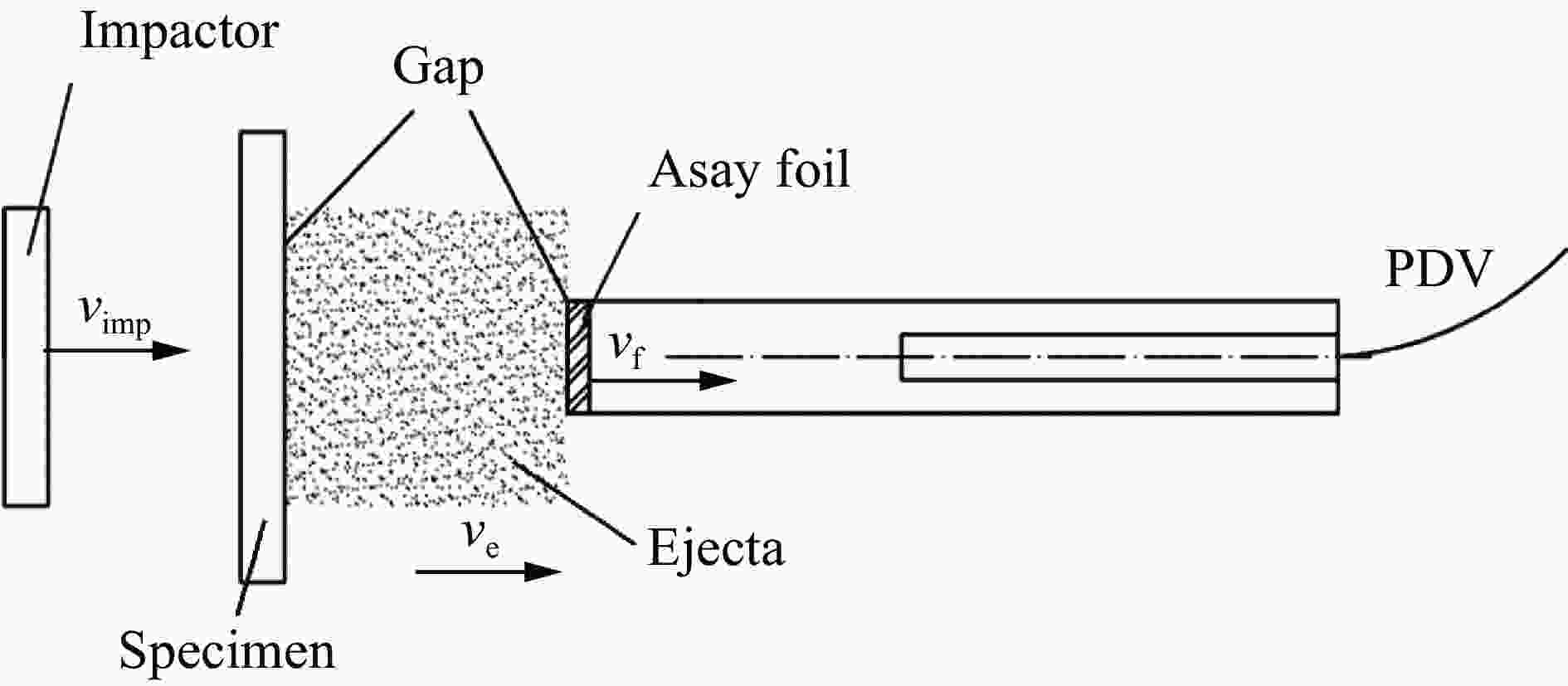
An improved Asay foil method for measuring areal density of ejecta under complex loading conditions
-
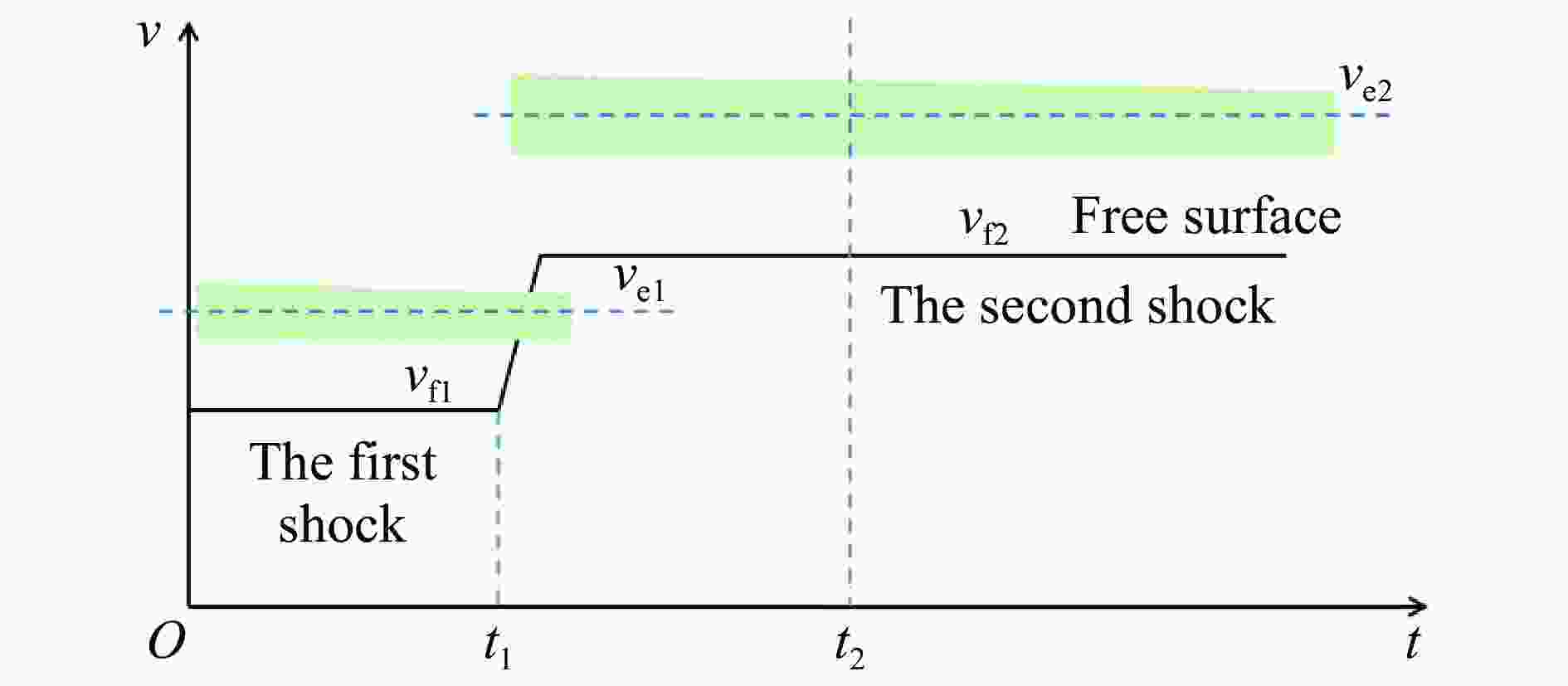
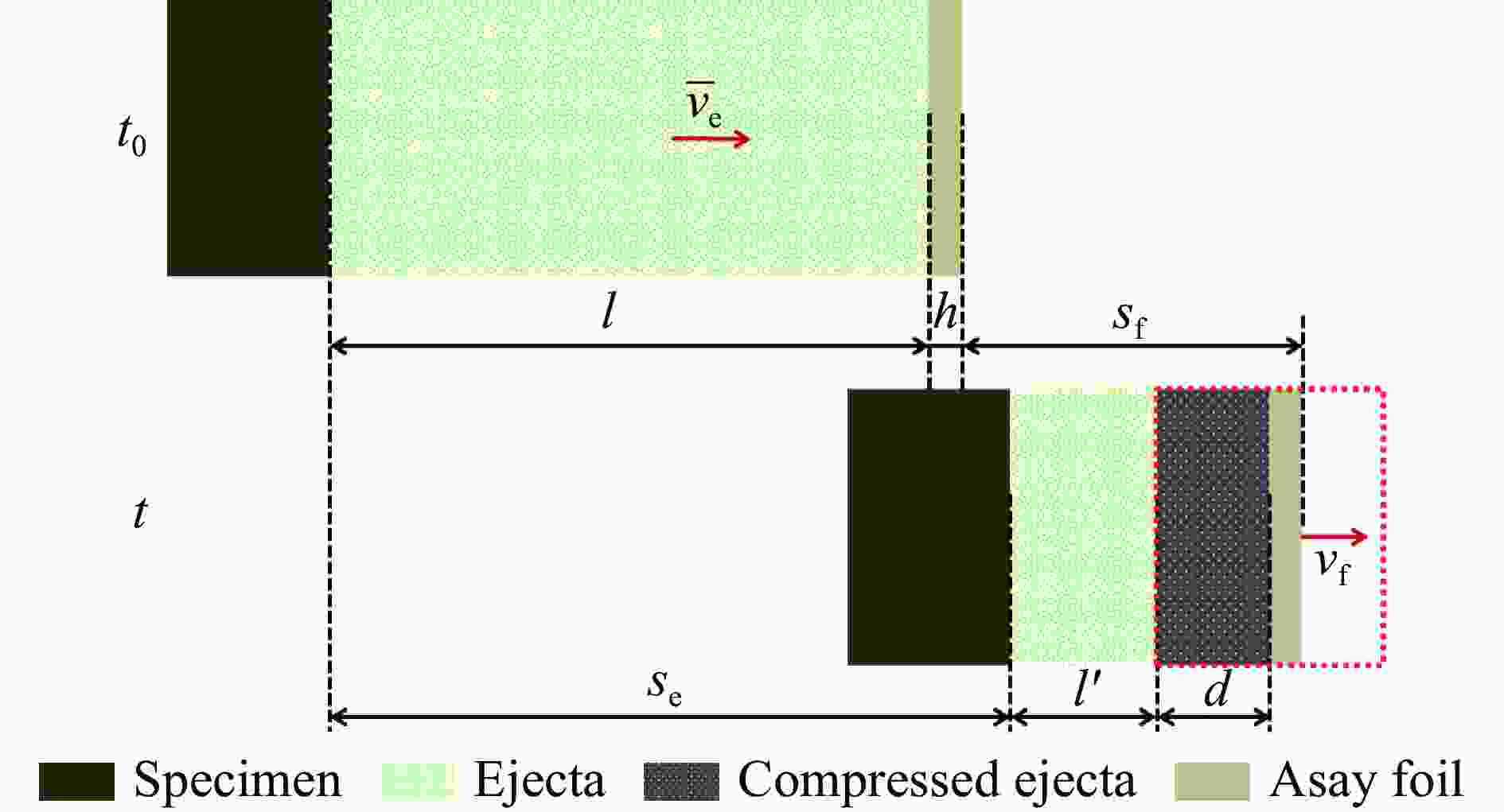
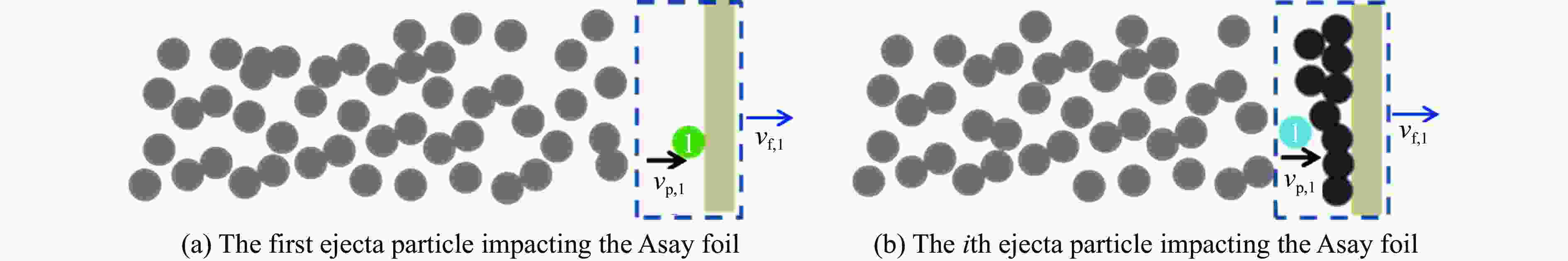
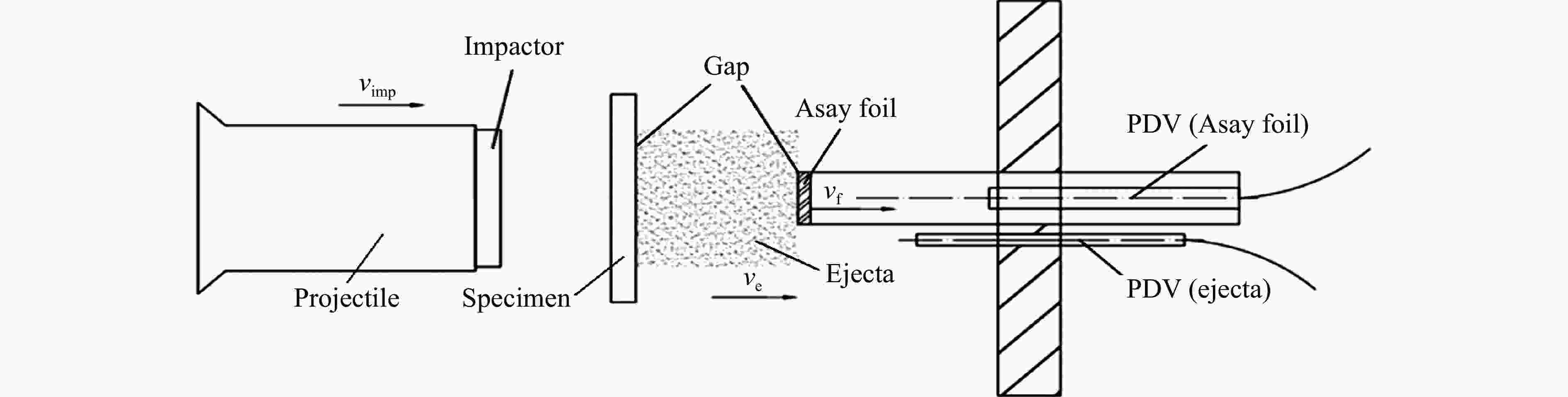
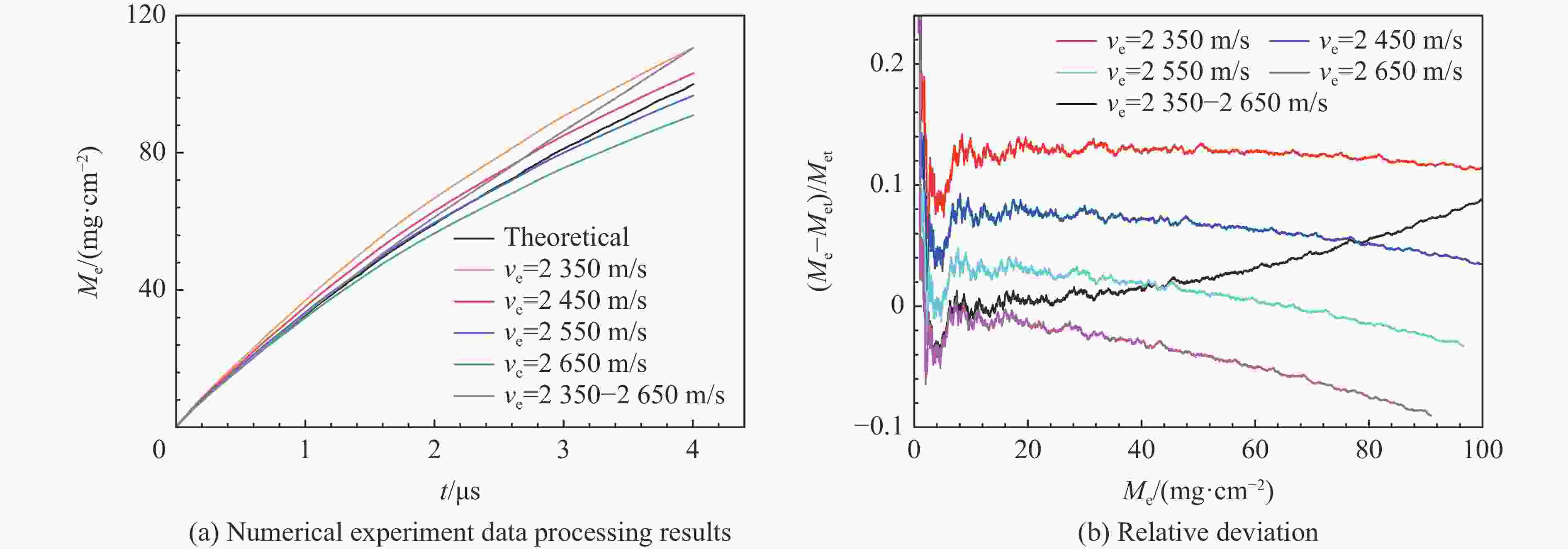
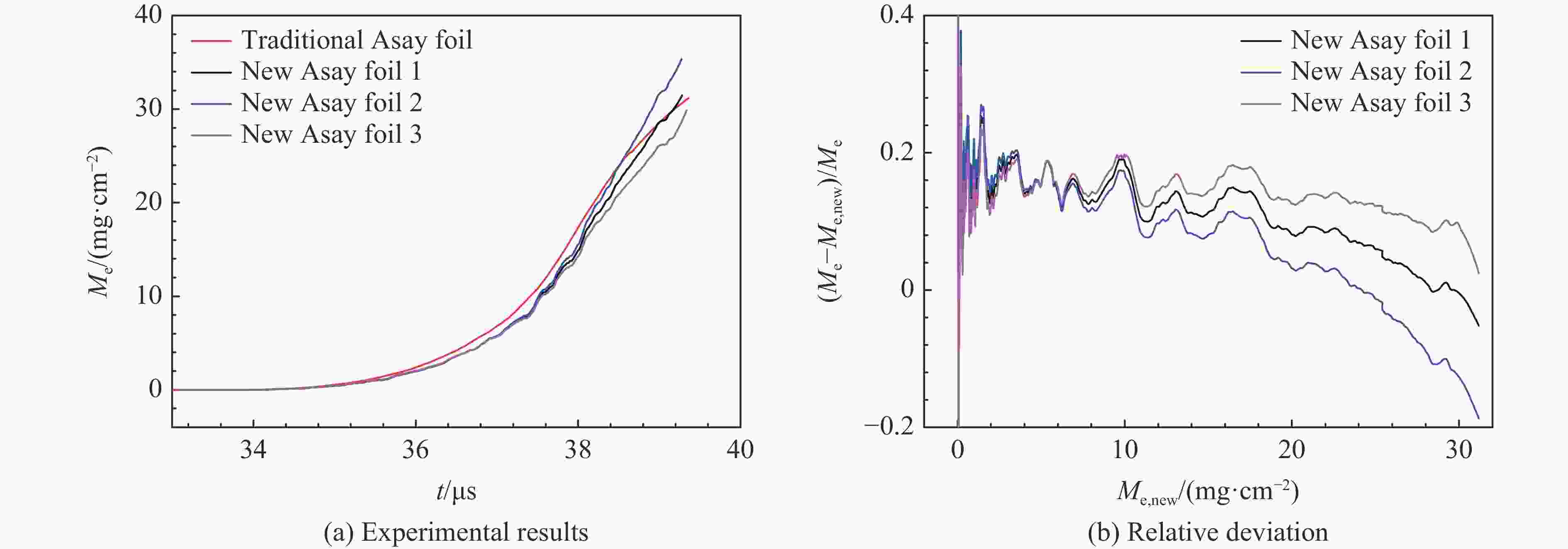
摘要: 为了解决传统Asay膜方法不适用于复杂加卸载条件下微喷射物质面密度测量的问题,采用光子多普勒速度计(photonic Doppler velocimetry, PDV)测量微喷射物质速度结合传统Asay膜方法的膜速曲线发展了测试复杂加载条件下微喷射面密度的新方法。采用数值实验和轻气炮实验对新方法进行了分析和评估。针对3种典型微喷射物质速度分布情况,利用数值实验分析评估了实际应用场景下因PDV给出的微喷物速度偏离理论值对面密度测量的影响,通过对PDV给出的微喷物速度线性插值处理,可确保新方法与理论值测量偏差小于20%。通过轻气炮加载预置粉末样品实验对比评估了新方法和传统方法的测量效果,采用2种方法分别处理同一发实验数据,结果显示,新方法相较于传统Asay膜方法的测量偏差小于20%。Abstract: The Asay foil has been a widely applied diagnostic in ejecta measurement since its design was first reported in 1976. An Asay foil is a foil of a known mass (or areal density), whose velocity changed when it is impacted by ejecta. The Foil velocity is measured using velocimetry and the ejecta velocity is inferred from the initial gap between foil and free surface and the ejecta fly time. The mass of the impacting ejecta can then be inferred from the change in momentum of the foil. In some cases, the ejecta spray out from complex loading conditions such as double shock loading condition, the initial gap and fly time are unable to measure accurately, thus the Asay foil method doesn’t work. Therefore, it is necessary to develop an Asay foil method that does not depend on the initial gap and fly time. An improved Asay foil method is then developed based on the traditional Asay foil method. This method uses photonic Doppler velocimetry (PDV) to obtain the ejecta velocity in the testing area of the Asay foil probe, and the Asay foil probe obtains the foil velocity curve after the ejecta collides with the foil. Based on spatial position constraints and precise temporal correlation, the combination of the two velocity curve results can provide the total amount and distribution of ejecta under complex loading conditions. A numerical experimental method was used to generate ejecta particle groups with different distribution states, as well as the PDV velocity curve and Asay foil velocity curve to analyze the applicability of the method. In addition, the numerical experimental analysis results were verified using light gas gun experiments. The numerical experimental analysis results show that this method has good applicability in three typical ejecta distribution cases, with a deviation of less than 20% between the measured value and the theoretical value. The results of the light gas gun tests indicate that the deviation between the improved method and the traditional Asay foil method is less than 20%.
-
Key words:
- ejecta /
- Asay foil /
- photonic Doppler velocimetry /
- areal density
-
表 1 不同数值实验条件下的数据处理参数
Table 1. Data processing parameters under different numerical experiment conditions
面密度
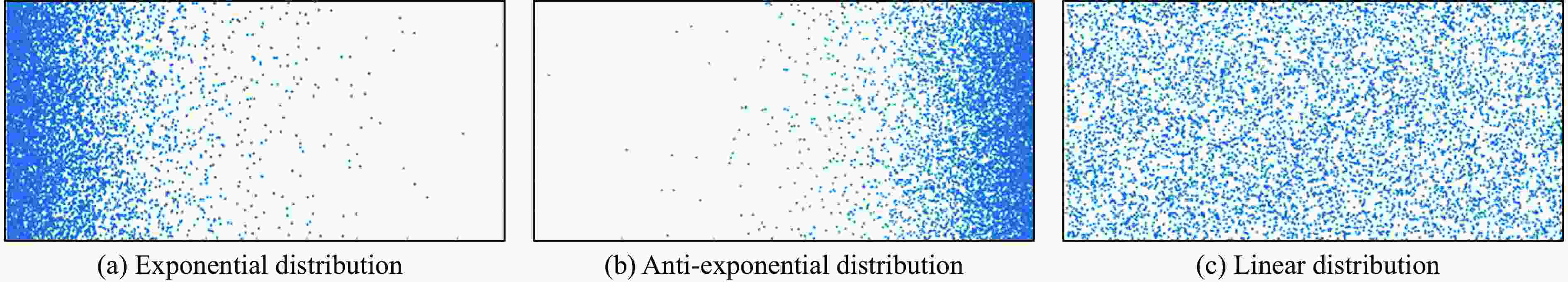
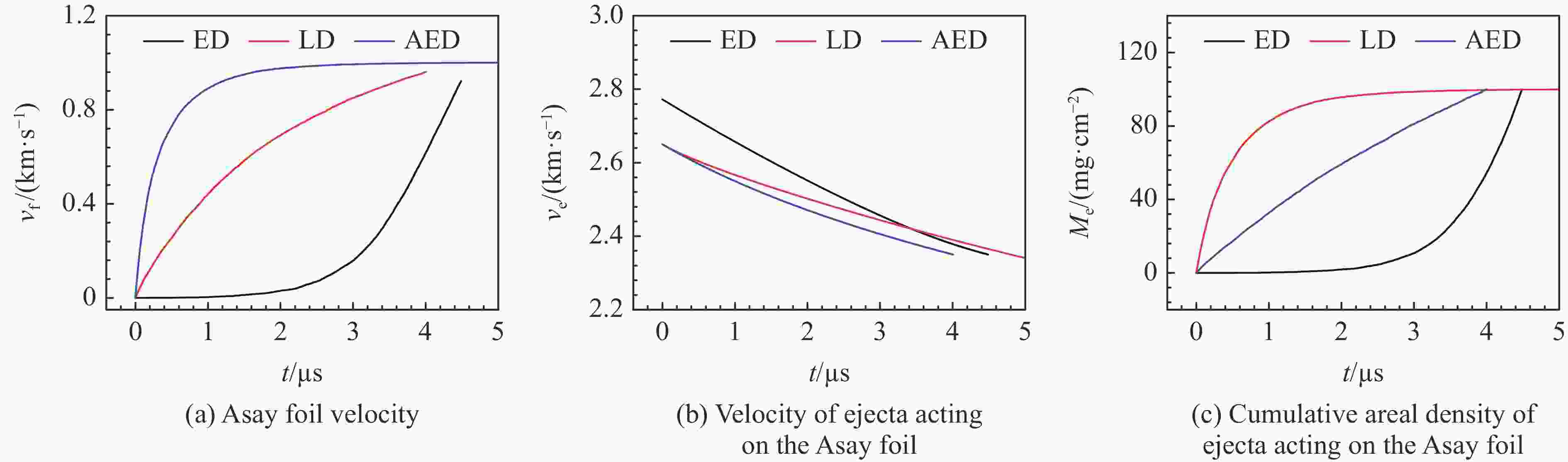
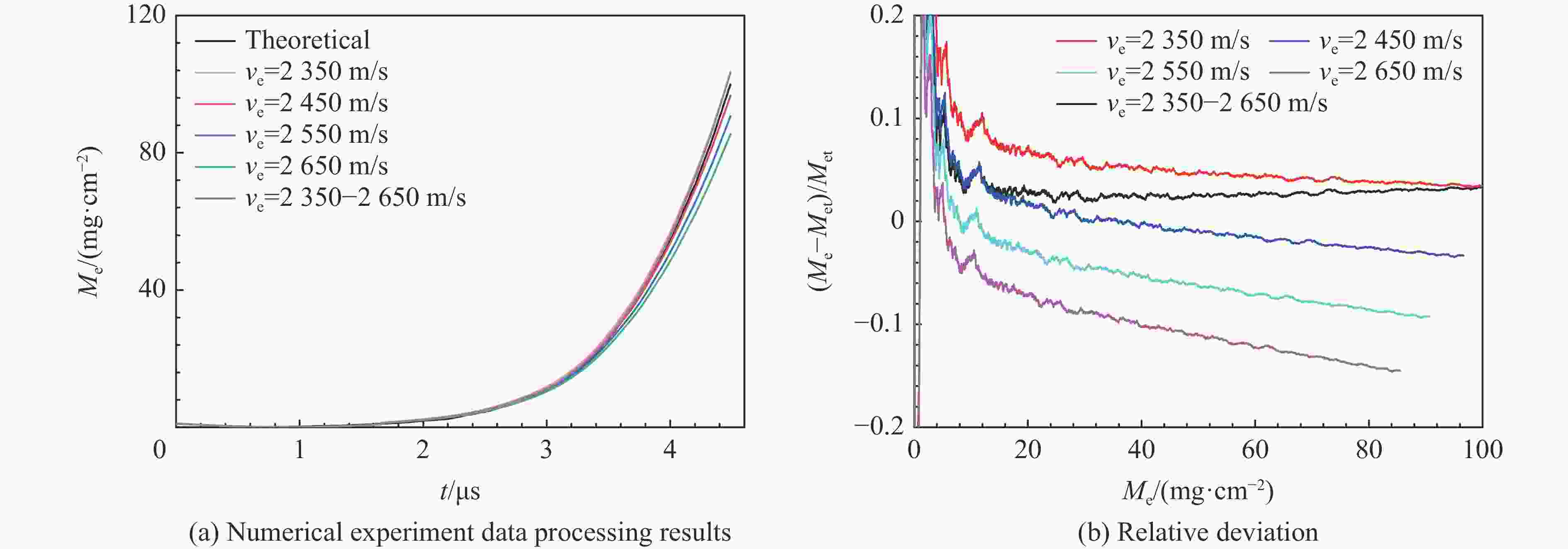
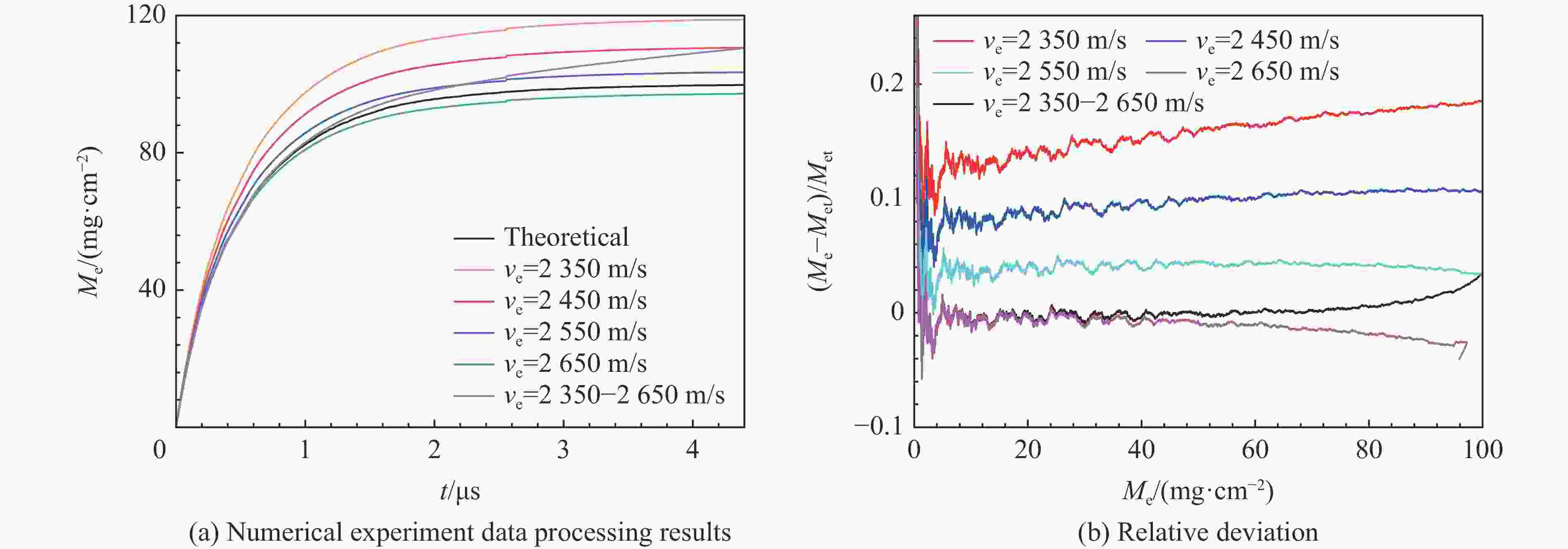
分布情况t1/μs t2/μs ve1/(m·s−1) ve2/(m·s−1) Me,l=10 mg/cm2 Me,l=20 mg/cm2 Me,l=40 mg/cm2 Me,l=10 mg/cm2 Me,l=20 mg/cm2 Me,l=40 mg/cm2 指数 0 2.950 3.355 3.785 2772.70 2460.83 2426.11 2393.23 反指数 0 0.046 0.101 0.240 2649.99 2644.86 2639.21 2625.85 线性 0 0.268 0.587 1.251 2649.99 2620.40 2588.02 2528.43 表 2 两种Asay膜数据处理方法使用的参数
Table 2. Parameters used in two different Asay foil data processing methods
方法 l/mm t0/μs mf/(mg·cm−2) t1/μs t2/μs ve1/(m·s−1) ve2/(m·s−1) 传统Asay膜法 19.5 28.33 156 新Asay膜法1 156 34.05 39.33 4180 2026 新Asay膜法2 156 34.05 39.33 4380 1826 新Asay膜法3 156 34.05 39.33 3980 2226 -
[1] WALSH J M, SHREFFLER R G, WILLIG F J. Limiting conditions for jet formation in high velocity collisions [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1953, 24(3): 349–359. DOI: 10.1063/1.1721278. [2] ZELLNER M B, GROVER M, HAMMERBERG J E, et al. Effects of shock-breakout pressure on ejection of micron-scale material from shocked tin surfaces [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2007, 102(1): 013522. DOI: 10.1063/1.2752130. [3] ZELLNER M B, DIMONTE G, GERMANN T C, et al. Influence of shockwave profile on ejecta [J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2009, 1195(1): 1047–1050. DOI: 10.1063/1.3294980. [4] BUTTLER W T, ORÓ D M, OLSON R T, et al. Second shock ejecta measurements with an explosively driven two-shockwave drive [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2014, 116(10): 103519. DOI: 10.1063/1.4895053. [5] ASAY J R, BERTHOLF L D. Model for estimating the effects of surface roughness on mass ejection from shocked materials: SAND-78-1256 [R]. Albuquerque: Sandia National Laboratory, 1978. DOI: 10.2172/6793637. [6] BUTTLER W T, SCHULZE R K, CHARONKO J J, et al. Understanding the transport and break up of reactive ejecta [J]. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena, 2021, 415: 132787. DOI: 10.1016/j.physd.2020.132787. [7] ASAY J R, MIX L P, PERRY F C. Ejection of material from shocked surfaces [J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1976, 29(5): 284–287. DOI: 10.1063/1.89066. [8] ASAY J R. Thick-plate technique for measuring ejecta from shocked surfaces [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1978, 49(12): 6173–6175. DOI: 10.1063/1.324545. [9] 马云, 汪小松, 李欣竹, 等. ASAY膜法测量微物质喷射总质量不确定度的初步实验研究 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2006, 20(2): 207–210. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.2006.02.016.MA Y, WANG X S, LI X Z, et al. Study of the uncertainty of the ejected mass measured by ASAY foil method [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2006, 20(2): 207–210. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.2006.02.016. [10] BELL D J, ROUTLEY N R, WHITEMAN G, et al. The development of a smaller Asay foil diagnostic [J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2018, 1979(1): 080001. DOI: 10.1063/1.5044843. [11] MCCLUSKEY C W, WILKE M D, ANDERSON W W, et al. Asay window: a new spall diagnostic [J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2006, 77(11): 113902. DOI: 10.1063/1.2336753. [12] CHEN Y T, HONG R K, CHEN H Y, et al. An improved Asay window technique for investigating the micro-spall of an explosively-driven tin [J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2017, 88(1): 013904. DOI: 10.1063/1.4973699. [13] KARKHANIS V, RAMAPRABHU P, BUTTLER W T, et al. Ejecta production from second shock: numerical simulations and experiments [J]. Journal of Dynamic Behavior of Materials, 2017, 3(2): 265–279. DOI: 10.1007/s40870-017-0091-9. [14] WILLIAMS R J R, GRAPES C C. Simulation of double-shock ejecta production [J]. Journal of Dynamic Behavior of Materials, 2017, 3(2): 291–299. DOI: 10.1007/s40870-017-0107-5. [15] WENG J D, TAN H, HU S L, et al. New all-fiber velocimeter [J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2005, 76(9): 093301. DOI: 10.1063/1.2008989. -






 下载:
下载: