Damage characteristic of target penetrated by WF/Zr-MG and 93W rods
-
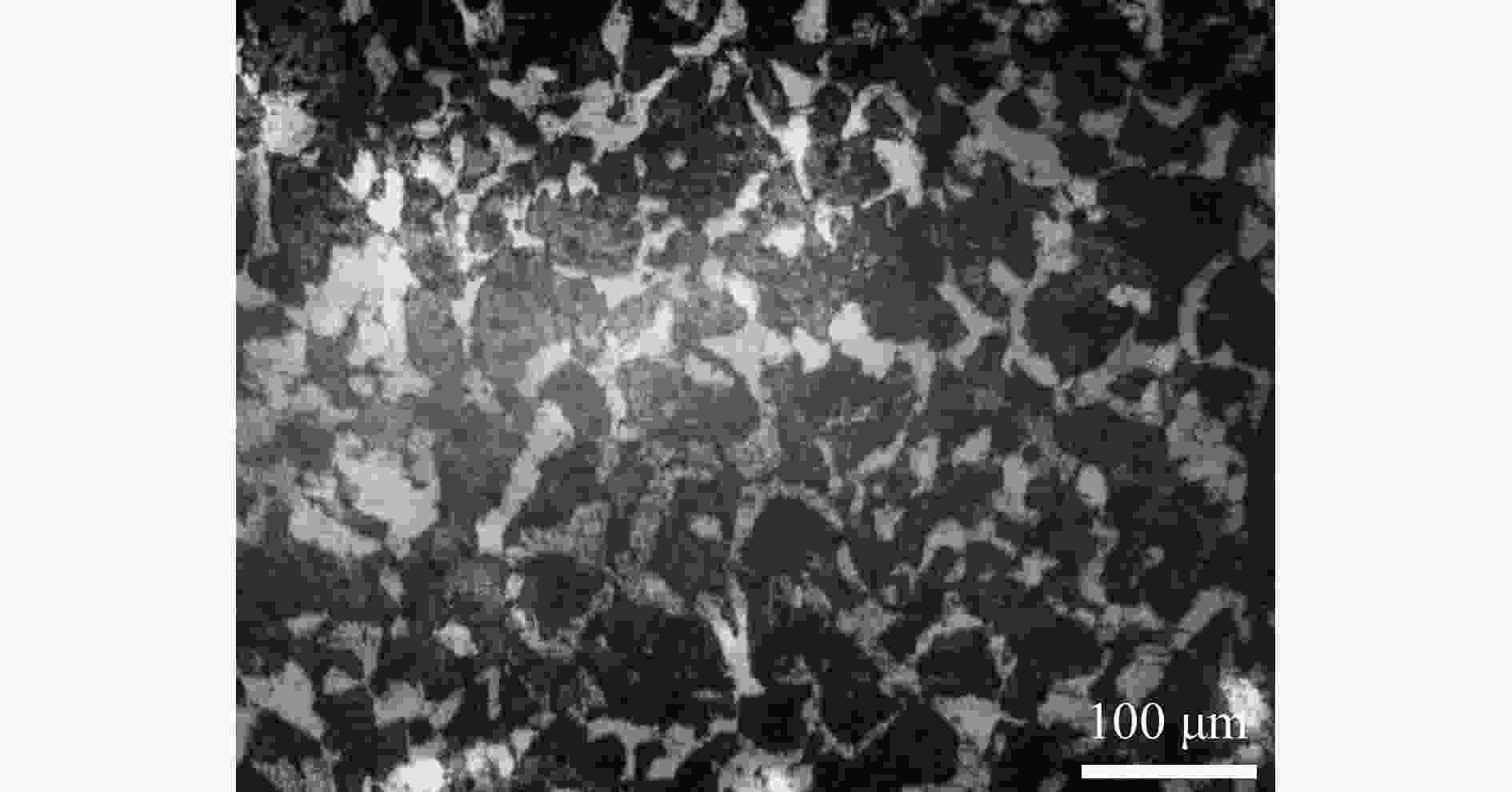
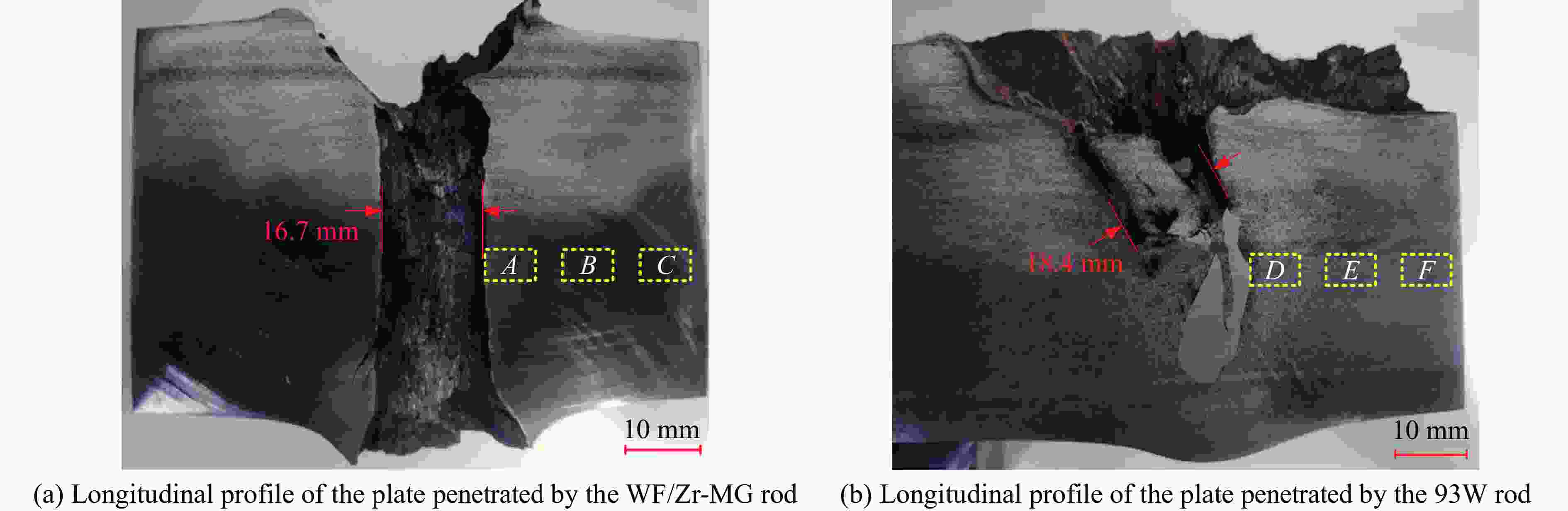
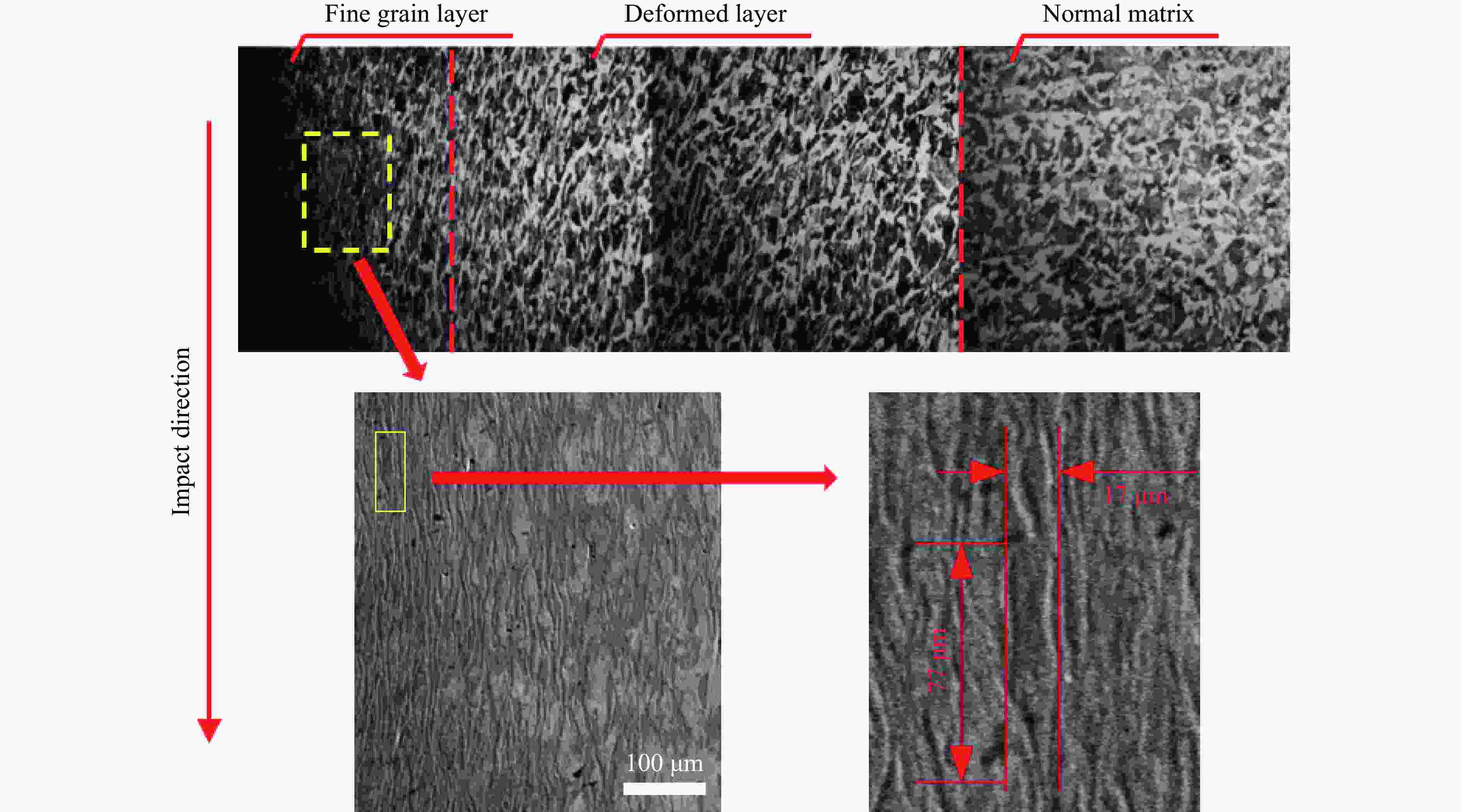
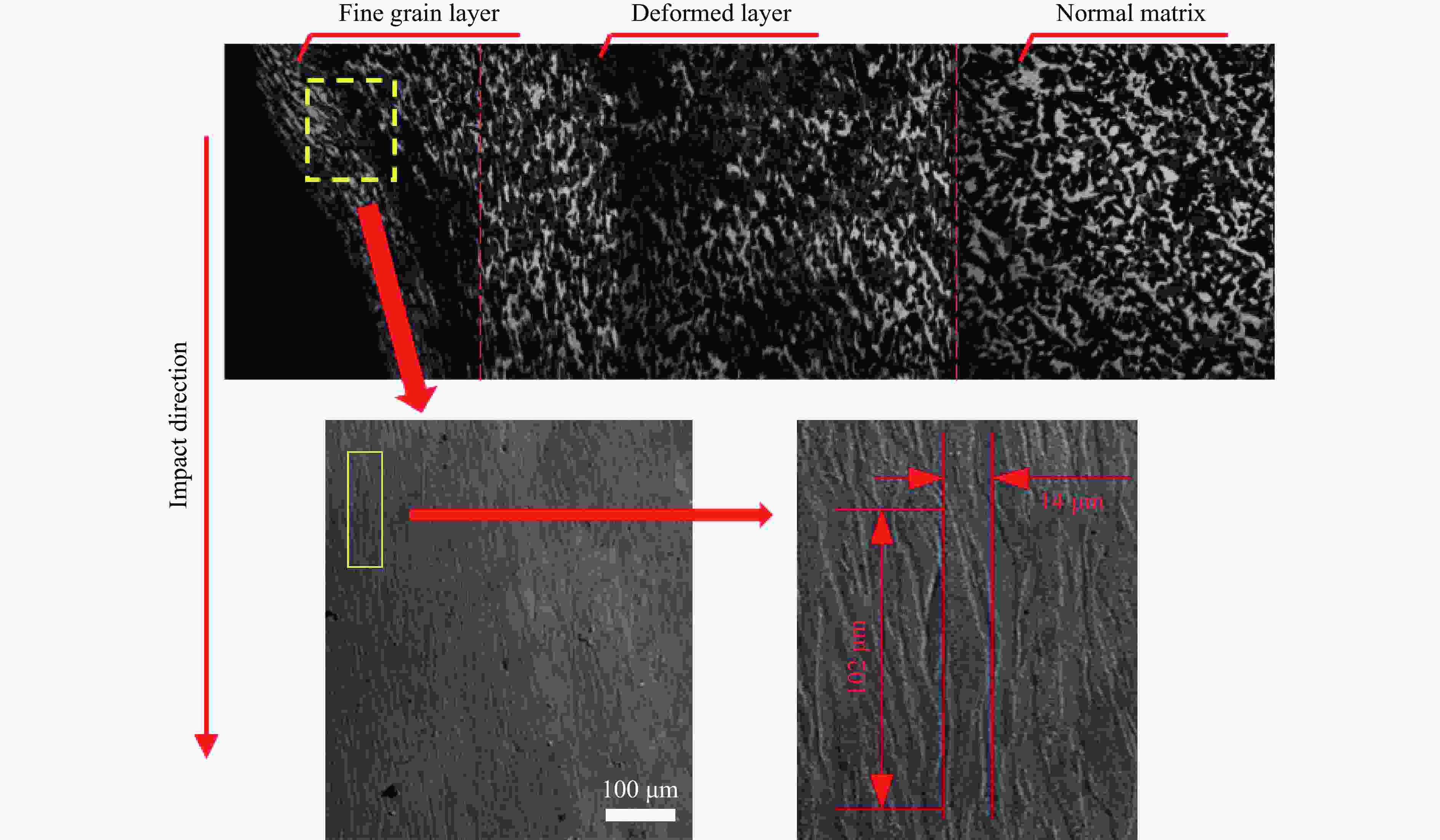
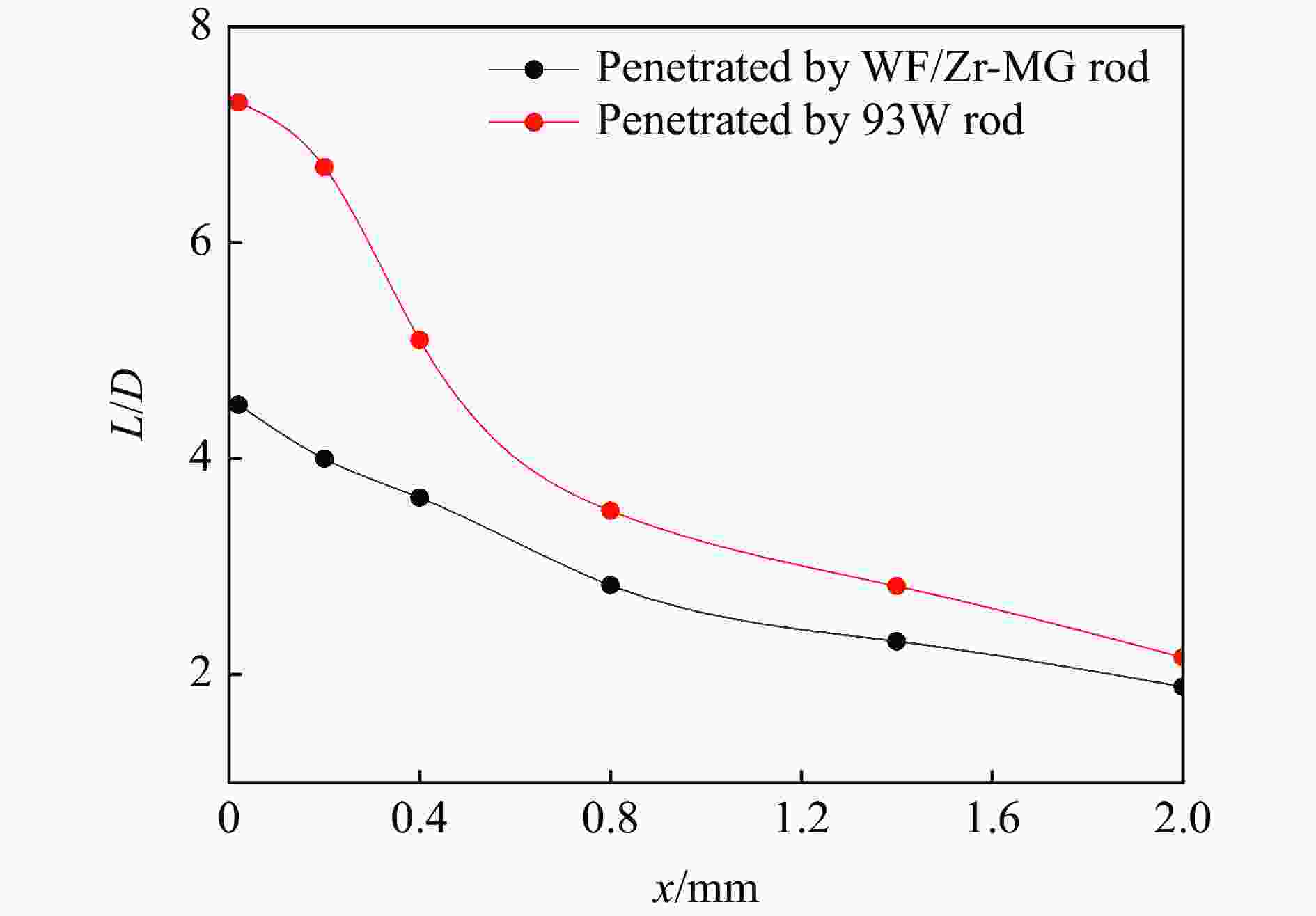
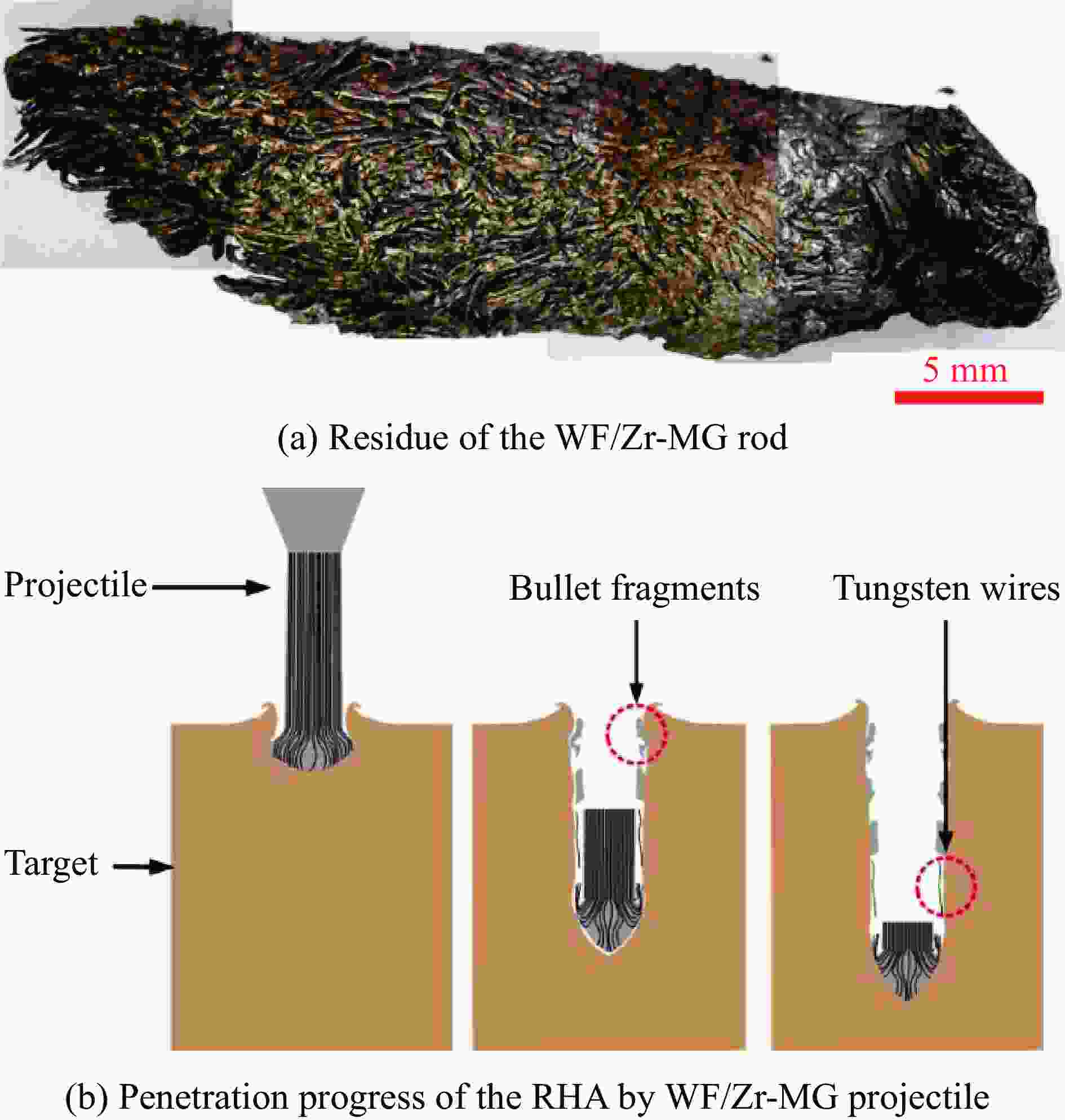
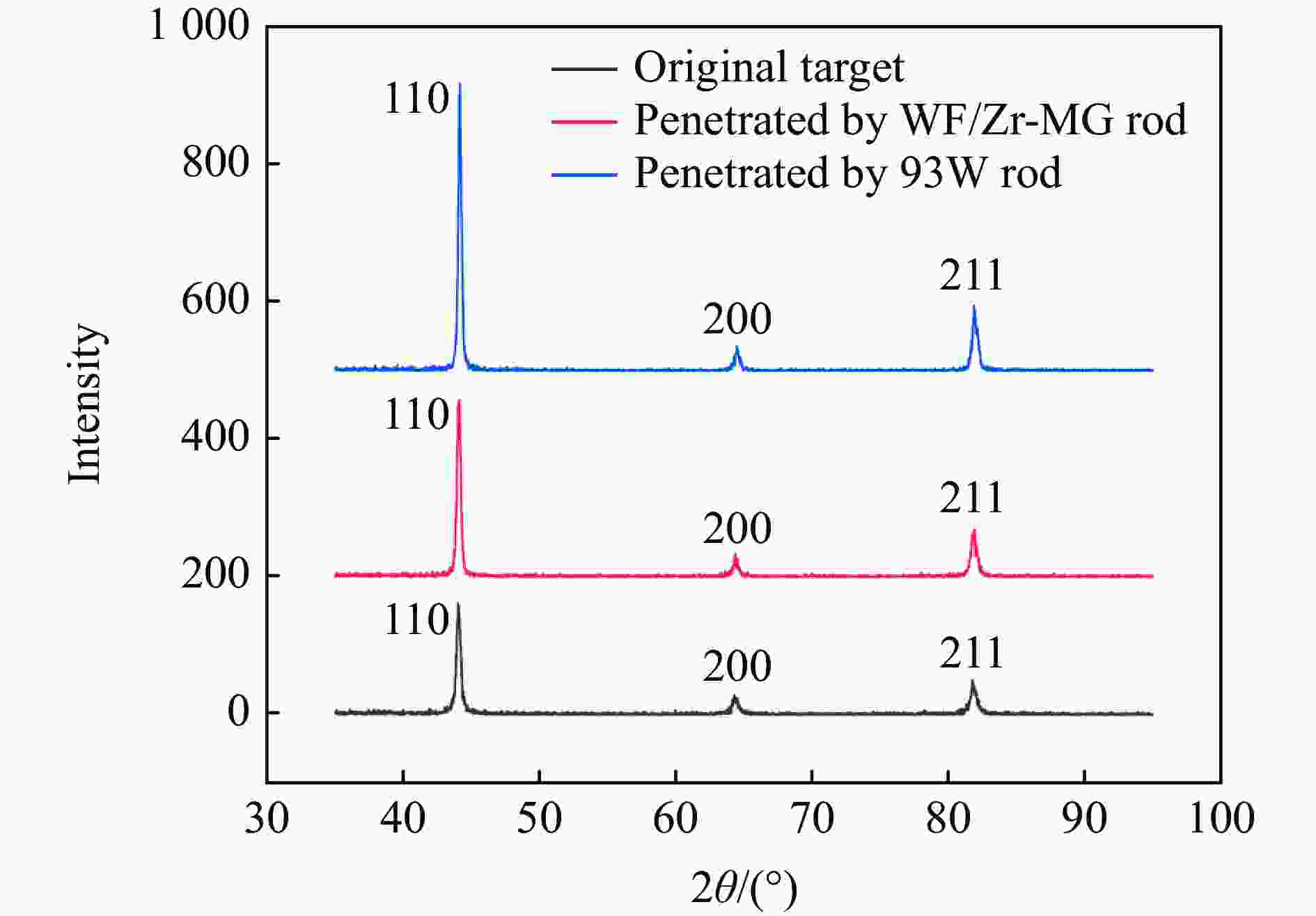
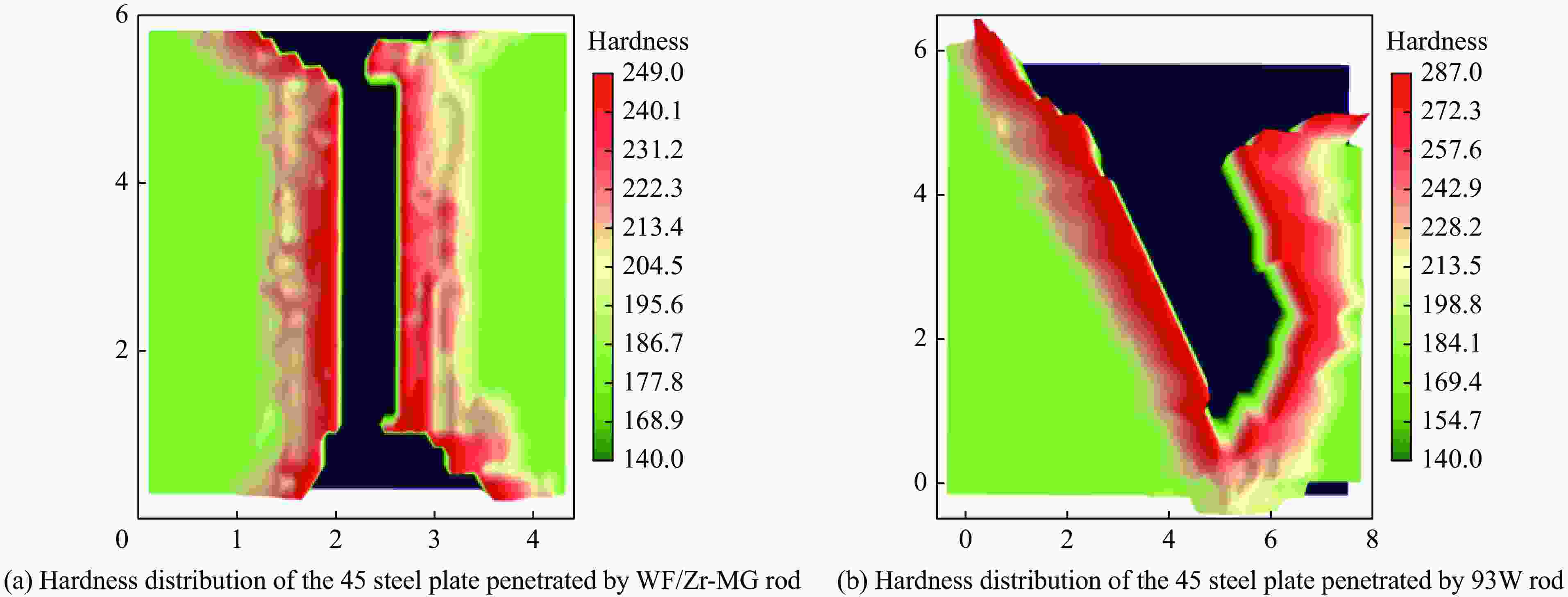
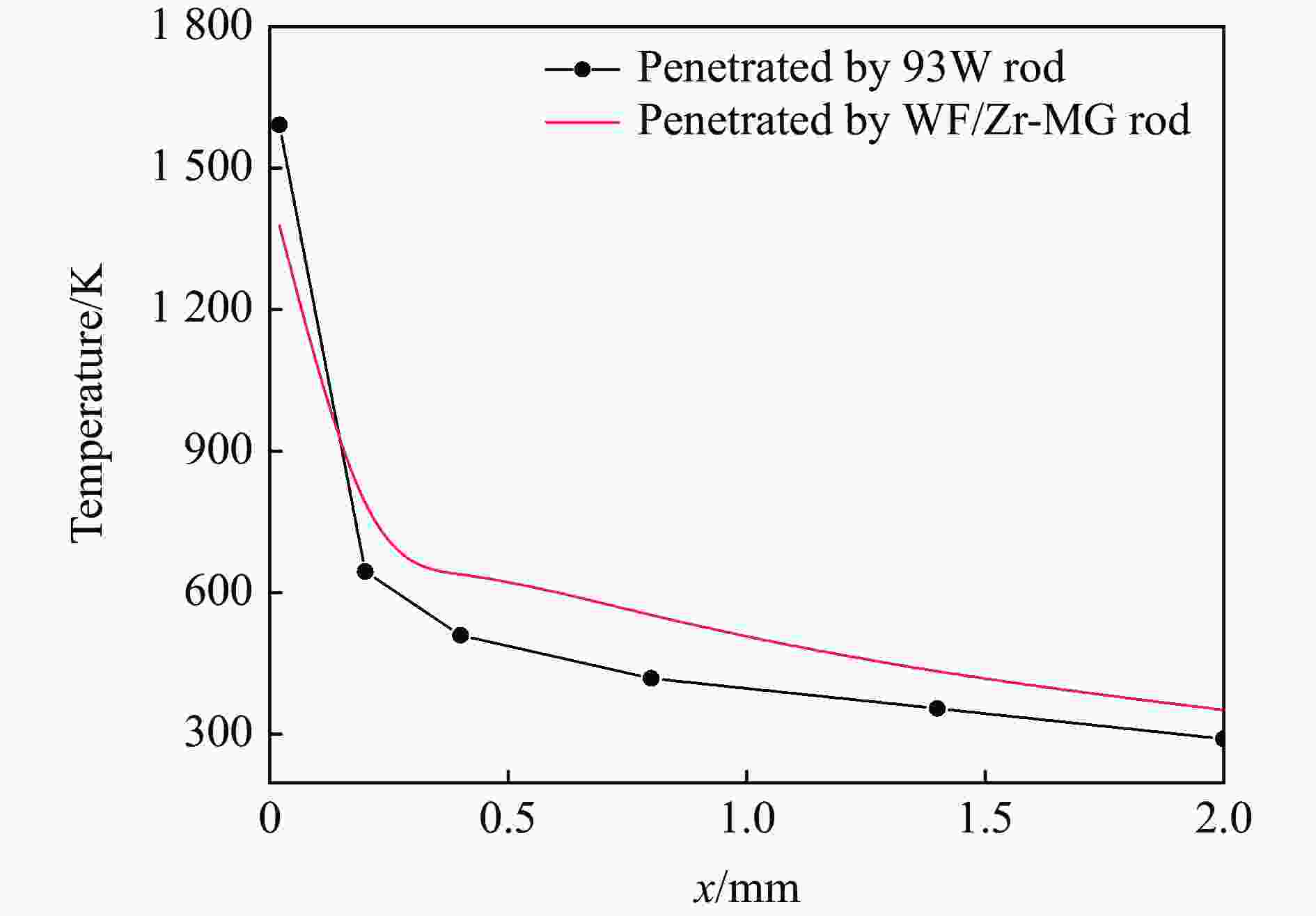
摘要: 为研究钨丝/锆基非晶复合材料(WF/Zr-based bulk metallic glass matrix composite,WF/Zr-MG)及93W合金两种弹芯材料对于45钢靶板的侵彻特征机理与损伤特征,利用上述两种弹芯进行对比开展侵彻试验,在宏观和微观层面对侵彻结果进行分析,其中,宏观定量化表征量采用等效直径进行研究,微观层面利用扫描电镜、光学显微镜、XRD衍射仪与显微维氏硬度仪对靶板的微观形貌、相变及硬度特征进行表征。试验结果表明,WF/Zr-MG弹芯完全贯穿靶板,而93W合金弹芯残留于靶板之中,其等效扩孔直径分别为16.7和18.4 mm,前者较后者低10.18%,WF/Zr-MG弹芯的穿甲能力高于93W合金弹芯。在微观角度,WF/Zr-MG与93W合金弹芯侵彻后弹坑细晶层晶粒长径比分别为4.5和7.3,其维氏硬度HV的峰值分别为249和287,其中高硬度层宽度分别为10.2和8.9 mm。前者对应靶板高硬度层更宽的原因是Zr基非晶合金在侵彻过程中持续释放热量,使其温度影响区较大,因此硬度提升的区域大。侵彻过程中,后者的靶板强度明显高于前者的,其主要原因为WF/Zr-MG弹芯发生屈曲回流,而93W合金弹芯产生蘑菇头现象,使得WF/Zr-MG弹芯对于靶板的挤压变形更小,晶粒拉长效果减弱,硬度峰值提升变小,靶板单位长度的能量损耗小,从而增强WF/Zr-MG复合材料弹芯的穿甲能力。
-
关键词:
- WF/Zr-MG复合材料 /
- 93W /
- 微观分析 /
- 硬度分析 /
- 损伤特征
Abstract: In order to compare and analyze the characteristic and mechanism of damaging on 45 steel target plate penetrated by the WF/Zr-MG and 93W rod, a penetration experiment under hypervelocity impact was carried out. The analysis of penetration was performed at both macro and micro levels, in which the macroscopic quantitative characterization quantity was studied by equivalent diameter of reamer, and the microscopic morphology, phase transition and hardness characteristics of the target plate were obtained by scanning electron microscopy, optical microscope, X-ray diffraction and microhardness tester.The experimental results indicate that the WF/Zr-MG rod completely penetrated the target plate, while the 93W rod remained in the target plate. The armor-piercing capacity of WF/Zr-MG rod is higher than that of 93W rod with equivalent reaming diameter of 16.7 mm and 18.4 mm respectively, and the former is 10.18% lower than the latter. From the microscopic perspective, the aspect ratios of the fine grain layer after penetrated by the WF/Zr-MG rod and the 93W rod are 4.5 and 7.3, respectively. In addition, the width of the high-hardness layer are 10.2 mm and 8.9 mm, with Vickers hardness HV peaks at 249 and 287, respectively. The wider high-hardness layer observed in the former case can be attributed to the continuous burning of the Zr-based amorphous alloy during the penetration process, resulting in a larger temperature affected zone and consequently a greater area of hardness enhancement. On the other hand, in the latter case, the strength of the target plate during penetration is significantly higher due to the buckling and backflow of the WF/Zr-MG rod, while the 93W alloy core exhibits a "mushroom head" phenomenon. This reduces extrusion deformation on the target plate, thereby weakening the effect of grain elongation, reducing the increase in hardness peak value, and minimizing energy loss per unit length of the target plate. Ultimately, it enhances the armor-piercing capability of the WF/Zr-MG rod.-
Key words:
- WF/Zr-MG /
- 93W /
- micro analysis /
- hardness analysis /
- damage characteristic
-
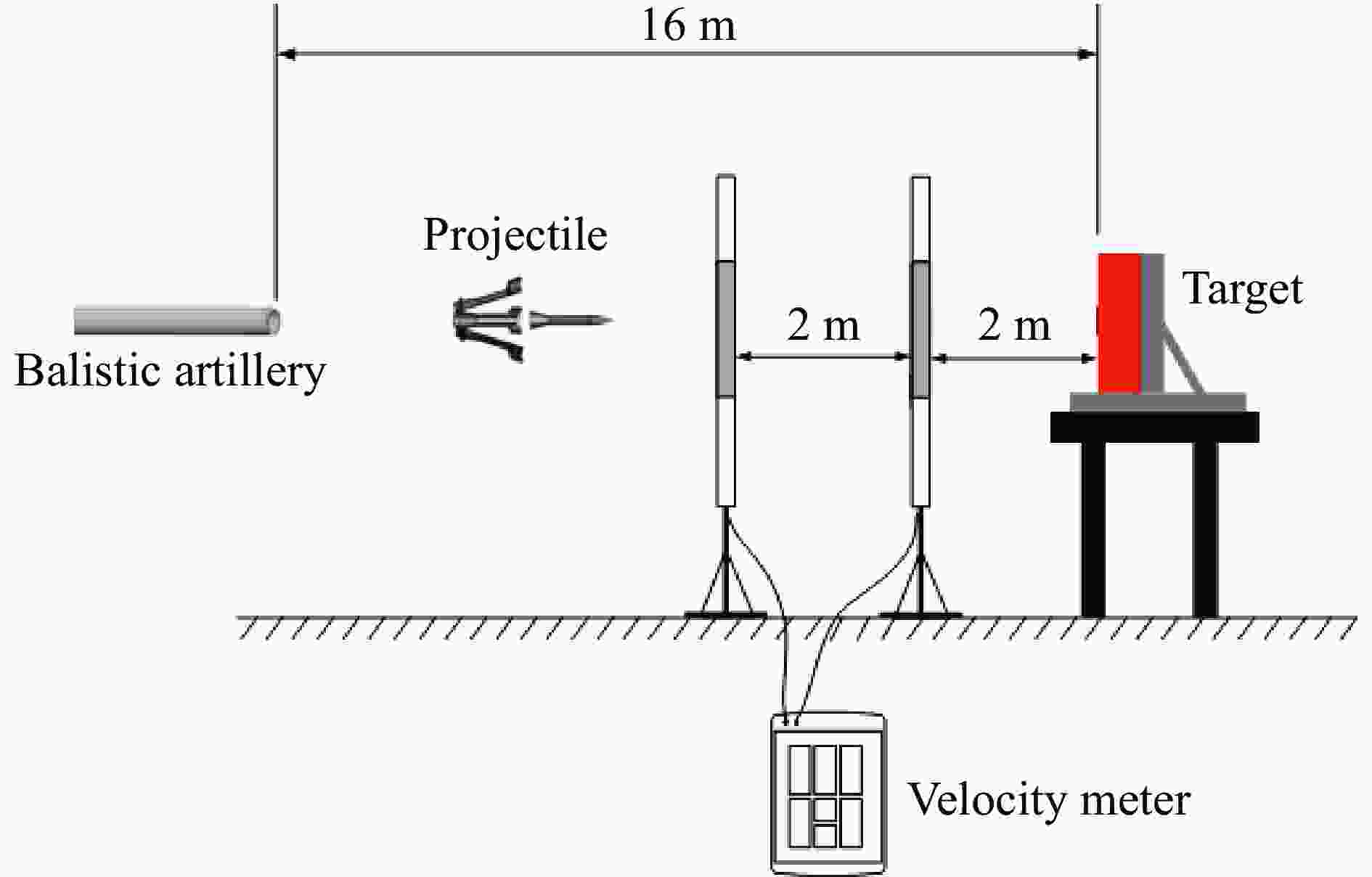
表 1 试验弹芯主要参数及状态
Table 1. Main parameters and test states of all projectiles used in the test
工况 材料 质量/g 侵彻速度/(m∙s−1) 1 93W 122.6±0.1 1558±50 2 WF/Zr-MG 121.9±0.1 1543±50 -
[1] WANG H K, LI Z Z, ZHANG Z H, et al. Microstructure evolution of 6252 armor steel under hypervelocity impact [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2022, 170(12): 104356. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2022.104356. [2] HE Y, ZHANG Z, YANG S, et al. Deformation and fracture mechanism of Ti-6Al-4V target at high and hyper velocity impact [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2022, 169(12): 104312. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2022.104312. [3] ZHENG Z, ZHU D, DING X, et al. Hypervelocity impact damage and microstructure evolution of woven Ti6Al4V fabric reinforced aluminum matrix composites [J]. Materials & Design, 2016, 108(10): 86–92. DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2016.06.075. [4] ZHOU F, DU C X, CHENG C, et al. Penetration performance and fragmentation mechanism behind target of tungsten fibre/zirconium-based bulk metallic glass matrix composite rod [J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2023, 112(4): 106160. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2023.106160. [5] 李名锐, 冯娜, 蔡青山, 等. 93W杆式弹超高速撞击多层Q345钢靶毁伤及微观分析 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2021, 41(2): 021408. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0303.LI M R, FENG N, CAI Q S, et al. Damage of a multi-layer Q345 target under hypervelocity impact of a rod-shaped 93W projectile [J]. Explosion And Shock Waves, 2021, 41(2): 021408. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0303. [6] 高华, 熊超, 殷军辉. 弹丸侵彻多层异质复合靶板中装甲钢变形细观和微观机理研究 [J]. 兵工学报, 2018, 39(8): 1565–1575. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2018.08.013.GAO H, XIONG C, YIN J H. Research on macroscopic and microscopic mechanisms of deformation of armor steel in multilayer heterogeneous compositetarget subjected to projectile [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2018, 39(8): 1565–1575. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2018.08.013. [7] 罗荣梅, 黄德武, 杨明川, 等. 杆式穿甲弹侵彻靶板时弹坑表面熔化快凝层研究 [J]. 兵工学报, 2015, 36(7): 1167–1175. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2015.07.003.LUO R M, HUANG D W, YANG M C, et al. Research on melted and rapidly solidified layer on the surface of crater penetrated by long tungsten rod [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2015, 36(7): 1167–1175. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2015.07.003. [8] 邹敏明, 郭珉, 柴东升, 等. 钨丝增强锆基非晶材料弹芯侵彻弹坑特征研究 [J]. 兵器材料科学与工程, 2021, 44(4): 56–60. DOI: 10.14024/j.cnki.1004-244x.20210514.009.ZOU M M, GUO M, CHAI D S, et al. Morphological characteristics of penetration crater of tungsten wire reinforced zirconium based amorphous matrix composite [J]. Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2021, 44(4): 56–60. DOI: 10.14024/j.cnki.1004-244x.20210514.009. [9] 侯杰, 陈曦, 杜忠华, 等. W-Cu-Zr基非晶粉末药型罩射孔弹侵彻行为研究 [J]. 兵器材料科学与工程, 2022, 45(4): 12–17. DOI: 10.14024/j.cnki.1004-244x.20220701.004.HOU J, CHEN X, DU Z H, et al. Penetration behavior of W-Cu-Zr amorphous powder liner [J]. Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2022, 45(4): 12–17. DOI: 10.14024/j.cnki.1004-244x.20220701.004. [10] 晁振龙, 姜龙涛, 陈圣朋, 等. 55%B4C/7075Al复合材料抗弹性能与损伤行为研究 [J]. 兵器材料科学与工程, 2020, 43(3): 1–7. DOI: 10.14024/j.cnki.1004-244x.20200115.005.CHAO Z L, JIANG L T, Chen S P , et al. Ballistic property and damage behavior of 55% B4C/7075Al composites [J]. Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2020, 43(3): 1–7. DOI: 10.14024/j.cnki.1004-244x.20200115.005. [11] 黄竣皓, 王琳, 刘小品, 等. Ti-6321钛合金力学性能和抗弹性能 [J]. 兵工学报, 2021, 42(1): 124–132. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2021.01.014.HUANG J H, WANG L, LIU X P, et al. Mechanical properties and ballistic performance of Ti-6321 alloy [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2021, 42(1): 124–132. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2021.01.014. [12] 李明兵, 王新南, 商国强, 等. 双态组织TC32钛合金的抗弹性能及损伤机制 [J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2021, 31(2): 365–372. DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-37761.LI M B, WANG X N, SHANG G Q, et al. Ballistic properties and failure mechanisms of TC32 titanium alloy with bimodal microstructure [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2021, 31(2): 365–372. DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-37761. [13] 苏冠龙, 龚煦, 李玉龙, 等. TC4在动态载荷下的剪切行为研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2015, 35(4): 527–535. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2015)04-0527-09.SU G L, GONG X, LI Y L, et al. Shear behavior of TC4 alloy under dynamic loading [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2015, 35(4): 527–535. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2015)04-0527-09. [14] 张博. 高速撞击条件下镁合金损伤行为及变形机制研究 [D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2020: 1–25. DOI: 10.27061/d.cnki.ghgdu.2020.001729. [15] 陈海华, 张先锋, 刘闯, 等. 高熵合金冲击变形行为研究进展 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2021, 41(4): 041402. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0414.CHEN H H, ZHANG X F, LIU C, et al. Research progress on impact deformation behavior of high-entropy alloys [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2021, 41(4): 041402. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0414. [16] 高玉魁, 陶雪菲. 高速冲击表面处理对金属材料力学性能和组织结构的影响 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2021, 41(4): 041401. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0342.GAO Y K, TAO X F. A review on the influences of high speed impact surface treatments on mechanical properties and microstructures of metallic materials [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2021, 41(4): 041401. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0342. [17] 夏龙祥. 钨纤维增强块体金属非晶复合材料侵彻行为研究 [D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2014: 11–22. DOI: 10.7666/d.Y2520745. [18] ZHOU F, DU C X, DU Z, et al. Penetration gain study of a tungsten-fiber/zr-based metallic glass matrix Composite [J]. Crystals, 2022, 12(2): 284. DOI: 10.3390/cryst12020284. [19] WALKER J. Hypervelocity penetration modeling: momentum vs. energy and energy transfer mechanisms [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2001, 26(1-10): 809–822. DOI: 10.1016/S0734-743X(01)00134-8. [20] ELSHENAWY T, ELBEIH A, LI Q. Influence of target strength on the penetration depth of shaped charge jets into RHA targets [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2018, 136: 234–242. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2017.12.041. [21] HALL E O. The deformation and ageing of mild steel: III discussion of results [C]// Proceedings of the Physical Society. Section B. London, UK: Institute of Physics and the Physical Society, 1951: 747. DOI: 10.1088/0370-1301/64/9/303. [22] 陈昊, 陶钢. 铜射流侵彻后45#钢穿孔处的微观组织分层研究 [J]. 南京理工大学学报, 2011, 35(4): 498–501. DOI: 10.14177/j.cnki.32-1397n.2011.04.001.CHEN H, TAO G. Microstructure’s delamination on bore of 45# steel penetrated by copper jet [J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2011, 35(4): 498–501. DOI: 10.14177/j.cnki.32-1397n.2011.04.001. [23] 胡昌明, 贺红亮, 胡时胜. 45号钢的动态力学性能研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2003, 23(2): 188–192.HU C M, HE H L, HU S S. Study on dynamic mechanical properties of No. 45 steel [J]. Explosion And Shock Waves, 2003, 23(2): 188–192. [24] 尚春明, 施冬梅, 张云峰等. Zr基非晶合金的燃烧释能特性[J]. 含能材料, 2020, 28(6): 564–568. DOI: 10.11943/CJEM2019219.SHANG C M, SHI D M, ZHANG Y F, at al. Combustion and energy release characteristics of zr-based amorphous alloys [J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials, 2020, 28(6): 564–568. DOI: 10.11943/CJEM2019219. [25] LI D F, DONG H Y, WU K M, at al. Effects of cooling after rolling and heat treatment on microstructures and mechanical properties of Mo-Ti microalloyed medium carbon steel [J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2020, 773(C): 138808. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2019.138808. -






 下载:
下载: