Influencing factors of penetration performance of an elliptical cross-section projectile
-
摘要: 为研究截面形状和头部曲径比对椭圆截面弹体侵彻性能的影响,开展了圆锥和椭圆锥压头的静态压痕试验,获得了不同截面压头缓慢贯入材料时的力-位移曲线。随后,基于30 mm弹道炮平台,开展了3种不同椭圆截面弹体在400~800 m/s撞击速度范围内正侵彻2A12厚铝靶试验,获得了靶体的破坏形貌及弹体侵彻深度。基于空腔膨胀模型及阻力函数修正系数,建立了椭圆截面弹体侵彻金属厚靶侵彻动力学模型,结合试验结果验证了模型的有效性,并系统分析了弹体截面形状和头部曲径比对侵彻性能的影响。研究结果表明,与圆锥压头相比,具有相同截面面积的椭圆锥压头贯入材料时阻力更大,当压头的截面长短轴比从1.00增大至2.00时,贯入阻力增大10.1%。当弹体截面面积相当,且各横截面保持长短轴比不变时,椭圆截面弹体的长短轴比越大,其侵彻性能越差;椭圆截面弹体侵彻性能随着截面长短轴比的增大和头部曲径比的减小而降低。Abstract: In order to study the influence of the cross-section shape and caliber radius head on the penetration performance of elliptical cross-section projectiles, the static deep indentation test of the elliptical cross-section conical indenters was carried out, and the force-displacement curves of different cross-section indenter slowly penetrating the material were obtained. Then, by means of a 30-mm-caliber ballistic gun platform, a series of experiments were carried out on 2A12 thick aluminum targets subjected to normal penetration by three kinds of 30CrMnSi2A steel projectiles with different elliptical cross-section shapes in the striking velocity ranging from 400 m/s to 800 m/s. The penetration depth of projectiles and the failure morphology of targets were experimentally obtained. The penetration dynamic model of projectile into thick metal target was established on the basis of the cavity expansion theory and resistance function correction coefficient. The correctness of the theoretical model is validated by the experimental results in this paper, and the influence of the cross-section shape and caliber radius head of the projectile on the penetration performance are systematically analyzed. The results show that the elliptical section indenter with the same cross-sectional area has higher resistance while slowly penetrating into the material. When the major-to-minor axis length ratio of the cross-sectional of indenters increases from 1.00 to 2.00, the material resistance increases by 10.1%. It is found that there is a large difference in the failure morphology of the target under the penetration of circular and elliptical cross-section projectiles, and the shape of the target tunnel area is consistent with the shape of the projectile cross-section. In addition, when the cross-sectional area of the projectile is equivalent and the major-to-minor axis length ratio of each cross-section was constant, the penetration performance of projectile decreases with the increase of the larger the major-to-minor axis length ratio. The penetration performance of projectile with elliptical cross-section decreases with the increase of the major-to-minor axis length ratio and the decrease of the caliber radius head of the projectile.
-
表 1 圆锥和椭圆锥压头的几何参数
Table 1. Main geometric parameters of circular and elliptical cross-section conical indenters
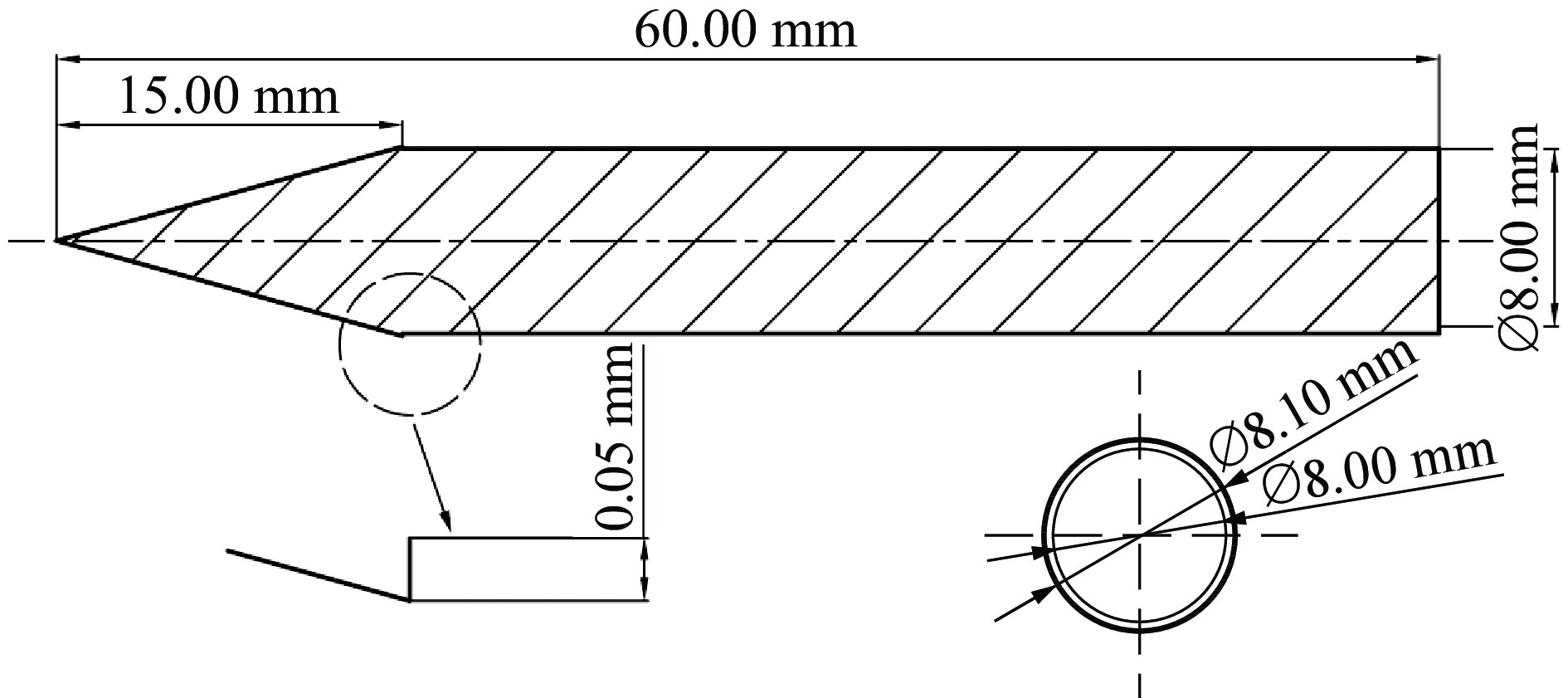
类型 横截面轮廓 2a/mm 2b/mm β 最大横截面面积/mm2 长度/mm CC1 
8.00 8.00 1.00 50.27 60.00 EC1 
9.80 6.53 1.50 50.27 60.00 EC2 
11.31 5.66 2.00 50.27 60.00 表 2 圆形和椭圆截面弹体的主要结构参数
Table 2. Main parameters of circular and elliptical cross-section projectiles
类型 弹体轮廓 β 最大横截面面积/mm2 m/g L/mm rCRH C1 
1.00 556 360 43.2 3.60 E1 
1.25 720 360 43.2 3.49 E2 
1.61 556 360 43.2 5.64 表 3 弹体侵彻2A12厚铝靶试验结果统计
Table 3. Test results of projectiles penetrating 2A12 thick aluminum targets
编号 类型 着角/(°) 俯仰角/(°) 偏航角/(°) v0/(m·s−1) Pe/mm 1 C1-1 0.39 0.41 0.08 773.1 252.77 2 E1-1 1.18 0.38 0.67 810.1 217.18 3 E2-1 1.49 0.41 1.74 816.2 274.55 4 C1-2 1.44 0.30 0.86 608.0 175.73 5 E1-2 0.95 0.26 1.87 604.2 143.93 6 E2-2 0.43 0.20 1.03 563.8 159.17 7 E1-3 0.41 0.53 2.79 398.3 72.92 8 E2-3 0.25 0.39 0 402.2 99.30 表 4 弹体侵彻深度计算结果与试验结果的误差
Table 4. Deviation of penetration depth between calculation results and test results
弹体编号 v0/(m·s−1) Pe/mm 相对试验结果的误差/% 试验结果 SCE模型 本文模型 SCE模型 本文模型 C1-1 773.1 252.77 285.98 285.98 13.14 13.14 E1-1 810.1 217.18 239.32 229.05 10.19 5.47 E2-1 816.2 274.55 319.24 289.24 16.28 5.35 C1-2 608.0 175.73 191.95 191.95 9.23 9.23 E1-2 604.2 143.93 150.33 144.25 4.45 0.22 E2-2 563.8 159.17 172.56 157.41 8.41 −1.11 E1-3 398.3 72.92 79.61 76.86 9.17 5.40 E2-3 402.2 99.30 100.17 92.25 0.88 −7.10 表 5 5种椭圆锥弹体结构的质量参数
Table 5. Main parameters of five typical elliptical cone projectiles
类型 弹体轮廓 2a/mm 2b/mm β m/g L/mm EC-1 
23.60 23.60 1.00 360 144 EC-2 
26.38 21.11 1.25 360 144 EC-3 
28.90 19.26 1.50 360 144 EC-4 
31.22 17.84 1.75 360 144 EC-5 
33.36 16.68 2.00 360 144 表 6 5种椭圆截面弹体结构的质量参数
Table 6. Main parameters of five typical elliptical cross-section projectiles
类型 弹体轮廓示意图 2a/mm 2b/mm β rCRH m/g L/mm ECS-1 
23.60 23.60 1.00 3.60 360 144 ECS-2 
28.90 19.26 1.50 5.28 360 144 ECS-3 
33.36 16.68 2.00 6.95 360 144 ECS-4 
28.90 19.26 1.50 3.60 360 144 ECS-5 
33.36 16.68 2.00 3.60 360 144 -
[1] 王文杰, 张先锋, 邓佳杰, 等. 椭圆截面弹体侵彻砂浆靶规律分析 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2018, 38(1): 164–173. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2017-0020.WANG W J, ZHANG X F, DENG J J, et al. Analysis of projectile penetrating into mortar target with elliptical cross-section [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2018, 38(1): 164–173. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2017-0020. [2] DONG H, LIU Z H, WU H J, et al. Study on penetration characteristics of high-speed elliptical cross-sectional projectiles into concrete [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2019, 132: 103311. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2019.05.025. [3] DONG H, WU H J, LIU Z H, et al. Penetration characteristics of pyramidal projectile into concrete target [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2020, 143: 103583. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2020.103583. [4] 王浩, 武海军, 闫雷, 等. 椭圆横截面弹体斜贯穿双层间隔薄钢板失效模式 [J]. 兵工学报, 2020, 41(S2): 1–11. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2020.S2.001.WANG H, WU H J, YAN L, et al. Failure mode of oblique perforation of truncated ogive-nosed projectiles with elliptic cross-section into double-layered thin steel plate with gap space [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2020, 41(S2): 1–11. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2020.S2.001. [5] 王浩, 潘鑫, 武海军, 等. 椭圆截面截卵形刚性弹体正贯穿加筋板能量耗散分析 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2019, 39(10): 103203. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0350.WANG H, PAN X, WU H J, et al. Energy dissipation analysis of elliptical truncated oval rigid projectile penetrating stiffened plate [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2019, 39(10): 103203. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0350. [6] 田泽, 王浩, 武海军, 等. 椭圆变截面弹体斜贯穿薄靶姿态偏转机理 [J]. 兵工学报, 2022, 43(7): 1537–1552. DOI: 10.12382/bgxb.2021.0367.TIAN Z, WANG H, WU H J, et al. Attitude deflection mechanism of projectiles with variable elliptical cross-sections obliquely perforating thin targets [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2022, 43(7): 1537–1552. DOI: 10.12382/bgxb.2021.0367. [7] 邓希旻, 田泽, 武海军, 等. 上下非对称结构弹体侵彻金属薄板的特性及薄板破坏形式 [J/OL]. 兵工学报, (2022-11-02) [2023-04-10]. http://www.co-journal.com/CN/ 10.12382/bgxb.2022.0724. DOI: 10.12382/bgxb.2022.0724.DENG X W, TIAN Z, WU H J, et al. Penetration characteristics and plate failure modes of asymmetric shaped projectiles penetrating thin metal targets [J/OL]. Acta Armamentarii, (2022-11-02) [2023-04-10]. http://www.co-journal.com/CN/ 10.12382/bgxb.2022.0724. DOI: 10.12382/bgxb.2022.0724. [8] DAI X H, WANG K H, LI M R, et al. Rigid elliptical cross-section ogive-nose projectiles penetration into concrete targets [J]. Defence Technology, 2021, 17(3): 800–811. DOI: 10.1016/j.dt.2020.05.011. [9] 刘子豪, 武海军, 高旭东, 等. 椭圆截面弹体侵彻混凝土阻力特性研究 [J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2019, 39(2): 135–141, 146. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2019.02.005.LIU Z H, WU H J, GAO X D, et al. Study on the resistance characteristics of elliptical cross-section projectile penetrating concrete [J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2019, 39(2): 135–141, 146. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2019.02.005. [10] LIU J W, ZHANG X F, WEI H Y, et al. Study on the penetration of elliptical cross-section projectiles into concrete targets: theory and experiment [J]. Latin American Journal of Solids and Structures, 2022, 19: 1–23. DOI: 10.1590/1679-78256939. [11] LIU J W, LIU C, ZHANG X F, et al. Research on the penetration characteristics of elliptical cross-section projectile into semi-infinite metal targets [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2023, 173: 104438. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2022.104438. [12] MA X H, ZHANG Q M, ZHANG X W. A model for rigid asymmetric ellipsoidal projectiles penetrating into metal plates [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2022, 163: 104140. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2021.104140. [13] 魏海洋, 张先锋, 熊玮, 等. 椭圆截面弹体斜侵彻金属靶体弹道研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2022, 42(2): 023304. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2021-0291.WEI H Y, ZHANG X F, XIONG W, et al. Oblique penetration of elliptical cross-section projectile into metal target [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2022, 42(2): 023304. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2021-0291. [14] 谭远深, 黄风雷, 皮爱国. 椭圆截面侵彻弹体结构优化设计与结构响应 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2022, 42(6): 063301. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2021-0436.TAN Y S, HUANG F L, PI A G. Structural optimization design and structural response of elliptical-section penetration projectiles [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2022, 42(6): 063301. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2021-0436. [15] 刘均伟, 张先锋, 赵瑶瑶, 等. 在椭圆横截面弹体正侵彻下有限厚铝靶的破坏模式及响应特性 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2022, 42(12): 123301. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2022-0249.LIU J W, ZHANG X F, ZHAO Y Y, et al. Failure modes and response characteristics of finite-thickness aluminum targets under normal penetration of elliptical cross-section projectiles [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2022, 42(12): 123301. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2022-0249. [16] BISHOP R F, HILL R, MOTT N F. The theory of indentation and hardness tests [J]. Proceedings of the Physical Society, 1945, 57(3): 147–159. DOI: 10.1088/0959-5309/57/3/301. [17] SATAPATHY S, BIESS S. Deep punching PMMA [J]. Experimental Mechanical, 2000, 4: 7–31. DOI: 10.1007/BF02327545. [18] TAMAGNA A, RIERA J D. Low speed penetration in solids [J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 1998, 179: 125–133. DOI: 10.1016/S0029-5493(97)00272-0. [19] WRIGHT S C, HUANG Y, FLECK N A. Deep penetration of polycarbonate by a cylindrical punch [J]. Mechanics of Materials, 1992, 13(4): 277–284. DOI: 10.1016/0167-6636(92)90020-E. [20] ROSENBERG Z, KOSITSKI R. Deep indentation and terminal ballistics of polycarbonate [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2017, 103: 225–230. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2017.01.018. [21] ROSENBERG Z, DEKEL E. The penetration of rigid long rods [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2009, 36(4): 551–564. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2008.06.001. [22] ROSENBERG Z, DEKEL E. A comment on “The effect of target inertia on the penetration of aluminum targets by rigid ogive-nosed long rods” by T. L. Warren, Int. J. Impact Eng. 2016 [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2016, 93: 231–233. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2016.02.009. [23] FORRESTAL M J, LUK V K, WATTS H A. Penetration of reinforced concrete with ogive-nose penetrators [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 1988, 24(1): 77–87. DOI: 10.1016/0020-7683(88)90100-x. [24] HANCHAK S J, FORRESTAL M J, YOUNG E R, et al. Perforation of concrete slabs with 48 MPa (7 ksi) and 140 MPa (20 ksi) unconfined compressive strengths [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1992, 12(1): 1–7. DOI: 10.1016/0734-743x(92)90282-x. [25] FORRESTAL M J, ALTMAN B S, CARGILE J D, et al. An empirical equation for penetration depth of ogive-nose projectiles into concrete targets [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1994, 15(4): 395–405. DOI: 10.1016/0734-743X(94)80024-4. [26] FORRESTAL M J, FREW D J, HANCHAK S J, et al. Penetration of grout and concrete targets with ogive-nose steel projectiles [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1996, 18(5): 465–476. DOI: 10.1016/0734-743X(95)00048-F. [27] FORRESTAL M J, HANCHAK S J. Penetration limit velocity for ogive-nose projectiles and limestone targets [J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2002, 69(6): 853–854. DOI: 10.1115/1.1480820. [28] JONES S E, RULE W K, JEROME D M, et al. On the optimal nose geometry for a rigid penetrator, including the effects of pressure-dependent friction [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2000, 24(4): 403–415. DOI: 10.1016/S0734-743X(99)00157-8. [29] FORRESTAL M J, LUK V K, ROSENBERG Z, et al. Penetration of 7075-T651 aluminum targets with ogival-nose rods [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 1992, 29(14/15): 1729–1736. DOI: 10.1016/0020-7683(92)90166-Q. [30] CHEN X W, LI Q M. Deep penetration of a non-deformable projectile with different geometrical characteristics [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2002, 27(6): 619–637. DOI: 10.1016/S0734-743X(02)00005-2. [31] LI Q M, CHEN X W. Dimensionless formulae for penetration depth of concrete target impacted by a non-deformable projectile [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2003, 28(1): 93–116. DOI: 10.1016/S0734-743X(02)00037-4. [32] FREW D J, FORRESTAL M J, CARGILE J D. The effect of concrete target diameter on projectile deceleration and penetration depth [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2006, 32(10): 1584–1594. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2005.01.012. [33] FORRESTAL M J, LUK V K. Dynamic spherical cavity-expansion in a compressible elastic-plastic solid [J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics and Materials, 1988, 55(2): 275–279. DOI: 10.1115/1.3173672. -







 下载:
下载: