Discontinuous impact fatigue failure model and microscopic mechanism of pure titanium under high strain-rate loading
-
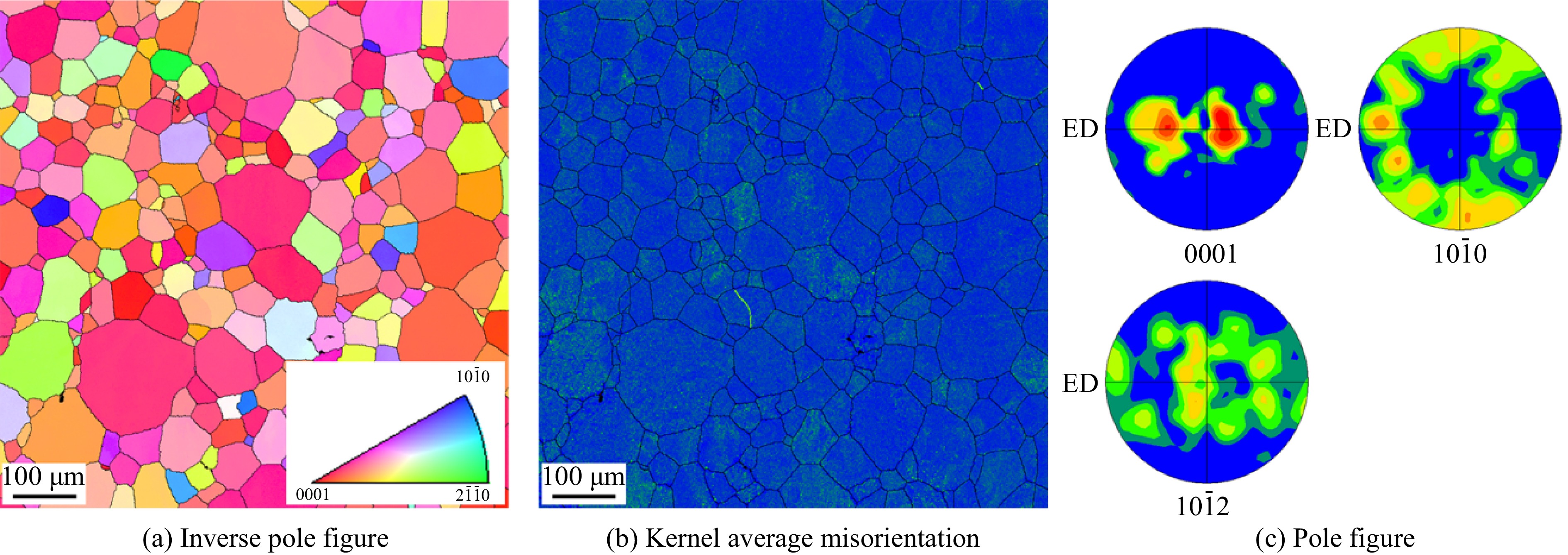
摘要: 基于传统的分离式霍普金森拉杆系统,设计了应变控制的冲击疲劳寿命测试实验,研究了冲击疲劳加载下纯钛的微观演化机制及冲击疲劳对材料宏观力学行为的影响。通过对不同冲击疲劳试验阶段的试样开展准静态力学性能测试,借助扫描电子显微镜 (scanning electron microscope, SEM) 和电子背散射衍射 (electron backscatter diffraction, EBSD) 技术表征试样在不同阶段的微观组织以及冲击疲劳失效后的断口形貌,研究纯钛在冲击疲劳失效过程中的循环硬化/软化规律及其微观演化机制。结果表明:通过改变子弹长度可以实现应变控制的冲击疲劳寿命测试;Manson-Coffin疲劳寿命模型可以较好地反映纯钛的冲击疲劳寿命与应变幅值之间的关系;纯钛在冲击疲劳失效过程中表现出循环硬化的现象,这主要是疲劳过程中孪生变形引起的细晶强化和塑性变形引起的应变硬化共同作用的结果,纯钛的冲击疲劳损伤主要表现为变形能力的损失。
-
关键词:
- 冲击疲劳 /
- 纯钛 /
- Manson-Coffin模型 /
- 微观组织
Abstract: The fatigue failure behavior of structural materials under repeated impact loads has always attracted much attention. Mastering its damage accumulation process and evolution mechanism at the micro-scale is the fundamental way to understand the impact fatigue failure mechanism. Due to the complexity of the impact fatigue load itself and the limitations of the current experimental equipment, there are still major problems in the study of impact fatigue failure of materials. Therefore, pure titanium was used as the research object and a strain-controlled impact fatigue life test was designed based on the traditional split Hopkinson tension bar system. The strain-controlled impact fatigue life test was achieved by changing the length of the striker, and the amplitude of the incident wave needed to be kept at the same level when using different striker tests. The relationship between strain amplitude and impact fatigue life was analyzed. The impact fatigue interruption experiments of 5 times, 10 times and 20 times were carried out with 100 mm bullets. The microstructure of the samples after different impact times were characterized by electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) and then the quasi-static mechanical properties were tested. The fracture morphology after impact fatigue failure was observed by scanning electron microscope (SEM). The cyclic hardening/softening law and its microscopic evolution mechanism of pure titanium during impact fatigue failure were studied. The results show that the strain-controlled impact fatigue life test can be realized by changing the striker length. The Manson-Coffin fatigue life model can better reflect the relationship between impact fatigue life and strain amplitude of pure titanium. Moreover, pure titanium exhibits cyclic hardening during impact fatigue failure, which is mainly due to the combined effect of fine grain strengthening caused by twin deformation and strain hardening caused by plastic deformation during fatigue. Finally, the impact fatigue damage of pure titanium is mainly manifested as the loss of deformation ability.-
Key words:
- impact fatigue /
- pure titanium /
- Manson-Coffin model /
- microstructure
-
表 1 不同冲击应变幅值下纯钛的冲击疲劳寿命
Table 1. Impact fatigue life of pure titanium under different impact strain amplitudes
Δεt/2 冲击疲劳寿命/次 0.017 58 62 0.023 21 23 25 0.026 12 16 17 0.035 10 8 11 0.051 5 6 7 0.070 4 4 4 -
[1] 刘正, 胡冶昌, 魏志芳. 复进簧冲击疲劳应力响应及其寿命预测 [C] //首届兵器工程大会论文集. 2017: 52–57. [2] 希弦. 微观航母之舰载机拦阻钩 [J]. 兵器知识, 2015(3): 72–75. DOI: 10.19437/j.cnki.11-1470/tj.2015.03.016.XI X. Arresting hook of carrier-based aircraft on aircraft carrier [J]. Ordnance Knowledge, 2015(3): 72–75. DOI: 10.19437/j.cnki.11-1470/tj.2015.03.016. [3] JOHNSON A A, STOREY R J. The impact fatigue properties of iron and steel [J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2007, 308(3/4/5): 458–466. DOI: 10.1016/j.jsv.2007.06.044. [4] YANG S S, BAI C Y, YANG Q, et al. Review on impart fatigue of metallic materials and structures [J]. Aeronautical Science & Technology, 2021, 32(2): 1–13. DOI: 10.19452/j.issn1007-5453.2021.02.001. [5] JGUCHI K T H, TAIRA S. Failure mechanisms in impact fatigue of metals [J]. Fatigue and Fracture of Engineering Materials and Srrucfures, 1979, 2(2): 165–176. DOI: 10.1111/j.1460-2695.1979.tb01352.x. [6] NAKAYAMA H, TANAKA T. Impact fatigue crack growth behaviors of high strength low alloy steel [J]. International Journal of Fracture, 1984, 26(9): 19–24. DOI: 10.1007/BF01152319. [7] TANAKA T, KINOSHITA K, NAKAYAMA H. Fatigue crack growth and microscopic crack opening behaviour under impact fatigue load [J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 1989, 11(2): 117–123. DOI: 10.1016/0142-1123(89)90006-6. [8] YANG P, LIAO X, ZHU J, et al. High strain-rate low-cycle impact fatigue of a medium-carbon alloy steel [J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 1994, 16(5): 327–330. DOI: 10.1016/0142-1123(94)90270-4. [9] ZHANG M, YANG P S, TAN Y X, et al. An observation of crack initiation and early crack growth under impact fatigue loading [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 1999, 271(1/2): 390–394. DOI: 10.1016/S0921-5093(99)00264-6. [10] 李会会, 易丹青, 刘会群, 等. 硬质合金冲击疲劳行为的研究 [J]. 硬质合金, 2014, 31(2): 100–111. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7292.2014.02.006.LI H H, YI D Q, LIU H Q, et al. Research on impact fatigue behaviour of cemented carbide [J]. Cemented Carbide, 2014, 31(2): 100–111. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7292.2014.02.006. [11] 陈鼎, 姚亮, 陈振华, 等. WC-Co类硬质合金的低周冲击疲劳性能研究 [J]. 稀有金属与硬质合金, 2017, 45(3): 71–76. DOI: CNKI:SUN:XYJY.0.2017-03-014.CHEN D, YAO L, CHEN Z H, et al. Study on low cycle impact fatigue performance of WC-Co cemented carbides [J]. Rare Metals and Cemented Carbides, 2017, 45(3): 71–76. DOI: CNKI:SUN:XYJY.0.2017-03-014. [12] STANTON L B. The resistance of materials to impact [J]. Proceedings of the Institute of Mechanical Engineers, 1908: 889–919. DOI: 10.1243/PIME_PROC_1908_075_019_02. [13] JOHNSON D J. The impact fatigue properties of pearlitic plain carbon steels [J]. Fatigue of and Fracture Engineering Materials and Structures, 1981, 4(3): 279–285. DOI: 10.1111/j.1460-2695.1981.tb01125.x. [14] JOHNSON A A. The low cycle impact fatigue properties of pearlitic plain carbon steels [J]. Fatigue and Fracture of Engineering Mateirals and Structures, 1985, 8(3): 287–294. DOI: 10.1111/j.1460-2695.1985.tb00428.x. [15] 张遥辉. 钢铁材料冲击疲劳行为综述 [J]. 中国设备工程, 2020(6): 211–216. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0711.2020.06.131.ZHANG Y H. Overview of impact fatigue behavior of steel materials [J]. China Plant Engineering, 2020(6): 211–216. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0711.2020.06.131. [16] SUN Q, LIU X R, LIANG K. Impact fatigue life prediction for notched specimen of steel AerMet100 subjected to high strain rate loading [J]. International Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2018, 10(3): 1850030. DOI: 10.1142/s1758825118500308. [17] WANG B W, QIAN C C, BAI C Y, et al. Study on impact fatigue test and life prediction method of TC18 titanium alloy [J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2023, 168: 1–17. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2022.107391. [18] GAO P F, LEI Z N, LI Y K, et al. Low-cycle fatigue behavior and property of TA15 titanium alloy with tri-modal microstructure [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2018, 736: 1–11. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2018.08.080. [19] 张欠欠, 刘晓燕, 雷罗, 等. 工业纯钛的室温低周疲劳行为 [J]. 塑性工程学报, 2019, 26(2): 219–224. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2012.2019.02.029.ZHANG Q Q, LIU X Y, LUO L, et al. Low-cycle fatigue behavior of commercially pure titanium at room temperature [J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2019, 26(2): 219–224. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2012.2019.02.029. [20] CHANG L, LV C, KITAMURA T, et al. Slip dominated planar anisotropy of low cycle fatigue behavior of commercially pure titanium [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2022, 854(9):143807. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2022.143807. [21] SONG X P, CHEN G L, GU H C. Low cycle fatigue behavior of commercial purity titanium in liquid nitrogen [J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2002, 24: 49–56. DOI: 10.1016/S0142-1123(01)00047-0. [22] ABDUL-LATIF A. Continuum damage model for low-cycle fatigue of metals: an overview [J]. International Journal of Damage Mechanics, 2021, 30(7): 1036–1078. DOI: 10.1177/1056789521991620. -







 下载:
下载: