A study of the design and calculation method of double-skin steel-concrete shield based on energy approach
-
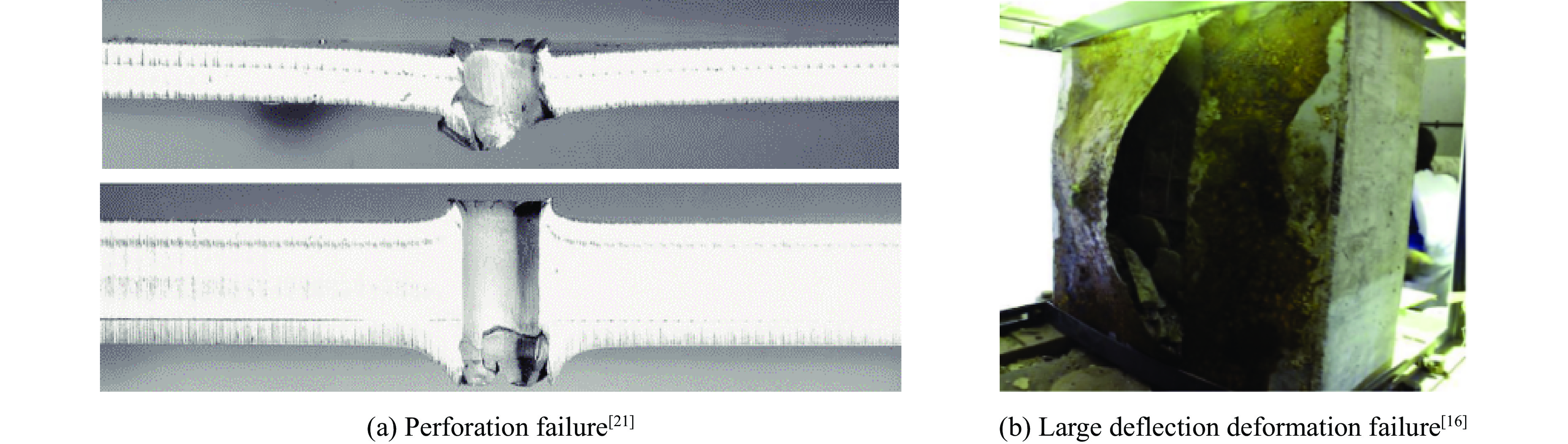
摘要: 为了深入探讨双钢板混凝土结构抗强冲击时后附钢板的耗能方式变化,基于最小耗能原理和无量纲化分析,反推得到了不同材料和结构尺寸下后附钢板耗能状态。结合混凝土强度极限条件,建立了兼顾塑性变形和侵彻贯穿破坏形态的后附钢板综合耗能计算公式以及后附钢板最小临界厚度解析表达式。计算结果表明,薄钢板综合耗能可达仅考虑贯穿效应耗能的4~5倍。基于能量守恒原理,提出了双钢板混凝土遮弹层防贯穿设计六步法,给出了弹体临界贯穿速度和弹体余速计算公式。该计算公式与已有钢板混凝土结构侵彻试验结果吻合较好。Abstract: The calculation method of double-skin steel-concrete shield based on the energy method is discussed. Under the premise of a rigid projectile, the main structures that affect the energy dissipation of projectile penetration are front and rear steel plates, internal concrete, tied bars and distribution layer. In this paper, the energy consumption of steel plate in elastic state, plastic state and plastic membrane state is analyzed. Based on the principle of minimum energy consumption and dimensionless analysis, the energy consumption states of the rear steel plate of different materials and structural dimensions are inversely deduced. Combined with the strength limit condition of concrete, the formula for calculating the comprehensive energy consumption of the rear steel plate considering the plastic deformation and the penetration failure mode is proposed, and the analytical expression for the minimum critical thickness of the rear steel plate is given. The calculation results indicate that the comprehensive energy consumption of the sheet steel plate can reach 4−5 times that of merely considering the penetration effect. In view of the restraint effect of steel plates on both sides of concrete, the current relatively mature formula of concrete penetration energy consumption is modified. Based on the principle of energy conservation, a six-step method for designing double-skin steel-concrete shield is proposed, and the formula for calculating the critical penetration velocity of the projectile is given. The theoretical results are then compared with the existing test data. It indicates that the calculation formulas proposed in this paper are in good agreement with the test results and can provide a scientific guideline for the design of double-skin steel-concrete shield. The main principle of the six-step method is to take a full account of the plastic deformation energy consumption of the rear steel plate and the anti-penetration energy consumption of the front steel plate. This method is beneficial to reduce the thickness of the double-skin steel-concrete shield and improve the protection effect.
-
表 1 钢板混凝土结构常用材料和结构参数
Table 1. Common material and structural parameters of steel plate concrete structure
Es/GPa Ys/MPa $\upsilon _{\rm{s}} $ $ \bar \varepsilon $ fc/MPa ρc/(kg·m−3) γ λp $ {\bar \lambda _\omega } $ 带拉筋 无拉筋 带拉筋 无拉筋 210 400 0.3 0.2 32 2400 12.50 5.63 7.63 2.51 3.41 210 400 0.3 0.2 80 2400 5.00 5.63 7.63 2.51 3.41 210 700 0.3 0.15 32 2400 21.88 5.63 7.63 2.18 2.95 210 700 0.3 0.15 80 2400 8.75 5.63 7.63 2.18 2.95 表 2 文献[14]侵彻试验结果与公式计算结果对比
Table 2. Comparison between penetration test results in reference [14] and calculation results in this paper
试验编号 迎弹面钢板厚度/
mm后附钢板厚度/
mm混凝土抗压强度/
MPa试验弹体着靶
速度/(m·s−1)试验结果 本文公式计算的临界
贯穿速度/(m·s−1)预测是否
准确St-1-1-A 1 1 26 316 未贯穿 344 准确 St-1-1-B 1 1 26 338 未贯穿 344 准确 St-1-1-C 1 1 26 349 贯穿 344 准确 St-1-2-A 1 2 26 320 未贯穿 354 准确 St-1-2-B 1 2 26 324 未贯穿 354 准确 St-1-2-C 1 2 26 331 未贯穿 354 准确 St-1-2 1 2 50 393 未贯穿 402 准确 St-2-1-A 2 1 26 335 未贯穿 354 准确 St-2-1-B 2 1 26 350 未贯穿 354 准确 St-2-1-C 2 1 26 431 贯穿 354 准确 表 3 公式计算结果与侵彻试验结果[16]的对比
Table 3. Comparison of calculation results with penetration test results[16]
试验
编号后附钢板
厚度/mm试验弹体着靶
速度/(m·s−1)试验
结果试验弹体余速/
(m·s−1)本文公式计算结果 临界贯穿速度/(m·s−1) 预测是否准确 弹体余速/(m·s−1) 与试验结果的误差/% 1-1 1 641.5 贯穿 272 572 准确 290 6.6 1-2 1 540 未贯穿 0 572 准确 0 0 1-3 1 601 贯穿 180 572 准确 184 2.2 1-4 1 679 贯穿 329 572 准确 365 10.9 1-5 1 737 贯穿 422 572 准确 464 10.0 -
[1] 任辉启, 穆朝民, 刘瑞朝, 等. 精确制导武器侵彻效应与工程防护 [M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016: 1–19.REN H Q, MU Z M, LIU R Z, et al. Penetration effects of precision guided weapons and engineering protection [M]. Beijing, China: Science Press, 2016: 1–19. [2] 吴应祥, 秦有权, 徐翔宇. 矢量型抗侵彻结构研究进展 [J]. 防护工程, 2022, 44(6): 36–42. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1854.2022.06.006.WU Y X, QIN Y Q, XU X Y. Progress on vector-based anti-penetration structure research [J]. Protective Engineering, 2022, 44(6): 36–42. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1854.2022.06.006. [3] 樊健生, 丁然, 聂鑫, 等. 高性能双钢板混凝土结构研究与应用 [J]. 建筑结构学报, 2022, 43(9): 55–72. DOI: 10.14006/j.jzjgxb.2022.0076.FAN J S, DING R, NIE X, et al. Research and application of high-performance double steel-plate reinforced concrete structures [J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2022, 43(9): 55–72. DOI: 10.14006/j.jzjgxb.2022.0076. [4] REMENNIKOV A M, KONG S Y. Numerical simulation and validation of impact response of axially-restrained steel-concrete-steel sandwich panels [J]. Composite Structures, 2012, 94(12): 3546–3555. DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2012.05.011. [5] REMENNIKOV A M, KONG S Y, UY B. The response of axially restrained non-composite steel-concrete-steel sandwich panels due to large impact loading [J]. Engineering Structures, 2013, 49: 806–818. DOI: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2012.11.014. [6] ZHAO W Y, GUO Q Q, DOU X Q, et al. Impact response of steel-concrete composite panels: experiments and FE analyses [J]. Steel and Composite Structures, 2018, 26(3): 255–263. DOI: 10.12989/scs.2018.26.3.255. [7] 安国青, 王蕊, 赵晖, 等. 双钢板混凝土组合板在撞击荷载下的动力响应 [J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 43(8): 1192–1200. DOI: 10.12068/j.issn.1005-3026.2022.08.017.AN G Q, WANG R, ZHAO H, et al. Dynamic response of double-skin steel-concrete composite panel under impact loading [J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 2022, 43(8): 1192–1200. DOI: 10.12068/j.issn.1005-3026.2022.08.017. [8] HASHIMOTO J, TAKIGUCHI K, NISHIMURA K, et al. Experimental study on behavior of RC panels covered with steel plates subjected to missile impact [C]//Proceedings of the 18th International Association for Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology. Beijing, China: IASMiRT, 2005: 2604–2615. [9] WALTER T A, WOLDE-TINSAE A M. Turbine missile perforation of reinforced concrete [J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 1984, 110(10): 2439–2455. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(1984)110:10(2439). [10] TSUBOTA H, KASAI Y, KOSHIKA N, et al. Quantitative studies on impact resistance of reinforced concrete panels with steel liners under impact loading. part 1: scaled model impact tests[C]//Proceedings of the 12th International Association for Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology. Stuttgart, Germany: IASMiRT, 1993: 169–174. [11] SUGANO T, TSUBOTA H, KASAI Y, et al. Local damage to reinforced concrete structures caused by impact of aircraft engine missiles. part 1: test program, method and results [J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 1993, 140(3): 387–405. DOI: 10.1016/0029-5493(93)90120-X. [12] BARR P, CARTER P G, HOWE W D, et al. Experimental studies of the impact resistance of steel faced concrete composites [C]//Proceedings of the 7th International Association for Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology. Chicago, USA: IASMiRT, 1983: 395–402. [13] MIZUNO J, KOSHIKA N, SAWAMOTO Y, et al. Investigation on impact resistance of steel plate reinforced concrete barriers against aircraft impact. part 1: test program and results [C]//Proceedings of the 18th International Association for Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology. Beijing, China: IASMiRT, 2005: 2566–2679. [14] ABDEL-KADER M, FOUDA A. Effect of reinforcement on the response of concrete panels to impact of hard projectiles [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2014, 63: 1–17. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2013.07.005. [15] KIM K S, MOON I H, CHOI H J, et al. A preliminary study on the local impact behavior of steel-plate concrete walls [J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2017, 102: 210–219. DOI: 10.1016/j.anucene.2016.12.006. [16] WU H, FANG Q, PENG Y, et al. Hard projectile perforation on the monolithic and segmented RC panels with a rear steel liner [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2015, 76: 232–250. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2014.10.010. [17] ABDEL-KADER M, FOUDA A. Equivalent concrete thickness for perforation of mild steel plates [J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2017, 135: 213–229. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2017.04.016. [18] 程毅, 刘军, 郑雨晴, 等. 钢板混凝土复合靶抗贯穿性能的理论与数值分析 [J]. 应用力学学报, 2020, 37(4): 1441–1449. DOI: 10.11776/cjam.37.04.B056.CHENG Y, LIU J, ZHENG Y Q, et al. Theoretical and numerical investigation of perforation resistance of steel-concrete composite target [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2020, 37(4): 1441–1449. DOI: 10.11776/cjam.37.04.B056. [19] BRUHL J C, VARMA A H, JOHNSON W H. Design of composite SC walls to prevent perforation from missile impact [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2015, 75: 75–87. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2014.07.015. [20] 王菲, 刘晶波, 韩鹏飞, 等. 核工程钢板混凝土墙防撞击贯穿实用计算方法 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2020, 40(10): 105101. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0020.WANG F, LIU J B, HAN P F, et al. A practical calculation method of steel plate concrete walls to resist perforation from missile impact in nuclear engineering [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2020, 40(10): 105101. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0020. [21] BØRVIK T, CLAUSEN A H, HOPPERSTAD O S, et al. Perforation of AA5083-H116 aluminium plates with conical-nose steel projectiles: experimental study [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2004, 30(4): 367–384. DOI: 10.1016/S0734-743X(03)00072-1. [22] 王明洋, 张胜民, 国胜兵. 接触爆炸作用下钢板-钢纤维混凝土遮弹层设计方法(I) [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2002, 22(1): 40–45. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1455.2002.01.008.WANG M Y, ZHANG S M, GUO S B. Design method of steel and steel-fiber concrete shelter plate under contact detonation [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2002, 22(1): 40–45. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1455.2002.01.008. [23] 王明洋, 钱七虎, 赵跃堂. 接触爆炸作用下钢板-钢纤维钢筋混凝土遮弹层设计方法(II) [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2002, 22(2): 163–168. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1455.2002.02.012.WANG M Y, QIAN Q H, ZHAO Y T. The design method for shelter plate of steel plate and steel fiber reinforced concrete under contact detonation [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2002, 22(2): 163–168. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1455.2002.02.012. [24] CHEN X W, HUANG X L, LIANG G J. Comparative analysis of perforation models of metallic plates by rigid sharp-nosed projectiles [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2011, 38(7): 613–621. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2010.12.005. [25] FORRESTAL M J, ALTMAN B S, CARGILE J D, et al. An empirical equation for penetration depth of ogive-nose projectiles into concrete targets [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1994, 15(4): 395–405. DOI: 10.1016/0734-743X(94)80024-4. [26] FORRESTAL M J, WARREN T L. Perforation equations for conical and ogival nose rigid projectiles into aluminum target plates [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2009, 36(2): 220–225. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2008.04.005. [27] CHEN X W, LI Q M. Deep penetration of a non-deformable projectile with different geometrical characteristics [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2002, 27(6): 619–637. DOI: 10.1016/s0734-743x(02)00005-2. [28] PENG Y, WU H, FANG Q, et al. A note on the deep penetration and perforation of hard projectiles into thick targets [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2015, 85: 37–44. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2015.06.013. [29] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部, 国家市场监督管理总局. 混凝土物理力学性能试验方法标准: GB/T 50081—2019 [S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2019: 145–146.Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation. Standard for test methods of concrete physical and mechanical properties: GB/T 50081—2019 [S]. Beijing, China: China Architecture and Building Press, 2019: 145–146. [30] PENG Y, WU H, FANG Q, et al. Residual velocities of projectiles after normally perforating the thin ultra-high performance steel fiber reinforced concrete slabs [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2016, 97: 1–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2016.06.006. [31] 张爽, 武海军, 黄风雷. 弹体侵彻钢筋混凝土靶开坑深度研究 [J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2018, 38(6): 565–571. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2018.06.003.ZHANG S, WU H J, HUANG F L. Investigation on crater depth of projectile penetrating into reinforced concrete target [J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2018, 38(6): 565–571. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2018.06.003. [32] KARAGIOZOVA D, YU T X, SHI S Y, et al. On the influence of elasticity on the large deflections response of circular plates to uniform quasi-static pressure [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2017, 131/132: 894–907. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2017.07.032. [33] KYOHEI K, PIAN T H H. Large deformations of rigid-plastic circular plates [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 1981, 17(11): 1043–1055. DOI: 10.1016/0020-7683(81)90012-3. [34] 纪冲, 龙源, 高振儒, 等. 弹丸冲击贯穿有限厚混凝土材料靶板的背面成坑效应 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2013, 32(4): 85–89,101. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2013.04.003.JI C, LONG Y, GAO Z R, et al. Rear face crater-forming of a limited-thickness concrete target due to projectile penetrating [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2013, 32(4): 85–89, 101. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2013.04.003. [35] CLOETE T J, NURICK G N. On the influence of radial displacements and bending strains on the large deflections of impulsively loaded circular plates [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2014, 82: 140–148. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2014.02.026. [36] 吴迪, 米国, 郭香华, 等. 空爆载荷作用下固支弹塑性圆板的动力学模型 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2022, 36(5): 054202. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.20220525.WU D, MI G, GUO X H, et al. Dynamic model of clamped elastoplastic circular plate under air blast loading [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2022, 36(5): 054202. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.20220525. [37] 王安宝, 邓国强, 张磊, 等. 混凝土侵彻公式的合理性分析 [J]. 防护工程, 2020, 42(6): 1–7. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1854.2020.06.001.WANG A B, DENG G Q, ZHANG L, et al. Analysis on the rationality of concrete penetration formula [J]. Protective Engineering, 2020, 42(6): 1–7. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1854.2020.06.001. [38] 龚自明, 方秦, 张亚栋, 等. 混凝土靶体侵彻不贯穿系数的试验研究 [J]. 兵工学报, 2009, 30(9): 1181–1186. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1093.2009.09.006.GONG Z M, FANG Q, ZHANG Y D, et al. Experimental investigation into coefficients of concrete targets to prevent perforation [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2009, 30(9): 1181–1186. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1093.2009.09.006. [39] 陈小伟. 穿甲/侵彻力学的理论建模与分析(上册) [M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019: 249–264.CHEN X W. Modelling on the perforation and penetration (I) [M]. Beijing, China: Science Press, 2019: 249–264. -







 下载:
下载: