A study of high-velocity penetration characteristics and resistance model of elliptical cross-section truncated ogive projectile
-
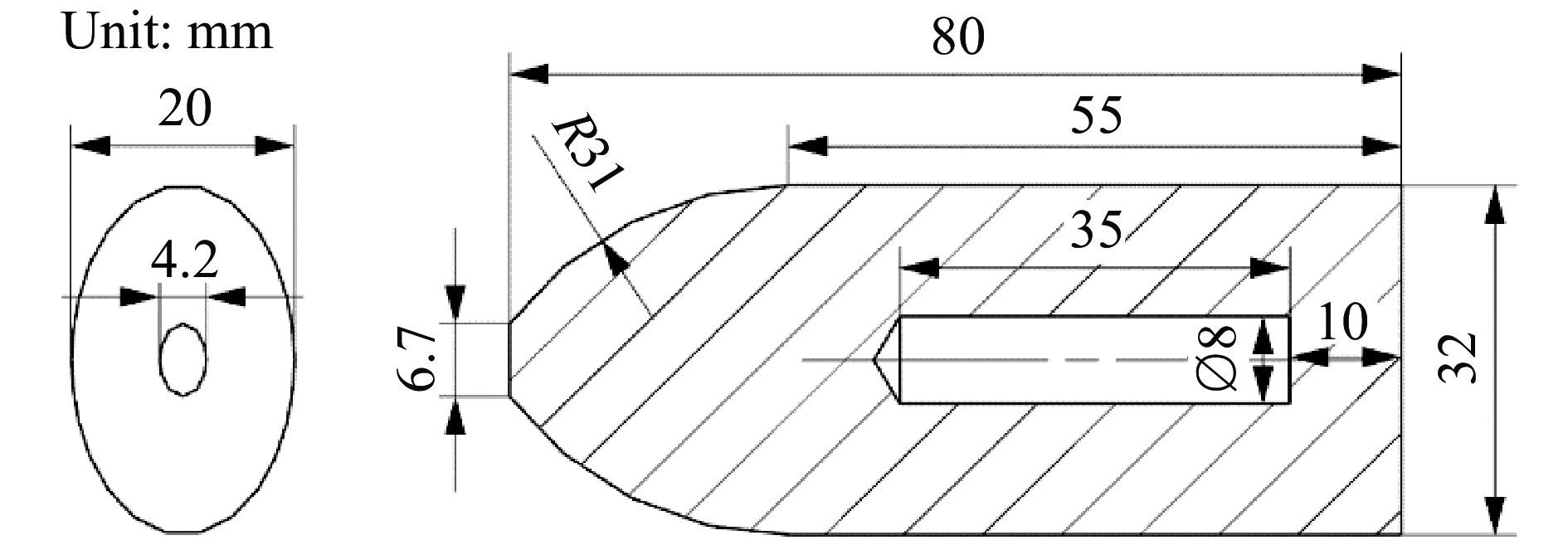
摘要: 随着高超声速武器系统的发展,具有更大空间利用率的异型截面弹体开始受到广泛关注,异型弹体的高速穿甲特性及毁伤机理是当前亟需解决的关键问题。基于典型反舰战斗部的截锥形头部结构及椭圆截面弹体外形,通过数值仿真方法研究了椭圆截面截锥弹体高速正贯穿金属薄板的阻力特性及薄板损伤机理,将弹体载荷分为剪切冲塞和延性扩孔阻力两部分,结合数值仿真结果提出了适用于椭圆截面平头弹、尖卵形弹的高速穿甲阻力函数及剩余速度解析模型,采用微分面力法和刚体动力学相结合的方法构建了椭圆弹正穿甲模型,并通过数值仿真结果验证了理论模型的有效性。结果表明:椭圆截面截锥弹体正贯穿金属薄板的过程分为载荷作用的头部侵入阶段和无载荷作用的弹身贯穿阶段,头部侵入阶段弹体对薄板的破坏模式分解为截锥平台造成的剪切冲塞和头部弧面的延性扩孔;高速冲击条件下椭圆截面尖卵形弹/平头弹对薄板的损伤与低速冲击时不同,尖卵形弹体贯穿薄板时发生延性扩孔破坏,薄板受平头弹高速冲击时出现剪切冲塞-延性扩孔相耦合的破坏模式;椭圆截面弹体正穿甲过程中所受阻力与截面积相等的圆截面弹体相同,区别在于椭圆截面弹体非对称结构外形导致载荷非均匀分布。Abstract: With the development of the hypersonic weapon system, the non-circular cross-section projectile with more space utilization has attracted extensive attention. The high-velocity penetration mechanism of the non-circular cross-section projectile is a crucial issue that must be solved. Based on the truncated conical head structure of a typical anti-ship warhead and the elliptical section projectile’s shape, the elliptical section’s resistance characteristics and damage mechanism of thetruncated cone projectile through the metal sheet at high velocity are studied by numerical simulation. The load applied on the projectile is divided into two parts: shear punching resistance and ductile enlargement resistance. Combined with the numerical simulation results, the high-velocity penetration resistance function and the analytical model of residual velocity are proposed, which are suitable for elliptic cross-section flat projectile and ogive projectile. The differential surface force method and rigid body dynamics are used to construct a normal penetration model, and numerical simulation results verify the validity of the theoretical model. The results show that the elliptical cross-section truncated cone projectile penetrating through the metal sheet can be divided into the head penetration stage under load and the body penetration stage without load. In the head invasion stage, the failure mode of the thin sheet due to project penetration is decomposed into the shear plugging caused by the truncated cone platform and the ductility enlargement of the curved surface of the head. Under high-velocity impact, the damage to the sheet caused by elliptic ogive projectile/blunt projectile is different from that caused by low-velocity impact. When the ogive projectile penetrates through the sheet, ductile enlargement failure occurs. When the sheet is impacted by blunt projectile at high velocity, the coupled failure mode of shear punching and ductile enlargement takes place. The resistance of the elliptical cross-section projectile is the same as that of the circular cross-section projectile with the same cross-sectional area. The difference is that the asymmetric structure of the elliptical cross-section projectile leads to non-uniform load distribution.
-
Key words:
- elliptical cross section projectile /
- plugging /
- enlargement /
- resistance function /
- penetration model
-
表 1 945钢仿真材料参数统计
Table 1. Material parameters of 945 steel used in numerical simulation
A/MPa B/MPa n C1 C2 E/GPa ν $ {\dot{\varepsilon }}_{0}/{\mathrm{s}}^{-1} $ T0/K Tm/K 451.6 797.73 0.75 −0.1589 0.012 210 0.33 3×10−4 293 1800 mT χ ρ/(g·cm−3) cp/(J·kg−1·K−1) D1 D2 D3 D4 $ {\varepsilon }_{\mathrm{f},\mathrm{t}} $ 0.859 0.9 7.85 452 0.35 1.11 −0.806 0.10 0.996 表 2 塑性冲击波速仿真结果
Table 2. Simulation results of the velocity of plastic shock wave
v0/(m·s−1) x1/mm t1/μs cs/(m·s−1) H/t1 式(32) 式(34) 700 0.376 0.542 5533.7 5497.1 4897.9 800 0.452 0.536 5600.6 5564.3 4968.6 900 0.480 0.537 5584.3 5547.4 5039.3 1000 0.511 0.515 5827.0 5788.5 5110.0 表 3 模型误差
Table 3. Relative deviation of the model
长短轴之比 初速/(m·s−1) 尖卵形弹 平头弹 余速/(m·s−1) 误差% 余速/(m·s−1) 误差% 仿真 模型 仿真 模型 1 700 688.8 685.9 −0.4 664.9 671.6 1.0 800 787.8 786.0 −0.2 759.8 764.9 0.7 900 887.1 885.9 −0.1 854.6 857.4 0.3 1000 986.5 985.7 −0.1 949.4 949.3 0.0 2 700 688.7 688.9 0.0 665.2 671.6 1.0 800 787.8 789.2 0.2 760.1 764.9 0.6 900 887.2 889.3 0.2 855.0 867.4 1.5 1000 986.8 989.2 0.2 949.8 949.2 −0.1 表 4 剩余速度对比表
Table 4. Comparison of the residual velocity
初速
/(m·s−1)剩余速度/(m·s−1)(λ=1.6,靶板厚度3 mm) 相对误差/% 剩余速度/(m·s−1)(λ=2,靶板厚度5 mm) 相对误差/% 本文模型 Recht-Ipson模型 本文模型 Recht-Ipson模型 100 91.0 22.5 −303.8 74.7 22.5 231.3 200 186.5 175.6 −6.2 158.1 97.5 62.2 300 284.1 282.7 −0.5 251.8 242.0 4.0 400 382.7 385.1 0.6 350.7 354.1 −1.0 500 482.0 485.9 0.8 453.1 459.0 −1.3 600 581.8 585.9 0.7 556.6 560.8 −0.7 700 681.8 685.5 0.5 658.4 661.1 −0.4 800 782.0 784.9 0.4 758.9 760.4 −0.2 900 881.4 884.1 0.3 858.6 859.1 −0.1 1000 980.6 983.1 0.3 957.7 957.5 0.0 -
[1] 董恒. 椭圆截面弹体侵彻混凝土靶作用过程与结构响应研究 [D]. 北京理工大学, 2021.DONG H. Penetration mechanism and structural response of elliptical cross-sectional projectile penetrating into concrete target[D]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology, 2021. [2] 王浩. 椭圆变截面弹体贯穿加筋板破坏模式与偏转机理研究 [D]. 北京理工大学, 2020.WANG H. The failure mode and deflection mechanism of projectiles with tapered-elliptic cross-section perforation into stiffened plates[D]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology, 2020. [3] DAI X H, WANG K H, LI M R, et al. Rigid elliptical cross-section ogive-nose projectiles penetration into concrete targets [J]. Defence Technology, 2021, 17(3): 800–811. DOI: 10.1016/j.dt.2020.05.011. [4] 魏海洋, 张先锋, 熊玮, 等. 椭圆截面弹体斜侵彻金属靶体弹道研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2022, 42(2): 023304. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2021-0291.WEI H Y, ZHANG X F, XIONG W, et al. Oblique penetration of elliptical cross-section projectile into metal target [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2022, 42(2): 023304. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2021-0291. [5] 田泽, 王浩, 武海军, 等. 椭圆变截面弹体斜贯穿薄靶姿态偏转机理研究 [J]. 兵工学报, 2022, 43(7): 1537–1552. DOI: 10.12382/bgxb.2021.0367.TIAN Z, WANG H, WU H J, et al. Attitude deflection mechanism of projectiles with variable elliptical cross-sections obliquely perforating thin targets [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2022, 43(7): 1537–1552. DOI: 10.12382/bgxb.2021.0367. [6] WU H J, DENG X M, DONG H, et al. Three-dimensional trajectory prediction and analysis of elliptical projectile [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2023, 174: 104497. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2023.104497. [7] LIU J W, LIU C, ZHANG X F, et al. Research on the penetration characteristics of elliptical cross-section projectile into semi-infinite metal targets [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2023, 173: 104438. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2022.104438. [8] 邓希旻, 田泽, 武海军, 等. 上下非对称结构弹体侵彻金属薄板的特性及薄板破坏形式[J]. 兵工学报, 2022. DOI: 10.12382/bgxb.2022.0724.DENG X M, TIAN Z, WU H J, et al. Penetration characteristics and plate failure modes of asymmetric shaped projectiles penetrating thin metal targets[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2022. DOI: 10.12382/bgxb.2022.0724. [9] BACKMAN M E, GOLDSMITH W. The mechanics of penetration of projectiles into targets [J]. International Journal of Engineering Science, 1978, 16(1): 1–99. DOI: 10.1016/0020-7225(78)90002-2. [10] RECHT R F, IPSON T W. Ballistic perforation dynamics [J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 1963, 30(3): 384. DOI: 10.1115/1.3636566. [11] AWERBUCH J, BODNER S R. Analysis of the mechanics of perforation of projectiles in metallic plates [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 1974, 10(6): 671–684. DOI: 10.1016/0020-7683(74)90050-x. [12] CHEN X W, LI Q M. Shear plugging and perforation of ductile circular plates struck by a blunt projectile [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2003, 28(5): 513–536. DOI: 10.1016/S0734-743X(02)00077-5. [13] WEN H M, JONES N. Low-velocity perforation of punch-impact-loaded metal plates [J]. Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology-Transactions of the Asme, 1996, 118(2): 181–187. DOI: 10.1115/1.2842178. [14] ROSENBERG Z, DEKEL E. Revisiting the perforation of ductile plates by sharp-nosed rigid projectiles [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2010, 47(22/23): 3022–3033. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2010.07.003. [15] CHEN X W, HUANG X L, LIANG G J. Comparative analysis of perforation models of metallic plates by rigid sharp-nosed projectiles [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2011, 38(7): 613–621. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2010.12.005. [16] MASRI R. Practical formulae for predicting the ballistic limit velocity of armour perforation by ductile hole growth [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2022, 167: 104219. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2022.104219. [17] CHEN X W, LI Q M, FAN S C. Initiation of adiabatic shear failure in a clamped circular plate struck by a blunt projectile [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2005, 31(7): 877–893. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2004.04.011. [18] BORVIK T, HOPPERSTAD O S, LANGSETH M, et al. Effect of target thickness in blunt projectile penetration of Weldox 460 E steel plates [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2003, 28(4): 413–464. DOI: 10.1016/S0734-743x(02)00072-6. [19] RUSINEK A, RODRíGUEZ-MARTíNEZ J A, ZAERA R, et al. Experimental and numerical study on the perforation process of mild steel sheets subjected to perpendicular impact by hemispherical projectiles [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2009, 36(4): 565–587. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2008.09.004. [20] 陈小伟, 梁冠军, 姚勇, 等. 平头弹穿透金属靶板的模式分析 [J]. 力学学报, 2009, 41(1): 84–90. DOI: 10.6052/0459-1879-2009-1-2007-572.CHEN X W, LIANG G J, YAO Y, et al. Perforation modes of metal plates struck by a blunt rigid projectile[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2009, 41(1): 84–90. DOI: 10.6052/0459-1879-2009-1-2007-572. [21] MAE H, TENG X, BAI Y, et al. Comparison of ductile fracture properties of aluminum castings: Sand mold vs. metal mold [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2008, 45(5): 1430–1444. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2007.10.016. [22] 李营. 反舰导弹舱内爆炸作用下舱室结构毁伤与防护机理 [D]. 武汉:武汉理工大学, 2017.LI Y. Damage and protective mechanism of cabins under anti-ship missile internal blast [D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2017. [23] DONG H, LIU Z H, WU H J, et al. Study on penetration characteristics of high-speed elliptical cross-sectional projectiles into concrete [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2019, 132: 103311. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2019.05.025. [24] 王浩, 潘鑫, 武海军, 等. 椭圆截面截卵形刚性弹体正贯穿加筋板能量耗散分析 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2019, 39(10): 103203. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0350.WANG H, PAN X, WU H J, et al. Energy dissipation analysis of elliptical truncated oval rigid projectile penetrating stiffened plate[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2019, 39(10): 69–80. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0350. [25] DENG X M, WU H J, YANG X, et al. Preformed fragment velocity distribution of elliptical cross-section projectile [J]. Latin American Journal of Solids and Structures, 2022, 19(1): e423. DOI: 10.1590/1679-78256835. [26] TENG X, WIERZBICKI T. Dynamic shear plugging of beams and plates with an advancing crack [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2005, 31(6): 667–698. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2004.03.013. [27] VERSHININ V V. Validation of metal plasticity and fracture models through numerical simulation of high velocity perforation [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2015, 67/68: 127–138. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2015.04.007. [28] MASRI R. Ballistically equivalent aluminium targets and the effect of hole slenderness ratio on ductile plate perforation [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2015, 80: 45–55. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2015.01.003. [29] MASRI R, DURBAN D. Quasi-static cylindrical cavity expansion in an elastoplastic compressible Mises solid [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2006, 43(25/26): 7518–7533. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2006.03.012. [30] STANLEY M. Lasl shock hugoniot data [M]. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1980. [31] LI Q M, JONES N. Shear and adiabatic shear failures in an impulsively loaded fully clamped beam [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1999, 22(6): 589–607. DOI: 10.1016/s0734-743x(99)00013-5. [32] BØRVIK T, LANGSETH M, O. SHOPPERSTAD, et al. Perforation of 12 mm thick steel plates by 20 mm diameter projectiles with flat, hemispherical and conical noses: part I: experimental study [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2001, 27(1): 19–35. DOI: 10.1016/S0734-743X(01)00034-3. [33] BEN-DOR G, DUBINSKY A, ELPERIN T. Shape optimization of high-speed penetrators: a review [J]. Open Engineering, 2012, 2(4): 473–482. DOI: 10.2478/s13531-012-0022-4. -







 下载:
下载: