Numerical simulation study on the mechanism and characteristics of high-speed water entry of hollow projectiles
-
摘要: 为分析空心弹高速入水的机理及其特性,基于雷诺时均Navier-Stokes方程、VOF(volume of fluid)多相流模型、Realizable k-ε湍流模型,引入Schnerr-Sauer空化模型和重叠网格技术对空心弹高速入水进行数值模拟研究,获得了通孔孔径和头部形状对空心弹的空化特性、空泡形态和入水运动特性的影响规律。研究显示数值计算的空泡形态和入水速度、位移曲线与实验结果吻合较好,验证了数值模拟方法的可行性。结果表明:当通孔孔径不同时,通孔孔径越大,空化现象越明显,通孔射流越长,但对空泡半径的影响不大;通孔孔径越小,空泡闭合时间越早,与水面碰撞产生的阻力系数峰值越高,空心弹入水稳定后其阻力系数也越大;无量纲直径在0.575~0.600之间时,空心弹的运动最为稳定。当头部锥角不同时,头部锥角越大,空泡直径越大,空化现象出现得越晚,但空化生成的速度更快;随着头部锥角的增大,阻力系数变大,空心弹的速度衰减变快,相同时间运动的距离较短;头部锥角越大,俯仰角的变化越小,空心弹的运动越稳定。Abstract: To analyze the mechanism and characteristics of high-speed water entry of hollow projectiles, a numerical simulation study of the high-speed water entry of the hollow projectiles was carried out based on the Reynolds average Navier-Stokes equation (RANS), the volume of fluid (VOF) multi-phase flow model, the realizable k-ε flux model, the Schnerr and Sauer aeration model, the six-degrees-freedom (6-DOF) motion simulation method, and the overlapping grid technology. The effects of through-hole aperture and head shape on the cavitation characteristics, cavity morphology, and water entry kinematic properties of the hollow projectile were obtained. The effectiveness of the calculation method was verified by comparing it with the water entry experiment. The results show that the numerically calculated cavity morphology and water entry velocity and displacement curves are in good agreement with the experimental results, which verify the effectiveness of the numerical simulation method. When the through-hole aperture is different, the larger the through-hole aperture, the more pronounced the cavitation phenomenon and the longer the through-hole jet, but the effect on the radius of the cavity is not significant. The smaller the through-hole aperture, the earlier the closure time, the higher the peak drag coefficient resulting from impact with the water surface, and the greater the drag coefficient after the hollow projectile has stabilized in the water. The movement of the hollow projectile is most stable when the dimensionless diameter is between 0.575 and 0.600. When the head cone angle is varied, the larger the head cone angle, the larger the diameter of the cavity, and the later the cavitation phenomenon begins, but the faster the cavitation is generated. As the head cone angle increases, the drag coefficient becomes larger and the velocity of the hollow projectile decays faster, moving a shorter distance at the same time. However, the larger the head cone angle, the smaller the change in pitch angle and the more stable the motion of the hollow projectile.
-
Key words:
- hollow projectile /
- cavity evolution /
- high-speed water entry /
- motion characteristics
-
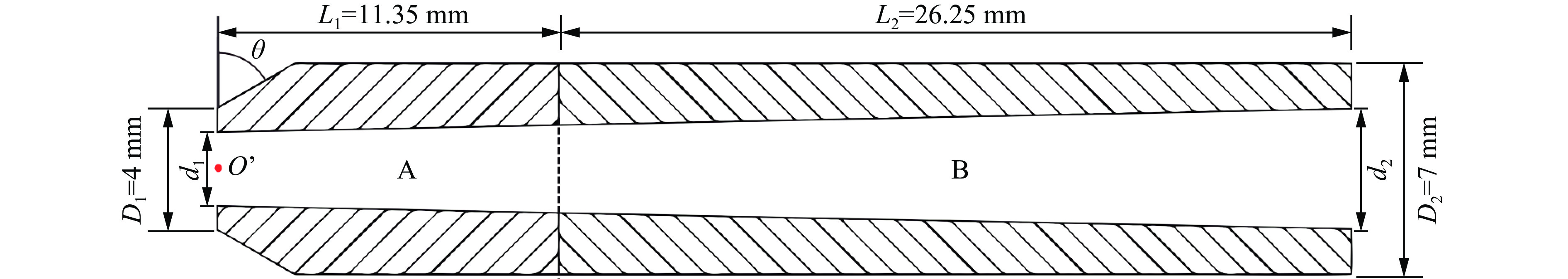
表 1 空心弹模型参数
Table 1. Model parameters of hollow projectiles
弹丸模型 d1/mm d2/mm θ/(°) m/g rC/mm S/mm2 M1 1.6 4 60 13.215 14.535 36.474 M2 2 4 60 12.837 14.612 35.343 M3 2.4 4 60 12.412 14.773 33.961 M4 2.8 4 60 11.938 14.952 32.327 M5 2.4 4 120 12.528 14.151 33.961 M6 2.4 4 180 12.576 14.014 33.961 -
[1] ZHAO Q, CHEN Z H, HUANG Z G, et al. Optimization of the aerodynamic configuration of a tubular projectile based on blind kriging [J]. Scientia Iranica, 2019, 26(1): 311–322. DOI: 10.24200/SCI.2017.20015. [2] 黄振贵, 李艳玲, 陈志华, 等. 空心弹的阻力特性与气动外形数值分析 [J]. 兵工学报, 2013, 34(5): 535–540. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2013.05.004.HUANG Z G, LI Y L, CHEN Z H, et al. Numerical investigations on the drag and aerodynamic characteristics of a hollow projectile [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2013, 34(5): 535–540. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2013.05.004. [3] WORTHINGTON A M, COLE R S IV. Impact with a liquid surface studied by the aid of instantaneous photography: Paper II [J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1900, 194(252): 175–199. DOI: 10.1098/rsta.1900.0016. [4] WORTHINGTON A M. A study of splashes [M]. New York: Longmans, Green, and Company, 1908: 25−76. [5] DE BACKER G, VANTORRE M, BEELS C, et al. Experimental investigation of water impact on axisymmetric bodies [J]. Applied Ocean Research, 2009, 31(3): 143–156. DOI: 10.1016/j.apor.2009.07.003. [6] TRUSCOTT T T, TECHET A H, BEAL D N. Shallow angle water entry of ballistic projectiles [C]//Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Cavitation. Michigan, USA: Ann Arbor, 2009: 1–14. [7] 陈先富. 弹丸入水空穴的试验研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 1985, 5(4): 70–73.CHEN X F. A method of observing both the motion of the free surface and the front of the mass-ejection of shocked lead [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 1985, 5(4): 70–73. [8] 施红辉, 周浩磊, 吴岩, 等. 伴随超空泡产生的高速细长体入水实验研究 [J]. 力学学报, 2012, 44(1): 49–55. DOI: 10.6052/0459-1879-2012-1-lxxb2011-062.SHI H H, ZHOU H L, WU Y, et al. Experiments on water entry of high-speed slender body and the resulting supercavitation [J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2012, 44(1): 49–55. DOI: 10.6052/0459-1879-2012-1-lxxb2011-062. [9] 宋武超, 王聪, 魏英杰, 等. 回转体倾斜入水空泡及弹道特性实验 [J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2016, 42(11): 2386–2394. DOI: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2015.0690.SONG W C, WANG C, WEI Y J, et al. Experiment of cavity and trajectory characteristics of oblique water entry of revolution bodies [J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronasutics, 2016, 42(11): 2386–2394. DOI: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2015.0690. [10] 赵成功, 王聪, 魏英杰, 等. 细长体水下运动空化流场及弹道特性实验 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2017, 37(3): 439–446. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2017)03-0439-08.ZHAO C G, WANG C, WEI Y J, et al. Experiment of cavitation and ballistic characteristics of slender body underwater movement [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2017, 37(3): 439–446. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2017)03-0439-08. [11] 罗驭川, 黄振贵, 高建国, 等. 截锥体头型弹丸低速斜入水实验研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2019, 39(11): 113902. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0498.LUO Y C, HUANG Z G, GAO J G, et al. Experiment research of low-speed oblique water-entry of truncated cone-shaped projectile [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2019, 39(11): 113902. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0498. [12] 朱珠, 罗松, 卢丙举, 等. 旋转射弹高速倾斜入水多相流场与弹道数值模拟 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2019, 39(11): 113901. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0315.ZHU Z, LUO S, LU B J, et al. Numerical simulation of multiphase flow field and trajectory of high-speed oblique water entry of rotating projectile [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2019, 39(11): 113901. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0315. [13] 邵志宇, 伍思宇, 曹苗苗, 等. 斜截头弹体入水的弹道特性 [J]. 兵工学报, 2022, 43(6): 1255–1265. DOI: 10.12382/bgxb.2021.0301.SHAO Z Y, WU S Y, CAO M M, et al. Water-entry trajectory of truncated cone-shaped projectile [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2022, 43(6): 1255–1265. DOI: 10.12382/bgxb.2021.0301. [14] 高旭东, 钱建平, 王晓鸣, 等. 空心弹丸流场数值模拟与阻力特性 [J]. 南京理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 29(2): 158–161.GAO X D, QIAN J P, WANG X M, et al. Flowfield calculation and drag characteristic of hollow projectile [J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2005, 29(2): 158–161. [15] 任登凤, 谭俊杰, 张军. 非结构隐式方法在空心弹丸流场模拟中的应用 [J]. 力学与实践, 2006, 28(5): 24–27. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0879.2006.05.005.REN D F, TAN J J, ZHANG J. Flowfield calculation of hollow projectile using implicit method based on unstructured meshes [J]. Mechanics in Engineering, 2006, 28(5): 24–27. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0879.2006.05.005. [16] 杜宏宝, 蒋锋, 黄振贵, 等. 内锥型空心弹阻塞临界入口锥角仿真研究 [J]. 南京理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 42(6): 642–646, 670. DOI: 10.14177/j.cnki.32-1397n.2018.42.06.002.DU H B, JIANG F HUANG Z G, et al. Simulation of critical inlet angle of inner conical hollow projectile under choke flow [J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2018, 42(6): 642–646, 670. DOI: 10.14177/j.cnki.32-1397n.2018.42.06.002. [17] 全鑫, 张红艳, 马铁华, 等. 内锥型空心弹阻塞喉径面积比的仿真研究 [J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2021, 42(4): 97–101. DOI: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2021.04.018.QUAN X, ZHANG H Y, MA T H, et al. Simulation research on critical area ratio of throat to entrance of inner conical hollow projectile under choke flow [J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2021, 42(4): 97–101. DOI: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2021.04.018. [18] WESSAM M E, HUANG Z G, CHEN Z H. Aerodynamic characteristics and flow field investigations of an optimal hollow projectile [C]// Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Mechanical Engineering and Mechanics. Yangzhou: ICMEM, 2014: 181–186. DOI: 10.13140/2.1.2037.9529. [19] SAVCHENKO Y N. Hydrodynamic characteristics of a disc with central duct in a supercavitation flow [M]//NESTERUK I. Supercavitation. Berlin: Springer, 2012: 107–113. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-23656-3_6. [20] HOU Y, HUANG Z G, CHEN Z H, et al. Different closure patterns of the hollow cylinder cavities with various water-entry velocities [J]. Ocean Engineering, 2021, 221: 108526. DOI: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.108526. [21] HOU Y, HUANG Z G, CHEN Z H, et al. Experimental investigations on the oblique water entry of hollow cylinders [J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 266: 112800. DOI: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.112800. [22] LIU H, ZHOU B, YU J W, et al. Experimental investigation on the multiphase flow characteristics of oblique water entry of the hollow cylinders [J]. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 272: 113902. DOI: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.113902. [23] SCHNERR G H, SAUER J. Physical and numerical modeling of unsteady cavitation dynamics [C]// 4th International Conference on Multiphase Flow. New Orleans, LO, USA: ICMF, 2001. [24] CHEN T, HUANG W, ZHANG W, et al. Experimental investigation on trajectory stability of high-speed water entry projectiles [J]. Ocean Engineering, 2019, 175: 16–24. DOI: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2019.02.021. -







 下载:
下载: