Effect of steel ratio on the impact resistance of GFRP tube concrete-encased steel composite members
-
摘要: 为了研究含钢率对GFRP(glass fiber reinforced polymer)管-钢骨混凝土组合构件抗冲击性能的影响,建立15个组合构件的数值模型,在验证模型正确的基础上,通过分析典型构件的冲击全过程、截面弯矩发展以及破坏时应变分布规律,研究构件在侧向冲击荷载作用下的破坏模式;通过分析构件冲击力时程曲线、侧移时程曲线以及能量变化情况,探究含钢率对不同长细比构件抗冲击性能的影响。结果表明:与未配置钢骨的构件相比,GFRP管-钢骨混凝土构件的抗冲击承载力提高了7%~134%,侧向位移减小了13%~68%。在侧向冲击荷载作用下,构件的破坏模式以弯曲破坏为主,同时伴随着GFRP管和混凝土冲击区域的局部破坏,抗弯刚度是影响构件抗冲击性能的主要因素之一。构件的抗冲击承载力随着含钢率的增高而提高,随着构件长细比的增大而降低。含钢率相差1.5%时,截面惯性矩较大的窄翼缘型钢对构件的抗冲击性能更有利。对于长细比大于20的构件,钢骨耗能是组合构件总能耗的主要组成部分。
-
关键词:
- GFRP管-钢骨混凝土组合构件 /
- 侧向冲击 /
- 含钢率 /
- 破坏模式
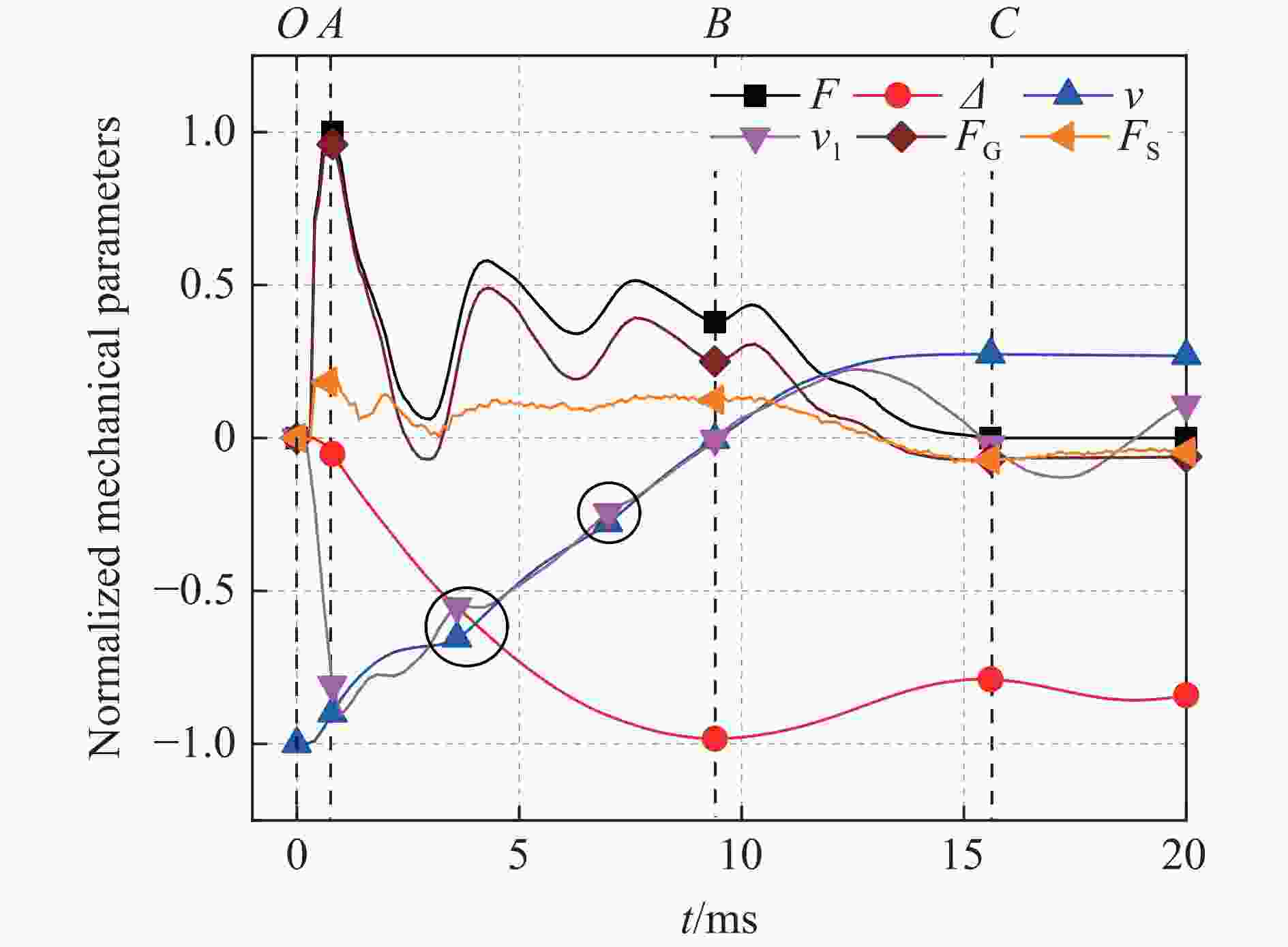
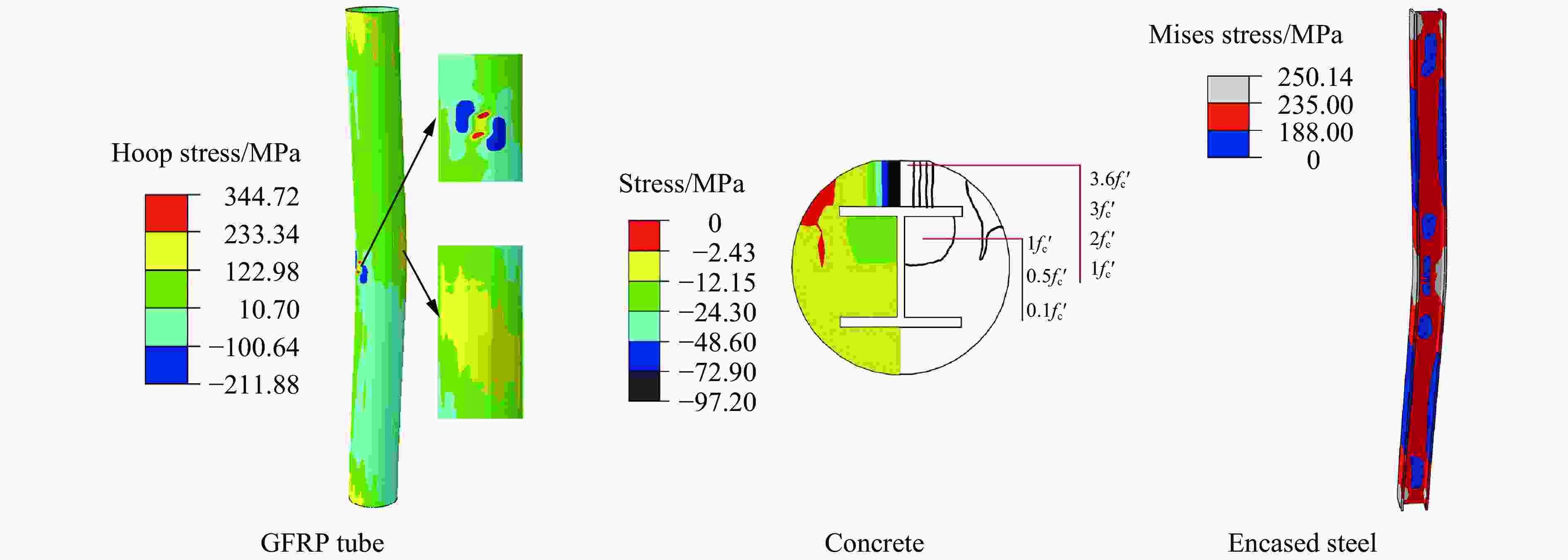
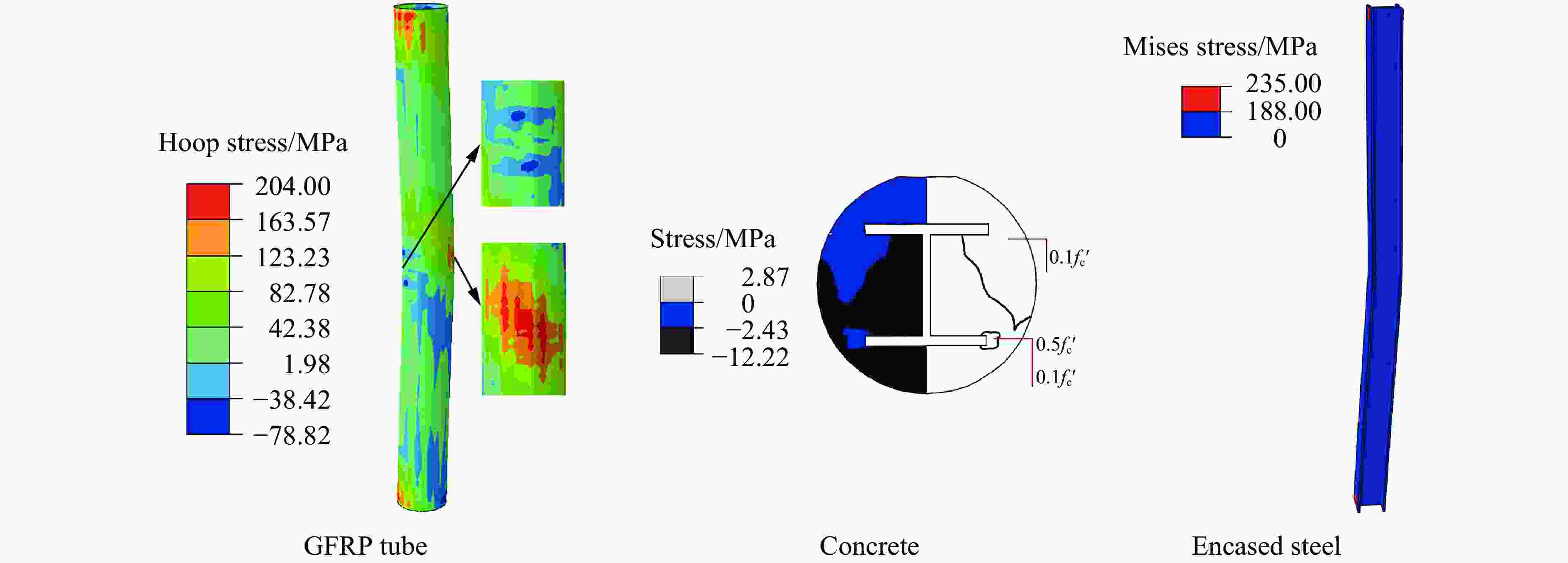
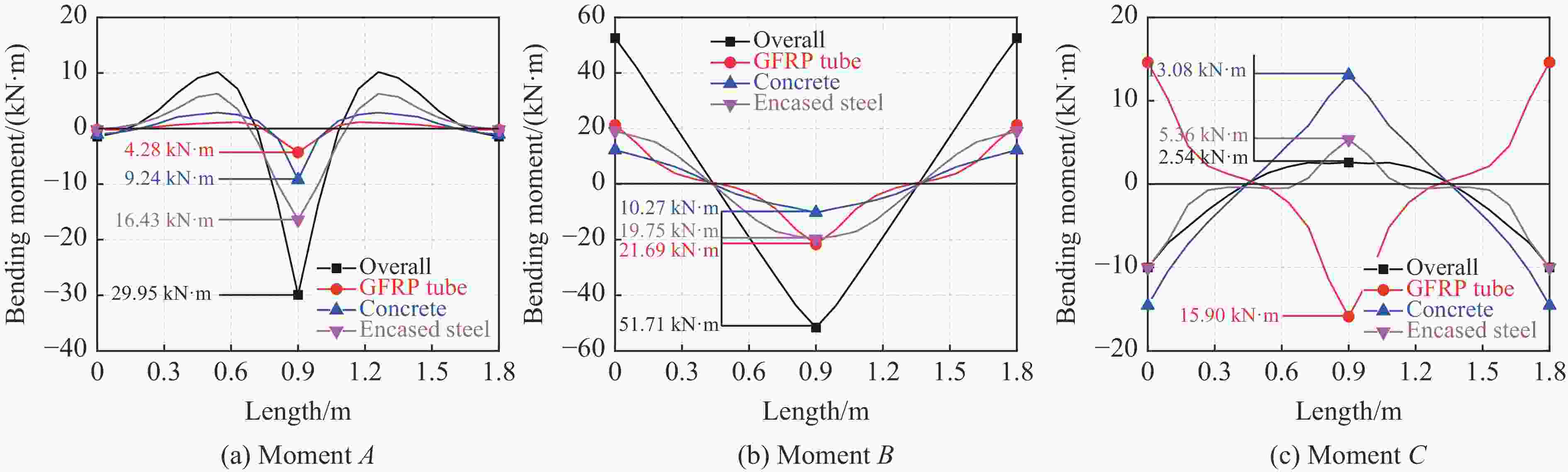
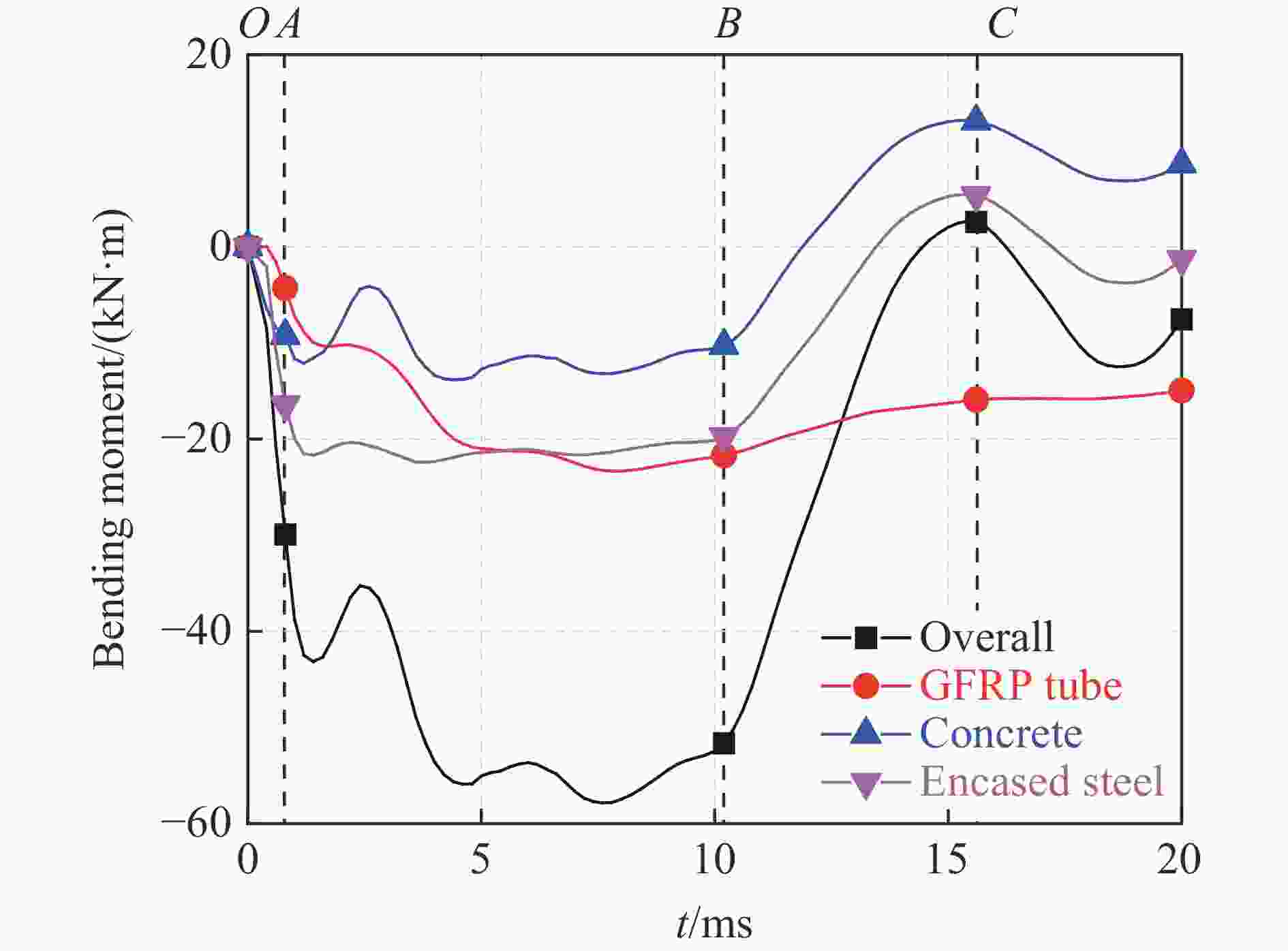
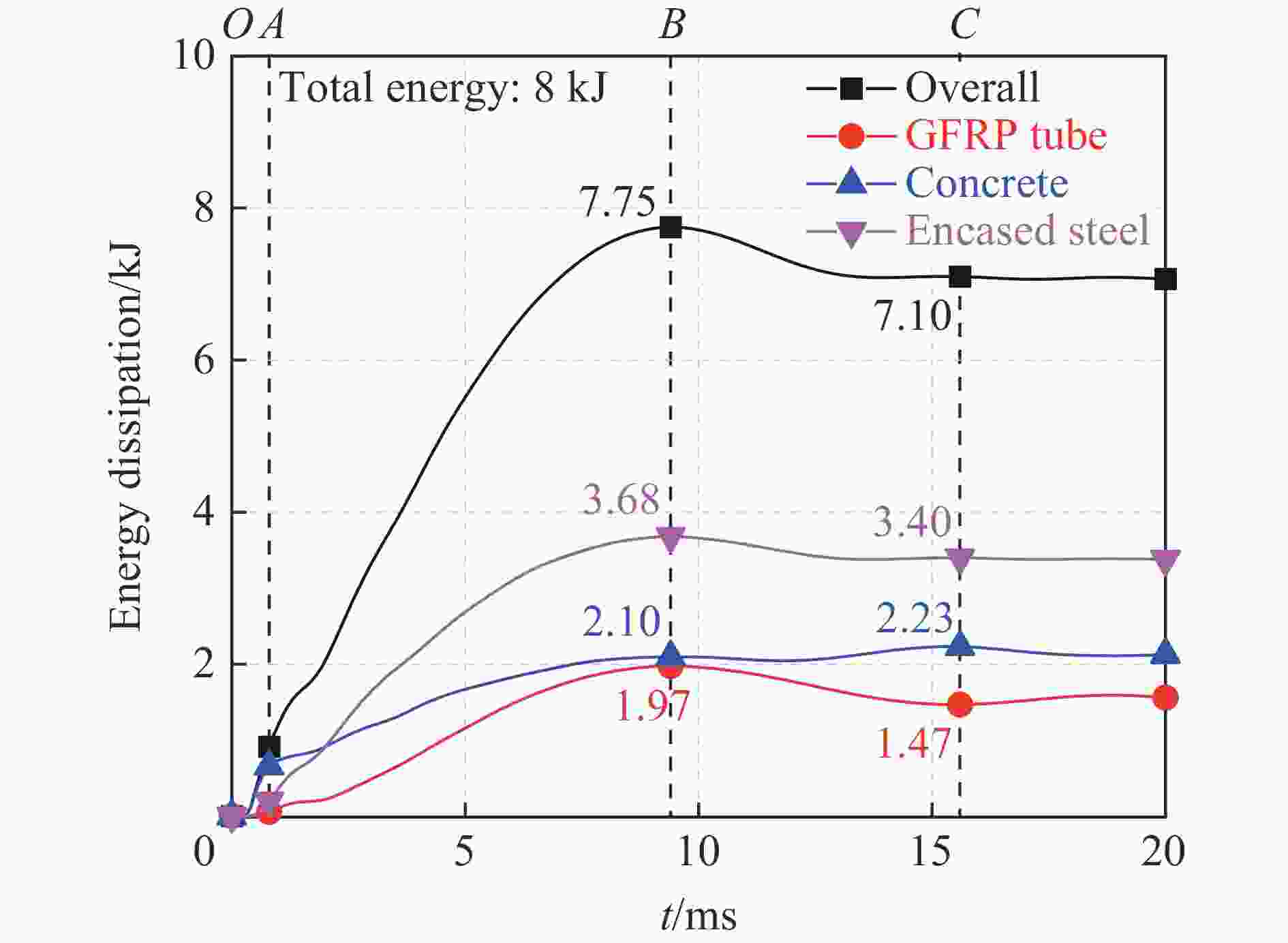
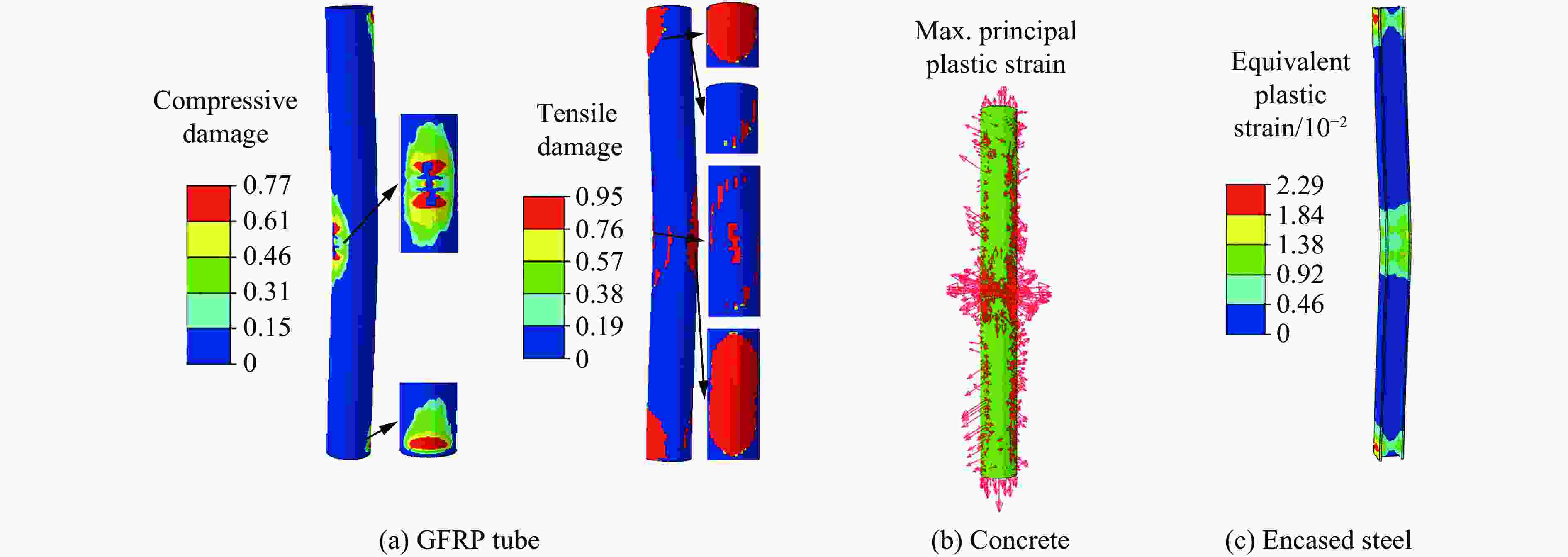
Abstract: To investigate the effect of the steel ratio on the impact resistance of glass fiber reinforced polymer (GFRP) tube concrete-encased steel composite members, 15 numerical models of composite members were established. The whole impact process, the dynamic response and the stress distribution of each composite member at different characteristic moments during the low-velocity impact were analyzed. The bending moment contributions at typical cross sections and the energy dissipation under different impact moments were explored. Meanwhile, the corresponding failure mode was determined, based on the maximum principal plastic strain distribution of concrete, tensile and compression damage of GFRP tube matrix, and equivalent plastic strain distribution of steel. Additionally, the effect of the steel ratio on the impact performance of members with different slenderness ratios was investigated by analyzing the time history curves of the impact force, displacement, energy transformation and energy consumption. The results show that the impact load-bearing capacity of GFRP tube concrete-encased steel members is improved by 7% to 134% and the lateral displacement is reduced by 13% to 68% compared with the GFRP tube concrete members. Furthermore, it can be observed that the failure mode of the members is mainly bending, and the concrete is crushed in the impact region. The bending stiffness has a significant influence on the impact performance of the member under lateral impact loading. The impact force of the member increases with the increase in the steel ratio, whereas the impact force of the member decreases with the increase in the slenderness ratio. Moreover, narrow flange steel with a higher moment of inertia is more favorable for the impact resistance of the member when the difference in steel ratio is 1.5%. The energy consumption of the encased steel is a major contributor to the total energy consumption of the member when the slenderness ratio is greater than or equal to 20. The GFRP tube plays a dual role in bearing the impact force and confining the concrete in a circumferential direction at the oscillation stage during the impact process. -
表 1 试件冲击力学性能
Table 1. Impact mechanical properties of specimens
表 2 低速冲击模型的参数
Table 2. Parameters for low velocity impact model
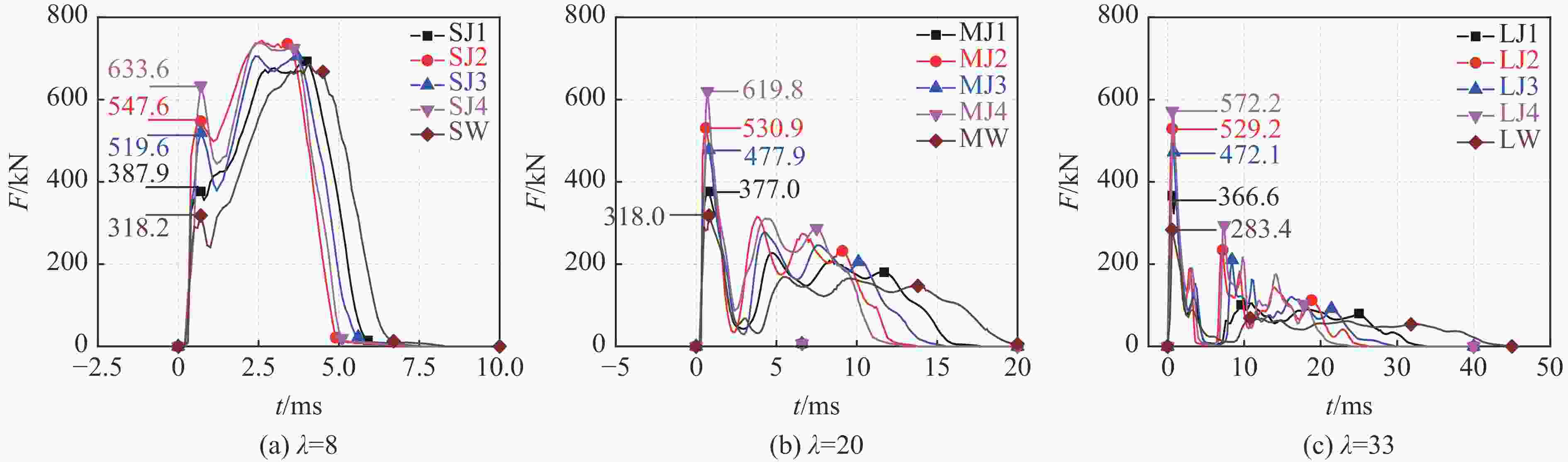
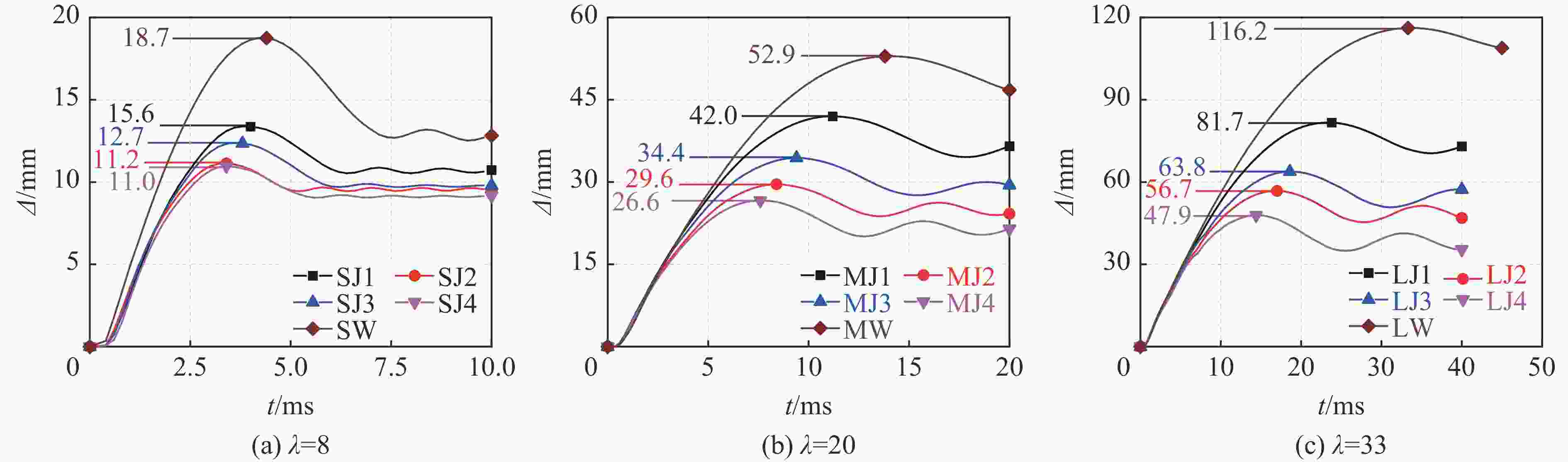
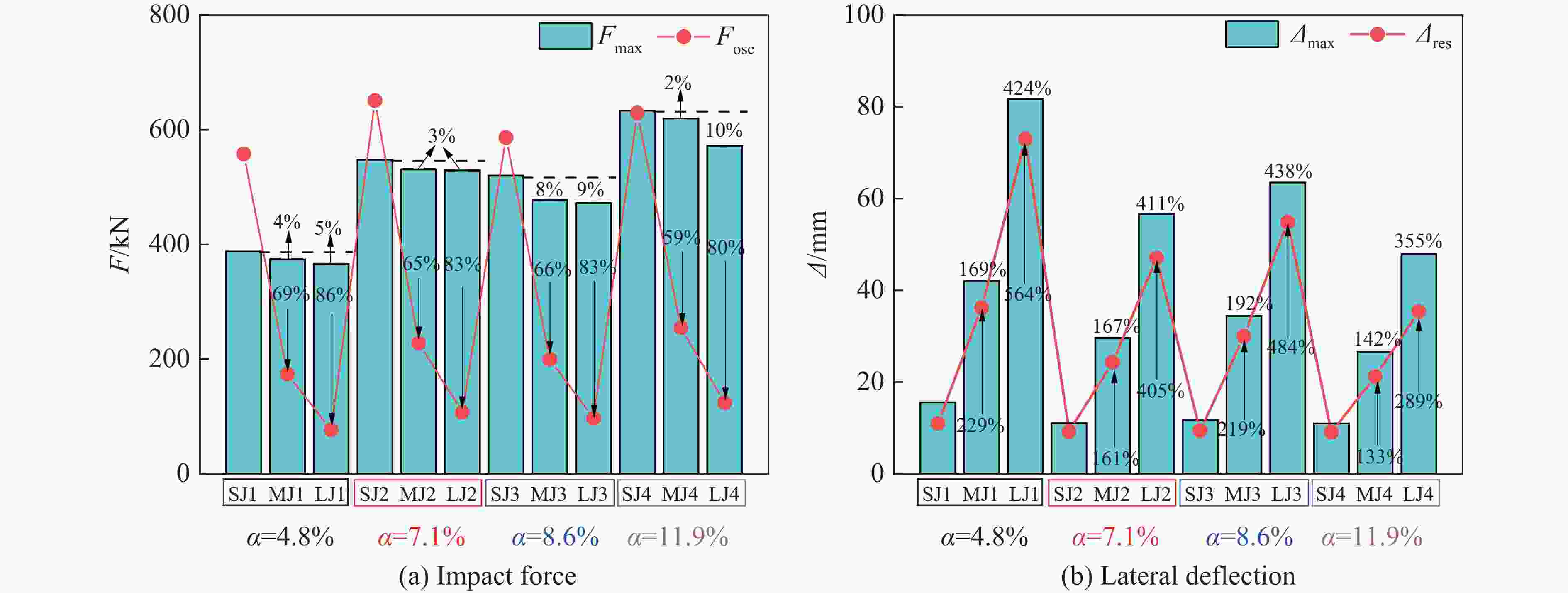
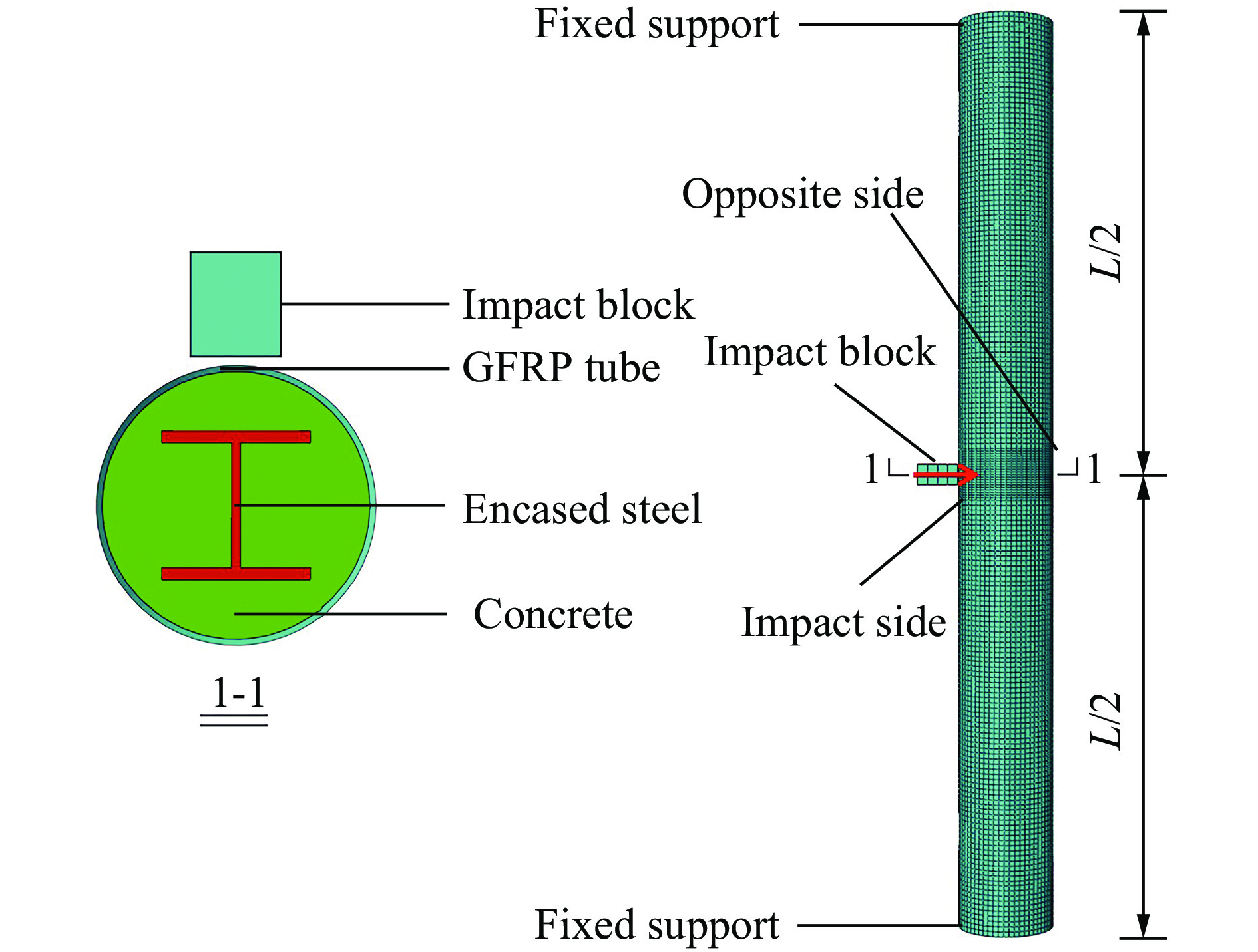
构件 L/mm λ H型钢 Fmax/kN Fosc/kN Δmax/mm 翼缘类型 α/% h×b×t1×t2/mm Ix/cm4 SW 700 8 — 0 — — 318 518 18.7 SJ1 700 8 窄 4.8 100×50×5×7 192 388 558 15.6 SJ2 700 8 窄 7.1 150×75×5×7 679 548 651 11.2 SJ3 700 8 宽 8.6 100×100×6×8 383 520 587 12.7 SJ4 700 8 宽 11.9 125×125×6.5×9 847 634 629 11.0 MW 1800 20 — 0 — — 318 138 52.9 MJ1 1800 20 窄 4.8 100×50×5×7 192 377 174 42.0 MJ2 1800 20 窄 7.1 150×75×5×7 679 531 228 29.6 MJ3 1800 20 宽 8.6 100×100×6×8 383 478 200 34.4 MJ4 1800 20 宽 11.9 125×125×6.5×9 847 620 255 26.6 LW 3000 33 — 0 — — 283 53 116.2 LJ1 3000 33 窄 4.8 100×50×5×7 192 367 77 81.7 LJ2 3000 33 窄 7.1 150×75×5×7 679 529 108 56.7 LJ3 3000 33 宽 8.6 100×100×6×8 383 472 97 63.8 LJ4 3000 33 宽 11.9 125×125×6.5×9 847 572 124 47.9 表 3 构件耗能
Table 3. Energy consumption of members
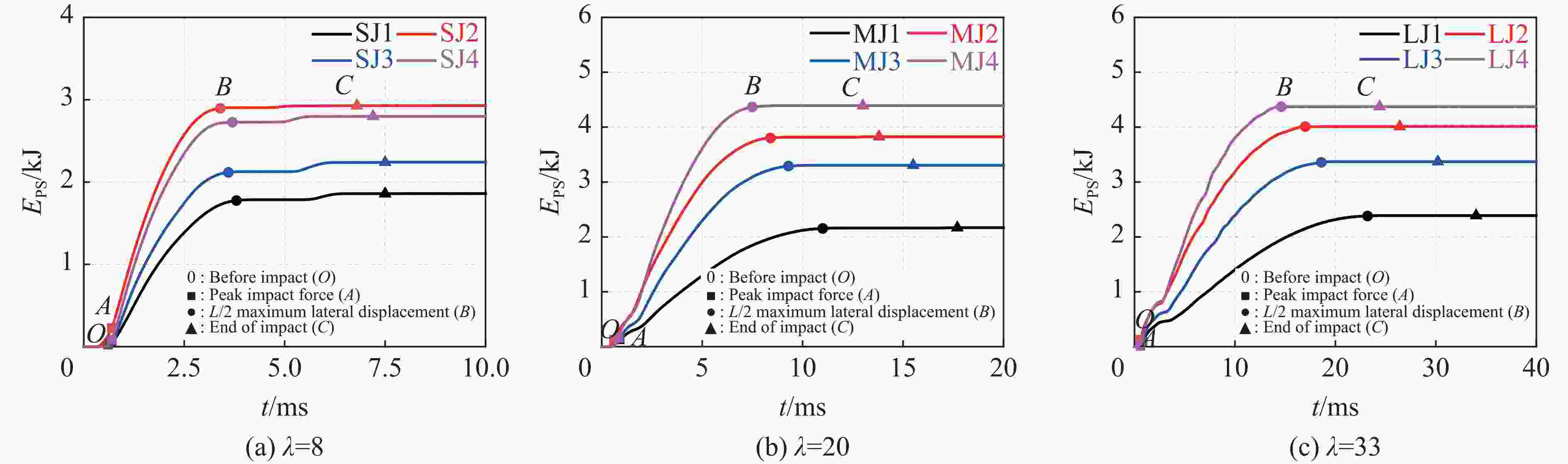
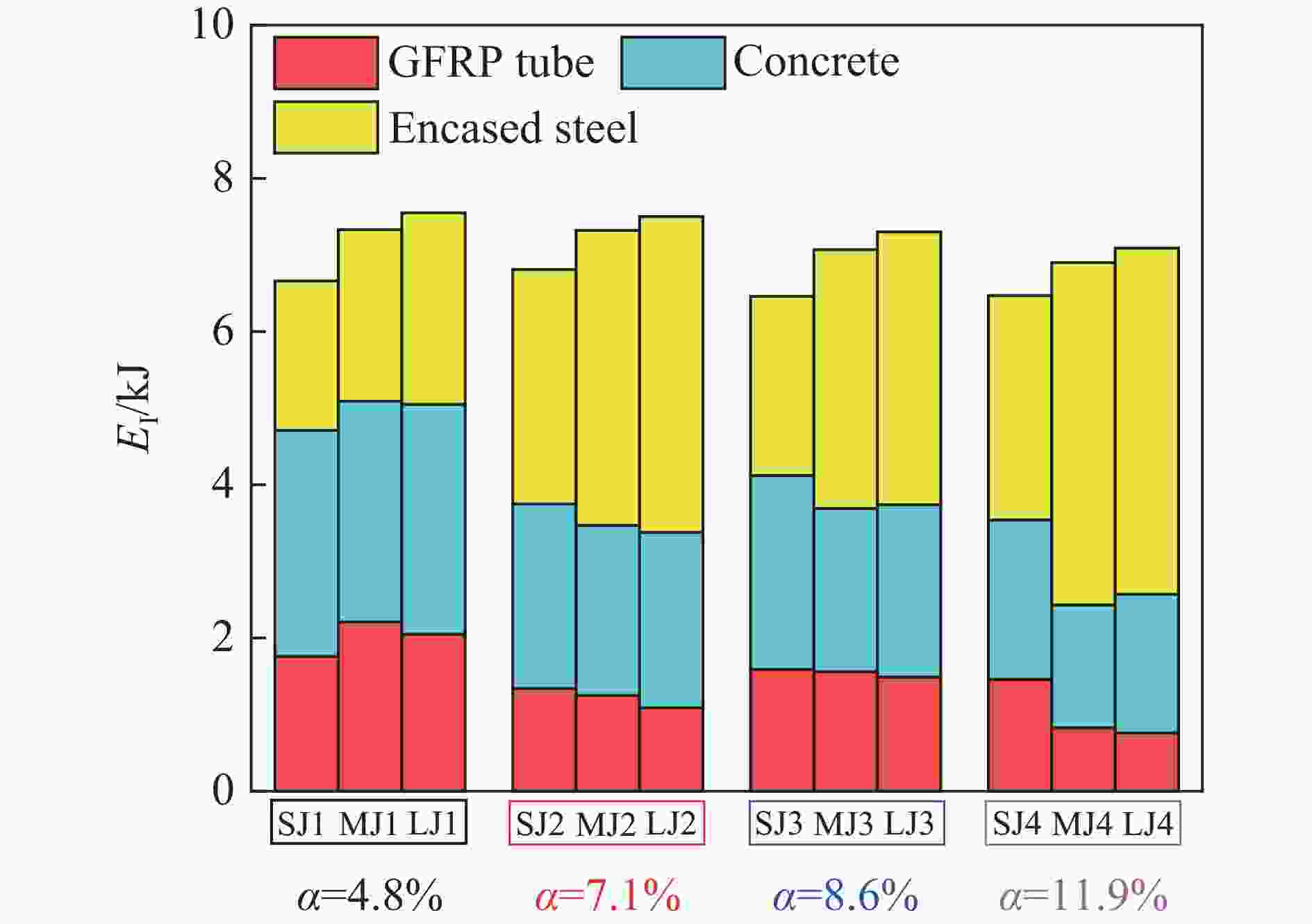
构件 EI/kJ EIC/kJ EIS/kJ EE/kJ EP/kJ EPS//kJ SW 6.46 4.10 2.94 3.38 SJ1 6.66 2.95 1.95 2.15 4.20 1.86 SJ2 6.81 2.41 3.06 1.79 4.79 2.93 SJ3 6.46 2.53 2.34 1.97 4.14 2.24 SJ4 6.47 2.08 2.93 1.77 4.41 2.80 MW 7.42 4.04 4.16 3.16 MJ1 7.33 2.88 2.24 2.66 4.36 2.17 MJ2 7.32 2.22 3.95 1.82 5.34 3.82 MJ3 7.07 2.13 3.38 2.00 4.84 3.31 MJ4 6.90 1.60 4.47 1.19 5.50 4.39 LW 7.60 4.02 4.23 3.25 LJ1 7.55 3.00 2.50 2.77 4.58 2.39 LJ2 7.50 2.29 4.12 1.78 5.56 4.01 LJ3 7.30 2.25 3.56 2.42 4.64 3.37 LJ4 7.09 1.81 4.52 1.25 5.60 4.37 -
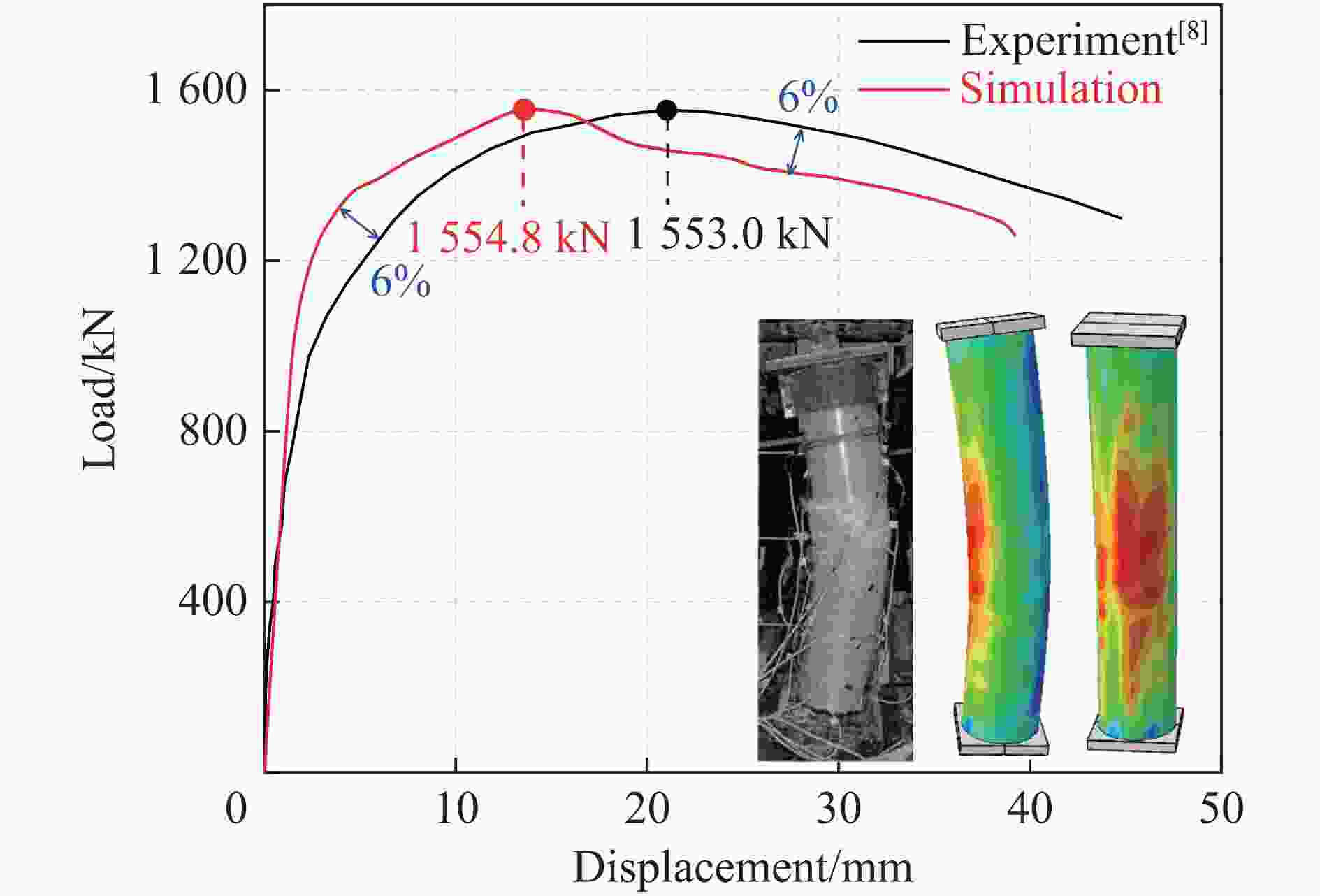
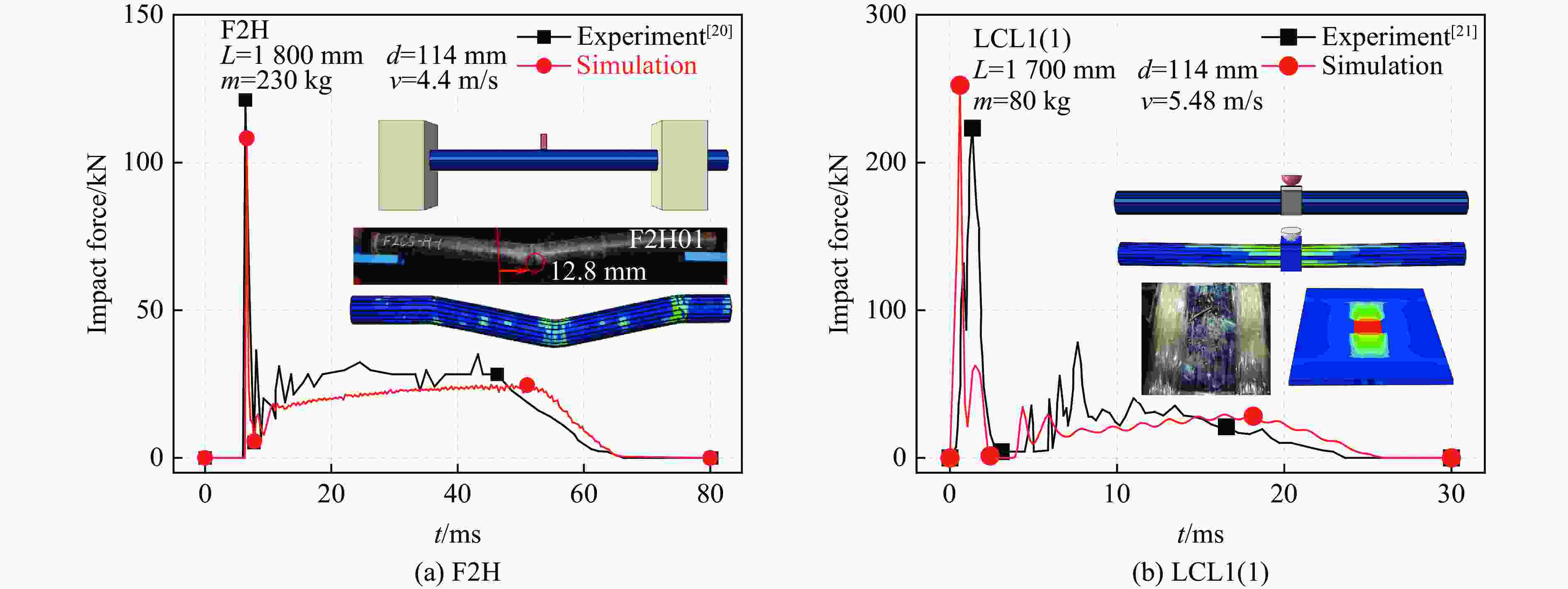
[1] 韩林海. 钢管混凝土结构-理论与实践 [M]. 3版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2017: 1–68.HAN L H. Concrete filled steel tubular structures-theory and practice [M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: Science Press, 2017: 1–68. [2] 吴智深, 汪昕, 吴刚. FRP增强工程结构体系 [M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2017: 1–106.WU Z S, WANG X, WU G. FRP reinforced engineering structural systems [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2017: 1–106. [3] 于冬雪, 于化杰, 黎红兵, 等. FRP建筑材料的结构性能及应用综述 [J]. 材料导报, 2021, 35(S2): 660–668.YU D X, YU H J, LI H B, et al. Structure, property and application as building materials of FRP: a review [J]. Materials Reports, 2021, 35(S2): 660–668. [4] 张海霞, 刘鹤, 孙云杰. 内置钢骨GFRP管混凝土中长柱偏压承载力分析 [J]. 合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 40(7): 965–970. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5060.2017.07.020.ZHANG H X, LIU H, SUN Y J. Analysis of bearing capacity of steel-encased concrete filled GFRP tubes middle-long column subjected to eccentric compression load [J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology (Natural Science), 2017, 40(7): 965–970. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5060.2017.07.020. [5] HUANG L, YU T, ZHANG S S. FRP-confined concrete-encased cross-shaped steel columns: effects of key parameters [J]. Composite Structures, 2021, 272: 114252. DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2021.114252. [6] KARIMI K, TAIT M J, EL-DAKHAKHNI W W. Analytical modeling and axial load design of a novel FRP-encased steel-concrete composite column for various slenderness ratios [J]. Engineering Structures, 2013, 46: 526–534. DOI: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2012.08.016. [7] YU T, LIN G, ZHANG S S. Compressive behavior of FRP-confined concrete-encased steel columns [J]. Composite Structures, 2016, 154: 493–506. DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2016.07.027. [8] 曹朋朋. FRP管约束钢骨混凝土中长柱偏压力学性能研究 [D]. 沈阳: 沈阳建筑大学, 2013: 13–63.CAO P P. Mechanical behavior of steel-encased concrete filled FRP tube column under unidirectional eccentric compression [D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Jianzhu University, 2013: 13–63. [9] PAN M L, WANG D Y, PEI W C, et al. Monotonic and cyclic compression behavior of axially loaded FRP-confined concrete-encased cross-shaped steel columns [J]. Composite Structures, 2023, 307: 116632. DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2022.116632. [10] ZHANG H X, JU S L, CHEN H. Seismic performance of GFRP tube concrete-encased steel composite columns under axial compression [J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2023, 200: 107641. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2022.107641. [11] 孙浩. 两端固支的GFRP管-钢骨混凝土构件抗冲击性能研究 [D]. 沈阳: 沈阳建筑大学, 2023: 13–73. DOI: 10.27809/d.cnki.gsjgc.2022.000253.SUN H. Study on impact resistance of steel-encased concrete filled GFRP tubes member with fixed ends [D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Jianzhu University, 2023: 13–73. DOI: 10.27809/d.cnki.gsjgc.2022.000253. [12] 白慧宇. GFRP管约束十字钢骨混凝土方柱轴向冲击性能研究 [D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2022: 14–100. DOI: 10.27061/d.cnki.ghgdu.2022.004620.BAI H Y. Axial impact behavior of GFRP tube-confined concrete-encased cross-shaped steel square columns [D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2022: 14–100. DOI: 10.27061/d.cnki.ghgdu.2022.004620. [13] 刘烨, 王蕊, 李志刚. CFRP-混凝土-钢管组合结构在低速侧向撞击下的动力响应 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2018, 38(4): 759–767. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2016-0349.LIU Y, WANG R, LI Z G. Finite element analysis of CFRP-concrete-steel composite structure under low velocity lateral impact loading [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2018, 38(4): 759–767. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2016-0349. [14] HSIAO H M, DANIEL I M, CORDES R D. Strain rate effects on the transverse compressive and shear behavior of unidirectional composites [J]. Journal of Composite Materials, 1999, 33(17): 1620–1642. DOI: 10.1177/002199839903301703. [15] HALLETT S R, RUIZ C, HARDING J. The effect of strain rate on the interlaminar shear strength of a carbon/epoxy cross-ply laminate: comparison between experiment and numerical prediction [J]. Composites Science and Technology, 1999, 59(5): 749–758. DOI: 10.1016/S0266-3538(98)00117-1. [16] LAM L, TENG J G. Stress-strain model for FRP-confined concrete under cyclic axial compression [J]. Engineering Structures, 2009, 31(2): 308–321. DOI: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2008.08.014. [17] TAO Z, WANG Z B, YU Q. Finite element modelling of concrete-filled steel stub columns under axial compression [J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2013, 89: 121–131. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2013.07.001. [18] Fib model code for concrete structures 2010 [Z]. Berlin: Ernst & Sohn, 2013. [19] 侯川川. 低速横向冲击荷载下圆钢管混凝土构件的力学性能研究 [D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2012: 50–51.HOU C C. Study on performance of circular concrete-filled steel tubular (CFST) members under low velocity transverse impact [D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2012: 50–51. [20] WANG R, HAN L H, TAO Z. Behavior of FRP-concrete-steel double skin tubular members under lateral impact: experimental study [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2015, 95: 363–373. DOI: 10.1016/j.tws.2015.06.022. [21] CHEN C, ZHAO Y H, LI J. Experimental investigation on the impact performance of concrete-filled FRP steel tubes [J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 2015, 141(2): 04014112. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)EM.1943-7889.0000833. [22] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 组合结构设计规范: JGJ 138—2016 [S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2016.Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Code for design of composite structures: JGJ 138—2016 [S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2016. [23] WU Q J, ZHI X D, LI Q X, et al. Experimental and numerical studies of GFRP-reinforced steel tube under low-velocity transverse impact [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2019, 127: 135–153. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2019.01.010. [24] SHARMA H, HURLEBAUS S, GARDONI P. Performance-based response evaluation of reinforced concrete columns subject to vehicle impact [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2012, 43: 52–62. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2011.11.007. [25] ZHU X, ZHAO P J, TIAN Y, et al. Experimental study of RC columns and composite columns under low-velocity impact [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2021, 160: 107374. DOI: 10.1016/j.tws.2020.107374. -






 下载:
下载: