| [1] |
王莹. 电爆炸导体及其应用 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 1986, 6(2): 184–192.WANG Y. Electrical exploding conductor and its applications [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 1986, 6(2): 184–192.
|
| [2] |
欧阳登焕. 铜箔和铜网格的电爆炸参数 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 1982, 2(4): 55–60.OUYANG D H. Electrically exploding parameters of copper foils and meshes [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 1982, 2(4): 55–60.
|
| [3] |
张永民, 姚伟博, 邱爱慈, 等. 金属丝电爆炸现象研究综述 [J]. 高电压技术, 2019, 45(8): 2668–2680. DOI: 10.13336/j.1003-6520.hve.20180615006.ZHANG Y M, YAO W B, QIU A C, et al. Review of wire electrical explosion phenomena [J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2019, 45(8): 2668–2680. DOI: 10.13336/j.1003-6520.hve.20180615006.
|
| [4] |
吴坚, 阴国锋, 范云飞, 等. 金属丝电爆炸研究进展-(Ⅱ): 水环境 [J]. 高电压技术, 2018, 44(12): 4003–4012. DOI: 10.13336/j.1003-6520.hve.20181126030.WU J, YIN G F, FAN Y F, et al. Review of electrical exploding wires-(Ⅱ): underwater [J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2018, 44(12): 4003–4012. DOI: 10.13336/j.1003-6520.hve.20181126030.
|
| [5] |
ANTONOV O, GILBURD L, EFIMOV S, et al. Generation of extreme state of water by spherical wire array underwaterelectrical explosion [J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2012, 19(10): 102702. DOI: 10.1063/1.4757984.
|
| [6] |
TANG T G, REN G W, GUO Z L, et al. An improved technique of expanding metal ring experiment under high explosive loading [J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2013, 84(4): 043908. DOI: 10.1063/1.4802255.
|
| [7] |
张寒虹, 陈志福, 张弛. 水中电爆炸的实验研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2002, 22(4): 363–367.ZHANG H H, CHEN Z F, ZHANG C. Experimental reserches on underwater wire exploding [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2002, 22(4): 363–367.
|
| [8] |
伍俊英, 冯长根, 陈朗, 等. 金属电爆炸等离子体辐射温度测量 [J]. 战术导弹技术, 2006(5): 31–33. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1300.2006.05.007.WU J Y, FENG C G, CHEN L, et al. Plasma radiation temperature measurement of metal explosion [J]. Tactical Missile Technology, 2006(5): 31–33. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1300.2006.05.007.
|
| [9] |
金涌, 栗保明. 铜丝电爆炸的光谱分析 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2014, 34(2): 252–256. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2014)02-0252-05.JIN Y, LI B M. Spectral analysis on electrical explosion of copper wire [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2014, 34(2): 252–256. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2014)02-0252-05.
|
| [10] |
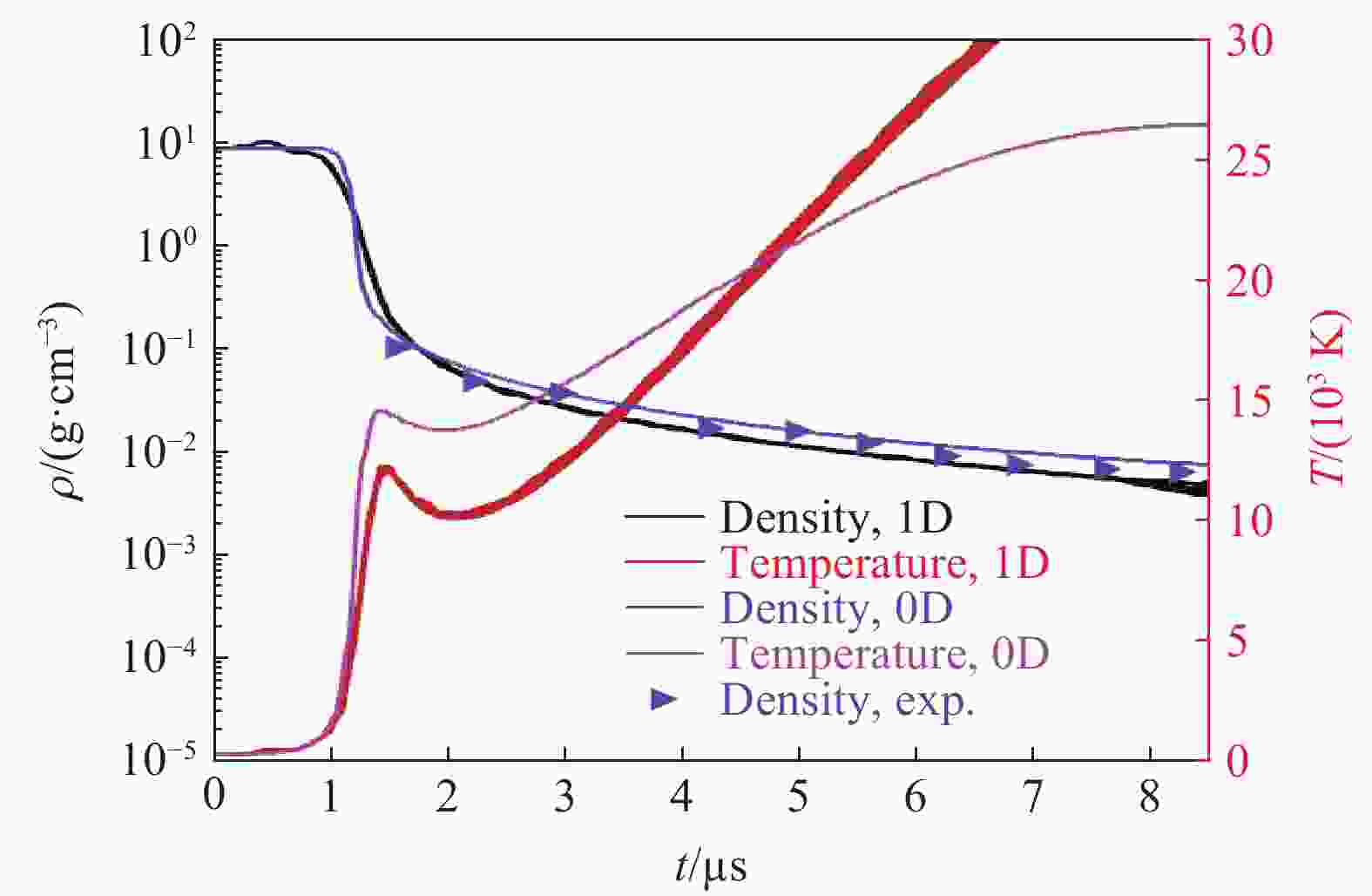
朱鑫磊, 邹晓兵, 赵屾, 等. 电爆金属丝质量密度分布的演变过程 [J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2014, 26(4): 045014. DOI: 10.11884/HPLPB201426.045014.ZHU X L, ZOU X B, ZHAO S, et al. Evolution of mass density distribution of electrical explosion of metal wires [J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2014, 26(4): 045014. DOI: 10.11884/HPLPB201426.045014.
|
| [11] |
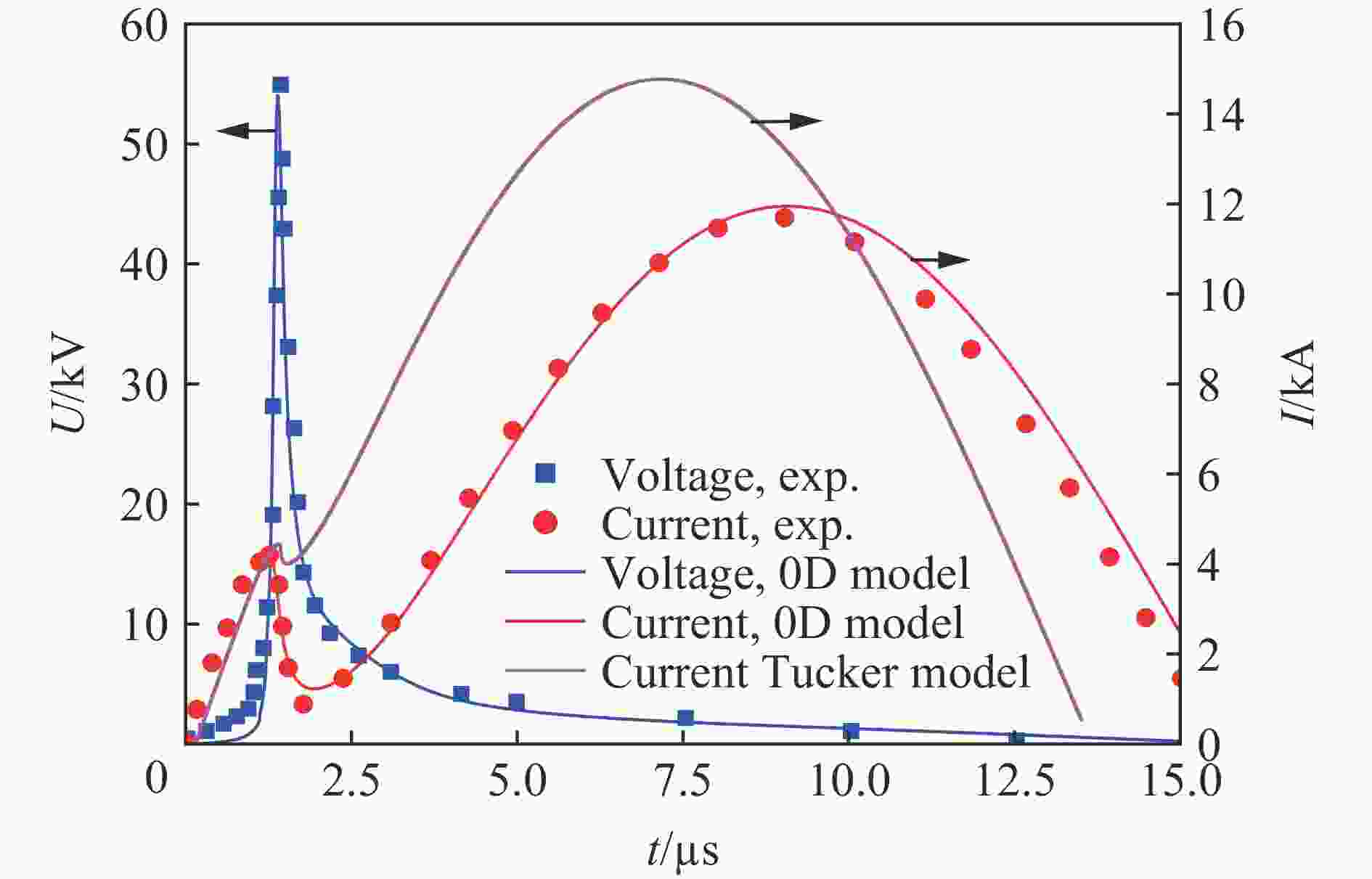
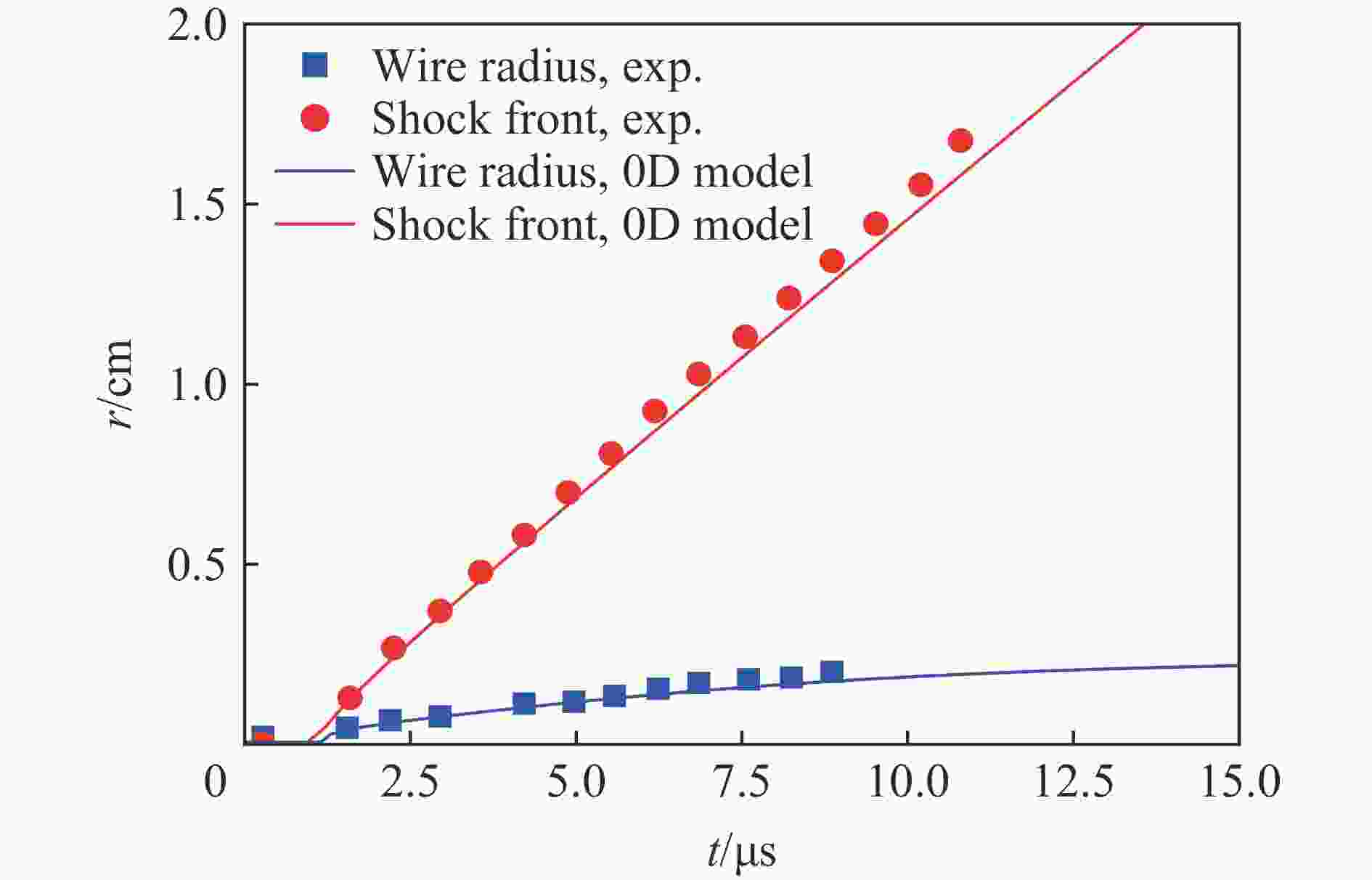
TUCKER T J. Behavior of exploding gold wires [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1961, 32(10): 1894–1900. DOI: 10.1063/1.1728259.
|
| [12] |
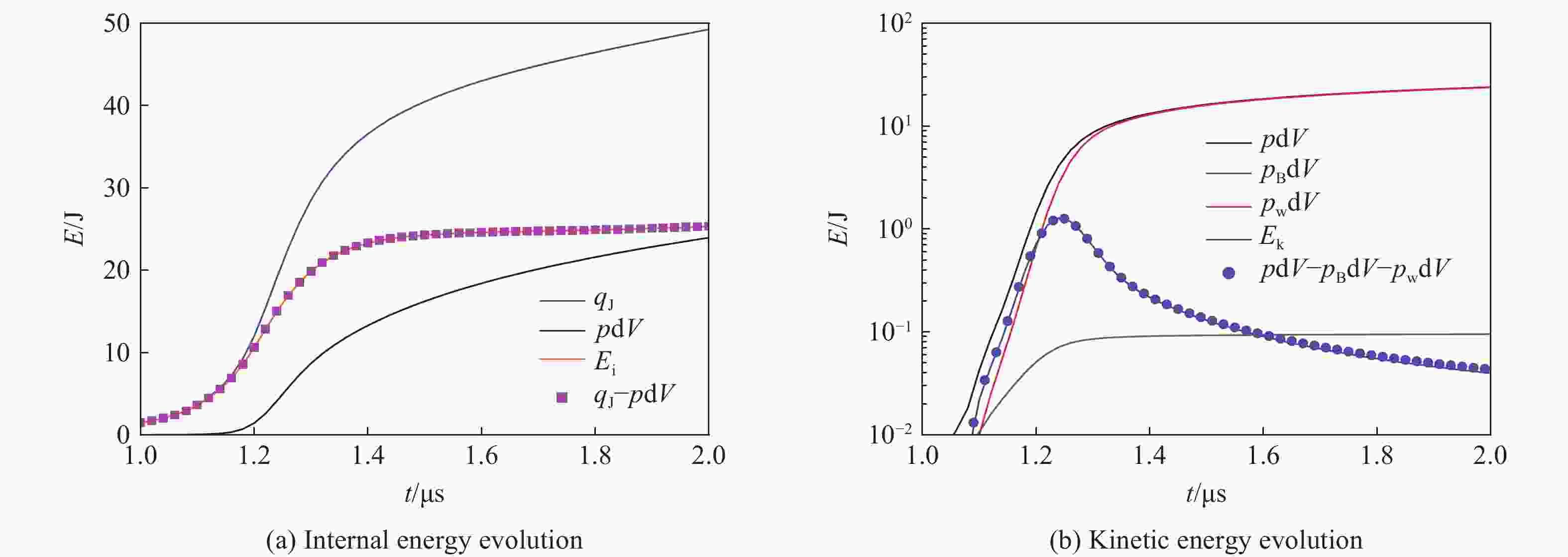
石桓通, 邹晓兵, 赵屾, 等. 并联金属丝提高电爆炸丝沉积能量的数值模拟 [J]. 物理学报, 2014, 63(14): 145206. DOI: 10.7498/aps.63.145206.SHI H T, ZOU X B, ZHAO S, et al. Numerical simulation of energy deposition improvment in electrical wire explosion using a parallel wire [J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2014, 63(14): 145206. DOI: 10.7498/aps.63.145206.
|
| [13] |
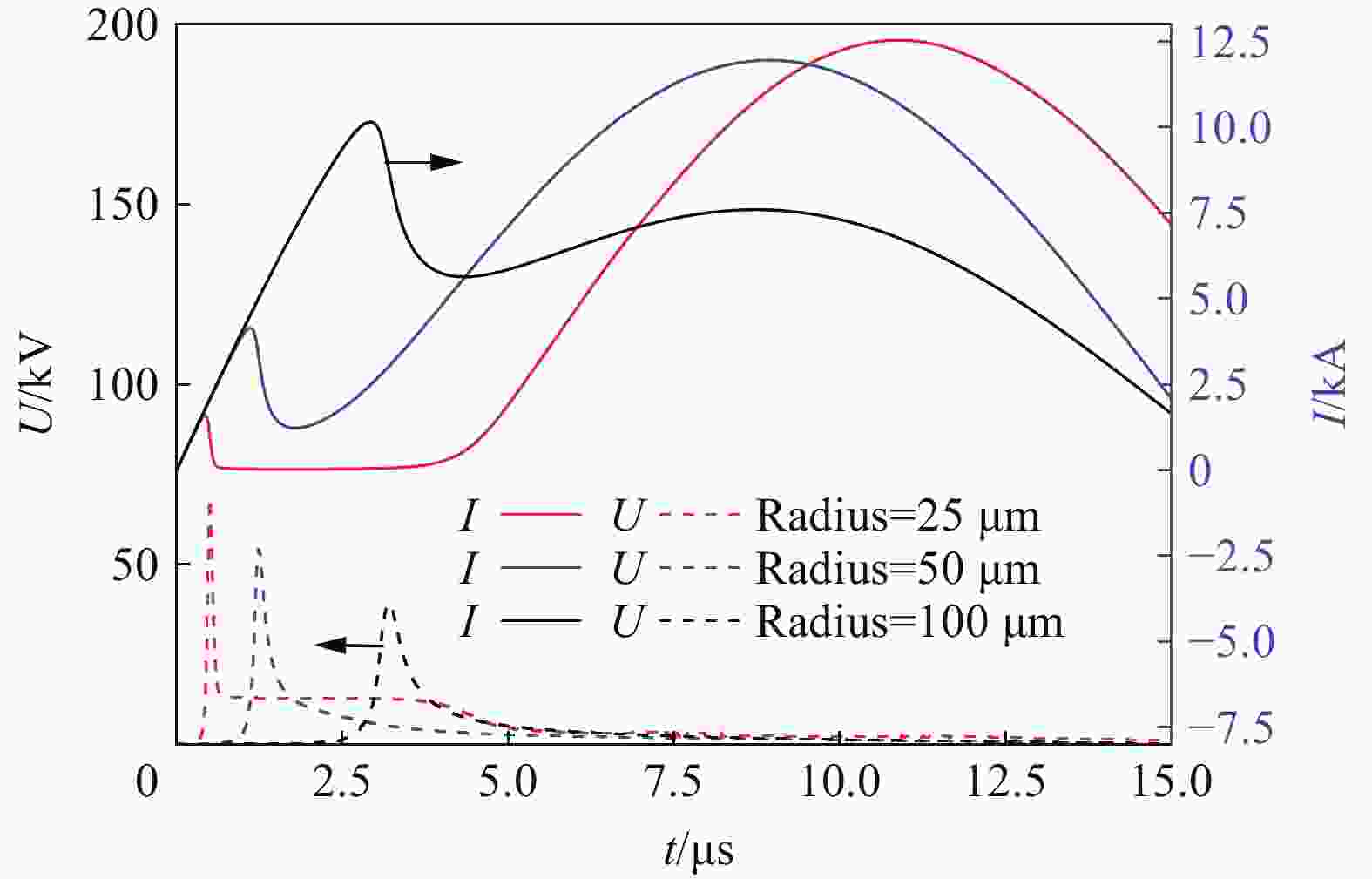
郭军, 邱爱慈. 熔丝电爆炸过程电气特性的数字仿真 [J]. 系统仿真学报, 2006, 18(1): 20–22, 40. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-731X.2006.01.006.GUO J, QIU A C. Digital simulation for fuse electrical characteristics in process of electrically exploding [J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2006, 18(1): 20–22, 40. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-731X.2006.01.006.
|
| [14] |
BLOOMBERG H W, LAMPE M, COLOMBANT D G. Early expansion in exploding multiple wire arrays [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1980, 51(10): 5277–5284. DOI: 10.1063/1.327482.
|
| [15] |
晁攸闯, 韩若愚, 李兴文, 等. 水中电爆炸放电通道特性0维数值模拟 [J]. 高电压技术, 2014, 40(10): 3112–3118. DOI: 10.13336/j.1003-6520.hve.2014.10.024.CHAO Y C, HAN R Y, LI X W, et al. Zero-dimensional simulation of discharge channel properties during underwater electrical wire explosion [J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2014, 40(10): 3112–3118. DOI: 10.13336/j.1003-6520.hve.2014.10.024.
|
| [16] |
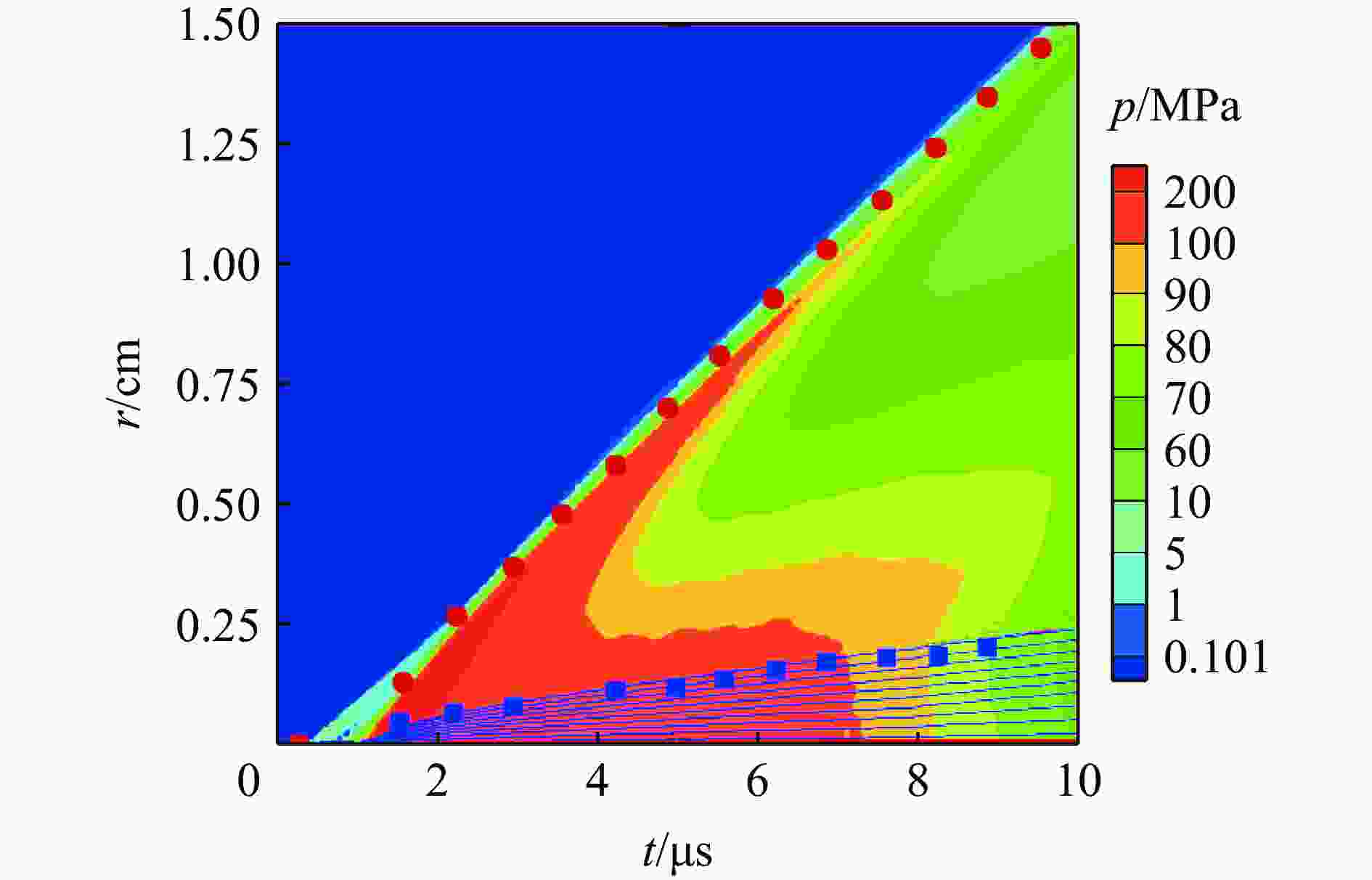
ROSOSHEK A, EFIMOV S, GUROVICH V, et al. Evolution of a shock wave generated by underwater electrical explosion of a single wire [J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2019, 26(4): 042302. DOI: 10.1063/1.5092321.
|
| [17] |
STEPHENS J, NEUBER A. Exploding-wire experiments and theory for metal conductivity evaluation in the sub-eV regime [J]. Physical Review E, 2012, 86(6): 066409. DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.86.066409.
|
| [18] |
CHUNG K J, LEE K, HWANG Y S, et al. Numerical model for electrical explosion of copper wires in water [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2016, 120(20): 203301. DOI: 10.1063/1.4968396.
|
| [19] |
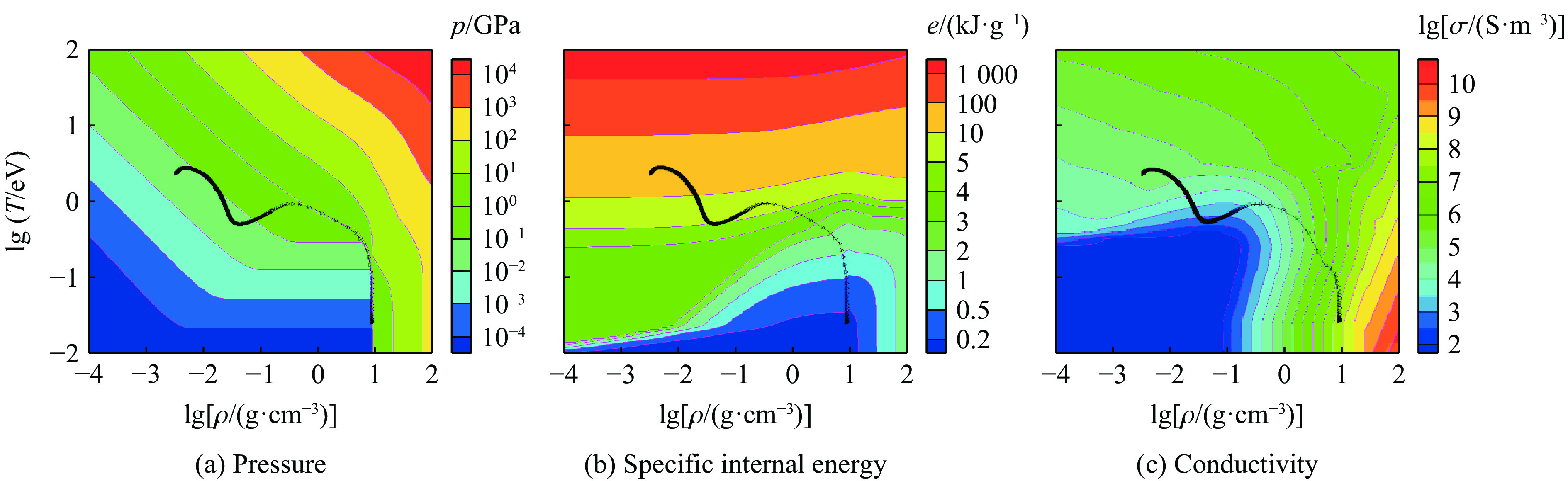
MORE R M, WARREN K H, YOUNG D A, et al. A new quotidian equation of state (QEOS) for hot dense matter [J]. The Physics of Fluids, 1988, 31(10): 3059–3078. DOI: 10.1063/1.866963.
|
| [20] |
LEE Y T, MORE R M. An electron conductivity model for dense plasmas [J]. The Physics of Fluids, 1984, 27(5): 1273–1286. DOI: 10.1063/1.864744.
|
| [21] |
DESJARLAIS M P. Practical improvements to the lee-more conductivity near the metal-insulator transition [J]. Contributions to Plasma Physics, 2001, 41(2/3): 267–270. DOI: 10.1002/1521-3986(200103)41:2/3<267::AID-CTPP267>3.0.CO;2-P.
|
| [22] |
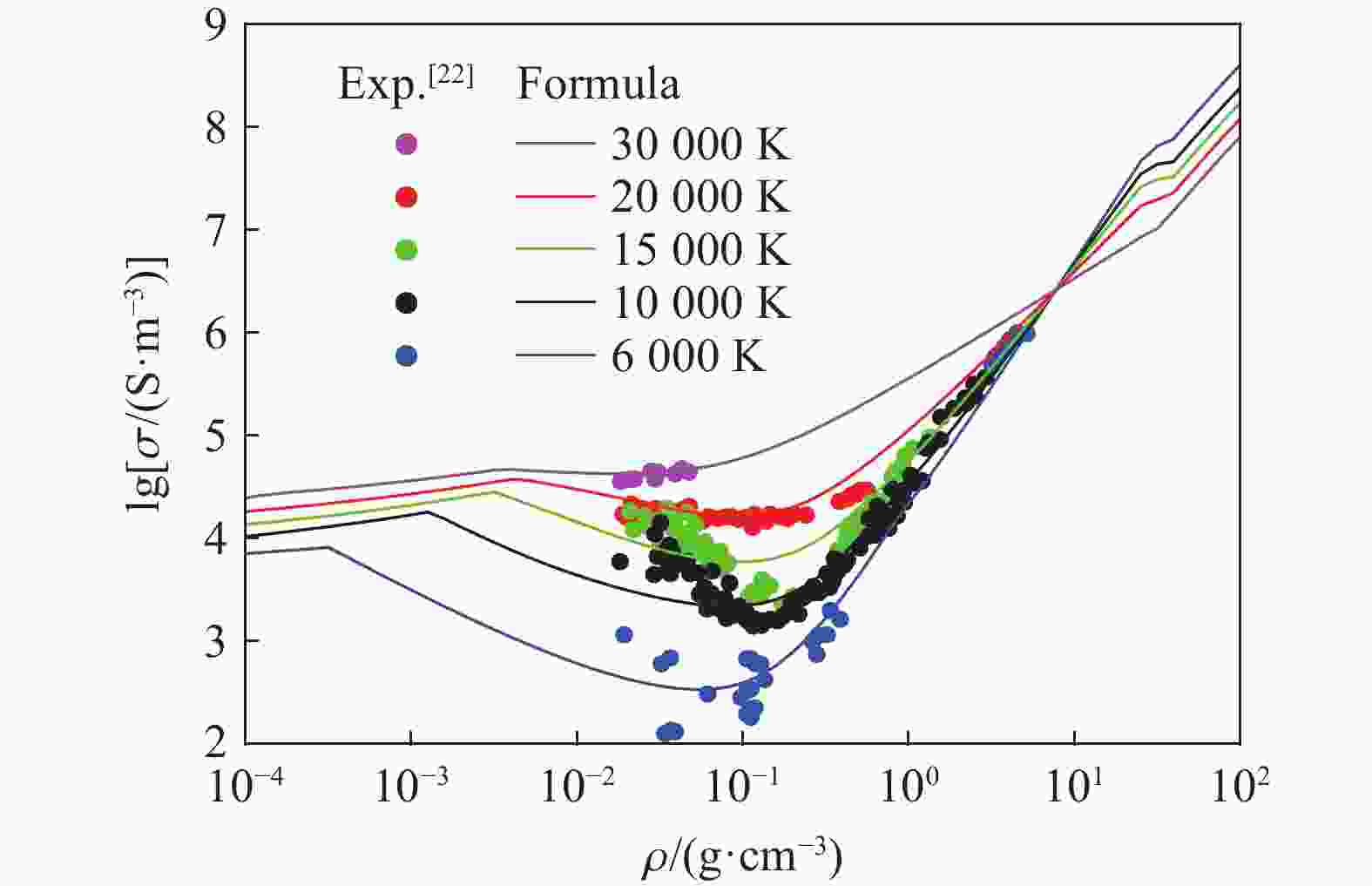
DESILVA A W, KATSOUROS J D. Electrical conductivity of dense copper and aluminum plasmas [J]. Physical Review E, 1998, 57(5): 5945–5951. DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.57.5945.
|
| [23] |
STEPHENS J, DICKENS J, NEUBER A. Semiempirical wide-range conductivity model with exploding wire verification [J]. Physical Review E, 2014, 89(5): 053102. DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.89.053102.
|






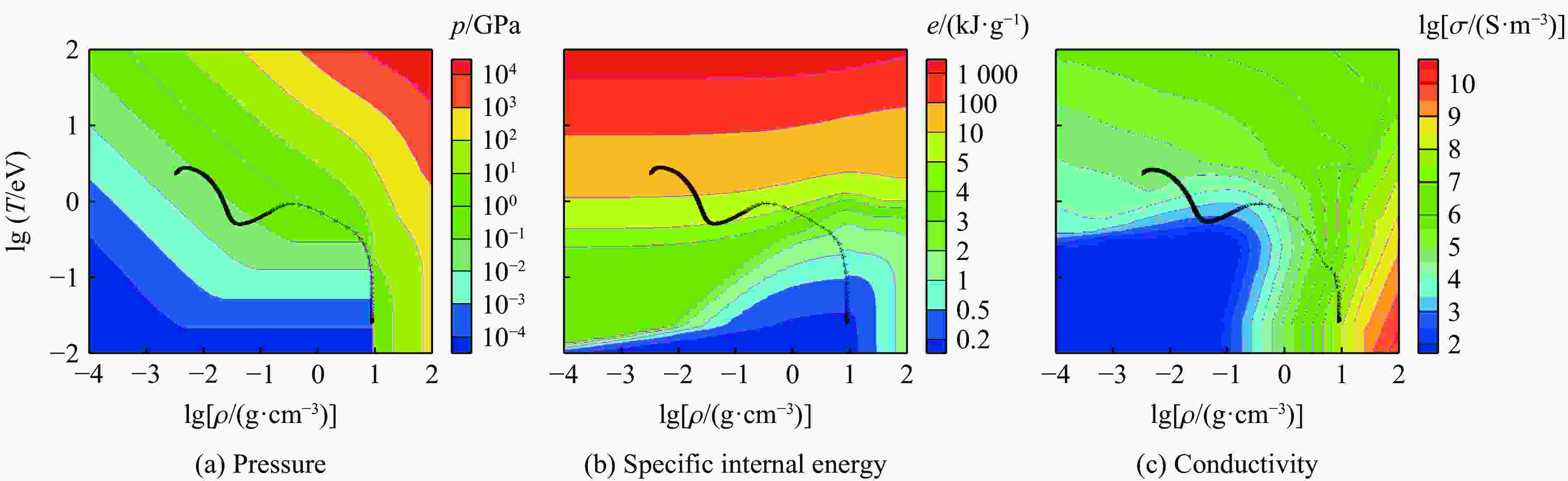
 下载:
下载: