Flexural damage assessment for UHPC panels under blast loadings
-
摘要: 为构建爆炸荷载作用下超高性能混凝土(UHPC)板弯曲损伤等级评估的p-I(压力-冲量)曲线:采用条带法进行截面分析,建立了考虑UHPC材料拉/压软化和塑性铰影响的UHPC简支单向板的非线性抗力方程和等效单自由度(ESDOF)理论模型;通过与六炮次爆炸实验中UHPC板的挠度时程,以及UFC 3-340-02和FHWA规范推荐方法的计算结果对比,验证了本文理论模型的可靠性;基于验证的ESDOF模型,构建了评估UHPC板的不同弯曲损伤等级的p-I曲线并开展了参数影响分析,提出并验证了UHPC板弯曲损伤评估的p-I曲线经验公式。结果表明:提高混凝土强度等级和钢筋屈服强度、增加受拉钢筋配筋率和板厚,以及减小净跨均可提升UHPC板的抗爆性能。Abstract: To establish the p-I (pressure-impulse) diagram for flexural damage assessment of ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) panels under blast loadings, cross-sectional analysis using the strip method was performed to establish the moment curvature relationship for simply supported one-way UHPC panels. This process involved considering the tensile/compressive softening of UHPC through the utilization of material constitutive models with softening properties and describing the strain rate effect of UHPC and reinforcement with the dynamic increase factor (DIF) that varies according to different strip layers. Subsequently, the nonlinear resistance function considering the effect of plastic hinge was developed, based on the moment curvature relationship and a simplified half-span symmetric beam model. Then, an equivalent single degree of freedom (ESDOF) theoretical model, adopting the nonlinear resistance function, was established and employed to predict the deflection-time histories of UHPC panels under explosions. The reliability of the above theoretical model was verified by comparing the predicted results with the deflection time histories of test UHPC panels in six shots of explosion tests. Additionally, the superiority of the proposed ESDOF model was proved by comparing with the corresponding calculation results obtained from the recommended methods using bilinear ideal elastic-plastic resistance functions based on the UFC 3-340-02 and FHWA codes. Furthermore, based on the verified ESDOF model, p-I diagrams for evaluating the flexural damage level of UHPC panels were established and parametric analysis was carried out. The results indicate that increasing the concrete strength grade, yield strength of reinforcement, tensile reinforcement ratio, and panel thickness, while reducing the clear span, are beneficial for the blast-resistant performance of UHPC panels. Finally, empirical formulae for p-I diagrams, taking into consideration the abovementioned influencing factors, were proposed and verified for assessing the flexural damage of UHPC panels. These formulae can serve as a valuable reference for evaluating blast-induced damage in UHPC panels.
-
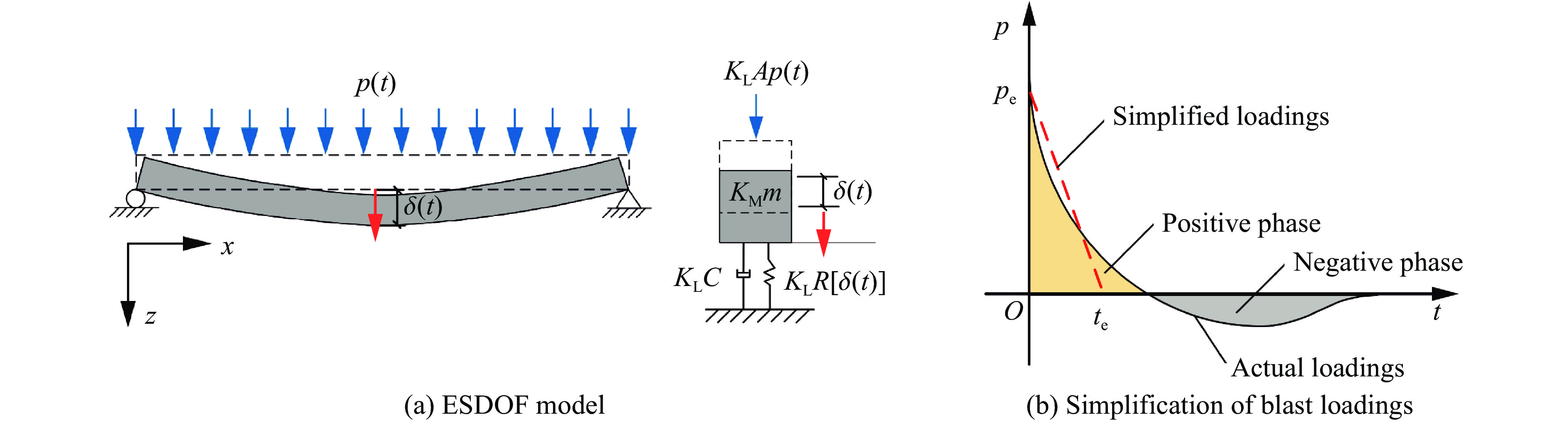
表 1 简化爆炸荷载特征参数
Table 1. Characteristic parameters of simplified blast loadings
表 2 UHPC板的尺寸、配筋及材料特性参数
Table 2. Dimensions, reinforcement and material properties parameters of UHPC panels
表 3 ESDOF模型预测峰值挠度与实验/数值模拟结果对比
Table 3. Comparisons of ESDOF model predicted and experimental/simulated maximum deflections
实验 试件 实验值/mm 模拟值/mm UFC 3-340-02 FHWA 本文 预测值/mm 误差/% 预测值/mm 误差/% 预测值/mm 误差/% Su等[1] UHPC-1 27.86 27.44 27.73 −0.5 17.39 −37.6 26.42 −5.2 UHPC-2 − 38.90 41.89 7.6 24.92 −35.9 37.25 −4.2 UHPC-3 − 48.13 55.98 16.3 32.56 −32.3 47.67 −1.0 Li等[2] UHPC-D4 72 − 123.99 72.2 49.95 −30.6 73.11 1.5 Mao等[3] A 110 − 113.24 2.9 88.24 −19.8 111.44 1.3 B 210 − 193.32 −7.9 145.24 −30.8 213.46 1.6 表 4 UHPC板弯曲损伤
$p{\text{-}}I $ 曲线经验公式相关参数Table 4. Parameters of the empirical formulae of flexural damage p-I diagrams for UHPC panels
影响因素 参数 表达式 θ=2° θ=5° 基准板 pb0 106 127 Ib0 1214 2228 βb 1.634 1.642 100≤fc/MPa≤250 $ {\eta _{{f_{\text{c}}}}} $ 0.717 + 0.325 (fc/150) − 0.042 (fc/150)2 0.251 + 1.065 (fc/150) − 0.319 (fc/150)2 $ {\lambda _{{f_{\text{c}}}}} $ 0.839 + 0.187 (fc/150) − 0.025 (fc/150)2 0.614 + 0.550 (fc/150) − 0.167 (fc/150)2 $ {\alpha _{{f_{\text{c}}}}} $ 0.951 + 0.065 (fc/150) − 0.013 (fc/150)2 0.993 + 0.002 (fc/150) + 0.005 (fc/150)2 300≤fy/MPa≤600 $ {\eta _{{f_{\text{y}}}}} $ 0.293 + 1.061 (fy/500) − 0.354 (fy/500)2 0.191 + 1.106 (fy/500) − 0.295 (fy/500)2 $ {\lambda _{{f_{\text{y}}}}} $ 0.635 + 0.571 (fy/500) − 0.206 (fy/500)2 0.534 + 0.700 (fy/500) − 0.233 (fy/500)2 $ {\alpha _{{f_{\text{y}}}}} $ 1.034 − 0.081 (fy/500) + 0.047 (fy/500)2 0.999 − 0.017 (fy/500) + 0.017 (fy/500)2 0.393A0/Ac≤ρt/%
≤1.728A0/Ac$ {\eta _{{\rho _{\text{t}}}}} $ 0.292 + 0.791 (ρtAc/0.864A0) − 0.087 (ρtAc/0.864A0)2 0.159 + 0.947 (ρtAc/0.864A0) − 0.123 (ρtAc/0.864A0)2 $ {\lambda _{{\rho _{\text{t}}}}} $ 0.619 + 0.448 (ρtAc/0.864A0) − 0.071 (ρtAc/0.864A0)2 0.524 + 0.572 (ρtAc/0.864A0) − 0.107 (ρtAc/0.864A0)2 $ {\alpha _{{\rho _{\text{t}}}}} $ 0.998 − 0.001 (ρtAc/0.864A0) + 0.005 (ρtAc/0.864A0)2 0.973 + 0.032 (ρtAc/0.864A0) − 0.005 (ρtAc/0.864A0)2 100≤h/mm≤250 ηh −0.294 + 0.928 (h/100) + 0.377 (h/100)2 −0.603 + 1.536 (h/100) + 0.071 (h/100)2 λh −0.452 + 1.353 (h/100) + 0.101 (h/100)2 −0.438 + 1.376 (h/100) + 0.062 (h/100)2 αh 0.834 + 0.211 (h/100) − 0.045 (h/100)2 0.928 + 0.090 (h/100) − 0.018 (h/100)2 1000≤L/mm≤4000 ηL 0.187 − 28.977 0.029L/2000 0.218 − 23.259 0.034L/2000 λL 0.492 − 2.586 0.200L/2000 0.533 − 2.265 0.210L/2000 αL 1.201 − 0.213 (L/2000) + 0.022 (L/2000)2 1.185 − 0.203 (L/2000) + 0.021 (L/2000)2 表 5 验证板的参数取值
Table 5. Parameter values for the validation panels
板编号 fc/MPa fy/MPa ρt/% h/mm L/mm 1 100 300 0.393 100 4000 2 200 300 0.864 200 3000 3 120 550 1.047 150 2500 -
[1] SU Q, WU H, SUN H S, et al. Experimental and numerical studies on dynamic behavior of reinforced UHPC panel under medium-range explosions [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2021, 148: 103761. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2020.103761. [2] LI J, WU C Q, HAO H. An experimental and numerical study of reinforced ultra-high performance concrete slabs under blast loads [J]. Materials & Design, 2015, 82: 64–76. DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2015.05.045. [3] MAO L, BARNETT S, BEGG D, et al. Numerical simulation of ultra high performance fibre reinforced concrete panel subjected to blast loading [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2014, 64: 91–100. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2013.10.003. [4] SCHLEYER G K, BARNETT S J, MILLARD S G, et al. UHPFRC panel testing [J]. The Structural Engineer, 2011, 89(23/24): 34–40. [5] LIN X S. Numerical simulation of blast responses of ultra-high performance fibre reinforced concrete panels with strain-rate effect [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 176: 371–382. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.05.066. [6] SU Q, WU H, FANG Q. Calibration of KCC model for UHPC under impact and blast loadings [J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2022, 127: 104401. DOI: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2021.104401. [7] US Department of Defense. Structures to resist the effects of accidental explosions, with change 2: UFC 3-340-02 [S]. Washington: US Department of Defense, 2008: 583-600. [8] SILVA P F, LU B G. Blast resistance capacity of reinforced concrete slabs [J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2009, 135(6): 708–716. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)ST.1943-541X.000001. [9] SILVA P F, LU B G. Improving the blast resistance capacity of RC slabs with innovative composite materials [J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2007, 38(5/6): 523–534. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2006.06.015. [10] JACQUES E. Blast retrofit of reinforced concrete walls and slabs [D]. Ottawa: University of Ottawa, 2011: 145–165. [11] MAAZOUN A, BELKASSEM B, REYMEN B, et al. Blast response of RC slabs with externally bonded reinforcement: experimental and analytical verification [J]. Composite Structures, 2018, 200: 246–257. DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2018.05.102. [12] WANG W, ZHANG D, LU F Y, et al. Pressure-impulse diagram with multiple failure modes of one-way reinforced concrete slab under blast loading using SDOF method [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2013, 20(2): 510–519. DOI: 10.1007/s11771-013-1513-z. [13] LIAO Z, TANG D G, LI Z Z, et al. Study on explosion resistance performance experiment and damage assessment model of high-strength reinforcement concrete beams [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2019, 133: 103362. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2019.103362. [14] 陈柏锟. 超高韧性水泥基复合材料及活性粉末混凝土靶板抗爆研究 [D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2021: 116–168.CHEN B K. Research on ultra-high toughness cementitious composites and reactive powder concrete slabs under blast loading [D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2021: 116–168. [15] HOU X M, CAO S J, RONG Q, et al. A P-I diagram approach for predicting failure modes of RPC one-way slabs subjected to blast loading [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2018, 120: 171–184. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2018.06.006. [16] 潘建军, 陈万祥, 郭志昆, 等. 基于P-I曲线的火灾后钢管RPC柱抗爆损伤评估方法 [J]. 防护工程, 2018, 40(5): 16–26.PAN J J, CHEN W X, GUO Z K, et al. Evaluation of fire and blast-damaged RPC-FST column based on pressure-impulse diagram [J]. Protective Engineering, 2018, 40(5): 16–26. [17] AALETI S, PETERSEN B, SRITHARAN S. Design guide for precast UHPC waffle deck panel system, including connections: FHWA-HIF-13-032 [R]. Washington: Federal Highway Administration, 2013: 49–51. [18] JACQUES E, LLOYD A, IMBEAU P, et al. GFRP-retrofitted reinforced concrete columns subjected to simulated blast loading [J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2015, 141(11): 04015028. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)ST.1943-541X.0001251. [19] JACQUES E, SAATCIOGLU M. Uncoupled compression membrane analysis of reinforced-concrete members subject to extreme loads [J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2020, 146(9): 04020189. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)ST.1943-541X.0002736. [20] 彭琦, 吴昊, 方秦, 等. 长持时平面爆炸波作用下-RC-梁动力响应研究 [J]. 建筑结构学报, 2023, 44(3): 87–101. DOI: 10.14006/j.jzjgxb.2021.0751.PENG Q, WU H, FANG Q, et al. Dynamic responses of RC beams under long-duration near-planar blast waves [J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2023, 44(3): 87–101. DOI: 10.14006/j.jzjgxb.2021.0751. [21] NAEIMI N. Experimental compressive behavior and numerical modeling of unconfined and confined ultra-high performance concrete [D]. Nevada: University of Nevada, Reno, 2020: 68–76. [22] MELANÇON C. Effect of high-performance concrete and steel materials on the blast performance of reinforced concrete one-way slabs [D]. Ottawa: University of Ottawa, 2016: 147. [23] 邹慧辉, 李明, 段建, 等. 钢筋动态本构模型及模型参数研究 [J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2022, 43(8): 193–202. DOI: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2022.08.031.ZOU H H, LI M, DUAN J, et al. Research on dynamic constitutive model and model parameters of steel bars [J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2022, 43(8): 193–202. DOI: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2022.08.031. [24] International Federation for Structural Concrete (FIB). Fib model code for concrete structures 2010 [S]. Berlin: Wilhelm Ernst & Sohn, 2013: 100. DOI: 10.1002/9783433604090. [25] JONES N. Structural impact[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1990: 348-349. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511624285 [26] MA L L, WU H, FANG Q. A unified performance-based blast-resistant design approach for RC beams/columns [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2023, 173: 104459. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2022.104459. [27] REN G M, WU H, FANG Q, et al. Effects of steel fiber content and type on static mechanical properties of UHPCC [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 163: 826–839. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.12.184. [28] AFGC Groupe De Travail BFUP. Bétons fibrés à ultra-hautes performances, recommandations [R]. Paris: Association Francaise de Génie Civil, 2013: 193-194. -







 下载:
下载: