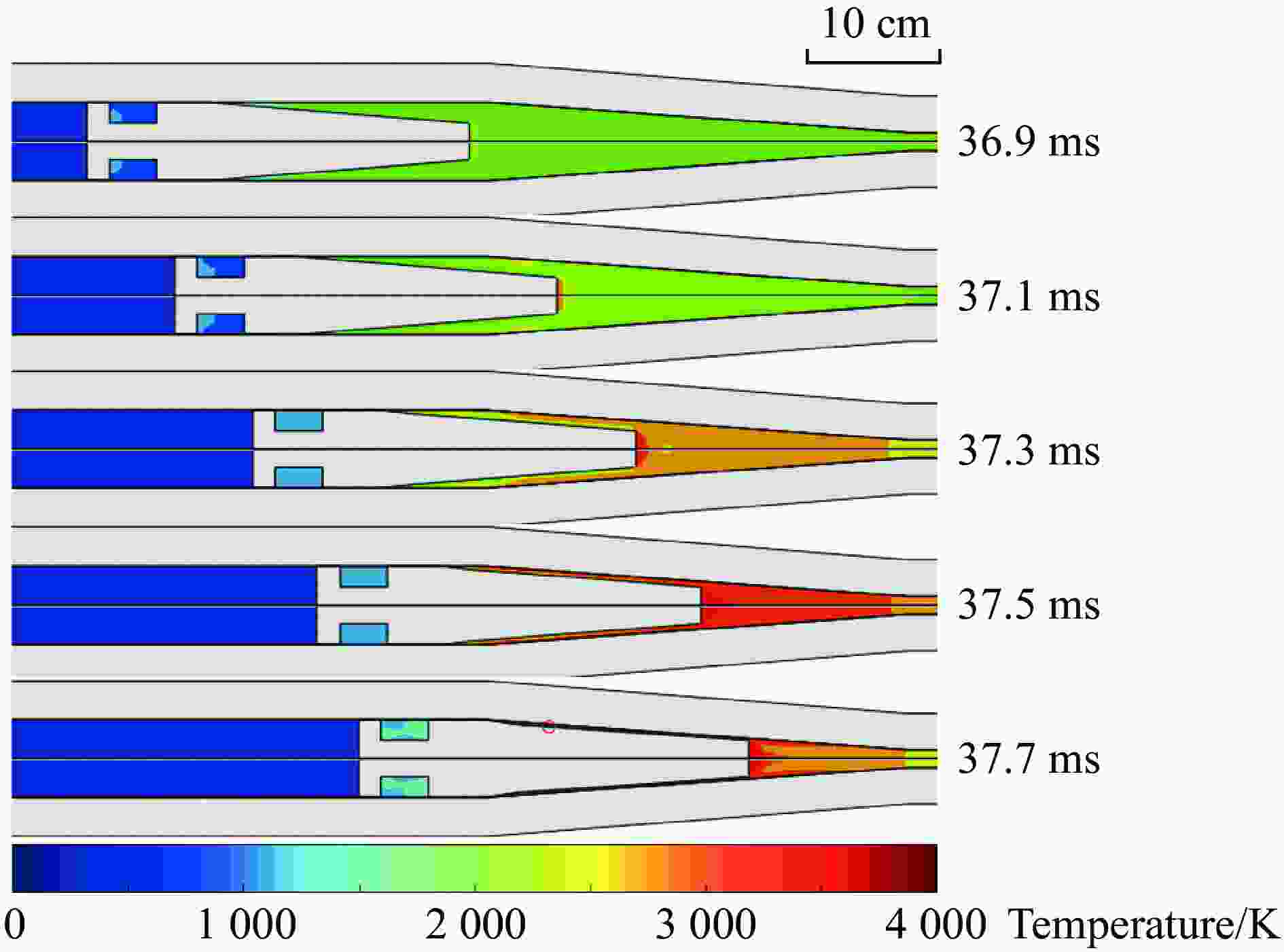
摘要: 二级轻气炮是一种常见的超高速发射装置,多年来其数值研究大多采用简化一维模型,鲜有三维有限元模型。以14 mm口径高压气体驱动二级轻气炮为研究对象,采用耦合欧拉-拉格朗日(coupled Eulerian-Lagrangian, CEL)算法,根据膜片破裂与否,将二级轻气炮模型解耦为2个分级三维数值模型。为确定实验难以测得的参数(材料摩擦因数和膜片破膜压力),设计正交试验,拟合确定活塞与泵管间摩擦因数为0.82,弹丸与发射管摩擦因数为0.30和膜片破膜压力为11.73 MPa。正交结果表明,摩擦因数对计算结果影响较大,在高压气体驱动二级轻气炮的计算中不应忽略。通过上述方法建立数字化高压气体驱动二级轻气炮,完整复现气炮发射过程,计算的弹丸终速与实验结果吻合度高。选取验证工况详细分析了气炮发射过程内流场变化,并呈现关键时刻的压力云图。该气炮简化方法、分级思想和关键参数确认方法可推广应用于固体发射药驱动、爆轰驱动等其他驱动形式的二级/多级轻气炮。
-
关键词:
- 二级轻气炮 /
- 正交试验 /
- 分级三维数值模型 /
- 耦合欧拉-拉格朗日算法
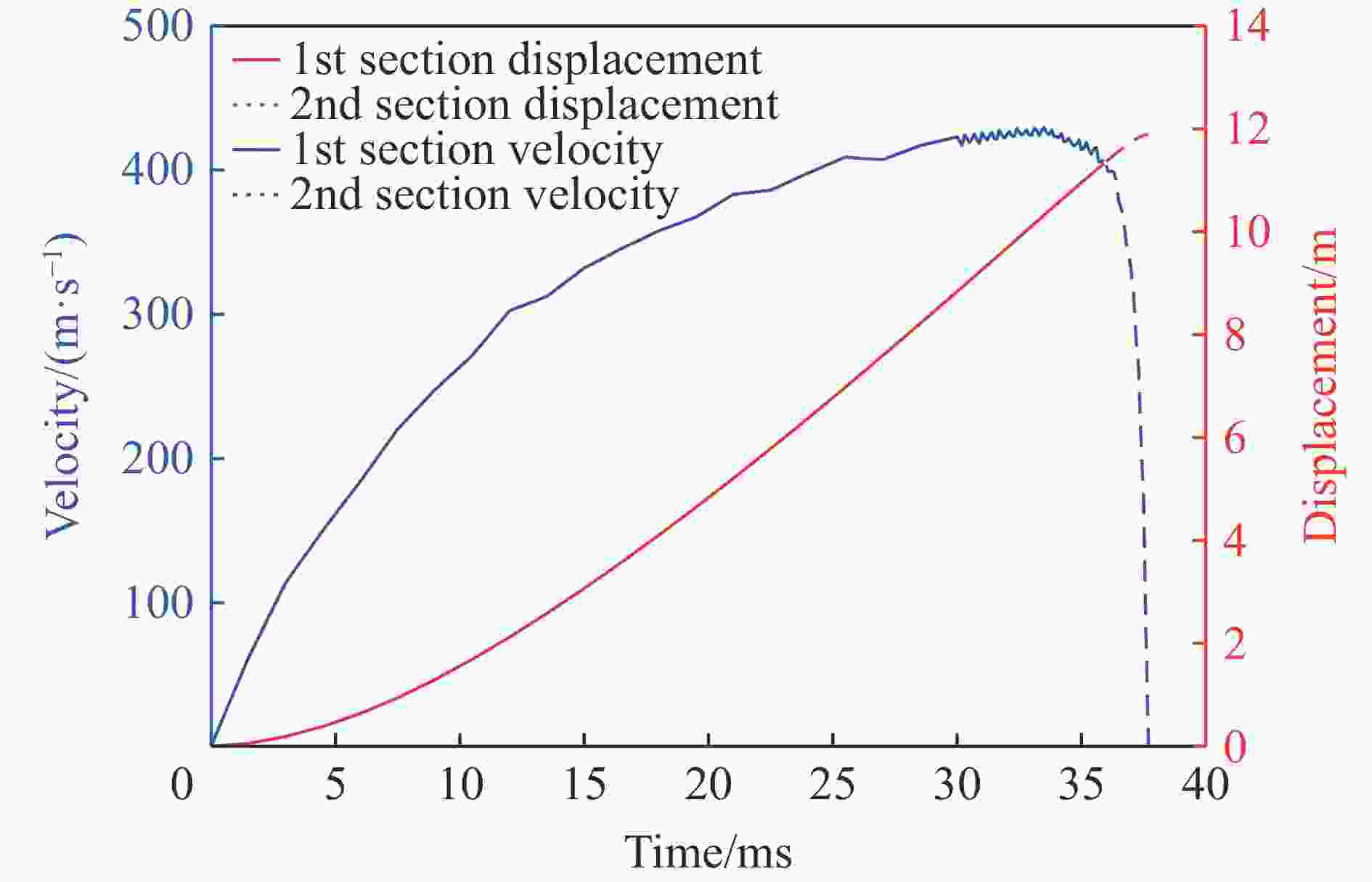
Abstract: A two-stage light gas gun is a common hypervelocity launcher. Over the years, most researchers adopted simplified one-dimensional models and rarely used three-dimensional finite element models. This paper used the coupled Eulerian-Lagrangian algorithm to calculate the gas-driven hydrodynamic field in a 14-mm-caliber two-stage light gas gun. The two-stage light gas gun was decoupled into two three-dimensional numerical models according to whether the diaphragm was broken. A three-factor four-level orthogonal test was carried out to get the material friction coefficient and the broken diaphragm pressure, which were difficult to measure in experiments. The ordinary least square method was used to calculate the orthogonal test data. The friction coefficient between the piston and the pump tube was 0.82, the friction coefficient between the projectile and the launch tube was 0.30, and the broken diaphragm pressure was 11.73 MPa. The orthogonal test showed that the friction coefficient and the broken diaphragm pressure significantly influenced the calculation results. The friction could not be ignored in calculating the launch process of the two-stage light gas gun. So keeping the gun body clean was necessary to improve the projectile velocity. The numerical model for the two-stage light gas gun was established based on the method mentioned above, which completely reproduced the launch process of the gas gun, and visually represented the change of the flow field. The velocities of the projectile were numerically obtained by the established model, which were highly consistent with the experimental results. In addition, the verification condition was selected to analyze the change of the flow field, and the pressure nephograms at the critical moments were given. It should be noted that the velocity range of the projectile was 3-5 km/s. The method is fully applicable for the projectile velocity below 3 km/s and is generalizable for the higher projectile velocity. The gas gun simplification method, grading idea and key parameter confirmation method can be extended to other two/multi-stage light-gas guns, such as solid propellant driven and detonation driven. -
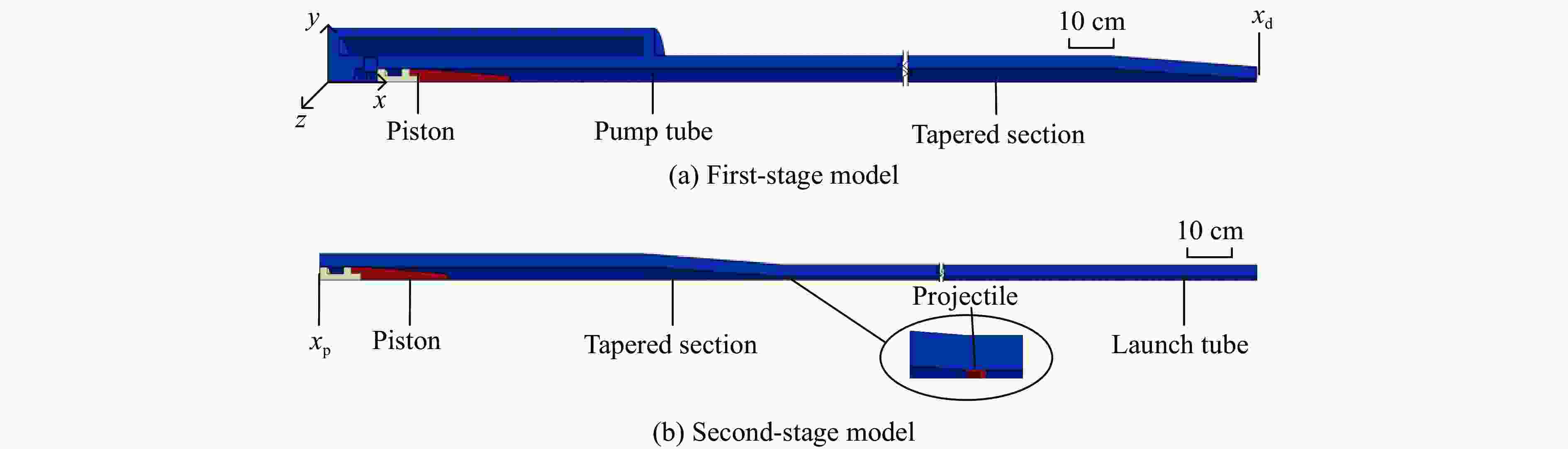
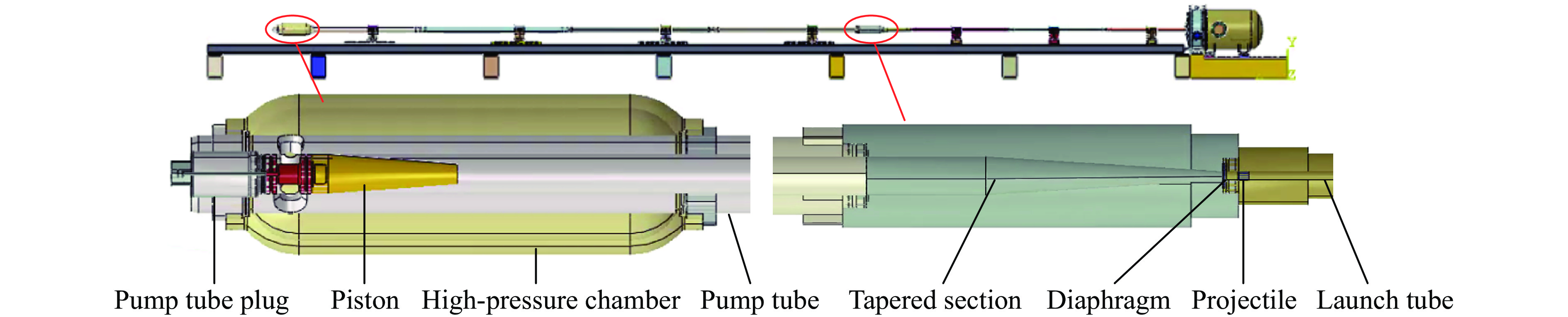
表 1 14 mm口径高压气体驱动二级轻气炮几何参数
Table 1. The geometrical parameters of the 14-mm-caliber two-stage light-gas gun
部件 长度/mm 内径/mm 入锥角度/(°) 高压气室 720 90 泵管 11820 60 发射管 6600 14 锥段 320 14~60 4.5 表 2 14 mm高压气体驱动二级轻气炮的实验参数
Table 2. Experimental parameters of the 14-mm-caliber two-stage light-gas gun
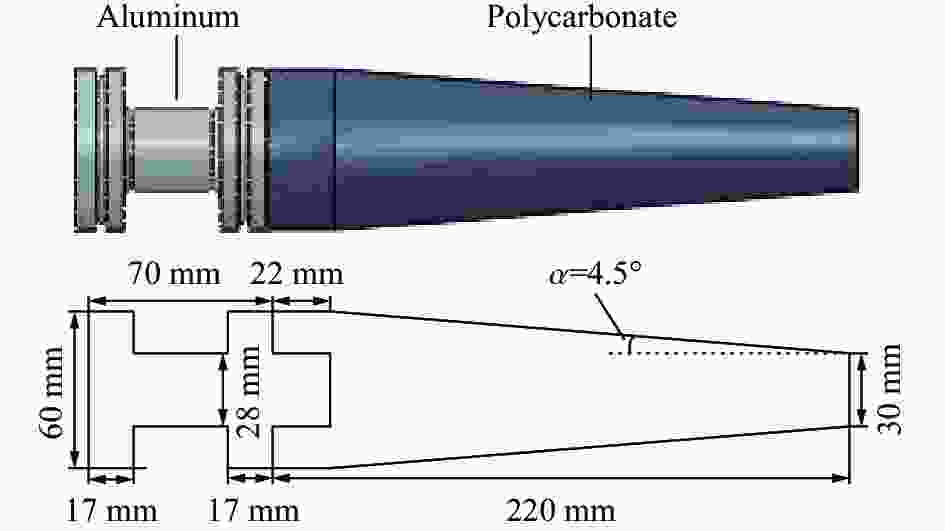
实验 高压气室初始压力/MPa 泵管初始压力/MPa 活塞质量/g 弹丸质量/g 膜片厚度/mm 弹丸终速/(m·s−1) 1 15.7 0.041 733 1.51 0.4 3 846 2 22.1 0.045 733 1.55 0.4 4 155 3 21.7 0.047 733 2.43 0.4 3 571 材料 密度/(kg·m−3) 泊松比 杨氏模量/GPa 初始屈服应力/MPa 硬化常数/MPa 应变硬化指数 温度系数 熔化温度/K 4340不锈钢 7900 0.33 200 280 802.5 0.622 1 1673 铝 2790 0.33 73.1 369 684 0.34 1.7 1000 表 4 气体材料参数
Table 4. Material parameters for gases
气体 R/(J·(mol·K)−1) 环境压力/Pa 比定容热容/(J·(kg·K)−1) 氦气 2077 0 3116 氮气 298.3 0 743 表 5 正交试验的因素及水平
Table 5. Factors and levels of orthogonal tests
水平 μ1 μ2 p/MPa 1 0.3 0.1 10 2 0.5 0.2 20 3 0.7 0.3 30 4 0.9 0.4 40 表 6 正交工况及弹丸终速
Table 6. The orthogonal cases as well as the final velocities of projectiles
计算工况 μ1 μ2 p/MPa v/(m·s−1) 计算工况 μ1 μ2 p/MPa v/(m·s−1) 试验1 试验2 试验3 试验1 试验2 试验3 1 0.3 0.1 10 4517 4835 4183 9 0.7 0.1 30 3645 4428 4597 2 0.3 0.2 20 4751 4959 4243 10 0.7 0.2 40 4230 4279 4622 3 0.3 0.3 30 4797 5194 4142 11 0.7 0.3 10 3568 4036 3396 4 0.3 0.4 40 4782 5039 4180 12 0.7 0.4 20 3469 4019 3264 5 0.5 0.1 20 4453 4396 4184 13 0.9 0.1 40 4581 4755 3842 6 0.5 0.2 10 4081 4290 3611 14 0.9 0.2 30 4412 4550 4030 7 0.5 0.3 40 3997 4375 3887 15 0.9 0.3 20 4232 4451 3786 8 0.5 0.4 30 4197 4029 3720 16 0.9 0.4 10 3840 3843 3742 表 7 正交试验结果分析
Table 7. Analysis of orthogonal test results
v/(m·s−1) 试验 1 试验 2 试验 3 μ1 μ2 p μ1 μ2 p μ1 μ2 p k1 4711.75 4299.00 4001.50 5006.75 4603.50 4251.00 4187.00 4201.50 3688.50 k2 4182.00 4368.50 4226.25 4272.50 4519.50 4456.25 3850.50 4126.50 3869.25 k3 3728.00 4148.50 4262.75 4190.50 4514.00 4550.25 3969.75 3802.75 4122.25 k4 4266.25 4072.00 4397.50 4399.75 4232.50 4384.00 3805.50 3682.00 4132.75 R 983.75 296.50 396.00 816.25 371.00 299.25 381.50 519.50 444.25 表 8 观测点的参数及波阵面平均速度
Table 8. Parameters for observation points and mean wavefront velocities at observation points
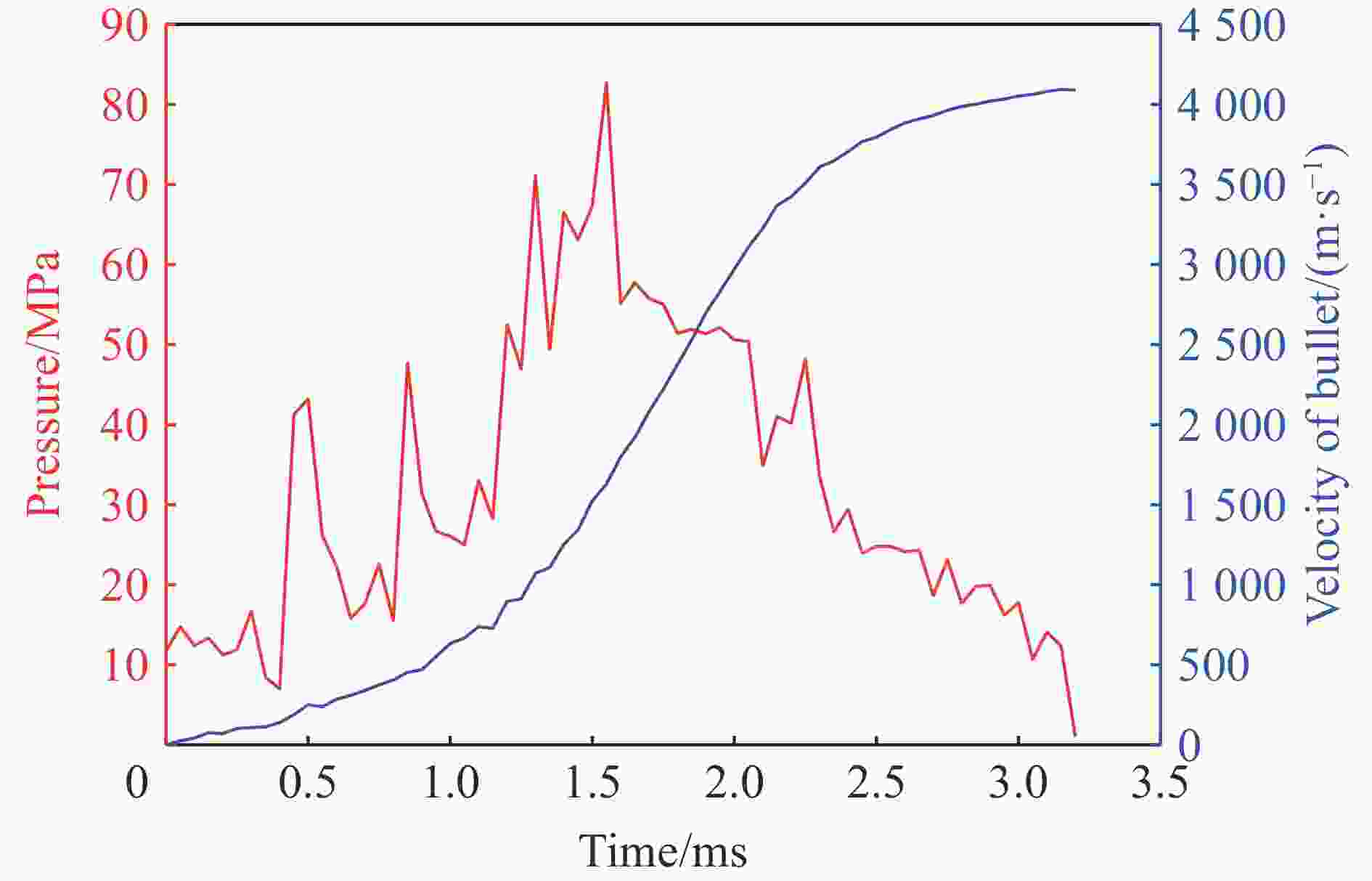
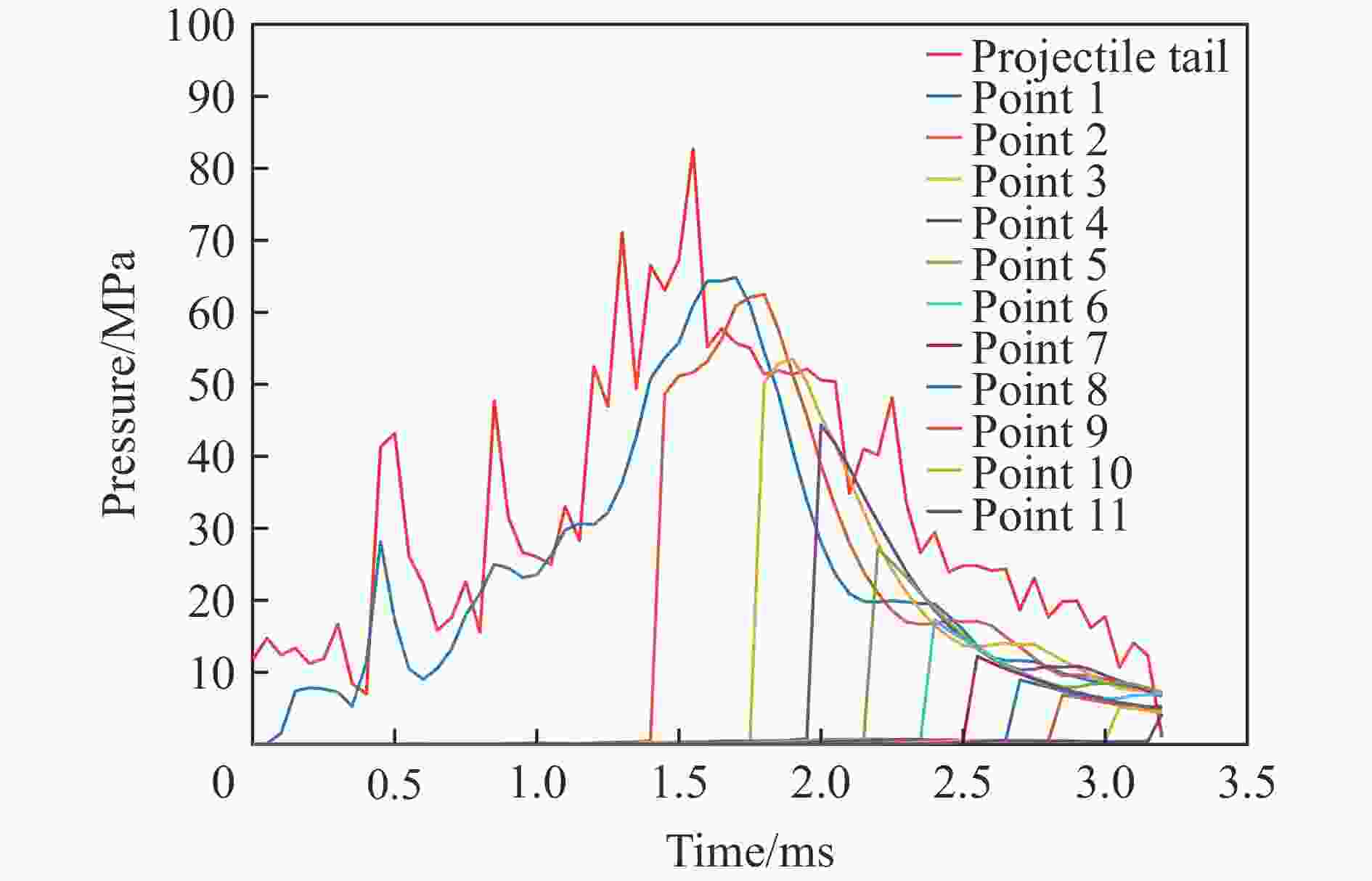
观测点 S/m ΔS/m t/ms Δt/ms c/(m·s−1) 观测点 S/m ΔS/m t/ms Δt/ms c/(m·s−1) 0 0 0 6 3.260 0.650 2.35 0.20 3250 1 0.018 0.018 0.05 0.05 360 7 3.900 0.640 2.50 0.15 4267 2 0.670 0.652 1.40 1.35 483 8 4.550 0.650 2.65 0.15 4333 3 1.310 0.640 1.75 0.35 1829 9 5.200 0.650 2.80 0.15 4333 4 1.960 0.650 1.95 0.20 3250 10 5.850 0.650 3.00 0.20 3250 5 2.610 0.650 2.15 0.20 3250 11 6.490 0.640 3.15 0.15 4267 -
[1] 龚自正, 杨继运, 张文兵, 等. 航天器空间碎片超高速撞击防护的若干问题 [J]. 航天器环境工程, 2007, 24(3): 125–130. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1379.2007.03.001.GONG Z Z, YANG J Y, ZHANG W B, et al. Spacecraft protection from the hypervelocity impact of space meteoroid and orbital debris [J]. Spacecraft Environment Engineering, 2007, 24(3): 125–130. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1379.2007.03.001. [2] BARKER L M, CHHABILDAS L C, TRUCANO T G, et al. High gas pressure acceleration of flier plates-experimental techniques [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1990, 10(1/2/3/4): 67–80. DOI: 10.1016/0734-743X(90)90049-2. [3] NONAKA S, TAKAYAMA K, KIBE S. Hypervelocity impact tests with bumper-walled structure against space debris [C]//36th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit. Reno, USA: AIAA, 1998: 800. DOI: 10.2514/6.1998-800. [4] 刘海明. 二级轻气炮内弹道过程计算机仿真 [D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2006.LIU H M. Computer emulation of interior ballistics process of two-stage light gas gun [D]. Nanjing, Jiangsu, China: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2006. [5] 杨继运. 二级轻气炮模拟空间碎片超高速碰撞试验技术 [J]. 航天器环境工程, 2006, 23(1): 16–22. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1379.2006.01.003.YANG J Y. Simulation of space debris hypervelocity impact using two stage light gas gun [J]. Spacecraft Environment Engineering, 2006, 23(1): 16–22. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1379.2006.01.003. [6] 张向荣, 朱玉荣, 林俊德, 等. 压缩氮气驱动的高速气炮实验技术 [J]. 航天器环境工程, 2015, 32(4): 343–348. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1379.2015.04.001.ZHANG X R, ZHU Y R, LIN J D, et al. Experimental technique of high velocity gas gun driven by compressed nitrogen [J]. Spacecraft Environment Engineering, 2015, 32(4): 343–348. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1379.2015.04.001. [7] ANGRILLI F, PAVARIN D, DE CECCO M, et al. Impact facility based upon high frequency two-stage light-gas gun [J]. Acta Astronautica, 2003, 53(3): 185–189. DOI: 10.1016/S0094-5765(02)00207-2. [8] 董石, 孟川民, 肖元陆, 等. 反应气体驱动二级轻气炮技术的初步研究 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2017, 31(2): 182–186. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.2017.02.011.DONG S, MENG C M, XIAO Y L, et al. Preliminary study of two-stage light gas gun using reactive gas as driving energy [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2017, 31(2): 182–186. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.2017.02.011. [9] TANG W Q, WANG Q, WEI B C, et al. Performance and modeling of a two-stage light gas gun driven by gaseous detonation [J]. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10(12): 4383. DOI: 10.3390/app10124383. [10] 张德志, 唐润棣, 林俊德, 等. 新型气体驱动二级轻气炮研制 [J]. 兵工学报, 2004, 25(1): 14–18. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1093.2004.01.004.ZHANG D Z, TANG R D, LIN J D, et al. Development of a new type gas-driven two-stage light gas gun [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2004, 25(1): 14–18. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1093.2004.01.004. [11] 尚甲豪, 邢好运, 汪球, 等. 气相爆轰驱动二级轻气炮内弹道数值模拟 [J]. 力学学报, 2022, 54(3): 810–821. DOI: 10.6052/0459-1879-21-437.SHANG J H, XING H Y, WANG Q, et al. Numerical research on interior ballistics of the two-stage light gas gun driven by gaseous detonation [J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2022, 54(3): 810–821. DOI: 10.6052/0459-1879-21-437. [12] 林俊德. 非火药驱动的二级轻气炮的发射参数分析 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 1995, 15(3): 229–240.LIN J D. A analysis of launching parameters for a two stage lioht gas gun not driven by powder [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 1995, 15(3): 229–240. [13] SEIGEL A E. The theory of high speed guns [R]. Paris, France: Advisory Group for Aerospace Research and Development, 1965. [14] GROTH C P T, GOTTLIEB J J. Numerical study of two-stage light-gas hypervelocity projectile launchers: UTIAS Report, No. 327 [R]. Toronto, Canada: University of Toronto, 1988. [15] PIACESI R, GATES D F, SEIGEL A E. Computer analysis of two-stage hypervelocity model launchers [R]. White Oak, Maryland, USA: Naval Ordnance Laboratory, 1963. DOI: 10.21236/ad0408675. [16] 胡天翔, 张庆明, 薛一江, 等. 初始条件对氢氧爆轰气体炮内弹道性能的影响规律 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2021, 35(6): 063301. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.20210779.HU T X, ZHANG Q M, XUE Y J, et al. Influence of initial conditions on the interior ballistic performance of hydrogen-oxygen detonation gas gun [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2021, 35(6): 063301. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.20210779. [17] NOH W F. CEL: a time-dependent, two-space-dimensional, coupled Eulerian-Lagrange code [R]. Livermore, USA: Lawrence Radiation Laboratory, 1963. [18] 黄洁, 梁世昌, 李海燕, 等. 二级轻气炮发射过程内弹道数值计算研究 [J]. 空气动力学学报, 2013, 31(5): 657–661. DOI: 10.7638/kqdlxxb-2012.0055.HUANG J, LIANG S C, LI H Y, et al. Numerical research on interior ballistics of the launch process of two-stage light gas gun [J]. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 2013, 31(5): 657–661. DOI: 10.7638/kqdlxxb-2012.0055. [19] SYONO Y, GOTO T. A two-stage light gas gun for shock wave research [J]. The Science Reports of the Research Institutes, Tohoku University, Serial A:Physics, Chemistry and Metallurgy, 1980, 29: 17–31. [20] JOHNSON G R, COOK W H. Fracture characteristics of three metals subjected to various strains, strain rates, temperatures and pressures [J]. Engineering fracture mechanics, 1985, 21(1): 31–48. DOI: 10.1016/0013-7944(85)90052-9. [21] JOHNSON G R, COOK W H. A constitutive model and data for metals subjected to large strains, high strain rates and hightemperatures [C]//The Seventh International Symposium on Ballistics. The Hague, Netherlands, 1983. [22] Grassia L, DAMORE A, SIMON S L. On the viscoelastic Poisson’s ratio in amorphous polymers [J]. Journal of Rheology, 2010, 54(5): 1009–1022. DOI: 10.1122/1.3473811. [23] SPAN R, LEMMON E W, JACOBSEN R T, et al. A reference equation of state for the thermodynamic properties of nitrogen for temperatures from 63.151 to 1000 K and pressures to 2200 MPa [J]. Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data, 2000, 29(6): 1361–1433. DOI: 10.1063/1.1349047. [24] MCCARTY R D, ARP V D. A new wide range equation of state for helium [M]//FAST R W. Advances in Cryogenic Engineering. Boston, USA: Springer, 1990: 1465–1475. [25] ANGRILLI F, DE CECCO M, PAVARIN D. Diagnostic procedure for two-stage light gas gun pellet injector by means of numerical analysis [J]. Fusion Technology, 1998, 34(3P2): 430–434. DOI: 10.13182/FST98-A11963651. -






 下载:
下载: