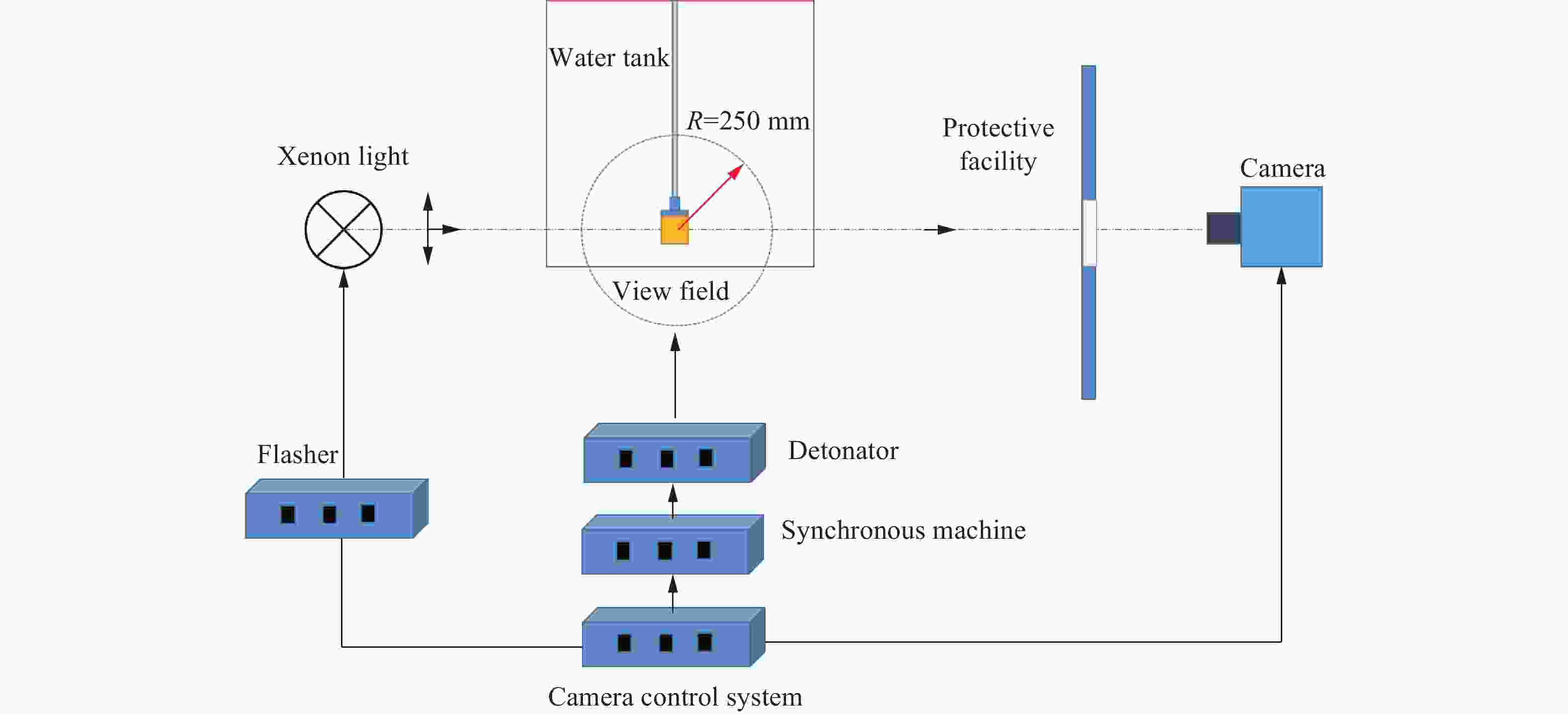
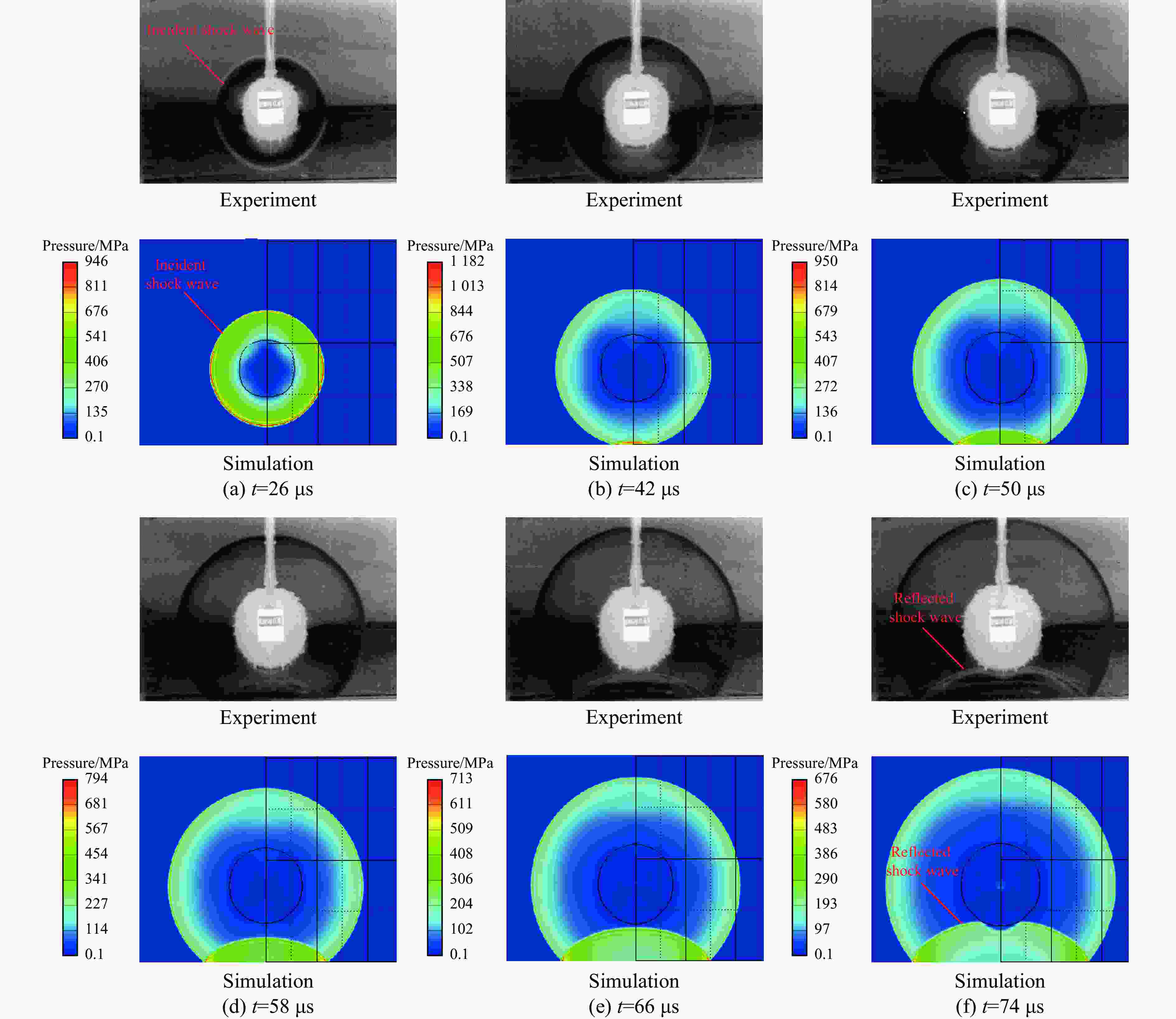
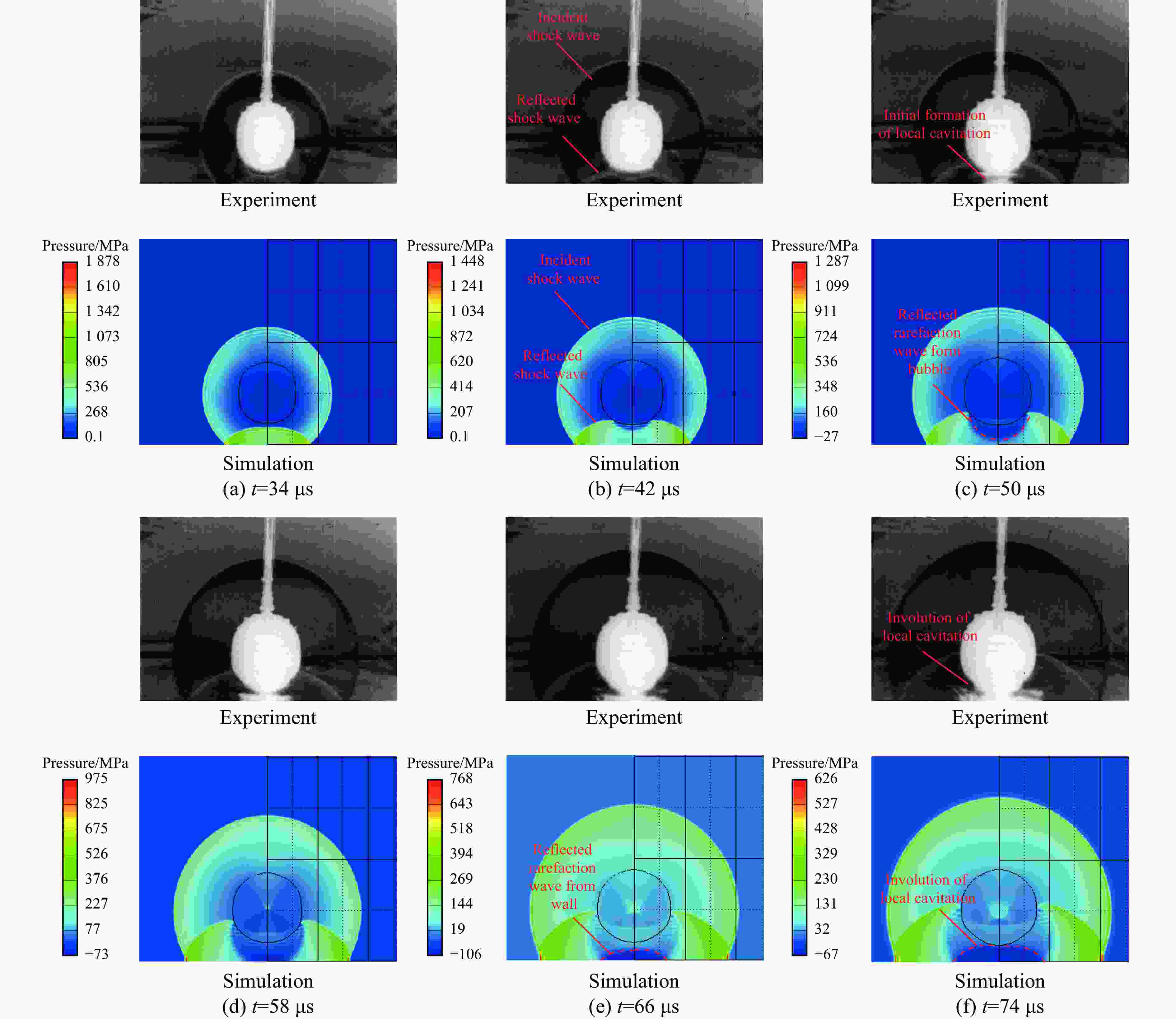
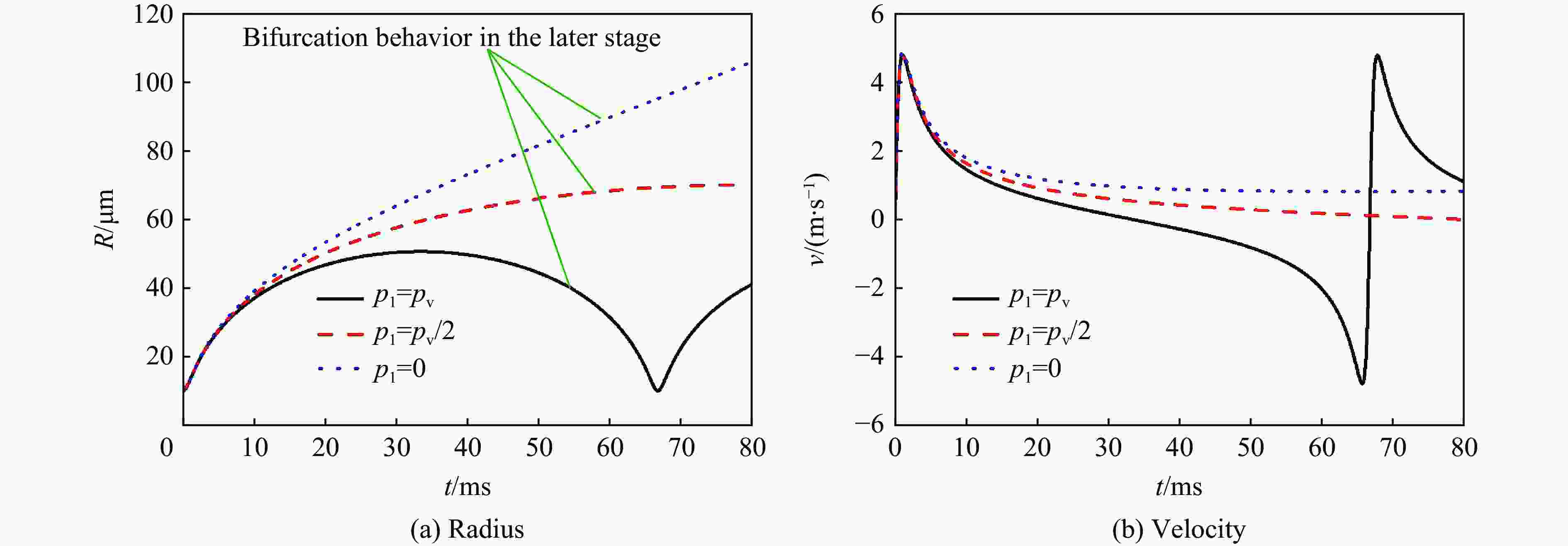
| [1] |
汪俊, 刘国振, 刘建湖, 等. 考虑空泡及再加载效应的水下爆炸流固相互作用分析 [J]. 兵工学报, 2014, 35(S2): 157–163.WANG J, LIU G Z, LIU J H, et al. Investigation of fluid-structure interaction under underwater explosion with effect of local cavitation and reloading [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2014, 35(S2): 157–163.
|
| [2] |
周章涛, 刘建湖, 裴红波, 等. 水下近距和接触爆炸流固耦合作用机理及加载效应研究 [J]. 兵工学报, 2017, 38(S1): 136–145.ZHOU Z T, LIU J H, PEI H B, et al. Fluid-structure interaction mechanism and loading effect in close-in and contact underwater explosions [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2017, 38(S1): 136–145.
|
| [3] |
TAYLOR G I. The pressure and impulse of submarine explosion waves on plates [J]. Compendium of Underwater Explosion Research, 1941, 1: 1155–1174.
|
| [4] |
李海涛, 朱锡, 黄晓明, 等. 水下爆炸冲击波作用下空化区域形成的特性研究 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2008, 22(2): 181–186. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.2008.02.019.LI H T, ZHU X, HUANG X M, et al. On the characteristics of cavitation formation subjected to underwater blast shock wave [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2008, 22(2): 181–186. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.2008.02.019.
|
| [5] |
李海涛, 朱石坚, 陈志坚, 等. 全入射角度下平板冲击波的壁压载荷及局部空化特性 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2014, 34(3): 354–360. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2014)03-0354-07.LI H T, ZHU S J, CHEN Z J, et al. Characteristics of wall pressure and cavitation on the plate subjected to underwater explosion shockwaves at any angle of incidence [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2014, 34(3): 354–360. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2014)03-0354-07.
|
| [6] |
RAJENDRAN R, LEE J M. A comparative damage study of air- and water-backed plates subjected to non-contact underwater explosion [J]. International Journal of Modern Physics B, 2008, 22(09n11): 1311–1318. DOI: 10.1142/S0217979208046700.
|
| [7] |
FELIPPA C A, DERUNTZ J A. Finite element analysis of shock-induced hull cavitation [J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 1984, 44(3): 297–337. DOI: 10.1016/0045-7825(84)90134-8.
|
| [8] |
ZONG Z, ZHAO Y J, YE F, et al. Parallel computing of the underwater explosion cavitation effects on full-scale ship structures [J]. Journal of Marine Science and Application, 2012, 11(4): 469–477. DOI: 10.1007/s11804-012-1157-7.
|
| [9] |
ZHANG A M, REN S F, LI Q, et al. 3D numerical simulation on fluid-structure interaction of structure subjected to underwater explosion with cavitation [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2012, 33(9): 1191–1206. DOI: 10.1007/s10483-012-1615-8.
|
| [10] |
SAUREL R, LEMETAYER O. A multiphase model for compressible flows with interfaces, shocks, detonation waves and cavitation [J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2001, 431: 239–271. DOI: 10.1017/S0022112000003098.
|
| [11] |
SANDUSKY H, CHAMBERS P, ZERILLI F, et al. Dynamic measurements of plastic deformation in a water-filled aluminum tube in response to detonation of a small explosives charge [J]. Shock and Vibration, 1999, 6(3): 125–132. DOI: 10.1155/1999/650860.
|
| [12] |
XIE W F, YOUNG Y L, LIU T G. Multiphase modeling of dynamic fluid-structure interaction during close-in explosion [J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2008, 74(6): 1019–1043. DOI: 10.1002/nme.2207.
|
| [13] |
PARK J. Application of the Runge Kutta Discontinuous Galerkin-Direct Ghost Fluid Method to internal explosion inside a water-filled tube [J]. International Journal of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering, 2019, 11(1): 572–583. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijnaoe.2018.10.002.
|
| [14] |
JIN Z Y, YIN C Y, CHEN Y, et al. Coupling Runge-Kutta discontinuous Galerkin method to finite element method for compressible multi-phase flow interacting with a deformable sandwich structure [J]. Ocean Engineering, 2017, 130: 597–610. DOI: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2016.12.013.
|
| [15] |
许亮, 冯成亮, 刘铁钢. 弹性板水下爆炸冲击载荷的修正虚拟流体方法分析 [J]. 计算物理, 2017, 34(1): 1–9. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-246X.2017.01.001.XU L, FENG C L, LIU T G. Analysis of impact load on elastic plate in underwater explosions with modified ghost fluid method [J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2017, 34(1): 1–9. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-246X.2017.01.001.
|
| [16] |
王龙侃, 丁松, 李涛, 等. 基于RKDG方法的近壁面水下爆炸空化特性研究 [C]//北京力学会第24届学术年会会议论文集. 北京: 北京力学会, 2018.
|
| [17] |
张之凡, 王成. 近场水下爆炸空化效应对结构的载荷特性研究 [C]//北京力学会第24届学术年会会议论文集. 北京: 北京力学会, 2018.
|
| [18] |
Century Dynamics Inc. AUTODYN theory manual version 4.3[Z]. Concord, CA, USA: Century Dynamic Inc. , 2003.
|
| [19] |
张林夫, 夏维洪. 空化与空蚀 [M]. 南京: 河海大学出版社, 1989.
|
| [20] |
黄继汤. 空化与空蚀的原理及应用 [M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 1991.
|
| [21] |
杨博凯, 卢义玉, 杨晓峰, 等. 空化水射流空泡溃灭过程的数值分析 [J]. 郑州大学学报(工学版), 2012, 33(4): 60–64. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6833.2012.04.014.YANG B K, LU Y Y, YANG X F, et al. Numerical analysis on collapse of cavitation bubble in a water jet flow [J]. Journal of Zhengzhou University (Engineering Science), 2012, 33(4): 60–64. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6833.2012.04.014.
|






 下载:
下载: