Dynamic response and energy absorption properties of sinusoidally curved three-dimensional negative Poissonʼs ratio sandwich panels subjected to blast loading
-
摘要: 具有优异能量吸收特性的负泊松比结构在抗爆炸冲击防护领域有广阔的应用前景。为进一步提升夹芯板的抗爆性能,提出了一种在X、Y方向力学特性相同的正弦曲边三维负泊松比夹芯板用于防爆保护。采用数值模拟方法,对夹芯板在空爆载荷下的动态响应和吸能特性进行了研究,分析了夹芯板塑性拉伸和弯曲对背面板变形模式和轴向偏转分布的影响,并探究了爆炸距离、炸药质量、面板厚度和芯层关键结构参数对夹芯板变形和能量吸收的影响。结果表明,在空爆载荷下,夹芯板的动态响应过程可分为芯层压缩、整体变形和自由振动3个阶段。后面板在纵向(X方向)和横向(Y方向)上的抗变形能力无明显差异。随着炸药质量增加和爆炸距离减小,夹芯板的后面板中心位移增加,芯层吸能占比减小。此外,采用薄前面板和厚后面板的夹芯板可以提高芯层的吸能占比。当分别增加相同的前、后面板厚度时,前面板厚度对减小后面板中心位移的影响更显著。当芯层厚度从0.6 mm减小至0.2 mm时,后面板中心位移减小49.0%,总能量吸收增加86.7%;芯层振幅从0.2 mm增大至1.0 mm时,后面板中心位移减小20.7%,总能量吸收大致不变;芯层高度从10 mm增大至18 mm时,后面板中心位移减小88.3%,总能量吸收增加56.9%;芯层宽长比从0.56减小至0.2时,后面板中心位移减小39%,总能量吸收增加47.4%。Abstract: The remarkable energy absorption properties of the negative Poissonʼs ratio structure offer extensive prospects for applications in blast protection. However, the existing in-plane configurations of two-dimensional auxetic honeycomb cores always represent anisotropic behavior. To further enhance the blast resistance of sandwich panels, a three-dimensional sinusoidal curved-edge sandwich panel with a negative Poissonʼs ratio effect in both the X and Y directions for blast protection was proposed. The dynamic response and energy absorption characteristics under air blast load were studied by numerical simulation. Deformation modes and axial deflection distribution caused by plastic stretching and bending of the back face sheet were investigated in detail. The effects of stand-off distance (SOD), explosive mass, panel thickness, and key geometric parameters of the core layer on deformation and energy absorption were discussed. The results show that the dynamic response process of the sandwich panel can be divided into three stages: core compression, overall deformation, and free vibration. Moreover, it is found that there is no significant difference in the ability to resist deformation of the sandwich structure along the longitudinal (X) and transverse (Y) directions. As the TNT mass increases and the SOD decreases, the central displacement of the back face sheet of the sandwich panel increases, leading to a decrease in the energy absorption ratio of the core layer. Furthermore, utilizing a sandwich panel with a thin front panel and a thick back panel can increase the energy absorption proportion of the core layer. When increasing the thickness of the front and back panels by the same amount, the thickness of the front panel has a more significant effect on reducing the center displacement of the back panel. When the core thickness decreases from 0.6 mm to 0.2 mm, the back panel center displacement decreases by 49.0%, and the total energy absorption increases by 86.7%. As the core amplitude increases from 0.2mm to 1.0mm, the back panel center displacement decreases by 20.7%, with the total energy absorption remaining roughly constant. With an increase in core height from 10mm to 18mm, the back panel center displacement decreases by 88.3%, and the total energy absorption increases by 56.9%. Furthermore, a decrease in core aspect ratio from 0.56 to 0.2 results in a 39% reduction in back panel center displacement and a 47.4% increase in total energy absorption. The results of this study can guide the design of energy-absorbing protection for sandwich panels.
-
夹层结构通常由2层刚度较大的面板和轻质多孔的芯层组成,这种结构突破了材料与结构的单一性,展现了轻质、高比强度、高比刚度及良好的抗冲击吸能特性,在航空航天、军事设施、公路桥梁等缓冲吸能防护领域已经得到广泛应用。当夹层结构受到冲击载荷时,芯层能够实现大的压缩变形,吸收大量的冲击能量。相比等质量的实体结构,夹层结构具有优越的抗爆性能[1-3]。Dharmasena等[1]和Uth等[3]通过实验和有限元模拟研究了蜂窝夹芯板的动态力学响应,发现相同质量下,蜂窝夹芯板的背面板偏转明显小于相同质量的实体结构,这是由于核心层优越的能量吸收能力和夹层结构较高的弯曲强度。夹芯板的防护作用关键在于芯层的设计和应用,目前已有许多芯层结构,例如蜂窝芯、波纹芯、I-V芯、H芯、点阵结构或实心泡沫芯等[4-13]。负泊松比蜂窝材料与传统夹层结构不同,它们在压缩过程中横向收缩,在拉伸过程中横向膨胀,能够提供更好的断裂韧性、剪切模量、能量吸收和较低的裂纹扩展速度[14-15]。因此,采用负泊松比材料作为夹芯板的芯层有利于在冲击载荷下吸收更多的能量,并降低传递到后面板的力量。这使得将负泊松比材料用于夹芯板的芯层,以提升其抗爆防护性能的方法上具有巨大潜力[16-21]。
二维负泊松比结构作为夹芯板芯层在爆炸防护上已被广泛研究,孙晓旺等[22]将内凹性负泊松比蜂窝夹芯板用于车辆底部防爆,与传统的防护组件相比,采用了负泊松比蜂窝夹芯层防护组件吸能的基板的最大位移和动能分别降低了13.72 mm和52.17%。杨德庆等[23]比较了不同负泊松比和层数结构排列的蜂窝结构的防爆性能,发现负泊松比效应蜂窝夹芯防护结构较传统防护结构具有良好的水下抗爆性能,且其水下抗爆性能随蜂窝胞元层数和胞元泊松比的增大而增强。孙魁远等[24]研究了厚度梯度型负泊松比蜂窝在防雷组件中的应用,发现在相同质量条件下,厚度梯度型负泊松比蜂窝芯层的组件具有更好的防护性能。卫禹辰等[25]以内凹蜂窝型梯度结构为研究对象,采用爆炸冲击实验与数值有限元法相结合的研究方法,通过改变胞元尺寸和胞元凹角对梯度蜂窝结构进行优化,分析了梯度结构在爆炸冲击环境下对冲击波的衰减效率及其力学响应规律。杨德庆等[26]采用数值方法对星型宏观负泊松比夹芯板在水下爆炸过程中的失效行为进行了研究,发现负泊松比效应蜂窝夹芯防护结构相较常规防护结构具有良好的水下抗爆性能。上述研究表明,二维负泊松比蜂窝展现了较好的抗爆性,并在一定程度上提升了防护结构的抗爆性能。
上述文献的芯层结构均由二维胞元轴向拉伸而成,其平面内的力学行为通常表现出各向异性的行为[27],当受到压力时,蜂窝芯层仅在一个方向上向迎爆面中心收缩,导致冲击区域的密度增大,从而有效地抵抗爆炸冲击载荷。与二维蜂窝结构相比,三维负泊松比结构能够在2个轴向上都向迎爆面中心收缩,从而进一步增大局部密度,提高局部强度以抵御更高的爆炸载荷。Gao等[28]在二维箭型蜂窝的基础上设计出一种三维双箭头箭型拉胀结构,通过相关参数化分析了双箭头蜂窝结构的能量吸收和耐撞性。Beharic等[29]制备了3种三维负泊松比夹芯板,并通过实验研究了这些夹芯板在冲击器冲击下的动态性能,发现胞芯的几何设计对夹层结构的能量吸收起着显著影响。杨泽水等[30]提出了一种新型三维负泊松比星型结构,通过冲击实验和有限元分析研究了该结构在不同的胞元设计角度下的吸能特性和抗冲击性能。Wang等[31]提出了一种新的三维双箭头负泊松比结构,并用有限元模拟研究了该结构在爆炸载荷下的动态响应,发现3种不同参数的夹芯板后面板中心变形均小于实体板,并对胞元参数进行了优化,获得了最佳的抗冲击形式。Imbalzano等[32-33]对一种新型的三维负泊松比夹层结构进行了数值研究,发现该结构能够有效降低后面板速度和变形量,提升夹芯板的抗爆性能。上述研究表明,三维负泊松比夹芯板在抗冲击和抗爆方面表现出优异的防护性能。
综上所述,虽然对于夹芯板结构的爆炸响应和设计问题已经取得了大量的研究成果,但主要集中在直边的二维或三维负泊松比夹芯板,对具有曲边的三维负泊松比夹芯板的研究较少。正弦曲边蜂窝结构具有负泊松比效应,已被证明具有高能量吸收能力和低峰值应力[34-36]。因此,本文中,基于这一设计思路,通过LS-DYNA有限元软件进行数值模拟,对引入正弦曲线的三维负泊松比夹芯板的抗爆性能和吸能特性开展研究,同时对芯层厚度、芯层高度、芯层宽长比和芯层振幅进行参数化研究,以探究这些参数对正弦曲线三维负泊松比夹芯板防爆性能的影响。
1. 几何模型和结构设计
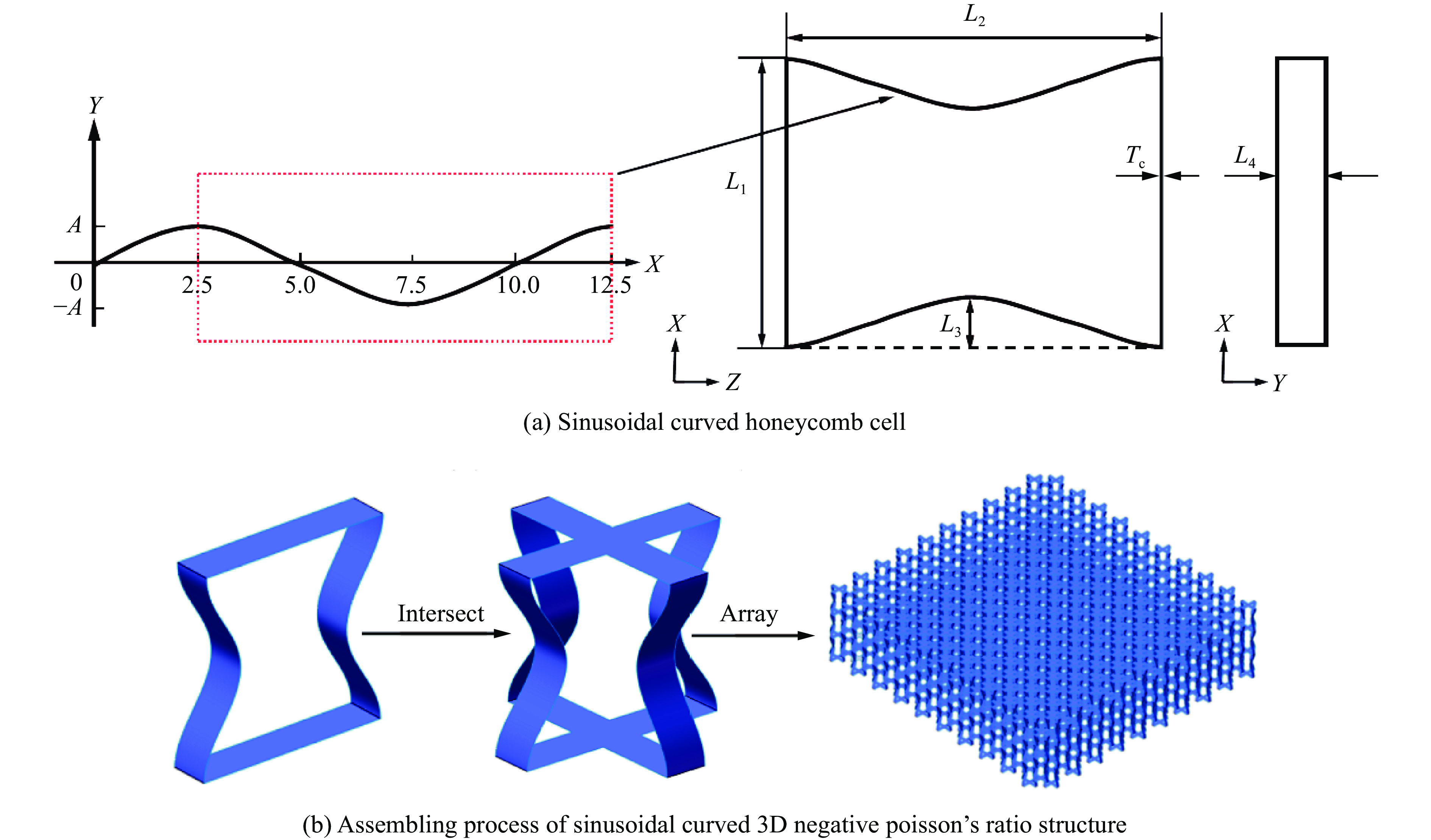
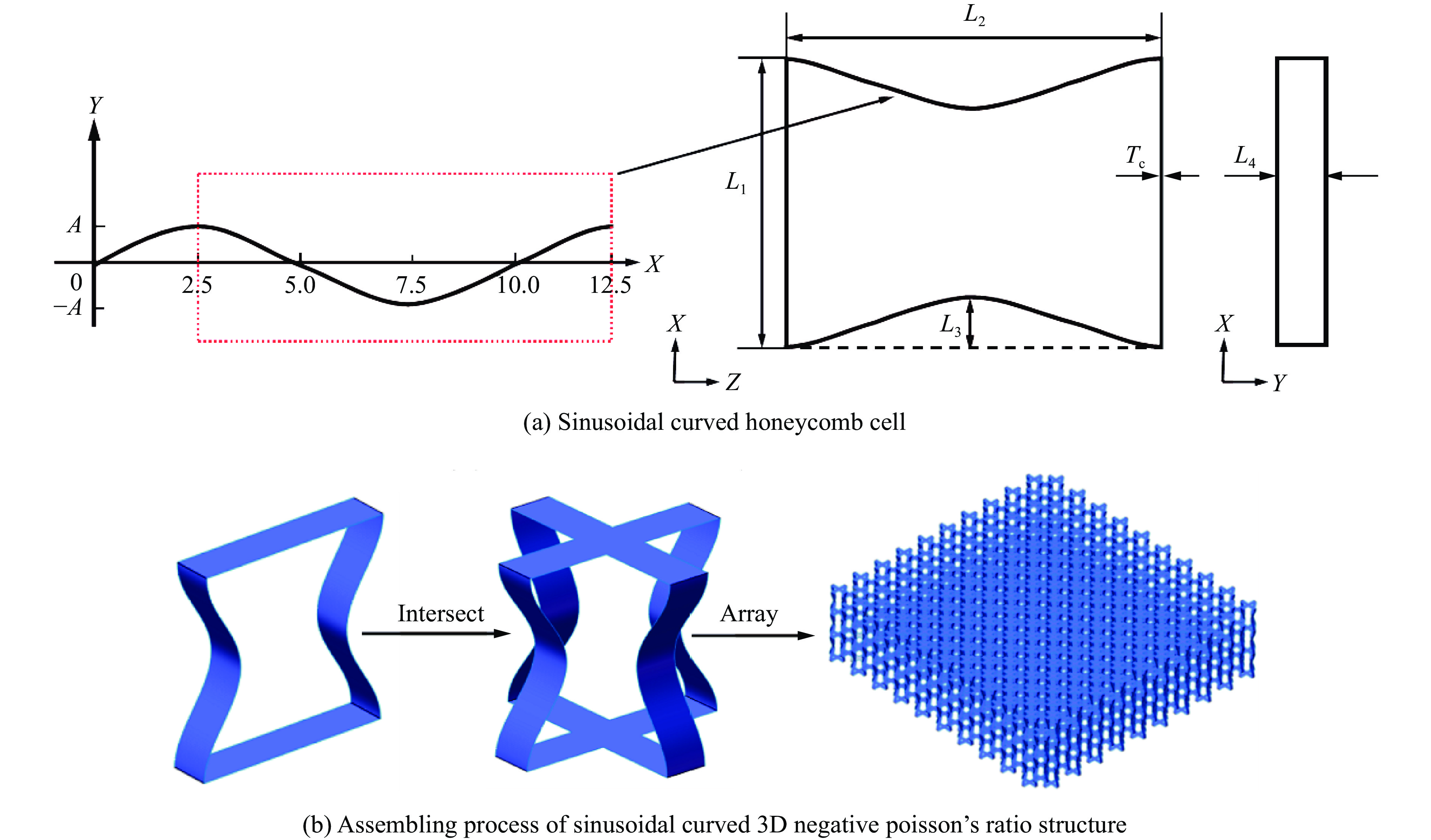
选择了一种具有负泊松比效应的正弦曲边蜂窝胞元,正弦曲线的基本函数方程为Y=A sin(WX),取A=1 mm, W=0.2π, X∈(2.5, 12.5)内的曲线来代替传统内凹蜂窝的两侧斜臂,从而得到如图1(a)所示的负泊松比蜂窝结构内凹胞元。其中,胞元长度L1为10 mm,芯层厚度Tc为0.4 mm,L2为单个胞元高度,其值与正弦曲线周期长度一致,此时内凹的长度L3 =2A,蜂窝胞元沿Y方向拉伸的宽度为L4。如图1(b)所示,通过组合2个垂直交叉的二维蜂窝结构,得到三维负泊松比结构单元,基于此单元进行旋转、平移、阵列可得到三维负泊松比结构。
1.1 材料属性
采用铝合金作为面板和芯层的基体材料,其中面板采用Al-1200铝合金制成,蜂窝夹芯采用Al-5052铝合金制成。在模拟中,使用LS-DYNA的3号材料(*MAT_PLASTIC_KINEMATIC)来模拟铝合金的力学行为。考虑到应变率效应对铝合金材料的影响较小,且本研究不涉及应变率对数值模拟结果的影响,因此没有考虑应变率的依赖性和硬化效应[27]。数值模拟中所采用的具体材料参数见表1[37]。
1.2 数值模型的建立
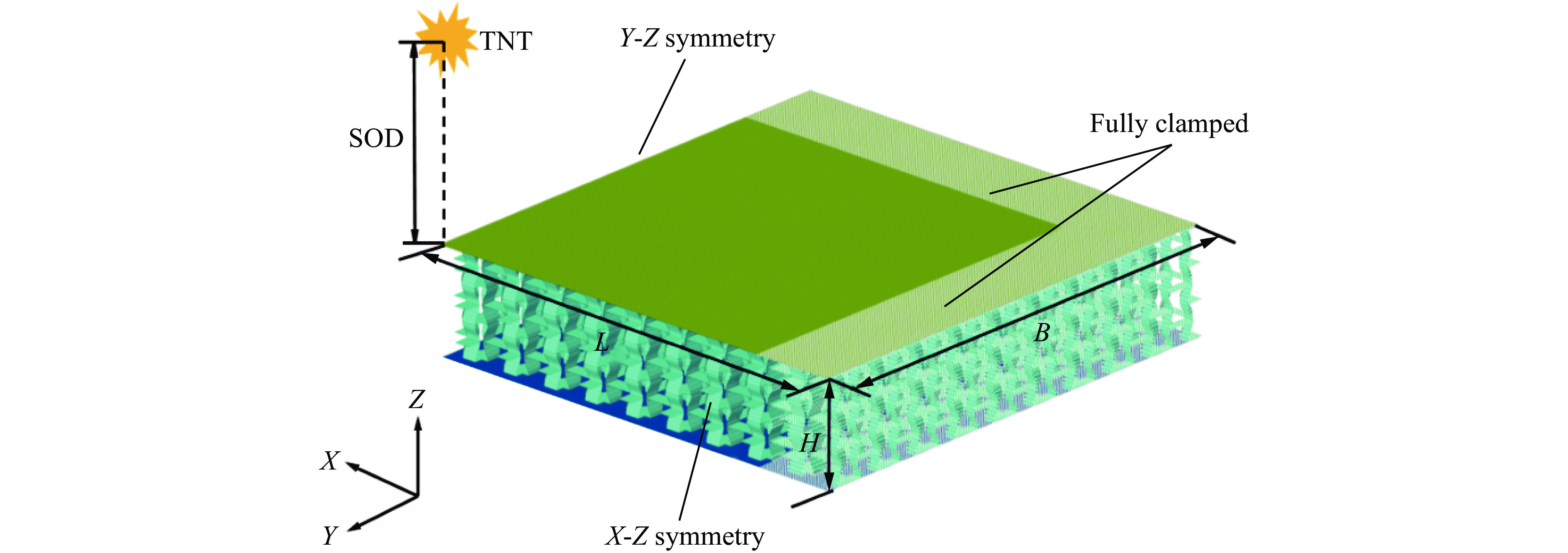
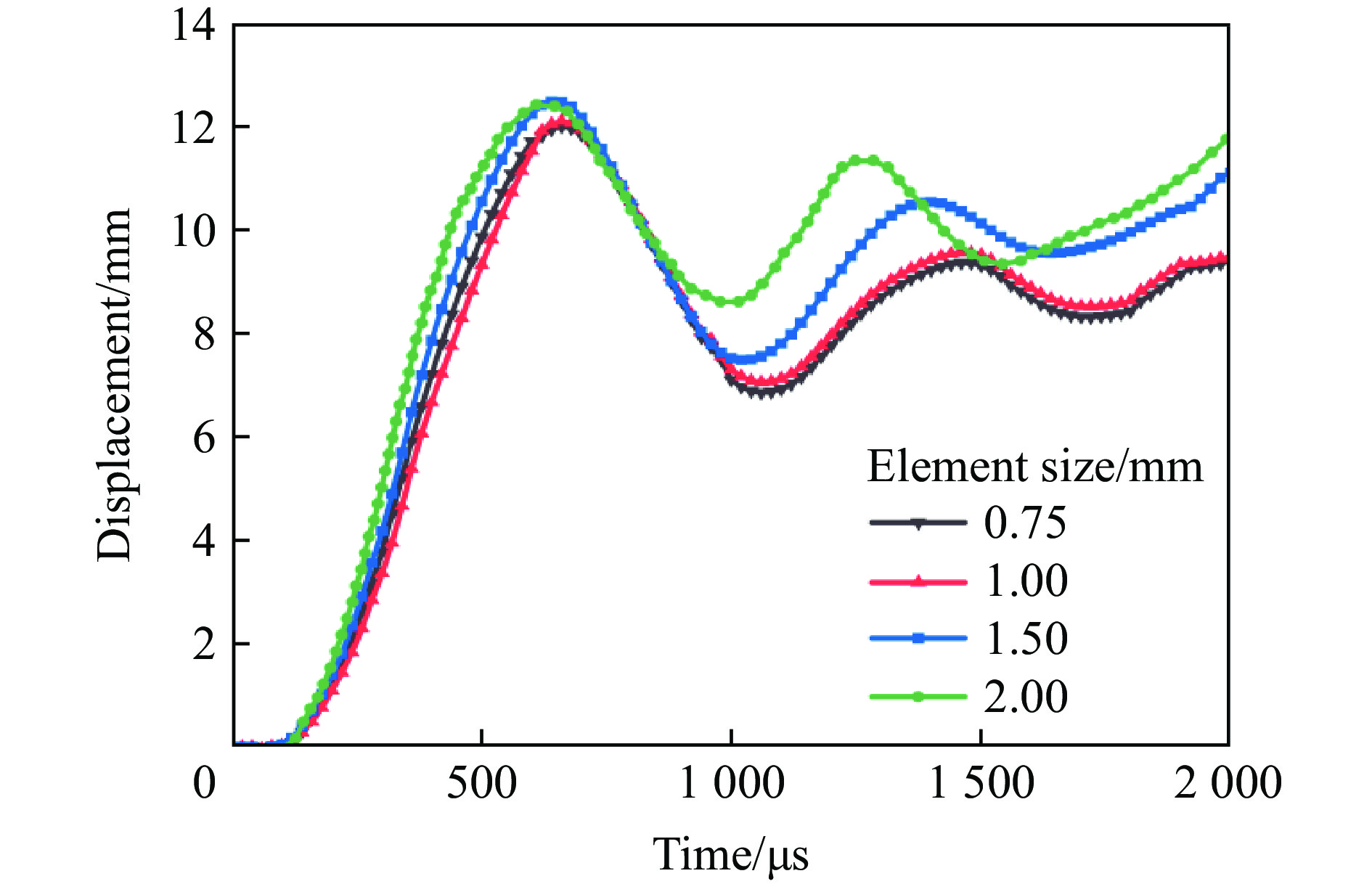
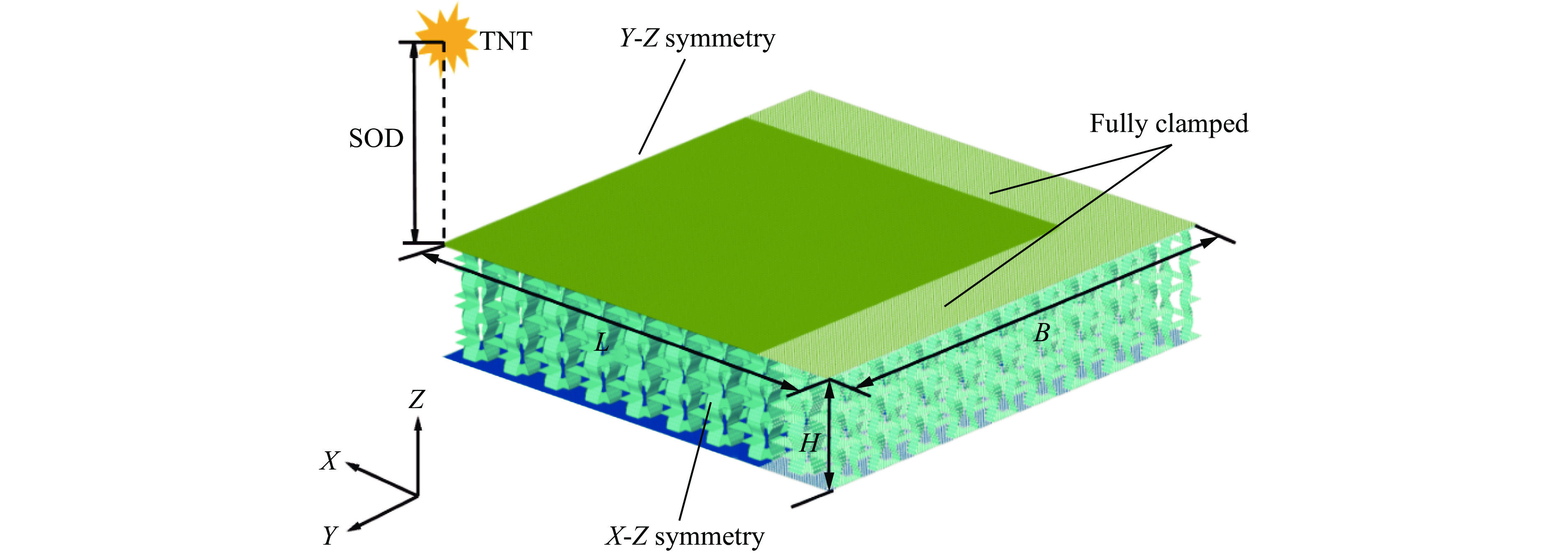
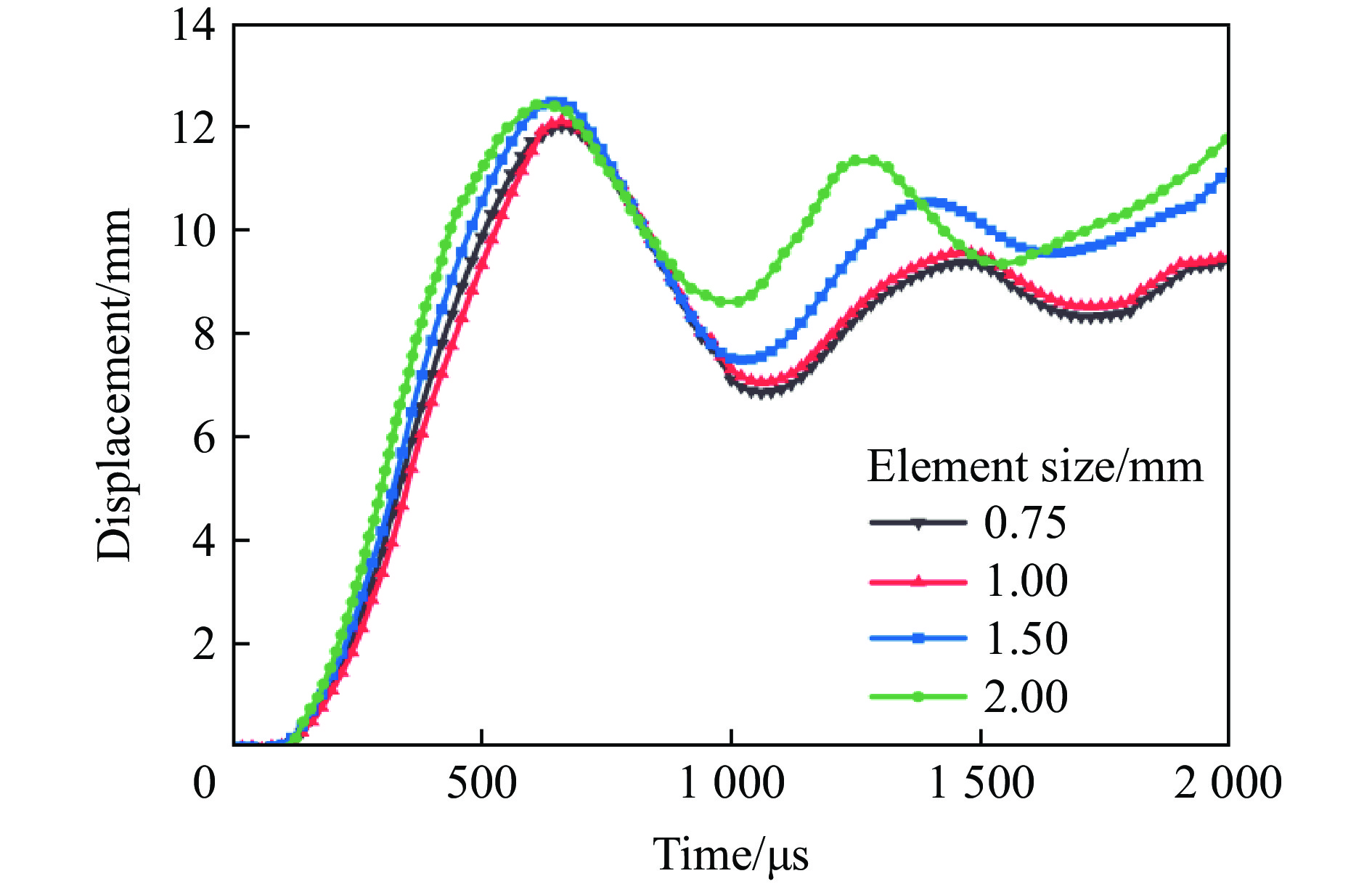
图2为夹芯板的1/4数值模型及其尺寸,夹芯板由前面板、后面板和芯层结构组成,1/4模型尺寸用长L、宽B和高H来表示,其中夹芯板的长和宽相等(L=B),高度H包括3层胞元高度L2、前后面板厚度Tf = Tb和黏附层厚度(在模拟中忽略)。1/4模型夹芯板的尺寸为LBH=150 mm×150 mm×32.4 mm,单层胞元高度L2为10 mm,前后面板厚度Tf =Tb均为1.2 mm,芯层厚度Tc为0.4 mm。在所有采用的模型中,夹芯板的几何形状保持不变。利用有限元软件LS-DYNA建立数值模型,壳单元用于面板和芯层,为了兼顾计算精度和时间成本,对数值模型的网格敏感性进行了分析。图3为在不同网格尺寸下夹芯板后面板中心点的位移-时间曲线,网格平均尺寸分别为2.00、1.50、1.00和0.75 mm。可以发现,当网格尺寸为1.00 mm时,进一步提升网格密度后,后面板中心位移曲线趋于稳定。因此,本文的所有模型均采用网格尺寸为1.00 mm。面板和芯层之间采用热熔胶粘接,其相互作用定义为*CONTACT _TIED_NODE_TO_SURFACE,并使用自动接触算法*CONTACT_AUTOMATIC_SINGLE_SURFACE避免夹层结构的自渗透。为了提高效率,采用对称边界条件(X-Z和Y-Z平面),建立1/4模型(LB=150 mm×150 mm)。此外,在板的周边设置完全固定的边界条件,1/4模型的爆炸有效作用面积为125 mm×125 mm。本文中采用的爆炸载荷施加方法为CONWEP空气爆炸模型[38],该模型已经成为现在空爆仿真的主要方法之一。输入信息包括等效TNT质量(Q)、爆炸类型(空气爆炸)和爆炸距离(stand-off distance, SOD)等,并通过关键词*LOAD_BLAST_SEGMENT_SET将爆炸载荷施加到上面板,采用的TNT装药为球形装药。具体的爆炸载荷下正弦曲边三维负泊松比夹芯板的设计方案如表2所示,A-1为对照组,Q-30和Q-40表示炸药质量分别为30、40 g的2组,S-80和S-120表示爆炸距离分别为80、120 mm的2组。
表 2 爆炸载荷下三维负泊松比夹芯板设计方案Table 2. Designs of 3D negative Poisson’s ratio sandwich panels subjected to blast loading编号 Tf/mm Tb/mm A/mm L2/mm 爆炸距离/mm Q/g 拉伸宽度L4/mm A-1 1.2 1.2 1 10 100 20 5 Q-30 1.2 1.2 1 10 100 30 5 Q-40 1.2 1.2 1 10 100 40 5 S-80 1.2 1.2 1 10 80 20 5 S-120 1.2 1.2 1 10 120 20 5 1.3 数值模型验证
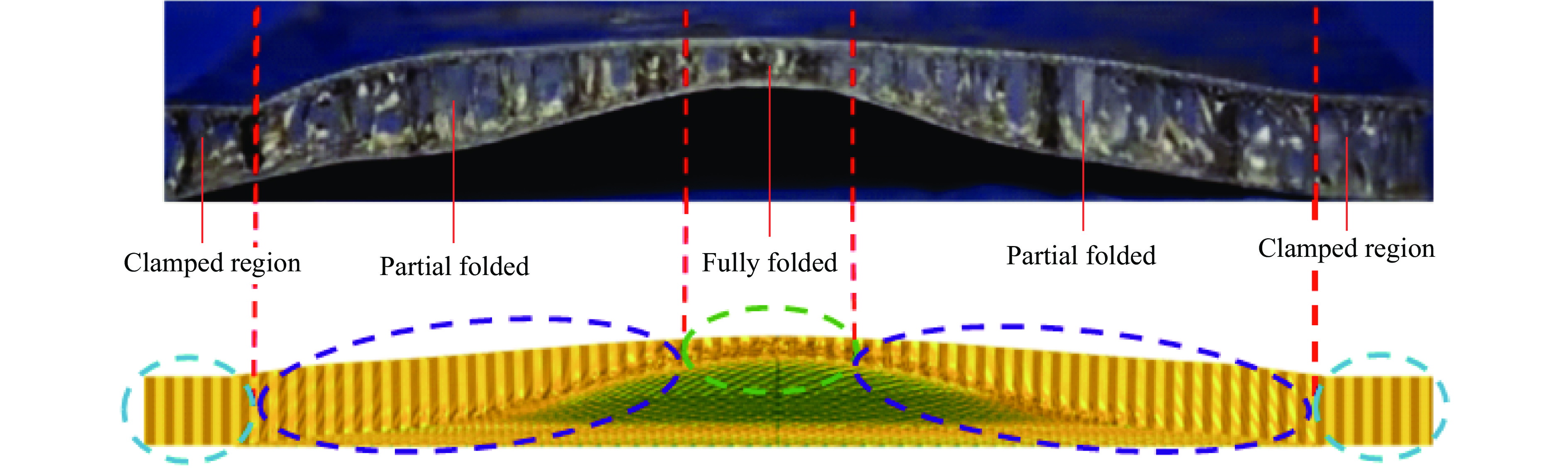
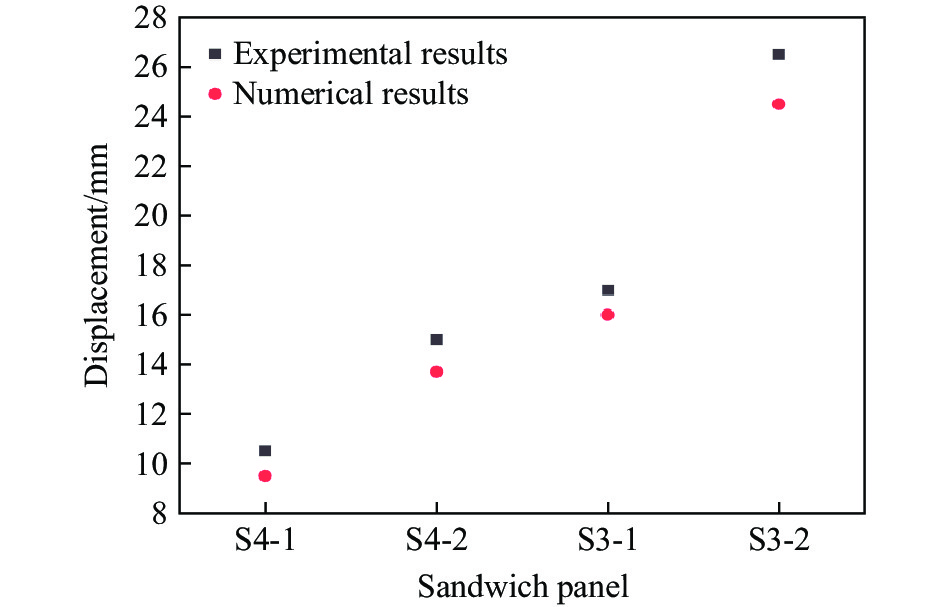
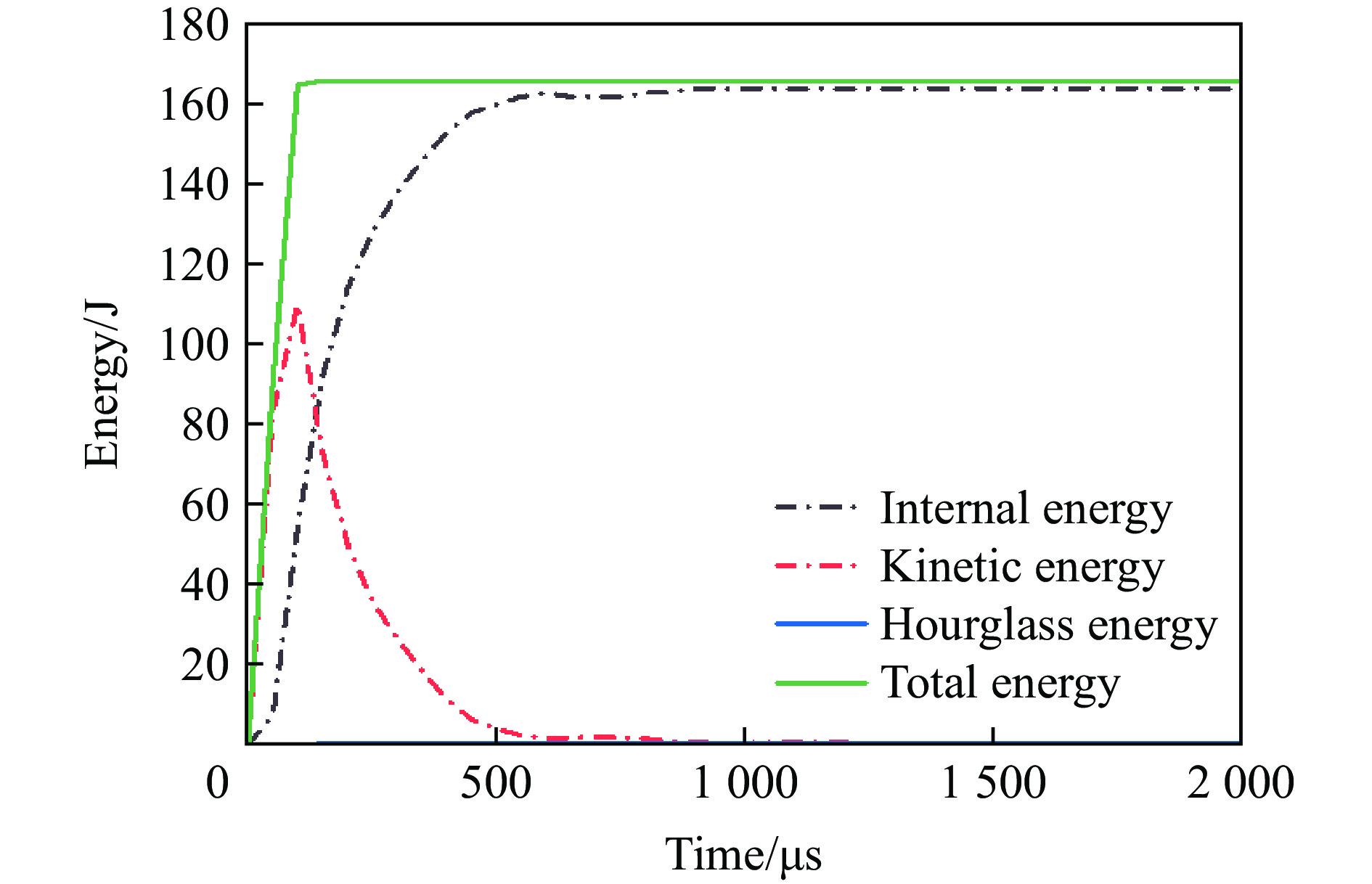
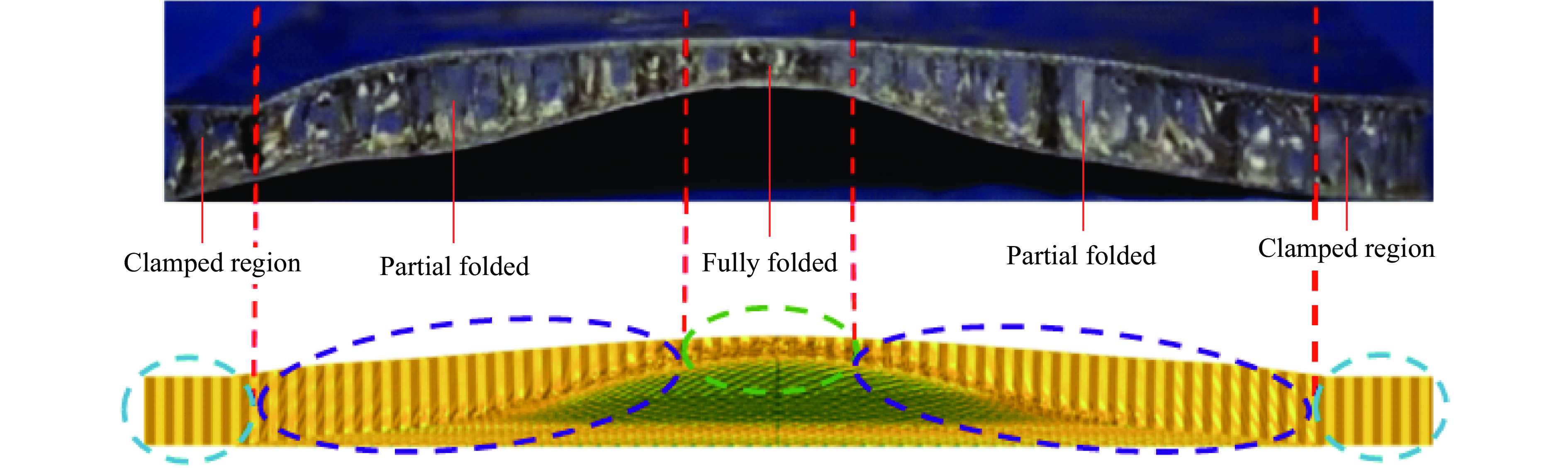
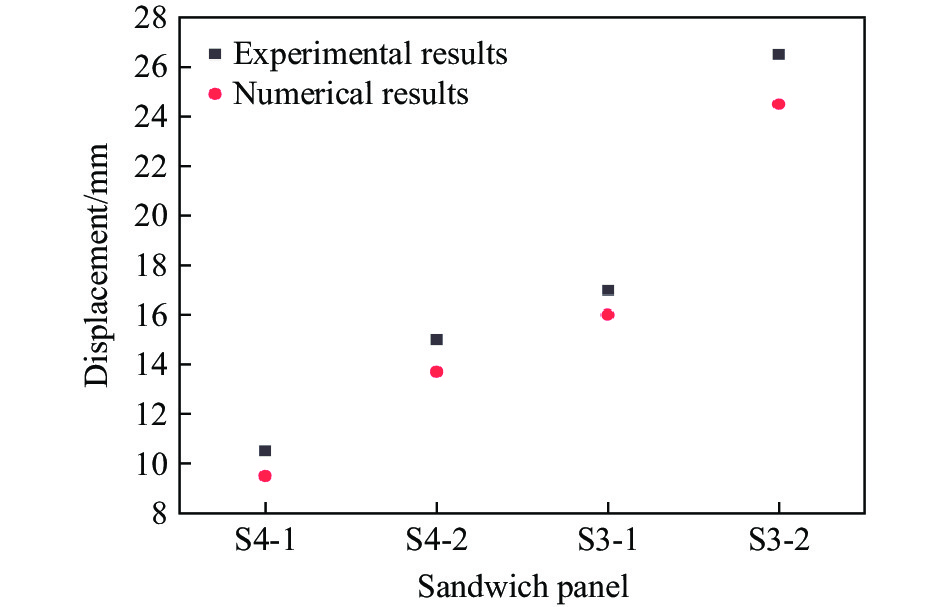
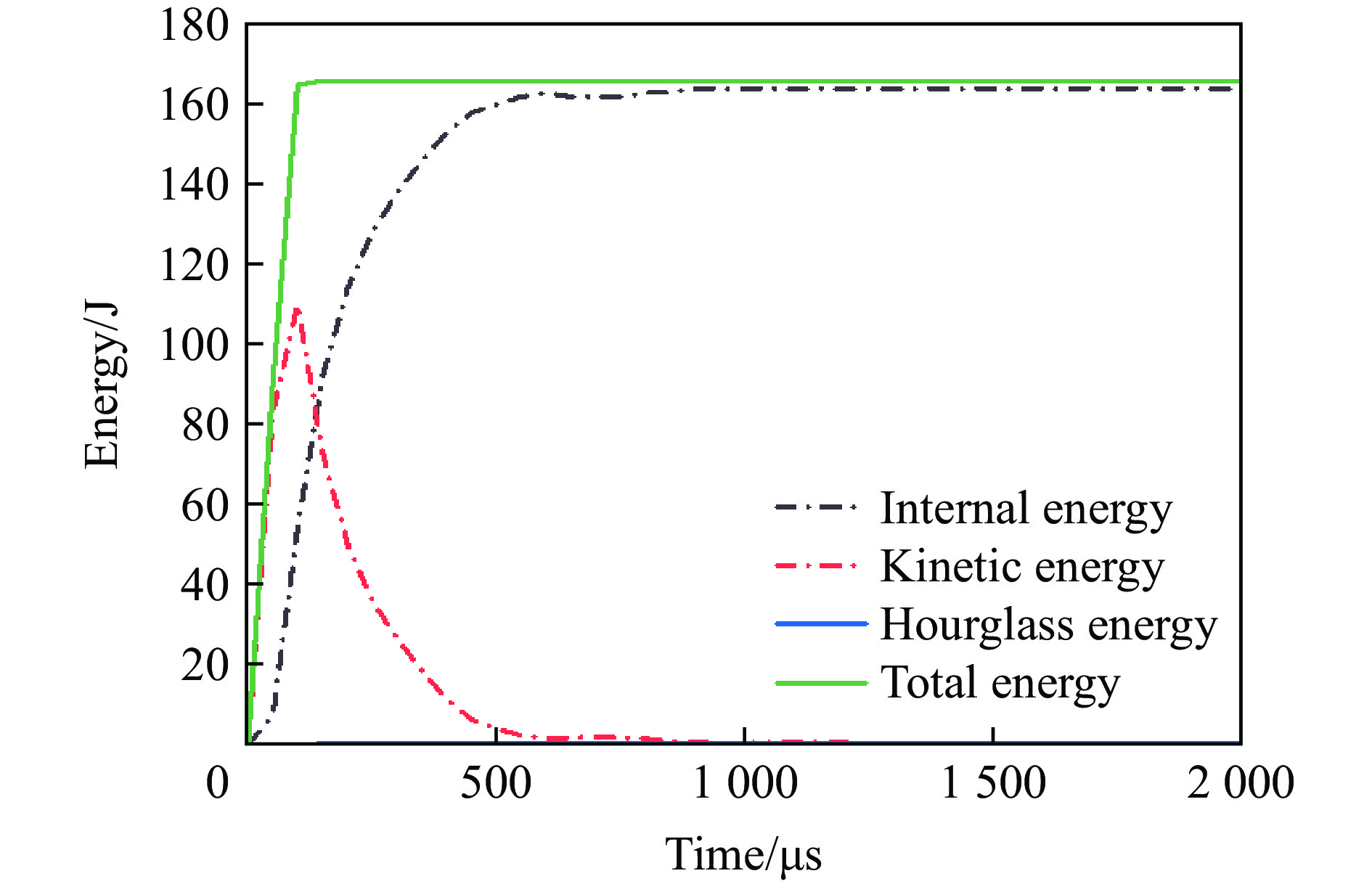
为验证本文中建立的数值模型的准确性,采用了一系列正六边形蜂窝夹芯板在爆炸载荷下的响应实验来验证数值方法的有效性[37,39],夹芯板的全模型尺寸为LBH=300 mm×300 mm×20 mm,芯层高度包括一层胞元高度L2和前后面板厚度Tf = Tb,正六边形蜂窝夹芯板和胞元结构几何参数如图4所示[37]。采用4组实验装置校准有限元模型,4组夹芯板的几何参数和爆炸参数见表3。正六边形蜂窝夹芯板(S4-1)在爆炸载荷下变形模式数值模拟结果和实验结果的对比如图5所示。可以看出,数值预测结果与实验结果在蜂窝夹层结构的主要变形特征区域基本一致,包括完全折叠区域、部分折叠区域和固定区域[39]。此外,通过比较实验和数值预测的背板中心位移(图6),发现S4-1、S4-2和S3-1之间存在微小的差异,而S3-2的差异较大(8%),这可以归因于边界条件和材料参数的简化。总体而言,通过与实验数据的比较,验证了数值模型的准确性和可靠性。除此之外,还对建立的三维负泊松比夹芯板的能量平衡进行了分析。图7展示了在爆炸载荷下夹芯板中各能量的时间曲线,结果显示结构中的动能、内能和沙漏能的总和等于总能量。沙漏能仅占总能量的0.4%,远低于通常用于评估数值建模准确性的5%阈值[40]。因此,整个爆炸响应过程中系统能量保持良好的平衡,这验证了建立的数值模型的准确性。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 动态响应过程
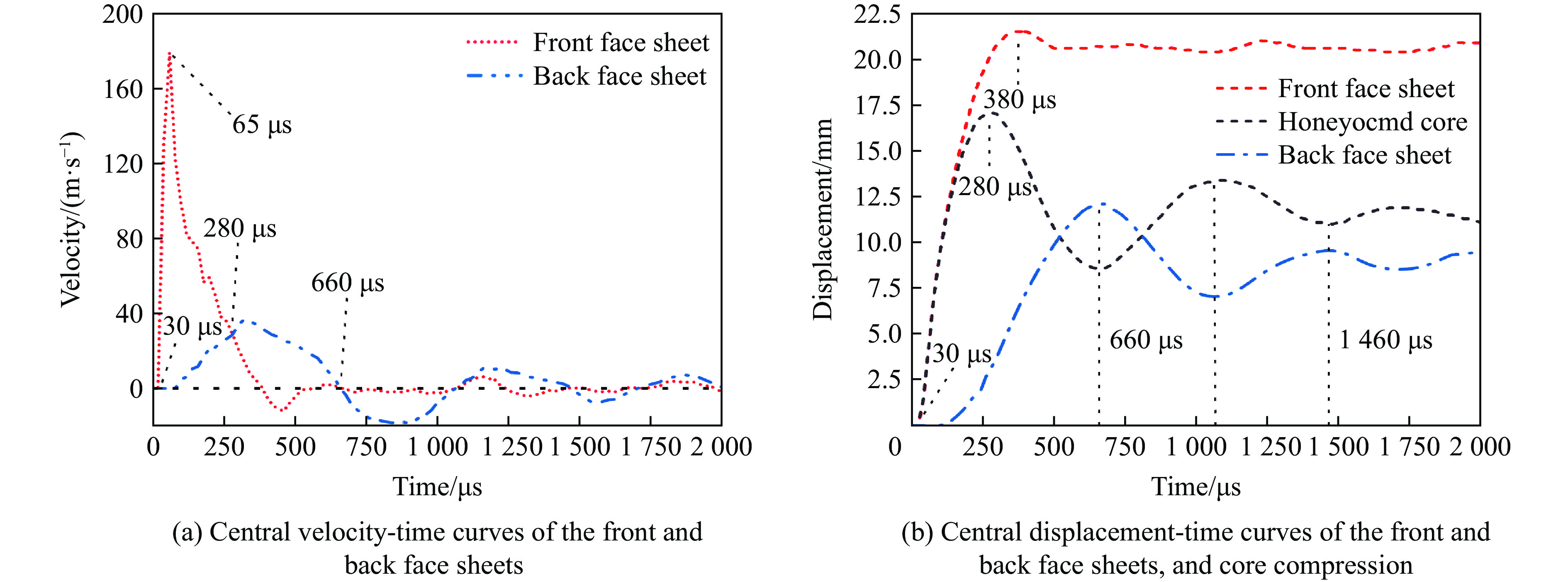
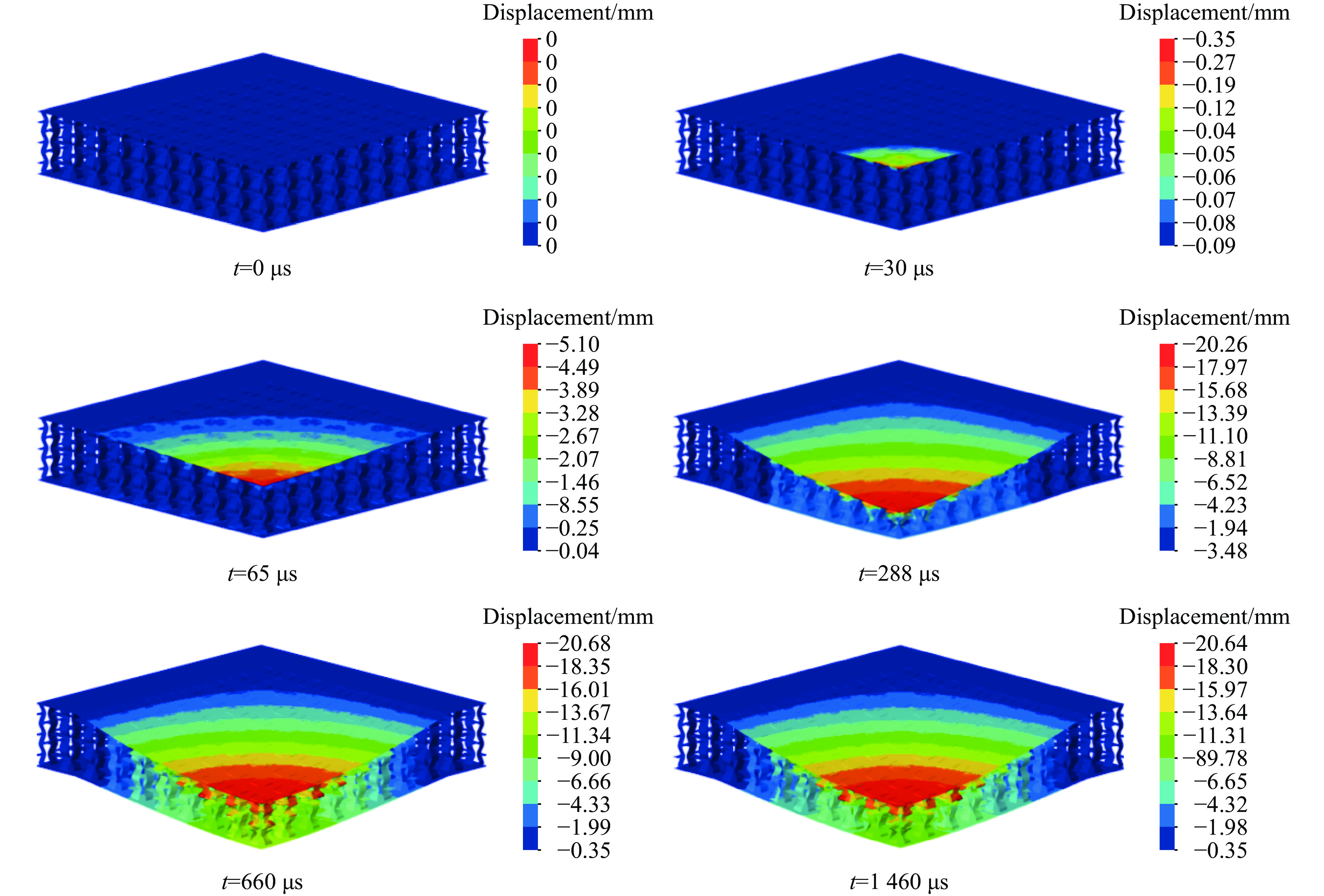
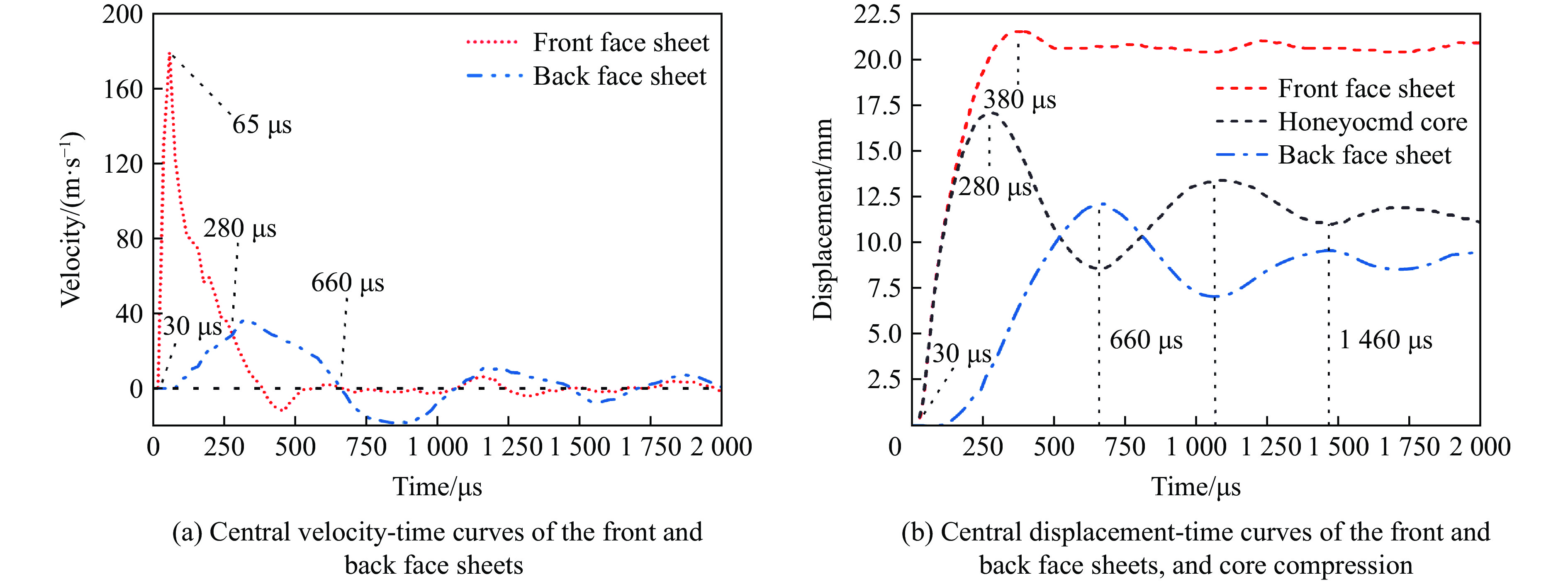
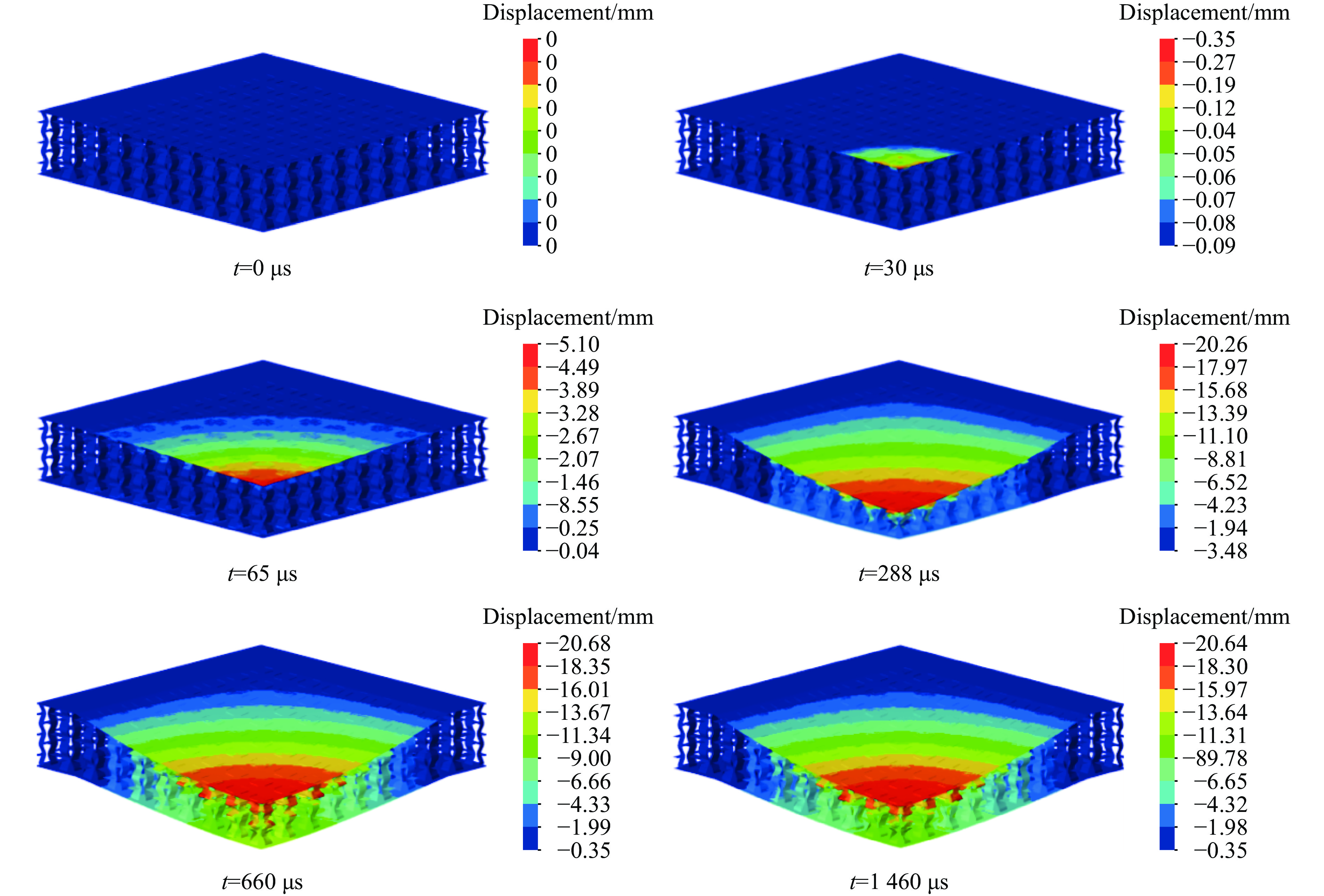
图8和图9分别给出了夹芯板前后面板中心点的速度和位移时间曲线以及夹芯板在各典型时刻的Z向位移云图。从图可发现,在t=30 μs时,前面板开始产生初始速度,此时爆炸冲击波与前面板接触,当t=65 μs时,前面板中心速度达到峰值,随后逐渐减小;在t=100 μs时,后面板开始产生初始速度;在t=315 μs时速度达到峰值,随后,后面板的速度逐渐降低。在t=280 μs时,前后面板的速度几乎相等,此时芯层压缩值达到最大。随后,由于弹性反弹,芯层压缩量开始下降,直到最终稳定在一个值(11.2 mm)。当后面板的速度降低到0(t=660 μs)时,后面板的中心位移达到最大值,此时芯层压缩量因弹性变形的反弹而达到最小值,此后芯层压缩量先增大后减小,最终在t=1 460 μs后进入小范围振动阶段,直到夹芯板静止时达到最终挠度。
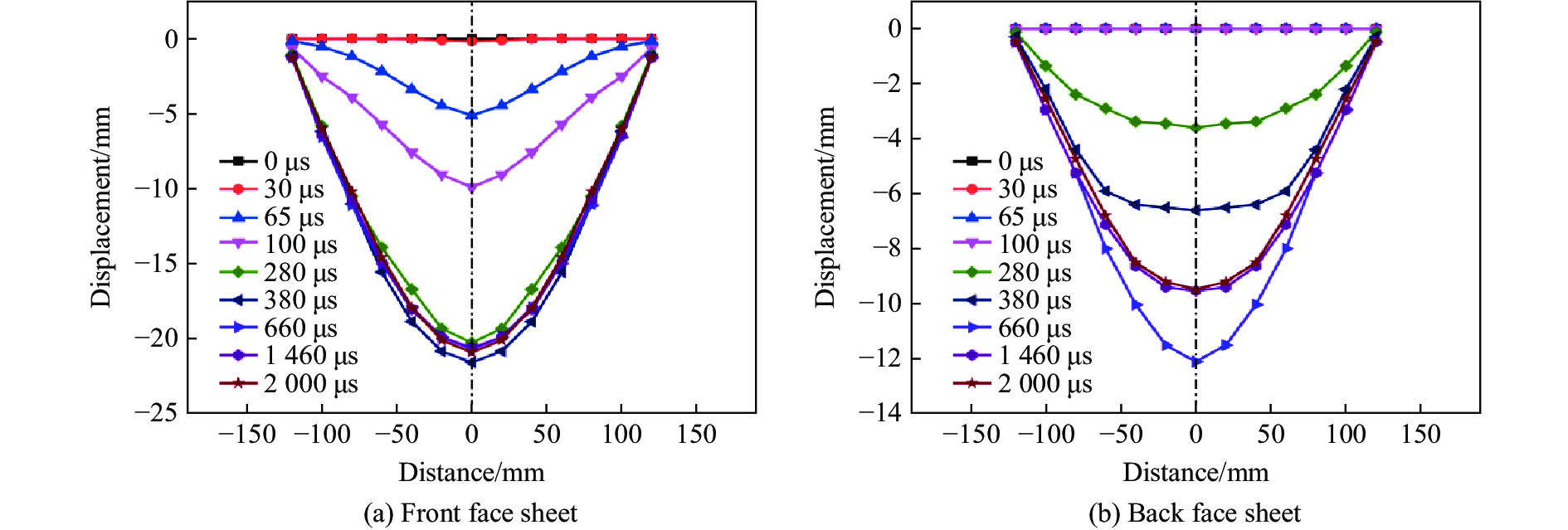
根据速度、位移和芯层压缩量时间曲线,夹芯板的响应过程可大致分为3个阶段:第1阶段(30~280 μs),前面板中心速度大于后面板中心速度,芯层被压缩;第2阶段(280~1460 μs),前后板均反弹,夹芯板整体变形;第3阶段(1 460~2 000 μs),夹芯板发生轻微振荡,通过塑性弯曲和拉伸逐渐静止,挠度逐渐趋于最终状态。图10为不同时刻前后面板距中心点不同距离处的位移分布。在不同的时间点上,由于载荷和边界条件的对称性,面板中心的偏转具有良好对称性,最大偏转都在面板中心位置。还可以发现,前后面板中心位移达到最大值的时间不同,前面板中心位移达到最大值的时间为380 μs,后面板中心位移达到最大值的时间为660 μs,Wang等[40]也发现了类似现象。
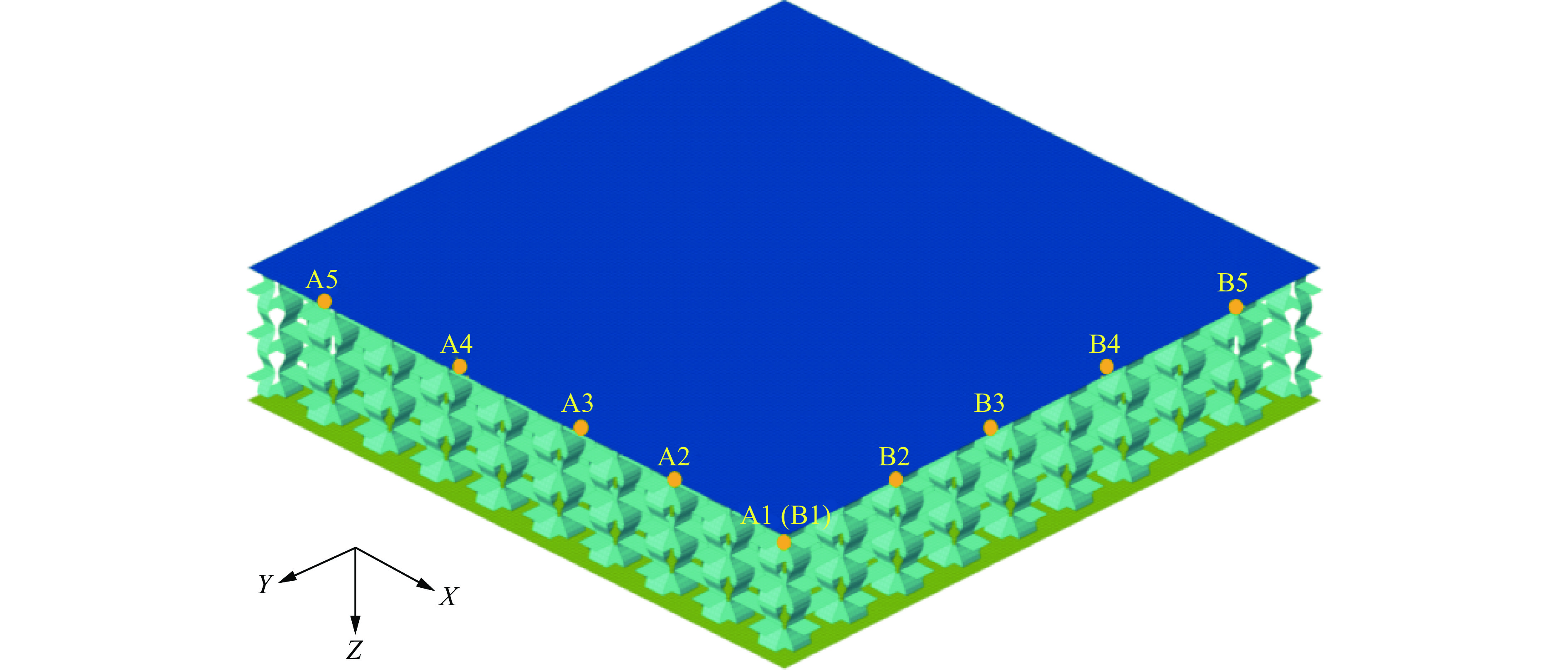
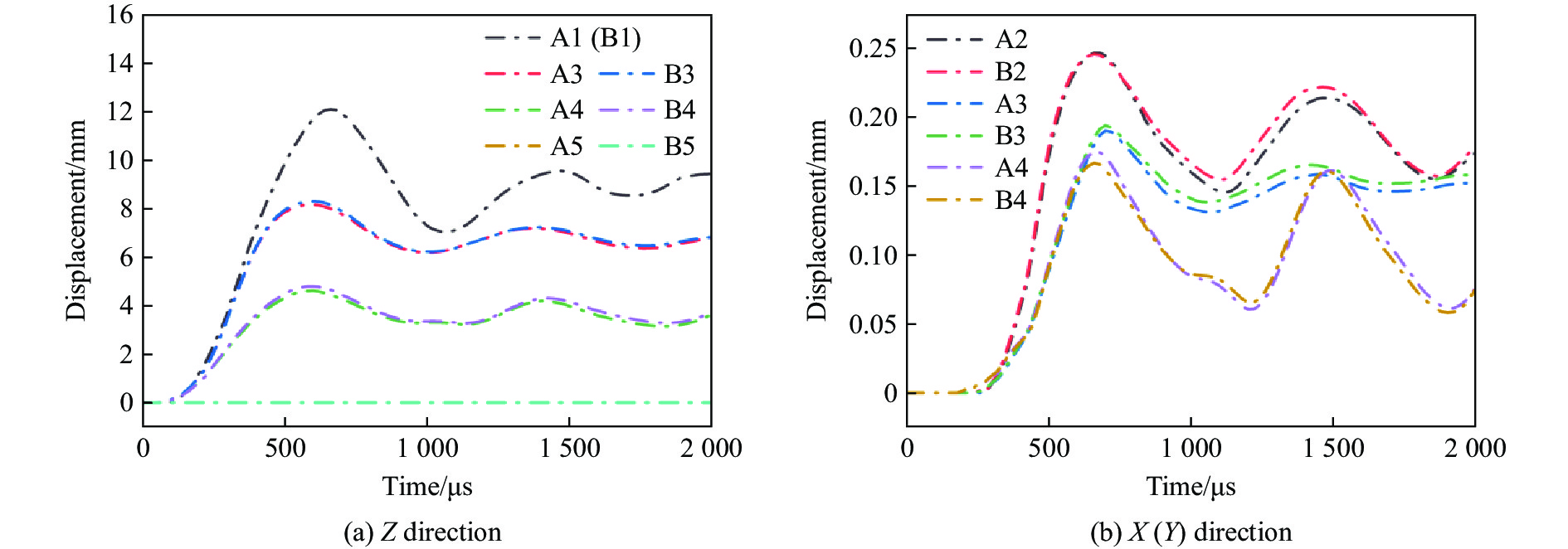
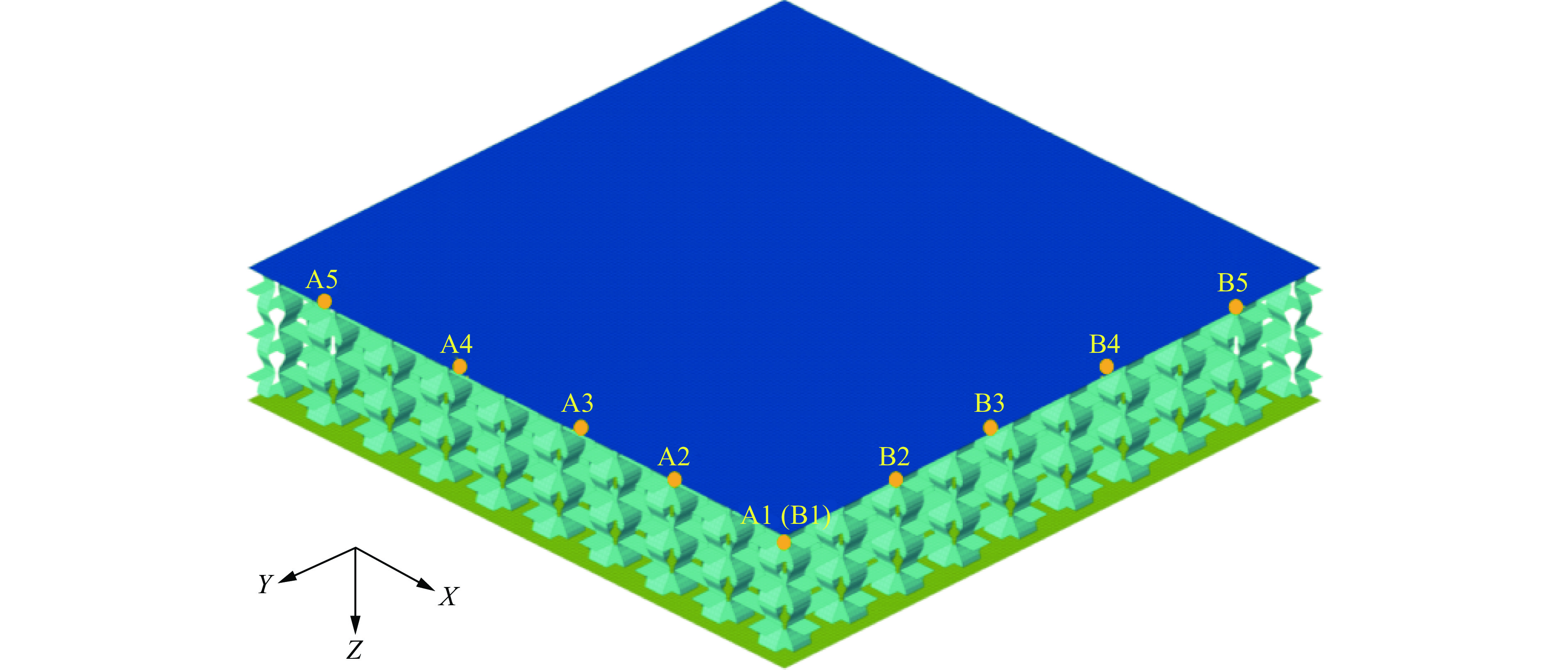
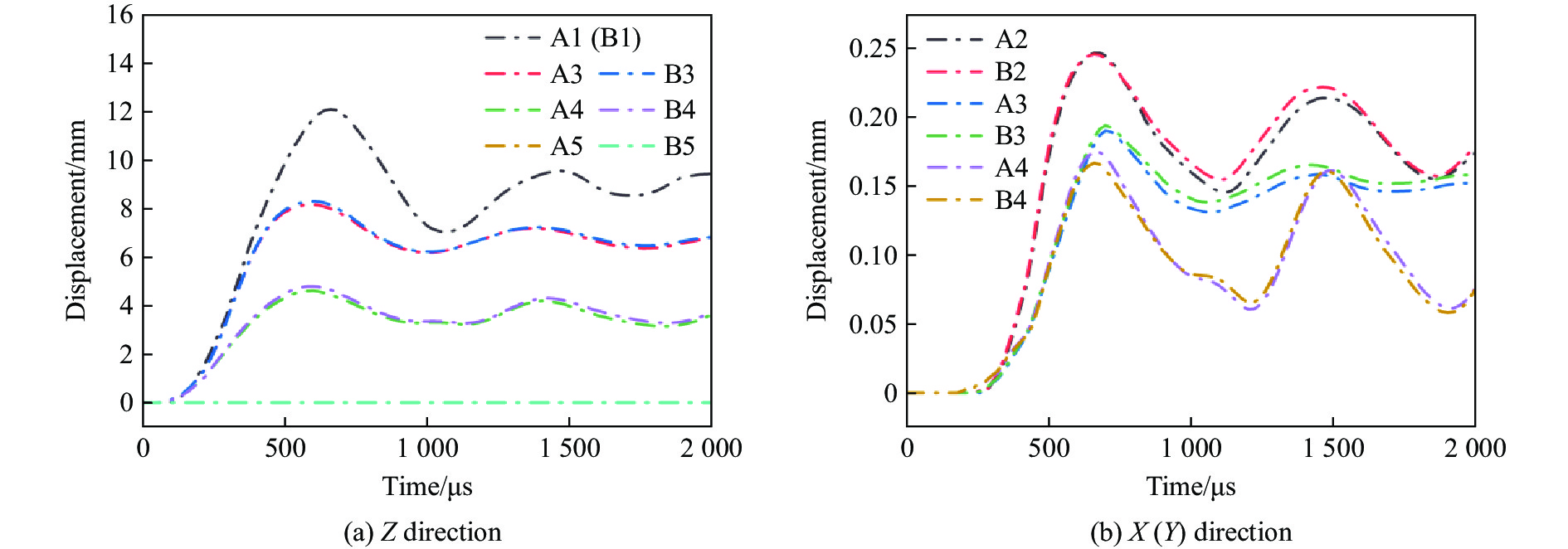
为了更好地了解背板的变形机理,在X-Z和Y-Z对称平面上的背板上选取了2组相同确切位置的节点(相邻2点间隔从A1至A5分别为30、30、30和40 mm),如图11所示。X(Y)方向拉伸状态可以通过沿X(Y)轴的位移来表示,而Z方向弯曲状态可以通过计算沿Z轴的位移来识别。后板上2组点的Z方向和X(Y)方向位移如图12所示。如图12(a)所示,B组点的Z向位移与A组对应点的位移几乎一致,这意味着背板在Y方向上的弯曲程度与X方向几乎相同。如图12(b)所示,A组(A2、A3、A4)沿Y轴和B组(B2、B3、B4)沿X轴的位移曲线趋势完全一致且高度重合,两者峰值相对误差均在8%以下,因而在X(Y)方向拉伸状态也可看为几乎相同,这种现象是因为正弦曲边三维负泊松比芯层在横向(X)和纵向(Y)方向均表现出负泊松比的特性。因此,在X方向和Y方向的芯层都得到充分变形,吸收更多的能量,从而削弱了前板通过芯层传递到背板的力(Z方向)。因此,施加在背板上沿X方向(XZ平面)的力(Z方向)与施加在背板上沿Y方向(YZ平面)的力(Z方向)大致相等,这可能导致沿Y方向(点B)的背板变形与沿X方向(点A)的背板变形大致相同。基于以上讨论,可以发现正弦曲边三维负泊松比芯层相比于内凹蜂窝芯层[27],在横(X)、纵(Y)方向都具有负泊松比效应,抗爆性能一致,克服了内凹蜂窝夹芯板背板沿纵向(Y)方向的变形大于沿横向(X)方向的缺点。
2.2 不同炸药质量的影响
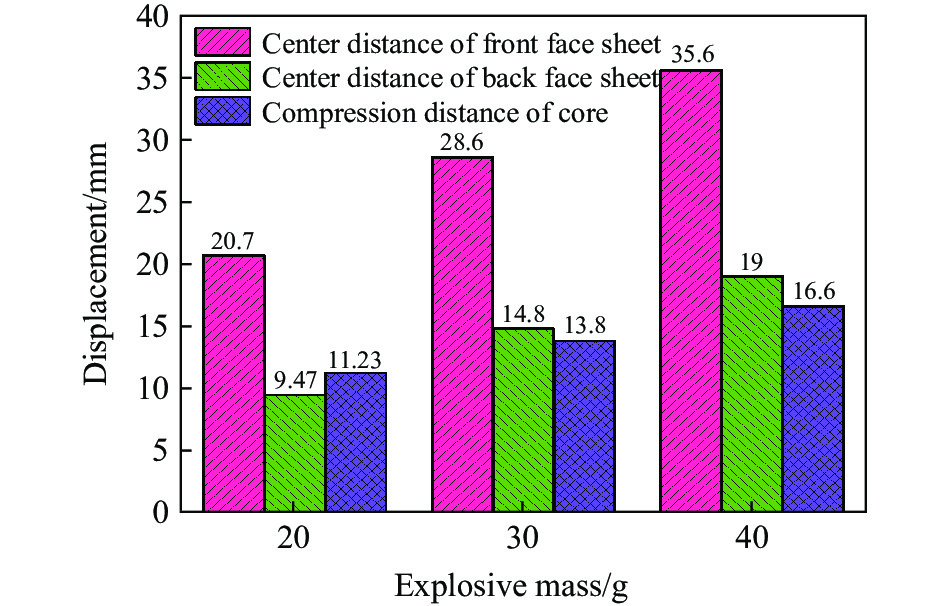
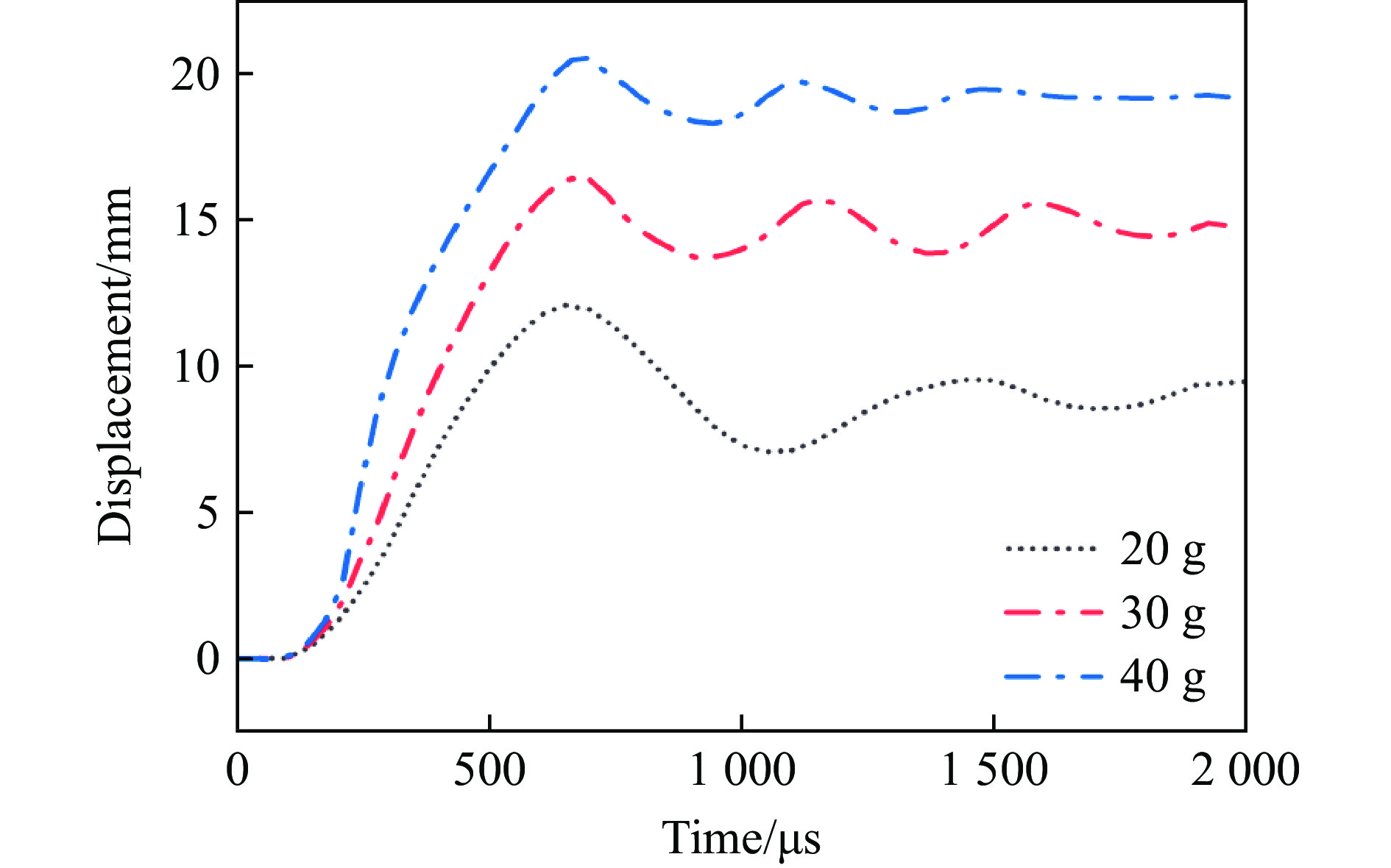
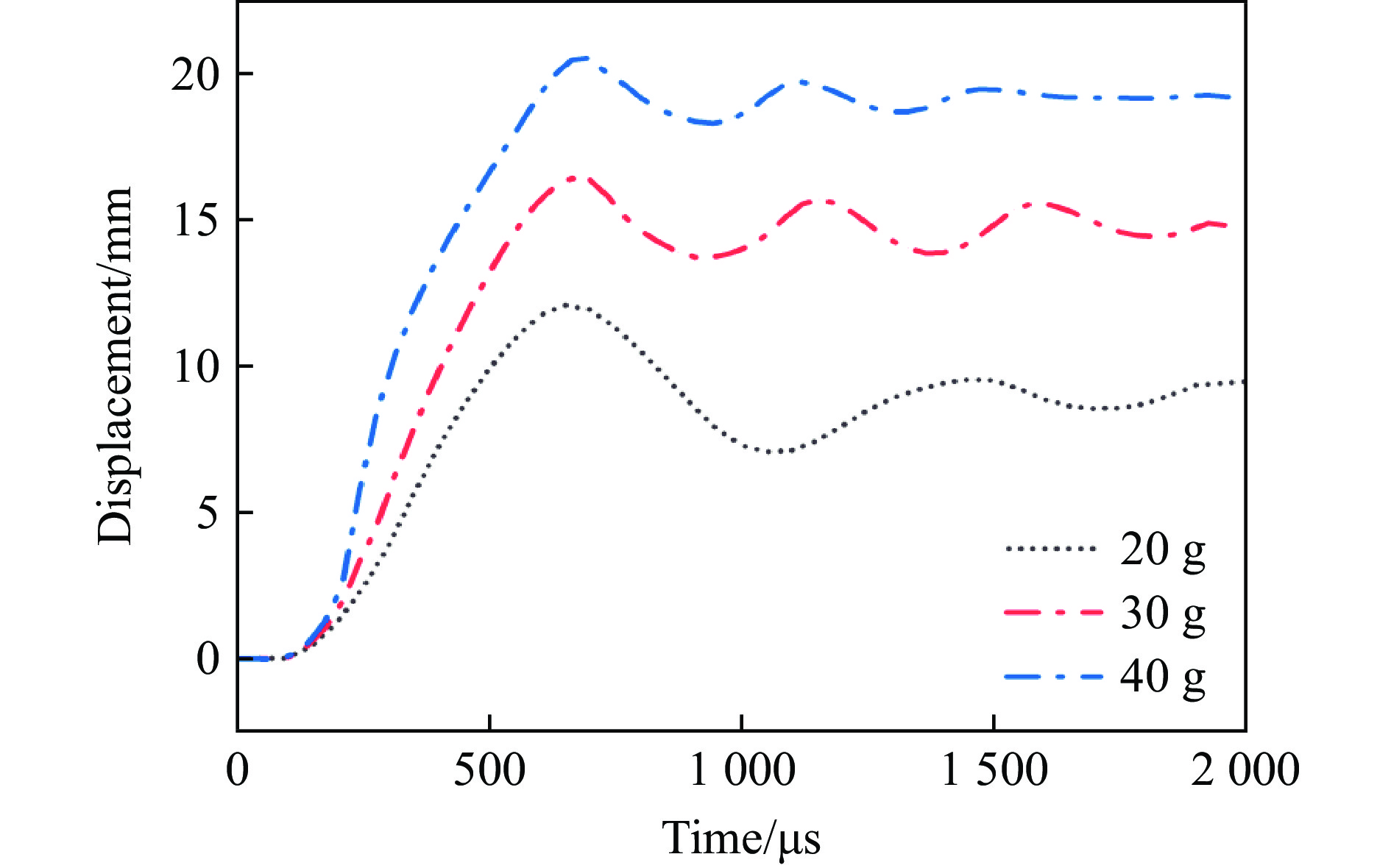
图13给出了不同炸药质量下夹芯板的前后面板中心位移和中心芯层压缩量的分布图,可以清楚地看到,后面板的中心位移峰值随炸药质量的增加而增大,当炸药质量为20、30和40 g时,后面板中心位移分别为9.47、14.8和19.0 mm。相对于40 g TNT的后面板中心位移,20 g和30 g TNT爆炸下的后面板中心位移减少了50.2%、22.1%。图14给出了不同炸药下后面板的中心位移时间曲线,炸药质量为20、30和40 g时,后面板中心位移达到峰值后反弹的距离分别约为3.78、2.12和1.83 mm,说明随着炸药质量的增加,后面板中心位移达到峰值后反弹的强度逐渐减弱。
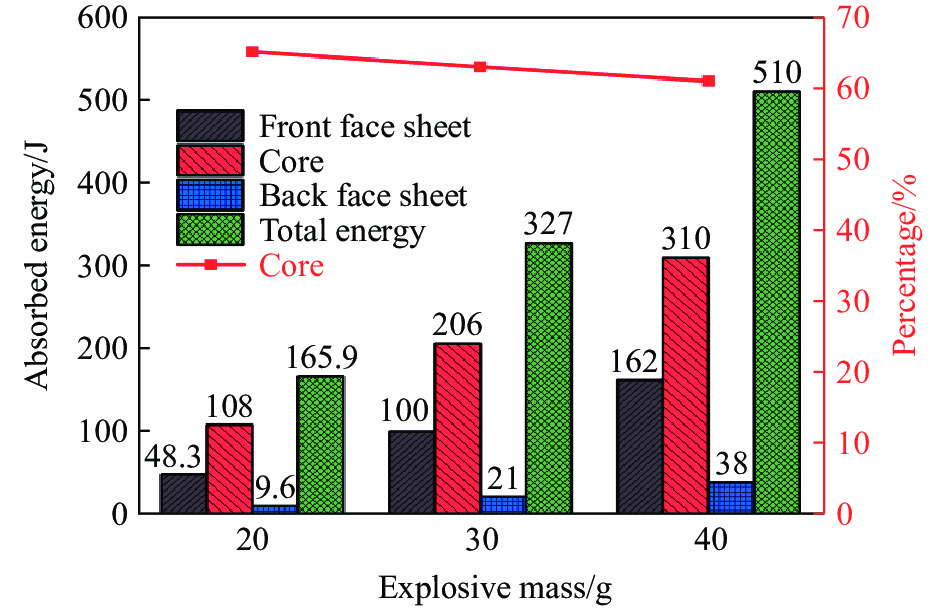
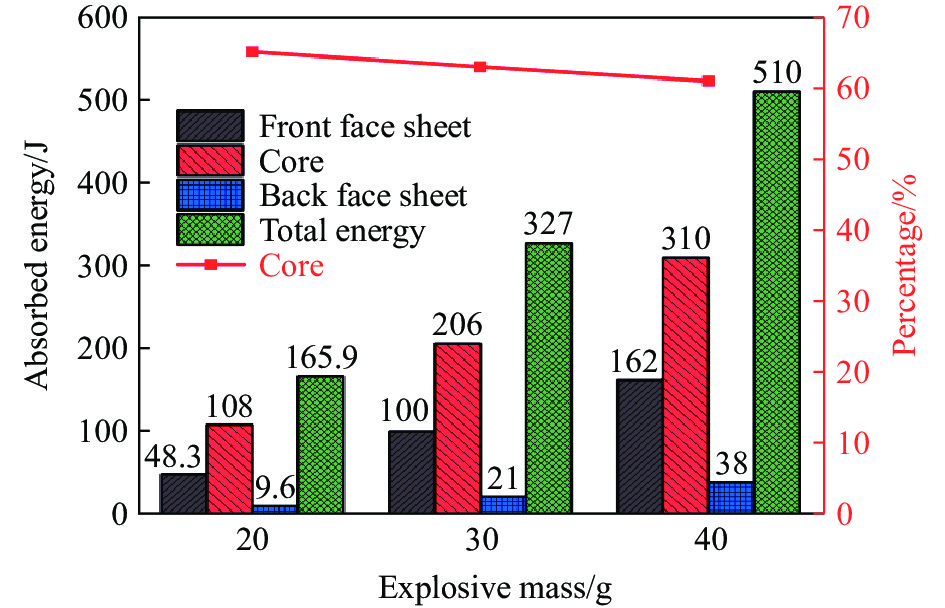
图15比较了不同炸药质量下夹芯板不同部件的能量吸收和芯层吸能占比。随着炸药质量的增加,夹芯板各部件吸收的能量增加,这是因为冲击波压力升高,导致各部件发生更大的塑性变形,从而增加了能量吸收。图中显示,芯层吸收了主要的爆炸冲击能量,占总吸收能量的60%以上,其次是前面板,后面板吸收能量最少。因此,提高芯层的能量吸收可以有效提升夹芯板的抗冲击性能。随着炸药质量的增加,芯层吸收的能量占比下降。这是因为在高冲击波压力下,夹芯板整体发生塑性变形,前后面板吸收的塑性变形能量逐渐增加,因此芯层吸收的能量占比逐渐降低。
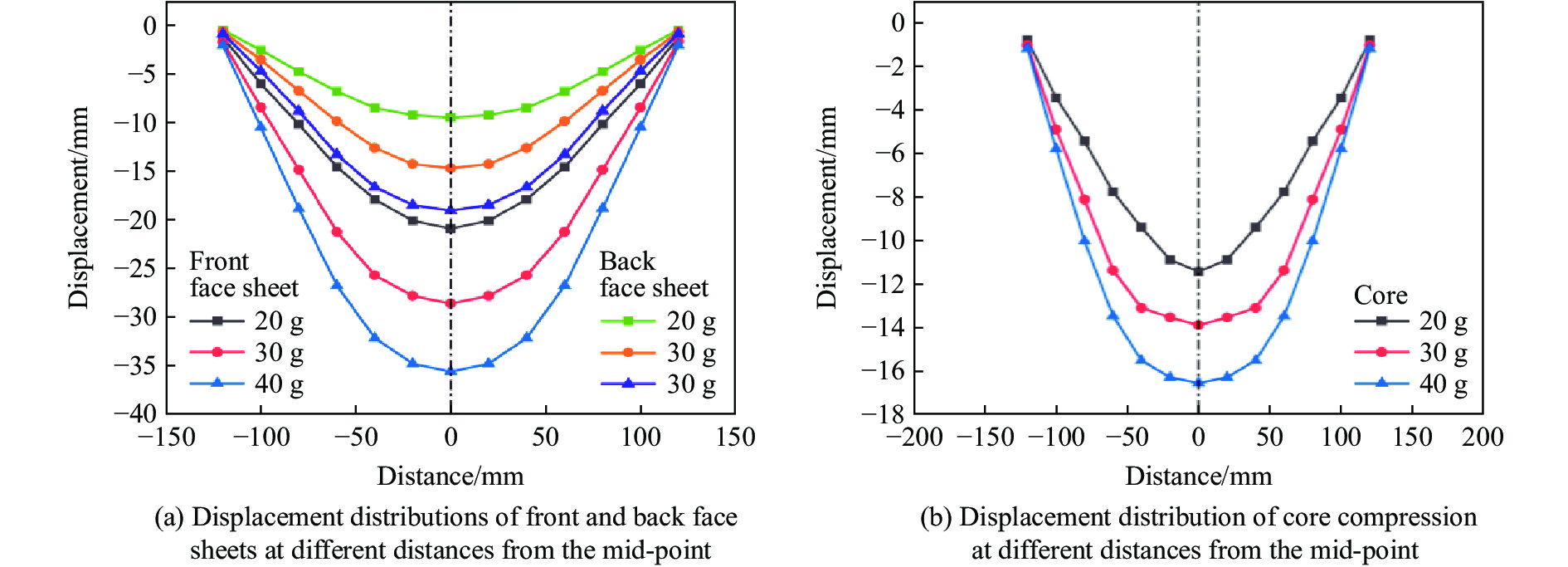
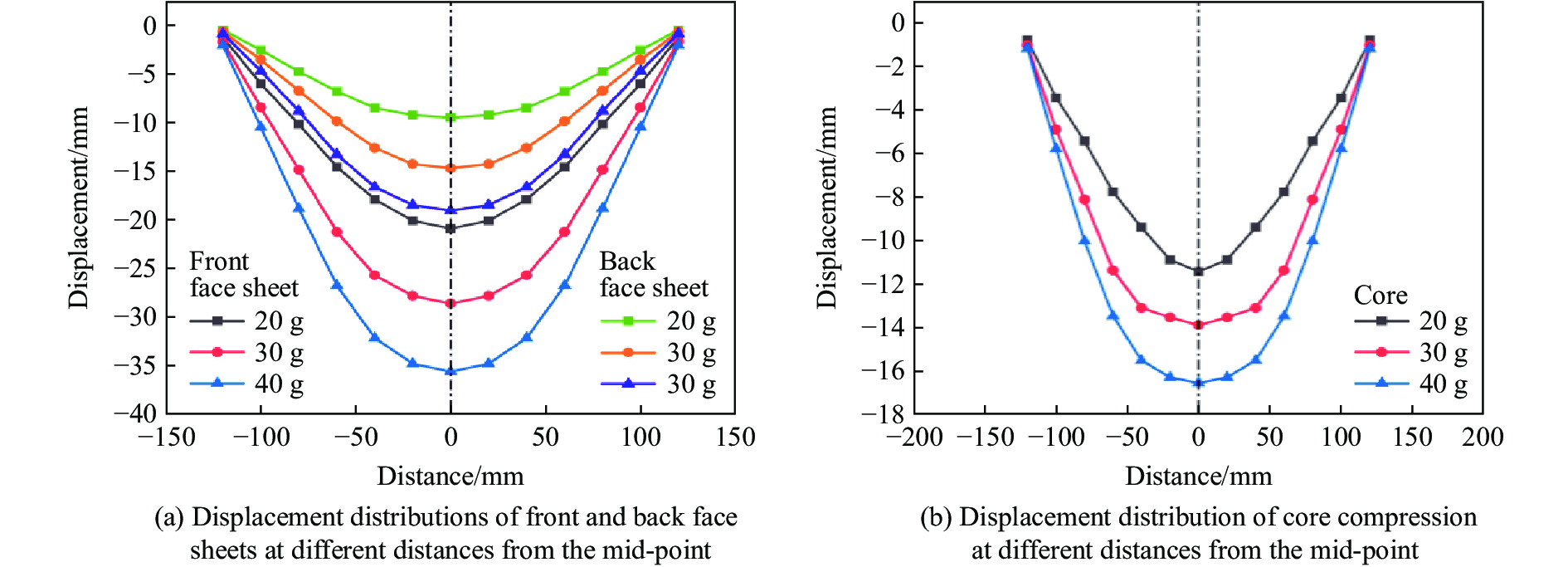
图16中绘制了不同炸药质量下前后面板距中心点不同位置处的位移分布曲线和芯层压缩位移分布曲线。可以看出,位移曲线在面板中心两侧具有良好的对称性,主要的变形区域集中在面板的中心区域周围,前后面板的最大变形均发生在中心处。随着炸药质量的逐渐增加,芯层变形面积逐渐增大,芯层压缩量逐渐增加。
2.3 不同爆距的影响
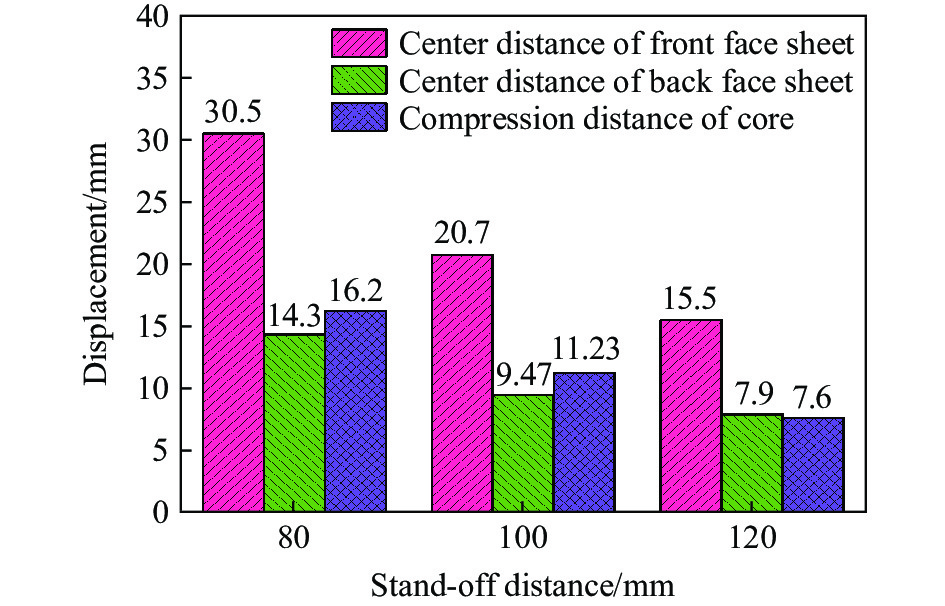
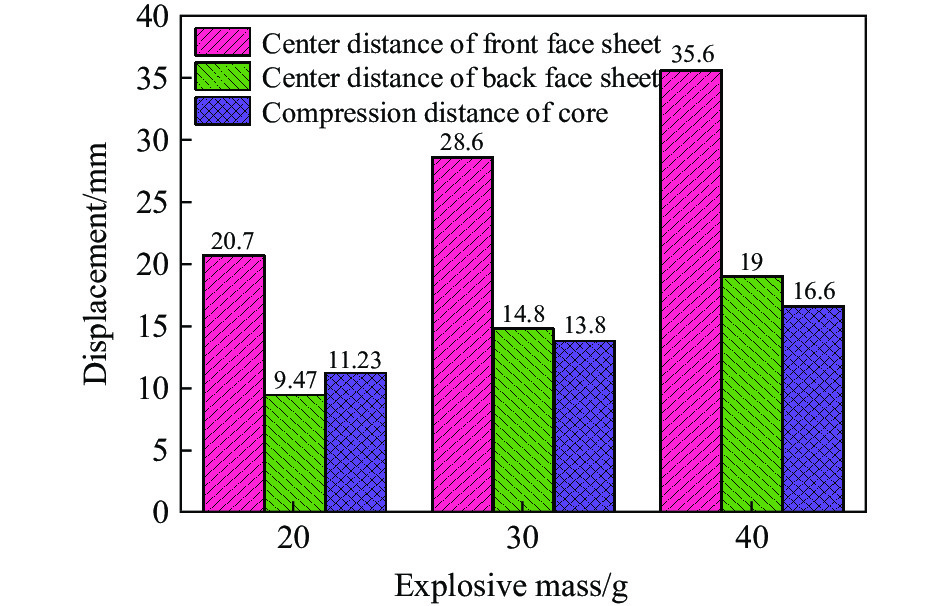
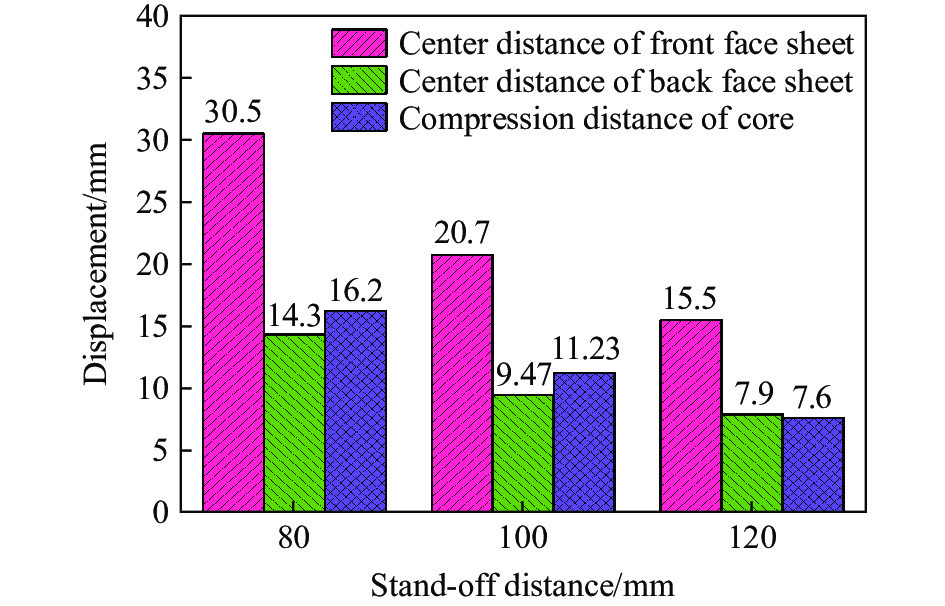
图17中给出了不同爆距下夹芯板的前后面板中心位移和中心芯层压缩量分布情况。在爆距分别为80、100和120 mm时,夹芯板前面板的中心位移分别为30.5、20.7和15.5 mm,后面板的中心位移分别为14.3、9.5和7.9 mm,芯层的压缩量分别为16.2、11.2和7.6 mm。随着爆距的增大,夹芯板前后面板的中心位移和芯层的压缩量均减小。当爆距从80 mm增大到100 mm和从100 mm增大到120 mm,前面板中心位移分别减小9.8和5.2 mm,后面板中心位移分别减少4.8和1.6 mm。然而,尽管爆距增大的幅度相同,但前后面板中心位移和芯层压缩量的变化幅度并不一致。爆距从80 mm增大到100 mm时夹芯板变形的减小量大于爆距从100 mm增大到120 mm情况下的,这主要是因为随着爆距的增大,爆炸载荷引起的冲击波压力呈指数衰减。因此,在较大的爆距下,爆炸冲击波的衰减幅度更大,从而导致作用在夹芯板上的压力脉冲减少[40]。
图18显示了夹芯板在不同爆炸距离下不同部件的能量吸收情况和芯层能量吸收的比例。随着爆距的增加,各部件的能量吸收值呈下降趋势。爆炸冲击能量主要由芯层吸收,在总能量吸收中占比超过60%,其次是前面板,后面板吸收能量最少。此外,随着爆距的增大,前面板和后面板的能量吸收比例下降,而芯层的能量吸收比例上升。
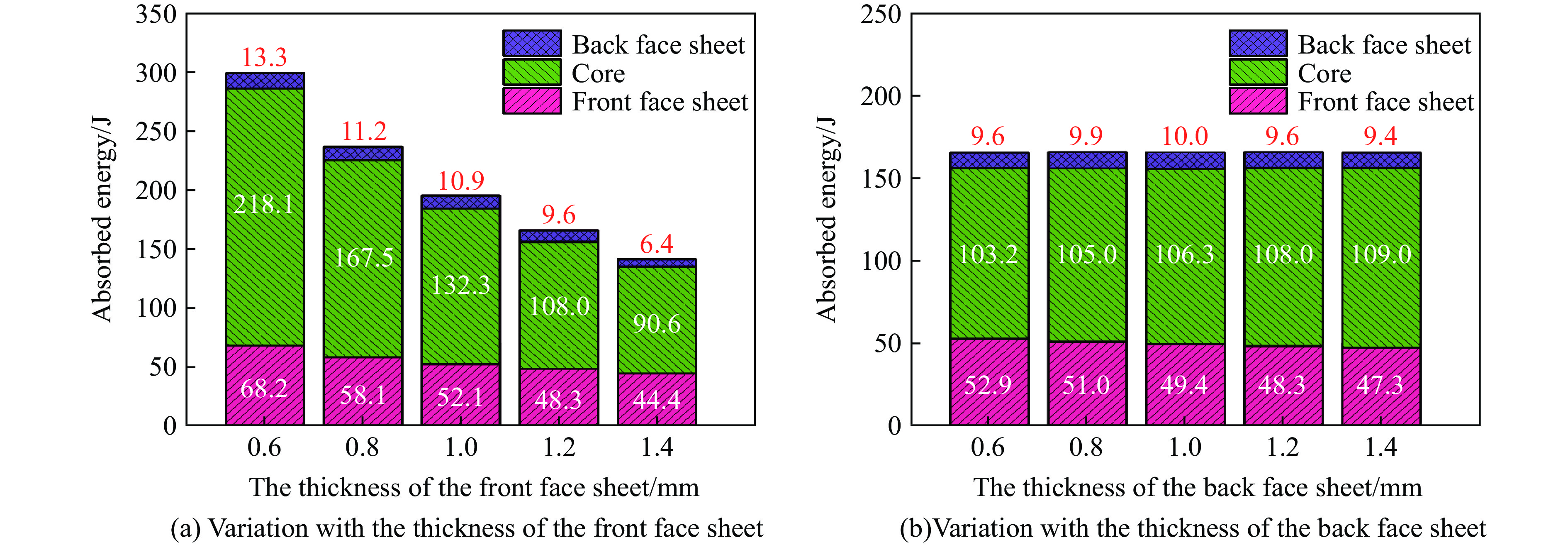
2.4 不同前后面板厚度的影响
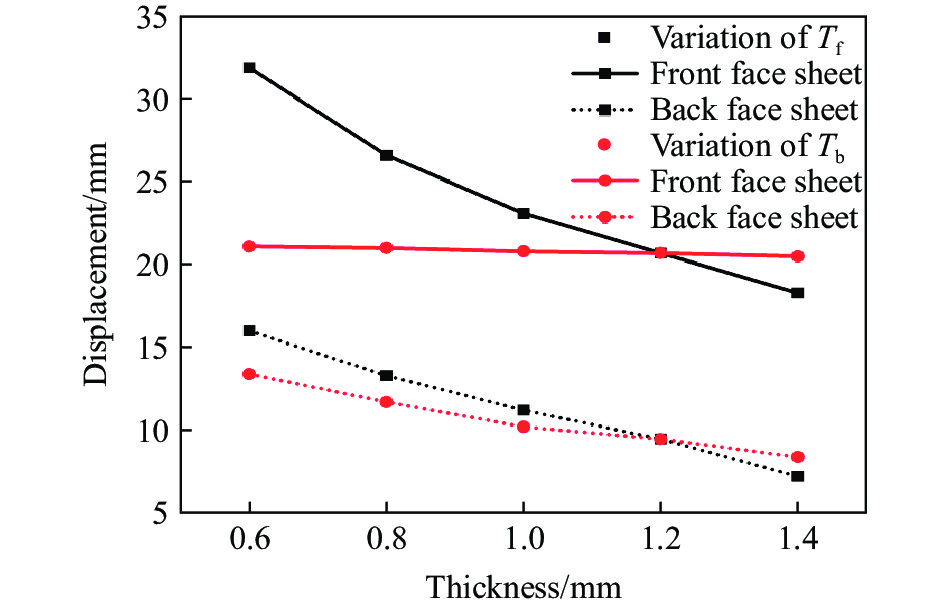
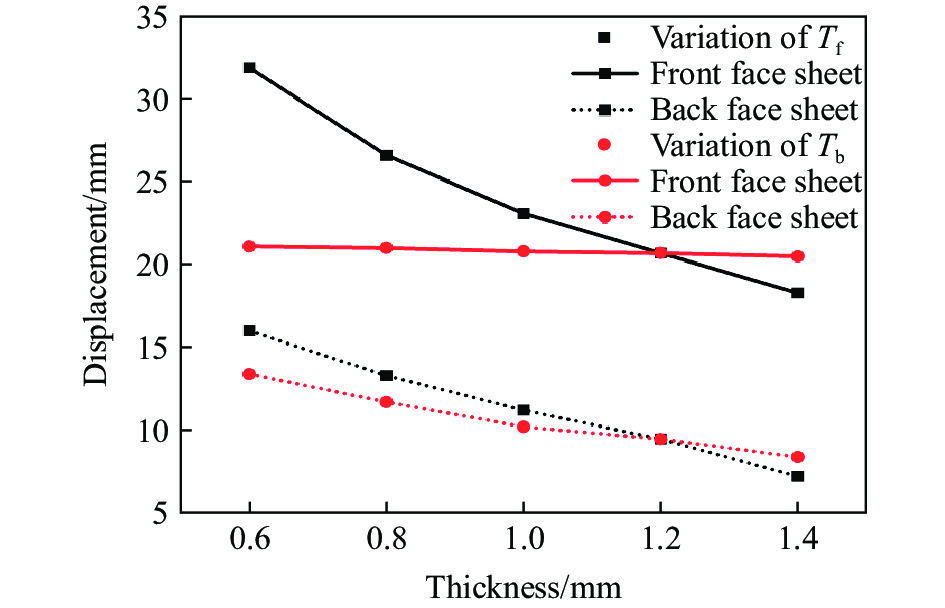
本节中除已研究的面板厚度参数变化外,其余参数均与表2中A-1的参数一致。为了研究面板厚度变化对前后面板中心位移的影响,使前后面板厚度范围均为0.6~1.4 mm,步长为0.2 mm,图19显示了改变前后板厚度对前后板中心位移影响。由图可知,前后面板中心位移都随着前面板厚度的增大而减小,这是因为前面板被设计成直接分散所受到的爆炸冲击波,因此前面板的刚度增加,使其能够抵抗更多爆炸冲击的能量。在相同的TNT质量和爆距下,当夹芯板的前面板厚度从0.6 mm增大到1.4 mm,后面板的中心位移降低55.0%。另一方面,改变后面板厚度对前面板中心位移的影响较小,后面板中心位移随着后面板厚度的增加而减小,1.4 mm相对于0.6 mm的后面板中心位移降低37.5%。通过观察前后面板中心位移曲线的差值,可以发现通过增加后板厚度,可以更有效地利用芯层来耗散更多的能量,因为后板的刚度增加为芯层的压缩提供了支撑条件。值得注意的是,尽管增大前后面板厚度都可以提高夹芯板的抗爆性能,但增大前面板厚度会使背板中心点的最大位移更小,表明前面板的影响更显著。
图20为不同前后面板厚度下的各部件能量吸收图,由图可知,增大前面板厚度对总能量耗散和芯层能量耗散有负面影响,随着前面板厚度的增大,能量耗散逐渐减小,当前面板厚度由0.6 mm增大到1.4 mm时,总能量耗散减少了52.8%,芯层能量耗散减少58.5%。因此,前面板较薄的夹芯板可以提高结构的吸能能力。还可发现,后面板厚度变化对夹层结构总能量耗散影响不大,因为后面板相对于其他部件(前面板和芯层)参与结构能量耗散的比例较小,大部分能量是由芯层耗散的,增大后面板厚度可以提高芯层的能量耗散占比,但并不能增加夹层结构耗散的总能量。
3. 芯层几何参数的影响
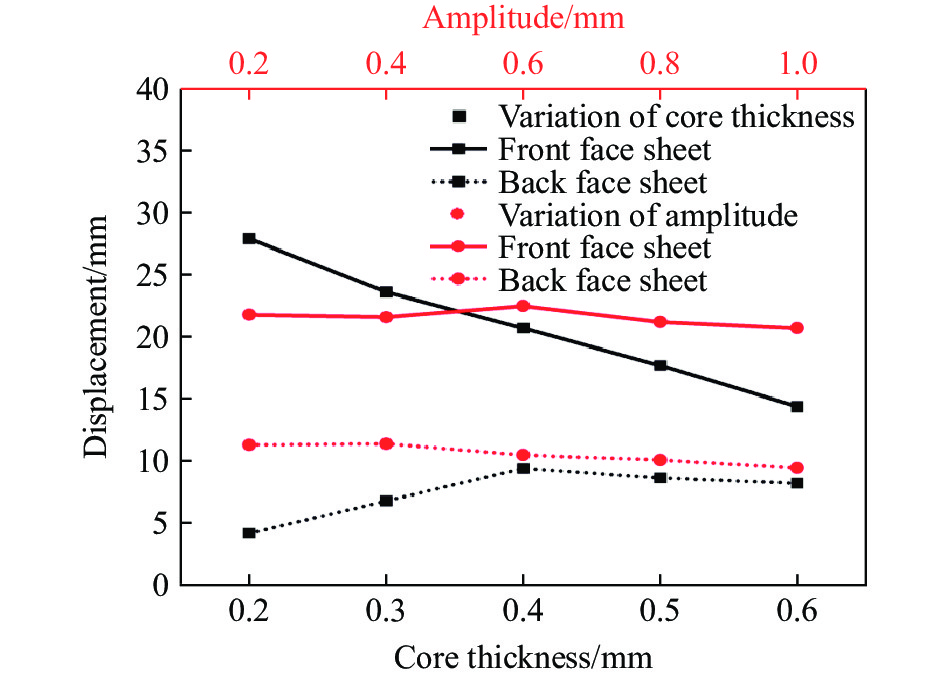
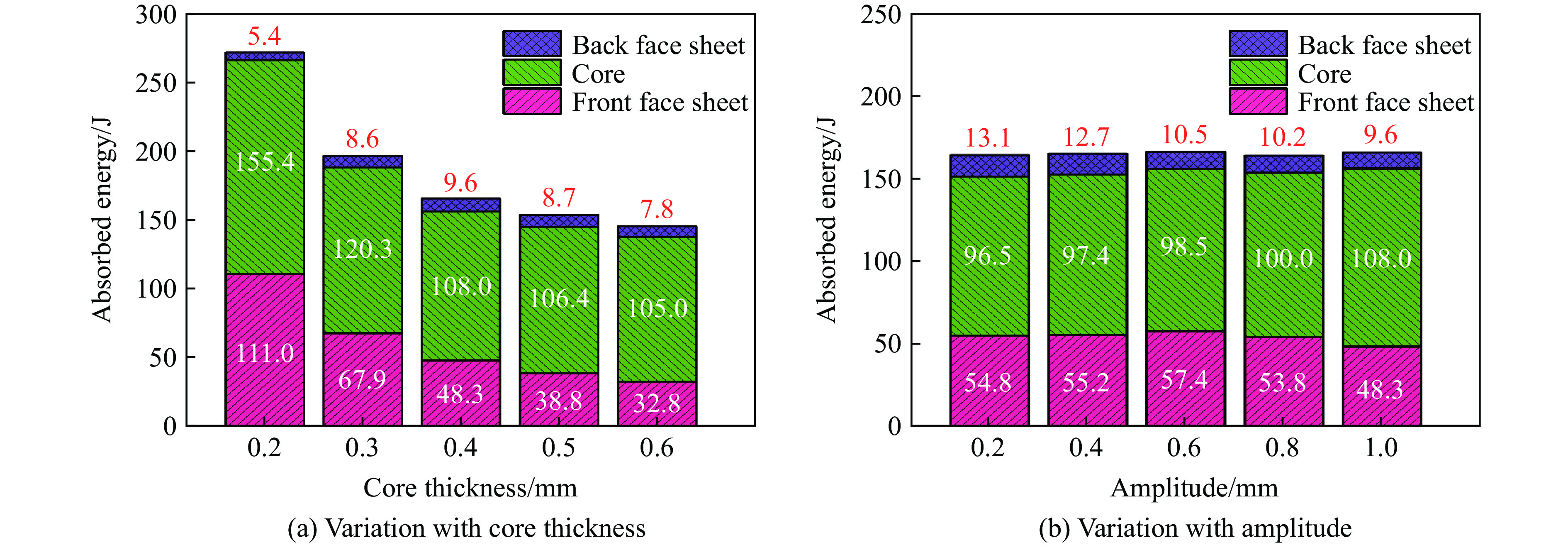
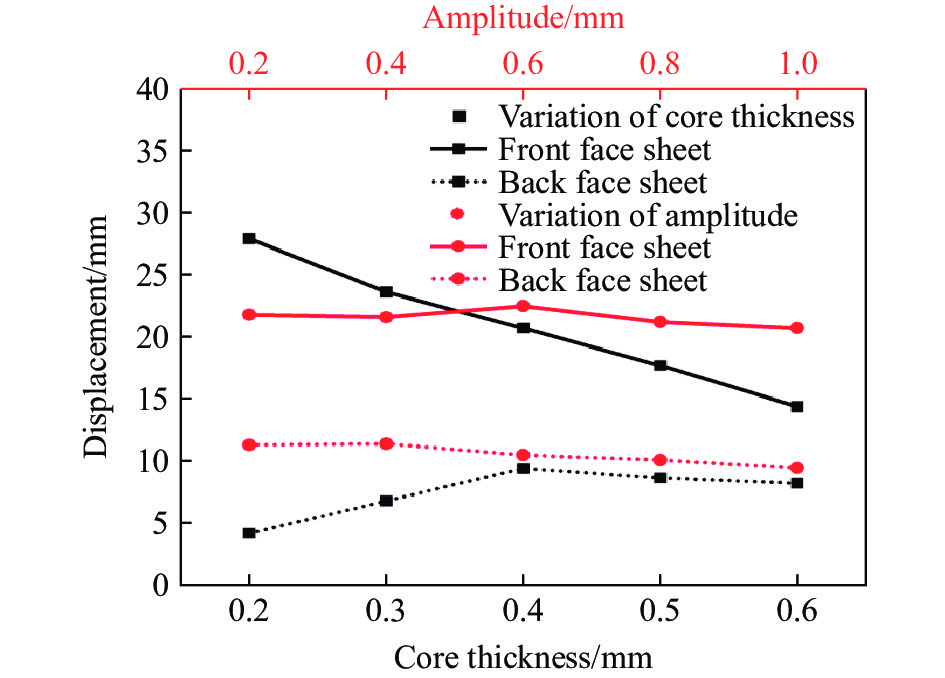
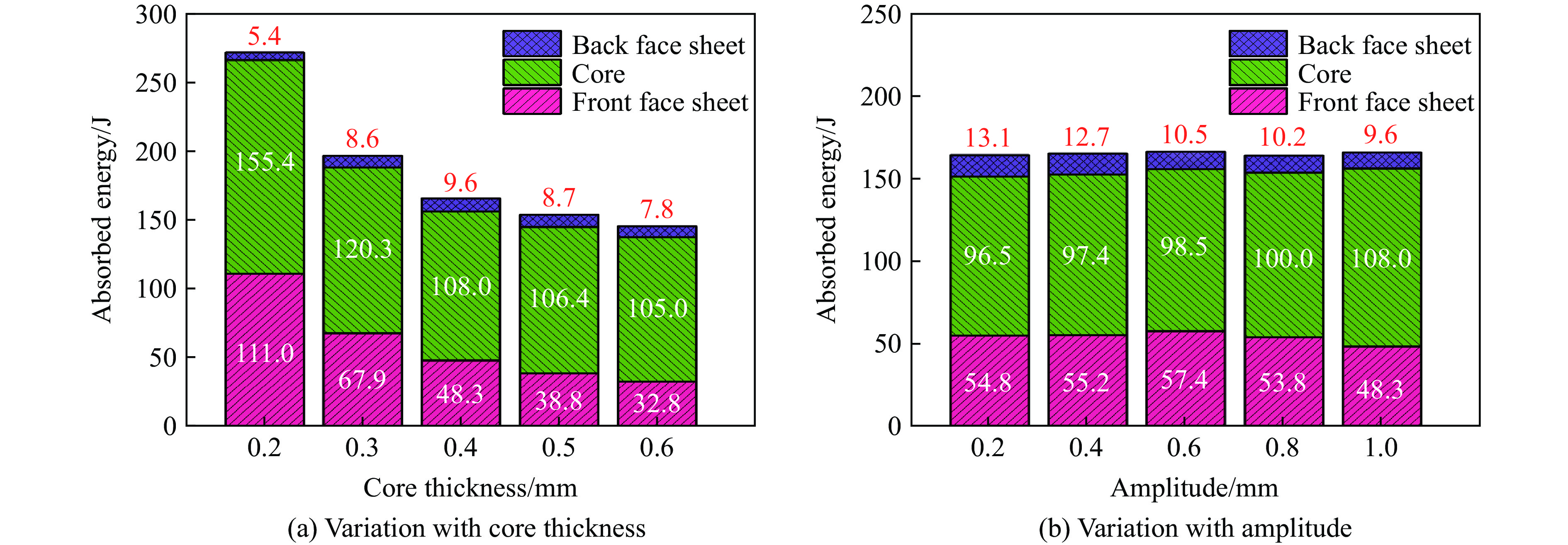
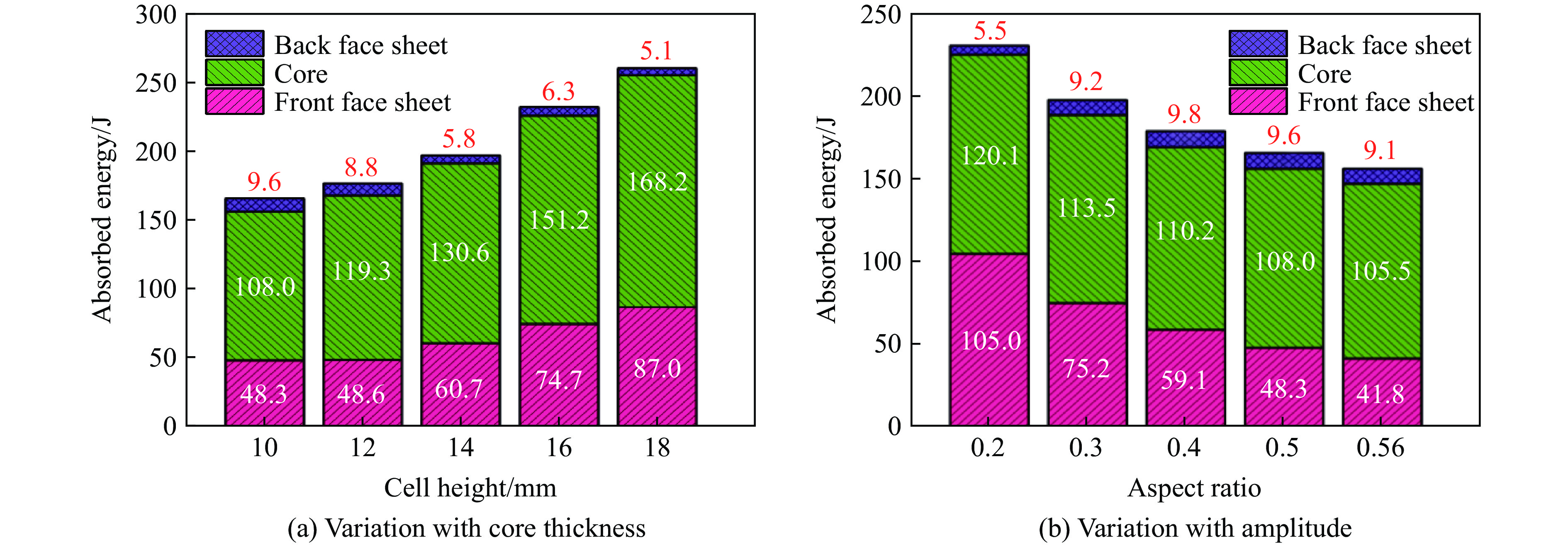
为了最大限度地提高夹层结构的保护水平,研究芯层参数对夹层结构抗爆性能的影响是至关重要的。本节中除已研究的参数变化外,其余参数均与表2中A-1的参数一致。本文中所研究的参数包括芯层厚度Tc、振幅A、宽长比L4/L1、芯层高度L2。通过选择Tc=0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6 mm来探究爆炸冲击波对夹芯板的影响。图21和图22描述了在不同芯层厚度和振幅条件下,前后面板中心位移以及不同部件的能量吸收图,由图21可知,随着芯层厚度的增大,前面板的中心位移逐渐减小,但后面板的中心位移有所增大,这主要由于芯层刚度的提高,为前面板提供了更强的支撑和抵抗变形的能力,同时也增强了传递给背板的力。当芯层厚度超过0.4 mm时,后面板中心位移逐渐减小,这可能是由于当芯层刚度提高到一定程度时,大部分能量被其刚度抵抗,但总体上后面板中心位移是增大的。由图21和图22(a)可知,当芯层厚度从0.6 mm减小至0.2 mm时,后面板中心位移降低了49.0%,夹芯板耗散的总能量提高了68.7%,这意味着较软的芯层能耗散更多的能量。
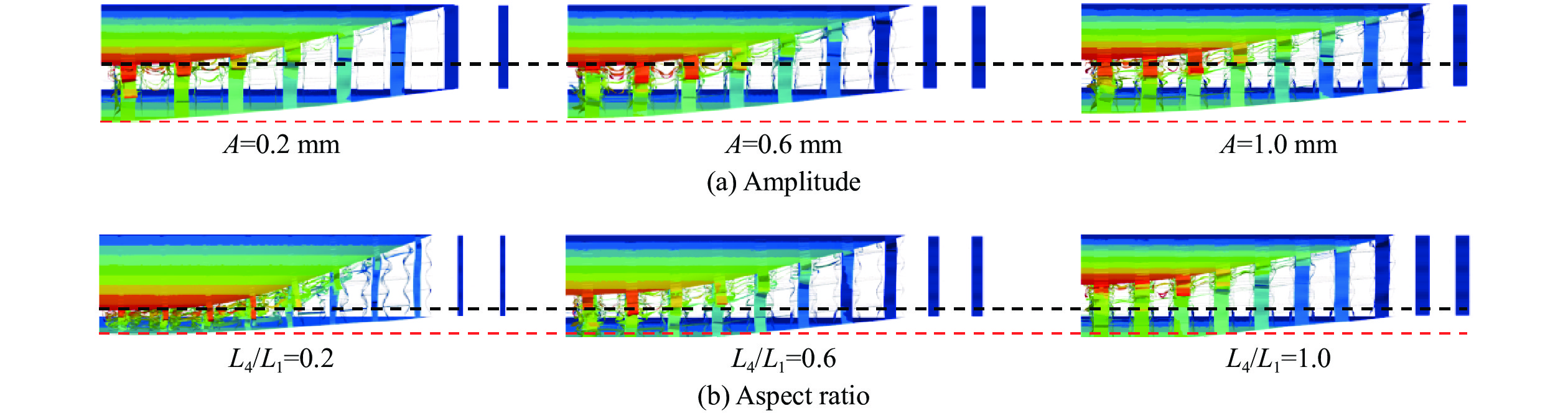
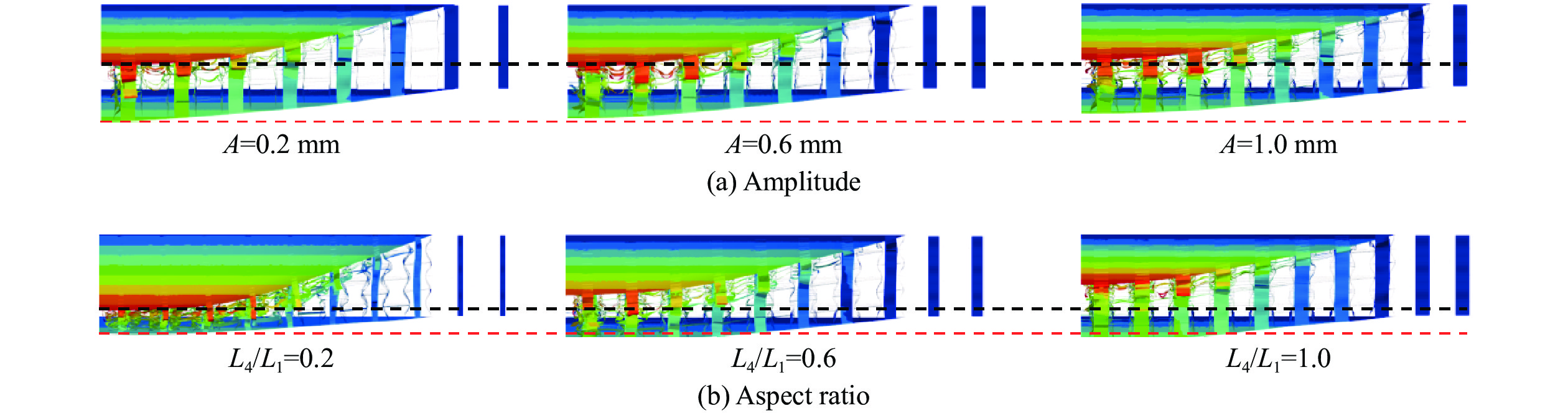
选择振幅A=0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1.0 mm,随着振幅的增大,单个蜂窝胞元结构内的凹陷程度增高。在相同载荷作用下,单个蜂窝胞元结构更容易发生变形。然而,由图2可知,在相同作用区域(125 mm×125 mm)内,连接2个胞元结构之间的长度L1保持不变,振幅的增大会导致蜂窝胞元结构的数量增加,从而在相同爆炸载荷下,单个蜂窝结构所受的力降低。这表明振幅的增大使蜂窝胞元结构更易变形,但同时降低了单个蜂窝结构的受力,这形成了一种制约关系。由图21可知,当振幅小于0.6 mm时,前面板中心位移增大,芯层压缩量增大,这表明芯层整体变形增大,且振幅的增大对变形的影响大于受力减小对变形的影响。然而,当振幅大于0.6 mm时,前面板中心位移减小,芯层压缩量减小,芯层整体变形减小,这意味着增大振幅对变形的影响小于受力减小对变形的影响。总地来看,从图21和23(a)可知,当芯层振幅从0.2 mm增大至1.0 mm时,后面板中心位移降低20.7%。另一方面,由图22(b)可知,芯层吸收的能量随振幅增加而逐渐增加,但对夹芯板总能量耗散的影响不大。
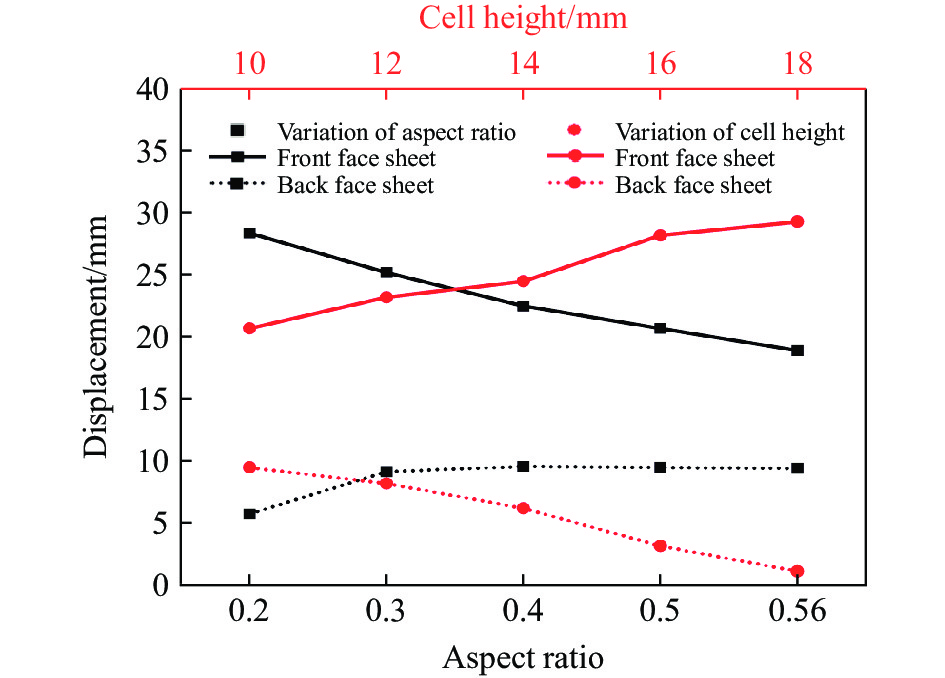
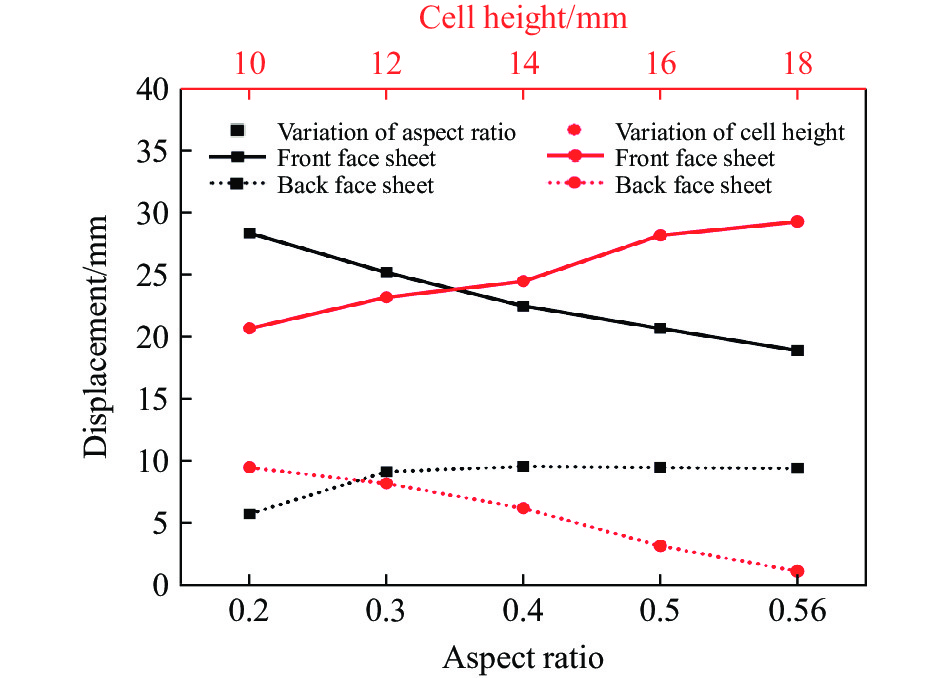
图24和图25给出了在不同芯层高度和宽长比条件下,前后面板的中心位移以及各部件的能量吸收图。选择宽长比L4/L1=0.20, 0.30, 0.40, 0.50, 0.56,其中保持L1始终为10 mm。随着宽长比的增大,前面板中心位移减少,后面板中心位移有所增加,当宽长比增加至0.4时,对于后面板中心位移的影响将变得不敏感,宽长比从0.56减小至0.2时,后面板中心位移降低39%。随着L4/L1的减小,蜂窝胞元结构与前面板接触的面积减少,从而在相同的爆炸载荷下,宽长比较小的芯层更容易发生变形,因此能够吸收更多的能量。根据图25(b),当L4/L1=0.20时,中间芯层和前面板的能量吸收最多。同样地,从图23(b)可以观察到此时前面板和芯层变形更充分,因此吸收了大量的能量。随着宽长比的增大,芯层和前面板的能量吸收逐渐减少,导致夹芯板的总能量耗散减少。具体而言,当L4/L1=0.20时,前面板和芯层吸收的能量是L4/L1=0.56时的1.53倍。选择芯层高度L2=10, 12, 14, 16, 18 mm。由图24可知,随着芯层高度逐渐增大,前面板中心位移逐渐增大,后面板中心位移减小,这是因为增大了芯层的变形空间,导致前面板和芯层的变形量增大,从而吸收更多的能量。芯层高度对结构的抗爆性能产生显著影响,通过使芯层高度增大80%,夹层结构的后面板中心位移可减小88.4%。
4. 相同壁厚下不同夹芯板的抗爆性能
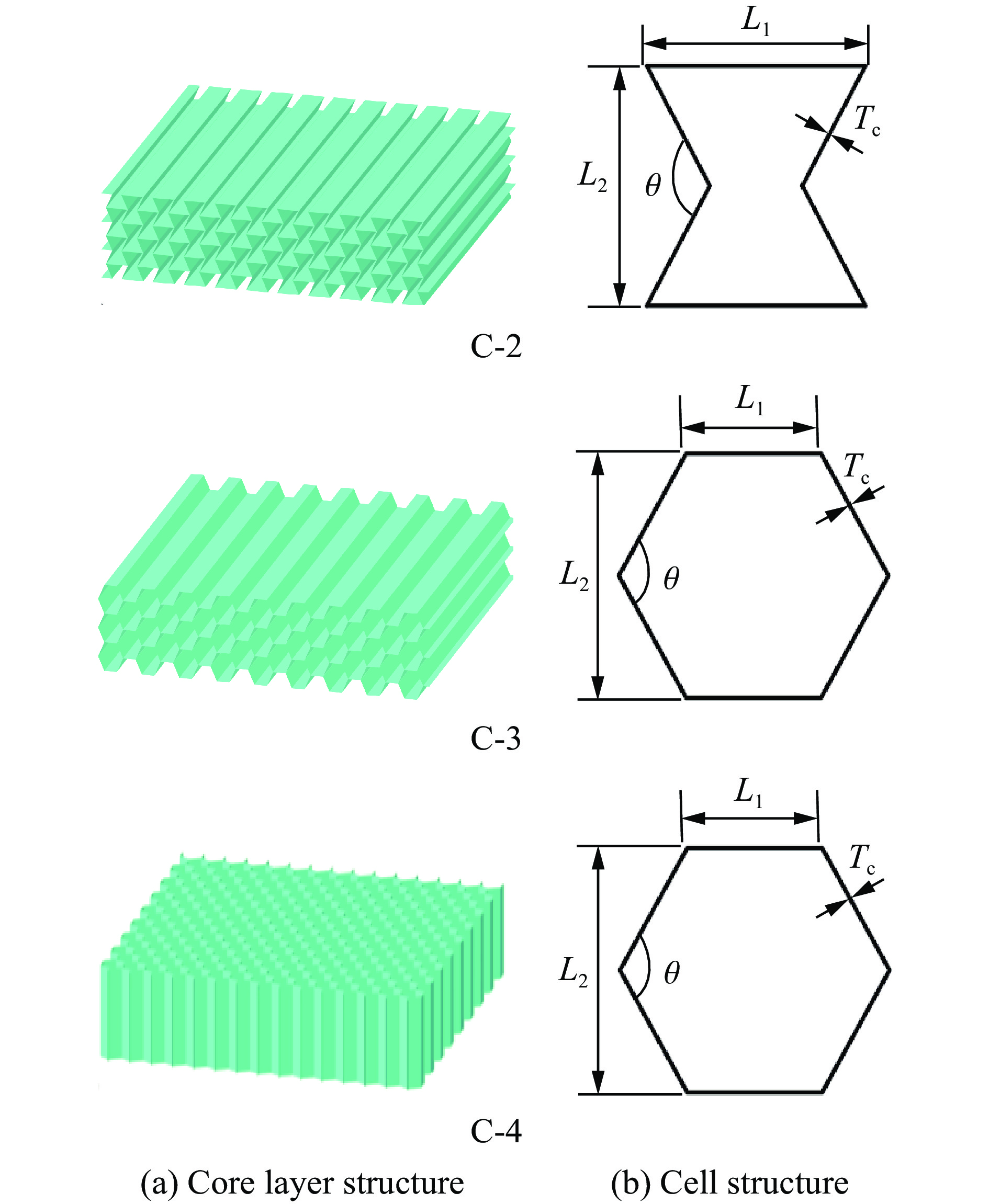
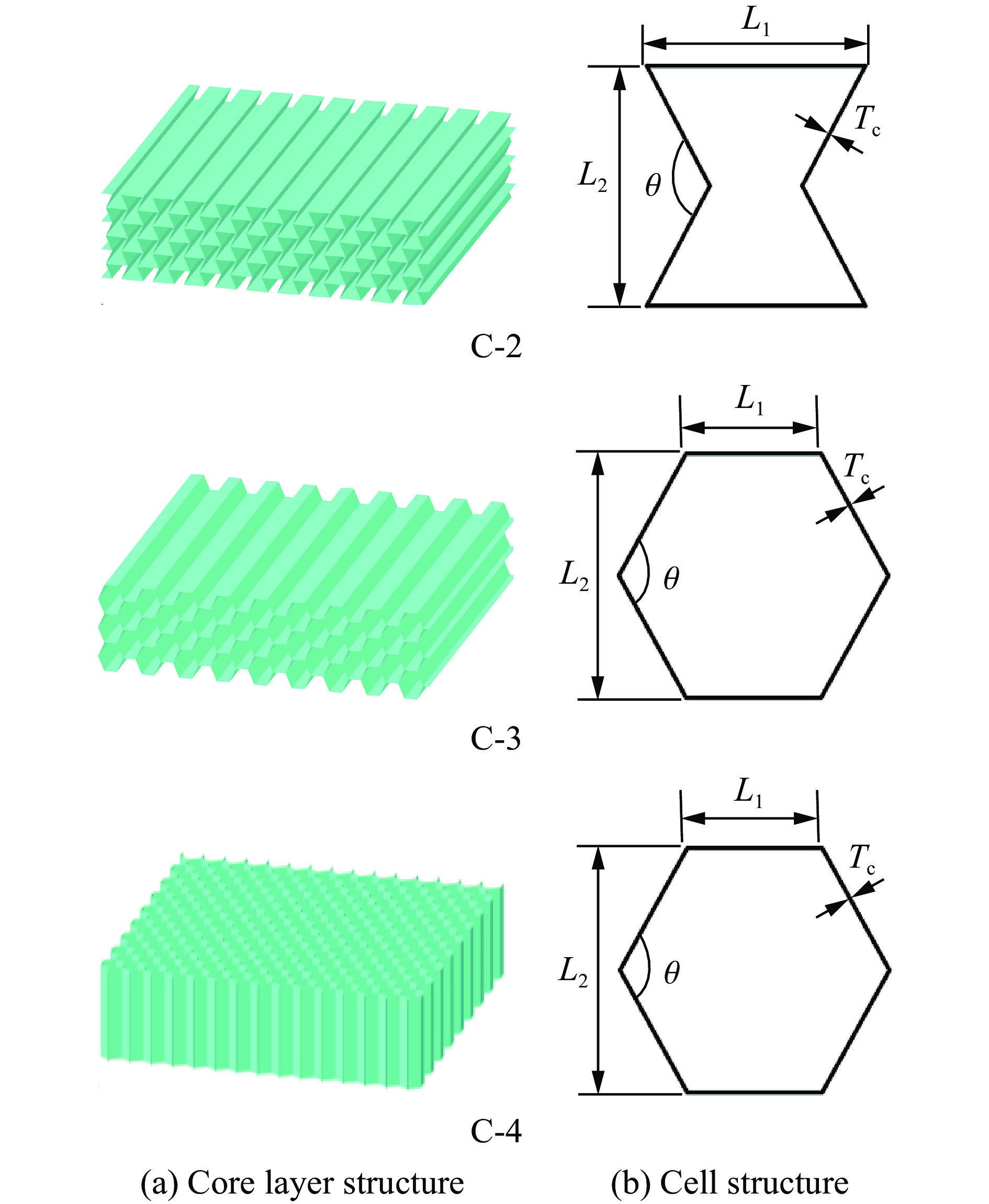
为了验证正弦曲边三维负泊松比夹芯板在抗爆炸冲击中防护效果的优越性,进行了3组蜂窝夹芯板的抗爆性能对比研究,3组研究中炸药质量均为30 g,爆炸距离均为100 mm,前后面板厚度均为1.2 mm,芯层厚度均为0.2 mm,夹芯板的整体尺寸为L=B=300 mm,整体高度为32.4 mm。采用与2.2节中相同的方法建立了数值模拟模型。其中,正弦曲边三维负泊松比夹芯板用C-1表示。图26中C-2呈现了内凹六边形蜂窝芯层结构和胞元结构几何参数,其整体尺寸与正六边形蜂窝材料基本保持一致,C-3中的(a)和(b)展示了面内正六边形蜂窝的胞元结构几何参数和芯层结构,而C-4中的(a)和(b)则展示了面外正六边形蜂窝的胞元结构几何参数和芯层结构。表4总结了4种蜂窝夹芯板的具体胞元结构几何参数和数值结果。
表 4 3种夹芯板的几何信息和模拟结果Table 4. Geometric information and simulation results for three sandwich panels编号 胞元长度
L1/mm胞元高度
L2/mm胞元夹角
θ/(°)胞元厚度
Tc/mm夹芯板总质量
M/g背面板中心最终
位移Db/mm结构总能量
吸收E/J比吸能
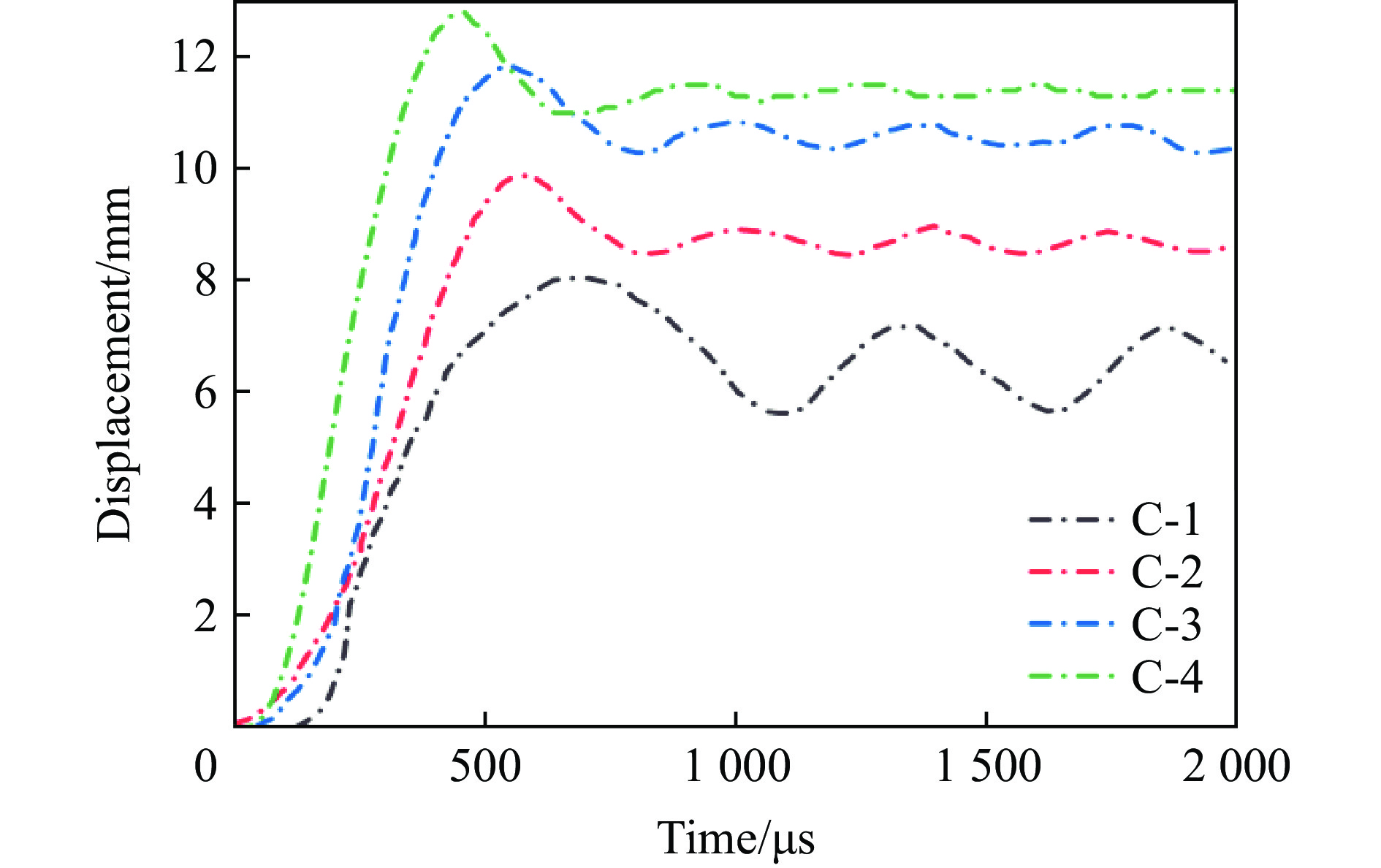
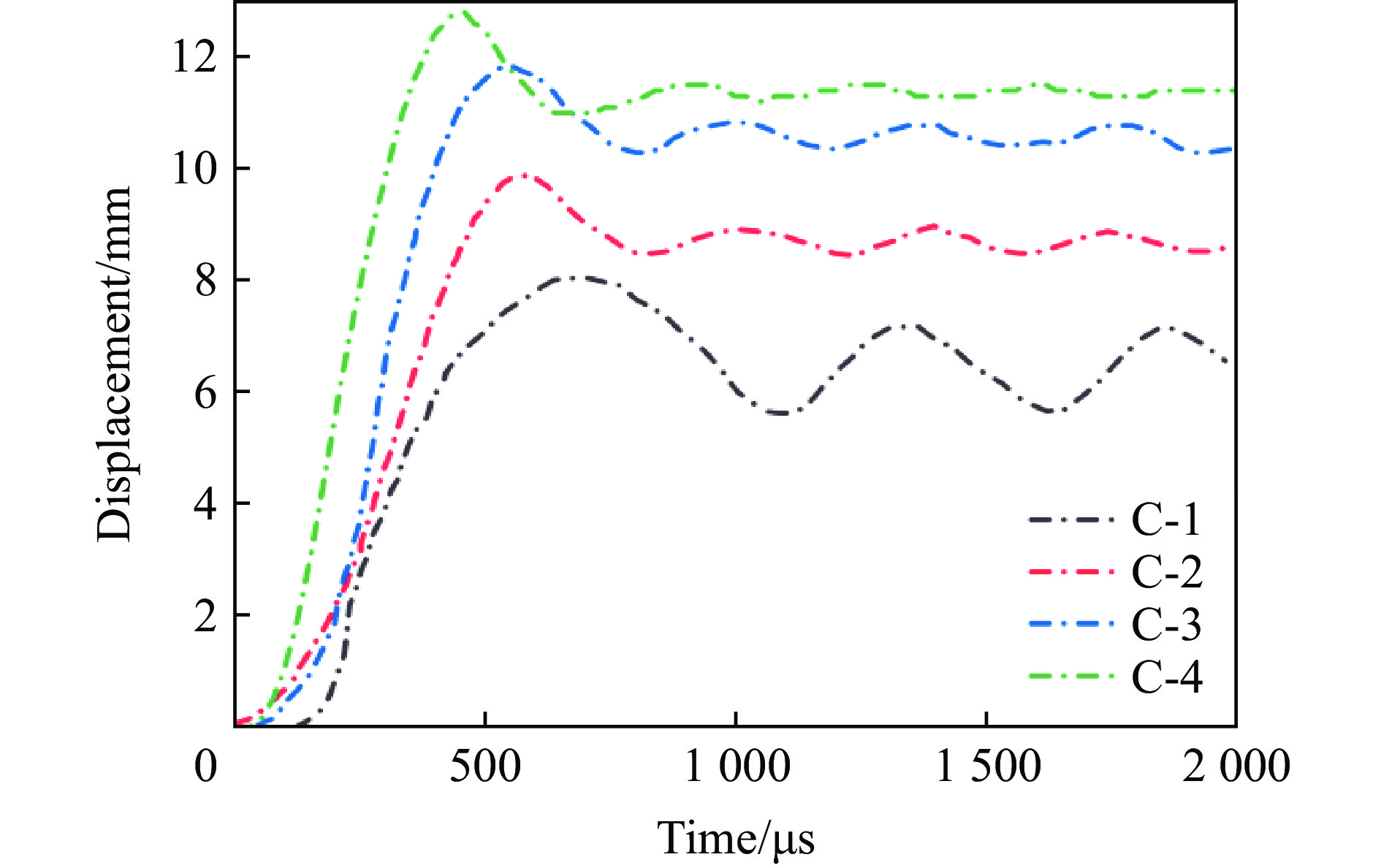
e/(J·g−1)C-1 10 10 − 0.2 211.64 6.58 382.6 1.81 C-2 10 10 120 0.2 257.66 8.67 316.1 1.23 C-3 5.77 10 120 0.2 229.13 10.4 256.6 1.12 C-4 5.77 10 120 0.2 226.20 11.4 236.3 1.04 选取后面板中心位移和结构比吸能(结构单位质量吸收的能量)作为抗爆性能评价指标[22]。表4的数值结果表明,与传统的内凹六边形蜂窝夹芯板以及面内和面外的正六边形蜂窝夹芯板相比,正弦曲边三维负泊松比夹芯结构表现出更高的比吸能,并且后面板中心位移分别减少了24.1%、36.7%和42.3%。从图27后面板中心位移曲线也可看出,在这四者中,正弦曲边三维负泊松比夹芯板后面板中心位移较小。
综上,正弦曲边三维负泊松比夹芯板相比于传统蜂窝夹芯板有较好的防爆性能。
5. 结 论
通过数值模拟的方法对空爆载荷下的正弦曲线三维负泊松比夹芯板的动态响应过程和能量吸收进行了研究,探究了爆距、炸药质量对能量吸收和变形挠度的影响,进一步研究了芯层结构几何参数对夹芯板抗爆性能的影响,主要结论如下。
(1)根据面板的中心速度和中心位移时间曲线,爆炸载荷下三维负泊松比夹芯板的动态响应过程主要分为3个阶段:芯层压缩吸能阶段、夹芯板整体塑性变形吸能阶段和夹芯板的自由振动阶段。在此过程中,大部分爆炸能量被芯层吸收。在不同爆炸载荷和不同爆距下,芯层吸收能量占比超过60%。芯层的吸收能量占比随着炸药量的增加而降低,随着爆距的增大而提高。
(2)前后面板的中心位移均随着前后面板厚度的增大而减小,当前后面板厚度分别从0.6 mm增大到1.4 mm时,后面板的中心位移分别减小了55%和37.5%,可知增大前面板厚度对减小后面板中心位移的影响更显著。采用薄前面板的夹芯板可以提高该结构的吸能能力。不同后面板厚度对前面板中心位移的影响较小,增大后面板厚度可以提高芯层的吸能占比,但对总能量耗散影响不大。
(3)在本文研究的芯层厚度范围内(0.2~0.6 mm),后面板中心位移随着芯层厚度的增大而增大,同时也会降低能量耗散,对结构的防护作用有负面影响。随着芯层振幅的增大,后面板中心位移有所减小,芯层吸收的能量逐渐增加,但对夹芯板总能量耗散的影响不大。
(4)芯层的宽长比L4/L1对其抗爆性能有较大影响。随着宽长比的增大,后面板中心位移增大,芯层吸收的能量减少,但宽长比增大到0.3时,后面板中心位移对宽长比会变得不敏感。宽长比为0.2时,后面板中心位移最小,相对于宽长比为0.56时,后面板中心位移减小64%。
(5)在本研究案例中,在相同壁厚条件下,与传统的内凹六边形蜂窝夹芯板以及面内和面外正六边形蜂窝夹芯板相比,正弦曲边三维负泊松比夹芯板表现出更高的吸能性能,同时后面板的中心位移分别减小了24.1%、36.7%和42.3%。
-
表 1 数值模拟中采用的铝合金主要材料参数[37]
Table 1. Main material parameters of aluminum alloy used in numerical simulation[37]
部件 材料 屈服应力/MPa 拉伸强度/MPa 杨氏模量/GPa 密度/(g·cm−3) 泊松比 面板 AL1200 140 160 70 2.7 0.3 芯层 AL5052 70 210 70 2.7 0.3 表 2 爆炸载荷下三维负泊松比夹芯板设计方案
Table 2. Designs of 3D negative Poisson’s ratio sandwich panels subjected to blast loading
编号 Tf/mm Tb/mm A/mm L2/mm 爆炸距离/mm Q/g 拉伸宽度L4/mm A-1 1.2 1.2 1 10 100 20 5 Q-30 1.2 1.2 1 10 100 30 5 Q-40 1.2 1.2 1 10 100 40 5 S-80 1.2 1.2 1 10 80 20 5 S-120 1.2 1.2 1 10 120 20 5 表 3 4组夹芯板的几何参数和爆炸参数[37]
Table 3. Geometric and explosion parameters for four sets of sandwich panels[37]
夹芯板 L2/mm 蜂窝边长L1/mm Tc/mm Q/g 爆炸距离/mm S4-1 18.4 5 0.04 10 150 S4-2 18.4 5 0.04 10 100 S3-1 18.4 3 0.04 15 100 S3-2 18.4 3 0.04 20 130 表 4 3种夹芯板的几何信息和模拟结果
Table 4. Geometric information and simulation results for three sandwich panels
编号 胞元长度
L1/mm胞元高度
L2/mm胞元夹角
θ/(°)胞元厚度
Tc/mm夹芯板总质量
M/g背面板中心最终
位移Db/mm结构总能量
吸收E/J比吸能
e/(J·g−1)C-1 10 10 − 0.2 211.64 6.58 382.6 1.81 C-2 10 10 120 0.2 257.66 8.67 316.1 1.23 C-3 5.77 10 120 0.2 229.13 10.4 256.6 1.12 C-4 5.77 10 120 0.2 226.20 11.4 236.3 1.04 -
[1] DHARMASENA K P, WADLEY H N G, XUE Z Y, et al. Mechanical response of metallic honeycomb sandwich panel structures to high-intensity dynamic loading [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2008, 35(9): 1063–1074. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2007.06.008. [2] ZHANG J X, ZHOU R F, WANG M S, et al. Dynamic response of double-layer rectangular sandwich plates with metal foam cores subjected to blast loading [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2018, 122: 265–275. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2018.08.016. [3] UTH T, DESHPANDE V S. Response of clamped sandwich beams subjected to high-velocity impact by sand slugs [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2014, 69: 165–181. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2014.02.012. [4] 张豪, 常白雪, 赵凯, 等. 三种蜂窝夹芯板的抗爆性能分析 [J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2022, 42(6): 557–566. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2021.225.ZHANG H, CHANG B X, ZHAO K, et al. Anti-explosion analysis of honeycomb sandwich panels with three kinds of core structures [J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2022, 42(6): 557–566. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2021.225. [5] 田力, 胡建伟. Ⅰ-Ⅴ型夹芯板在近爆冲击波和破片群联合作用下防爆性能研究 [J]. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 46(1): 32–46. DOI: 10.16339/j.cnki.hdxbzkb.2019.01.004.TIAN L, HU J W. Research on explosion protective properties of I-V sandwich panel under combined loading of close-range blast wave and fragments [J]. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences), 2019, 46(1): 32–46. DOI: 10.16339/j.cnki.hdxbzkb.2019.01.004. [6] 田力, 张浩. 冲击波和预制破片复合作用下H型钢柱损伤效应分析 [J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 46(3): 289–299. DOI: 10.11908/j.issn.0253-374x.2018.03.002.TIAN L, ZHANG H. Damage effect analysis of H-section steel columns subjected to synergistic effects of blast and prefabricated fragments [J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2018, 46(3): 289–299. DOI: 10.11908/j.issn.0253-374x.2018.03.002. [7] ZHANG C Z, CHENG Y S, ZHANG P, et al. Numerical investigation of the response of I-core sandwich panels subjected to combined blast and fragment loading [J]. Engineering Structures, 2017, 151: 459–471. DOI: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2017.08.039. [8] LI J F, QIN Q H, ZHANG J X. Internal blast resistance of sandwich cylinder with lattice cores [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2021, 191: 106107. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2020.106107. [9] 李勇, 肖伟, 程远胜, 等. 冲击波与破片对波纹杂交夹层板的联合毁伤数值研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2018, 38(2): 279–288. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2016-0224.LI Y, XIAO W, CHENG Y S, et al. Numerical research on response of hybrid corrugated sandwich plates subjected to combined blast and fragment loadings [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2018, 38(2): 279–288. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2016-0224. [10] QIN Q H, CHEN S J, LI K K, et al. Structural impact damage of metal honeycomb sandwich plates [J]. Composite Structures, 2020, 252: 112719. DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.112719. [11] ZHANG J X, QIN Q H, ZHANG J T, et al. Low-velocity impact on square sandwich plates with fibre-metal laminate face-sheets: analytical and numerical research [J]. Composite Structures, 2021, 259: 113461. DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.113461. [12] QIN Q H, XIA Y M, LI J F, et al. On dynamic crushing behavior of honeycomb-like hierarchical structures with perforated walls: experimental and numerical investigations [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2020, 145: 103674. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2020.103674. [13] ZHANG J X, ZHU Y Q, LI K K, et al. Dynamic response of sandwich plates with GLARE face-sheets and honeycomb core under metal foam projectile impact: experimental and numerical investigations [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2022, 164: 104201. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2022.104201. [14] ZHANG X W, YANG D Q. Mechanical properties of auxetic cellular material consisting of Re-entrant hexagonal honeycombs [J]. Materials, 2016, 9(11): 900. DOI: 10.3390/ma9110900. [15] BEZAZI A, SCARPA F. Mechanical behaviour of conventional and negative Poisson's ratio thermoplastic polyurethane foams under compressive cyclic loading [J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2007, 29(5): 922–930. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2006.07.015. [16] ABADA M, IBRAHIM A. Metallic ribbon-core sandwich panels subjected to air blast loading [J]. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10(13): 4500. DOI: 10.3390/app10134500. [17] WIERNICKI C J, LIEM P E F, WOODS G D, et al. Structural analysis methods for lightweight metallic corrugated core sandwich panels subjected to blast loads [J]. Naval Engineers Journal, 1991, 103(3): 192–202. DOI: 10.1111/j.1559-3584.1991.tb00949.x. [18] GIBSON L J, ASHBY M F. Cellular solids: structure and properties [M]. 2nd ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1997. DOI: 10.1017/CBO9781139878326. [19] LU G X, YU T X. Energy absorption of structures and materials [M]. Cambridge: Woodhead Publishing, 2003. [20] JING L, WANG Z H, NING J G, et al. The dynamic response of sandwich beams with open-cell metal foam cores [J]. Composites Part B:Engineering, 2011, 42(1): 1–10. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2010.09.024. [21] ZHANG P W, LI X, JIN T, et al. Dynamic response of circular metallic sandwich panels under projectile impact [J]. Journal of Sandwich Structures and Materials, 2017, 19(5): 572–594. DOI: 10.1177/1099636215626596. [22] 孙晓旺, 陶晓晓, 王显会, 等. 负泊松比蜂窝材料抗爆炸特性及优化设计研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2020, 40(9): 095101. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0011.SUN X W, TAO X X, WANG X H, et al. Research on explosion-proof characteristics and optimization design of negative Poisson’s ratio honeycomb material [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2020, 40(9): 095101. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0011. [23] 杨德庆, 张相闻, 吴秉鸿. 负泊松比效应防护结构抗爆抗冲击性能影响因素 [J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2018, 52(4): 379–387. DOI: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2018.04.001.YANG D Q, ZHANG X W, WU B H. The influence factors of explosion and shock resistance performance of Auxetic sandwich defensive structures [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2018, 52(4): 379–387. DOI: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2018.04.001. [24] 孙魁远, 孙晓旺, 张宏伟, 等. 厚度梯度型负泊松比蜂窝抗爆炸特性及优化 [J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2022, 43(4): 190–197. DOI: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2022.04.031.SUN K Y, SUN X W, ZHANG H W, et al. Anti-explosion characteristics and optimization of negative Poisson’s ratio honeycomb with thickness gradient [J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2022, 43(4): 190–197. DOI: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2022.04.031. [25] 卫禹辰, 袁梦琦, 钱新明, 等. 爆炸冲击环境下内凹蜂窝型梯度结构响应特性研究 [J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2021, 17(1): 5–11. DOI: 10.11731/j.issn.1673-193x.2021.01.001.WEI Y C, YUAN M Q, QIAN X M, et al. Research on response characteristics of concave honeycomb gradient structure under explosive impact environment [J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2021, 17(1): 5–11. DOI: 10.11731/j.issn.1673-193x.2021.01.001. [26] 杨德庆, 吴秉鸿, 张相闻. 星型负泊松比超材料防护结构抗爆抗冲击性能研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2019, 39(6): 065102. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0060.YANG D Q, WU B H, ZHANG X W. Anti-explosion and shock resistance performance of sandwich defensive structure with star-shaped auxetic material core [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2019, 39(6): 065102. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0060. [27] JIN X C, WANG Z H, NING J G, et al. Dynamic response of sandwich structures with graded auxetic honeycomb cores under blast loading [J]. Composites Part B:Engineering, 2016, 106: 206–217. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2016.09.037. [28] GAO Q, GE C Q, ZHUANG W C, et al. Crashworthiness analysis of double-arrowed auxetic structure under axial impact loading [J]. Materials and Design, 2019, 161: 22–34. DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2018.11.013. [29] BEHARIC A, EGUI R R, YANG L. Drop-weight impact characteristics of additively manufactured sandwich structures with different cellular designs [J]. Materials and Design, 2018, 145: 122–134. DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2018.02.066. [30] 杨泽水, 薛玉祥, 刘爱荣. 三维负泊松比星型结构冲击动力学研究 [J]. 工程力学, 2022, 39(S1): 356–363. DOI: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2021.05.S057.YANG Z S, XUE Y X, LIU A R. Study on the impact dynamics of three-dimensional star-shaped structure with negative Poisson’s ratio [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2022, 39(S1): 356–363. DOI: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2021.05.S057. [31] WANG Y L, ZHAO W Z, ZHOU G, et al. Analysis and parametric optimization of a novel sandwich panel with double-V auxetic structure core under air blast loading [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2018, 142/143: 245–254. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2018.05.001. [32] IMBALZANO G, TRAN P, NGO T D, et al. Three-dimensional modelling of auxetic sandwich panels for localised impact resistance [J]. Journal of Sandwich Structures and Materials, 2017, 19(3): 291–316. DOI: 10.1177/1099636215618539. [33] IMBALZANO G, TRAN P, LEE P V S, et al. Influences of material and geometry in the performance of auxetic composite structure under blast loading [J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2016, 846: 476–481. DOI: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.846.476. [34] XU F X, YU K J, HUA L. In-plane dynamic response and multi-objective optimization of negative Poisson's ratio (NPR) honeycomb structures with sinusoidal curve [J]. Composite Structures, 2021, 269: 114018. DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2021.114018. [35] 虞科炯, 徐峰祥, 华林. 正弦曲边负泊松比蜂窝结构面内冲击性能研究 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2021, 40(13): 51–59. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2021.13.007.YU K J, XU F X, HUA L. In plane impact performance of honeycomb structure with sinusoidal curved edge and negative Poisson’s ratio [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2021, 40(13): 51–59. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2021.13.007. [36] 邓小林, 刘旺玉. 一种负泊松比正弦曲线蜂窝结构的面内冲击动力学分析 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2017, 36(13): 103–109,154. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2017.13.016.DENG X L, LIU W Y. In-plane impact dynamic analysis for a sinusoidal curved honeycomb structure with negative Poisson’s ratio [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2017, 36(13): 103–109,154. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2017.13.016. [37] LI X, ZHANG P W, WANG Z H, et al. Dynamic behavior of aluminum honeycomb sandwich panels under air blast: experiment and numerical analysis [J]. Composite Structures, 2014, 108: 1001–1008. DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2013.10.034. [38] NEUBERGER A, PELES S, RITTEL D. Scaling the response of circular plates subjected to large and close-range spherical explosions. Part II: buried charges [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2007, 34(5): 874–882. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2006.04.002. [39] LIU J F, WANG Z G, HUI D. Blast resistance and parametric study of sandwich structure consisting of honeycomb core filled with circular metallic tubes [J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2018, 145: 261–269. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.03.005. [40] WANG E D, LI Q, SUN G Y. Computational analysis and optimization of sandwich panels with homogeneous and graded foam cores for blast resistance [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2020, 147: 106494. DOI: 10.1016/j.tws.2019.106494. 期刊类型引用(5)
1. 张保勇,张义宇,陶金,王亚军,刘传海,韩永辉,孙曼. 三明治结构复合材料对甲烷-空气混合气体爆炸传播规律的影响. 兵工学报. 2025(01): 128-137 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 肖俊华,万武举,郭之熙,梁希. 梯度双材料负泊松比蜂窝夹芯板局部冲击失效研究. 复合材料学报. 2025(03): 1689-1699 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 蒋伟忠,张毅,朱一林,王源隆,吴文旺,张传增,任鑫. 功能性负泊松比超材料研究进展与展望. 应用力学学报. 2025(03): 494-510 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 李小帅,黄静泊,谢晶,李建飞,许泽建,陈鹏万. 连接方式对蜂窝夹芯结构抗爆性能的影响规律研究. 包装工程. 2024(19): 29-40 .  百度学术
百度学术5. 刘洋,张天辉,刘志芳,李世强,雷建银. 重复爆炸荷载下双层蜂窝夹芯板的动力响应. 科技通报. 2024(11): 1-8+109 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(5)
-








 下载:
下载:


























 下载:
下载:



 百度学术
百度学术