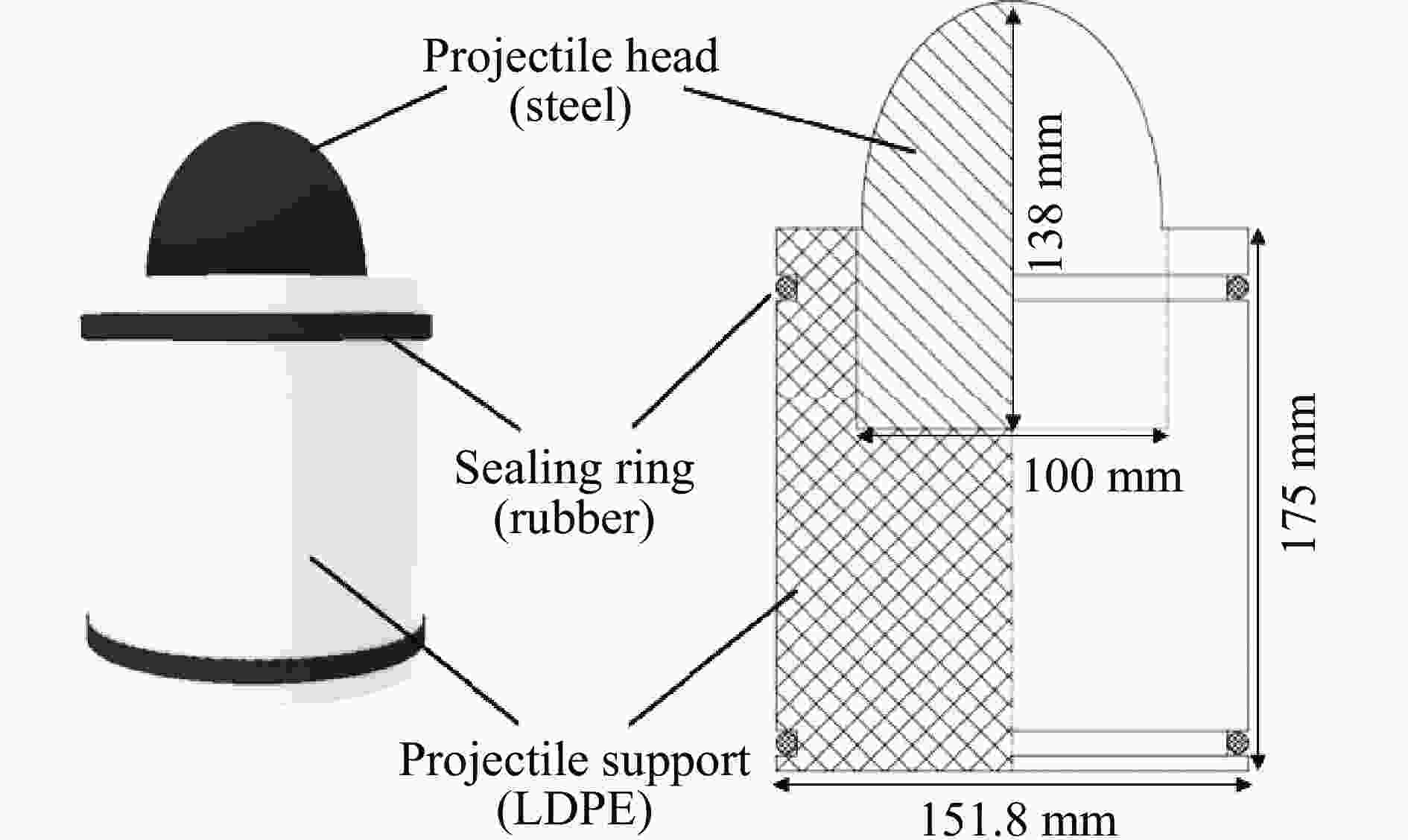
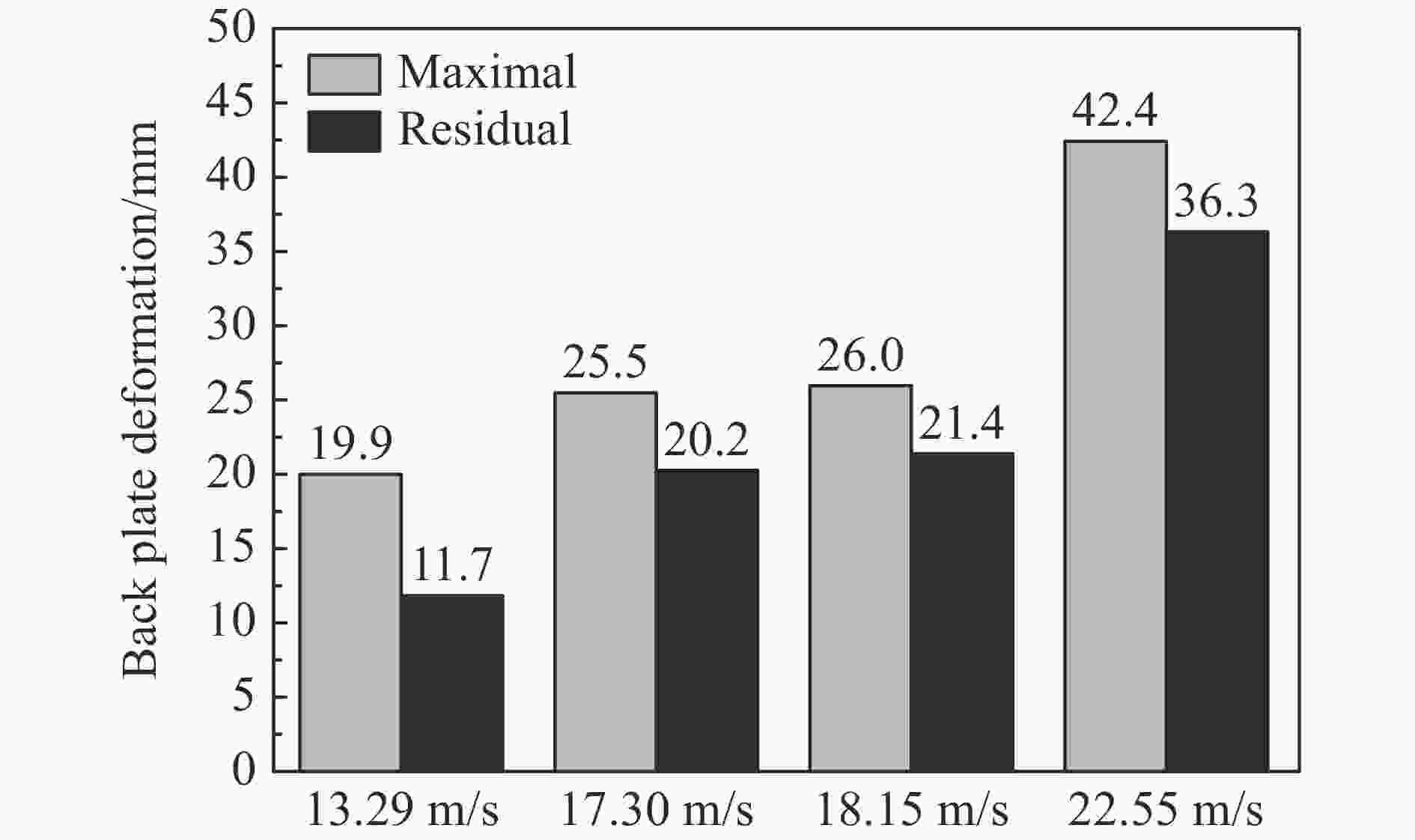
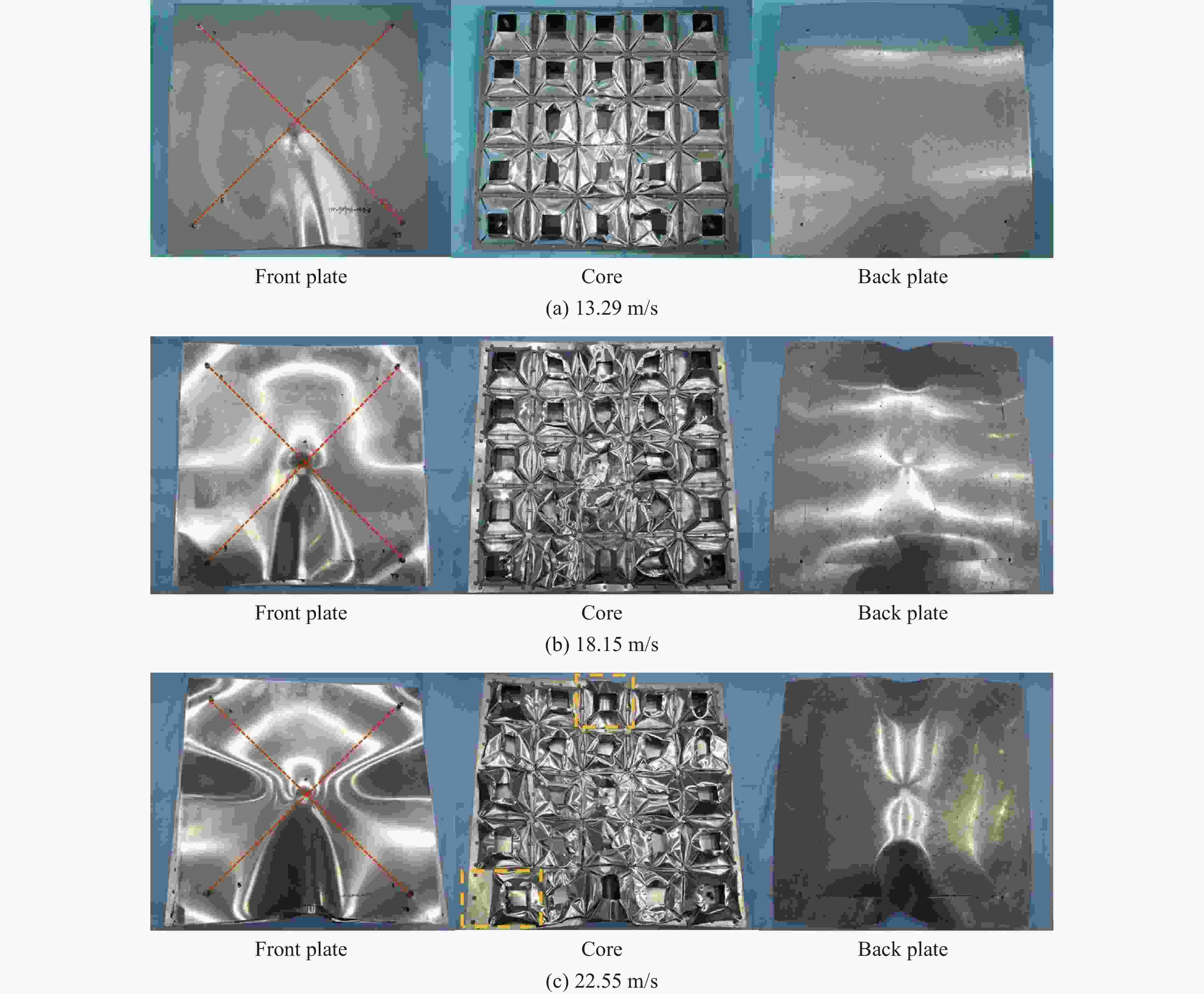
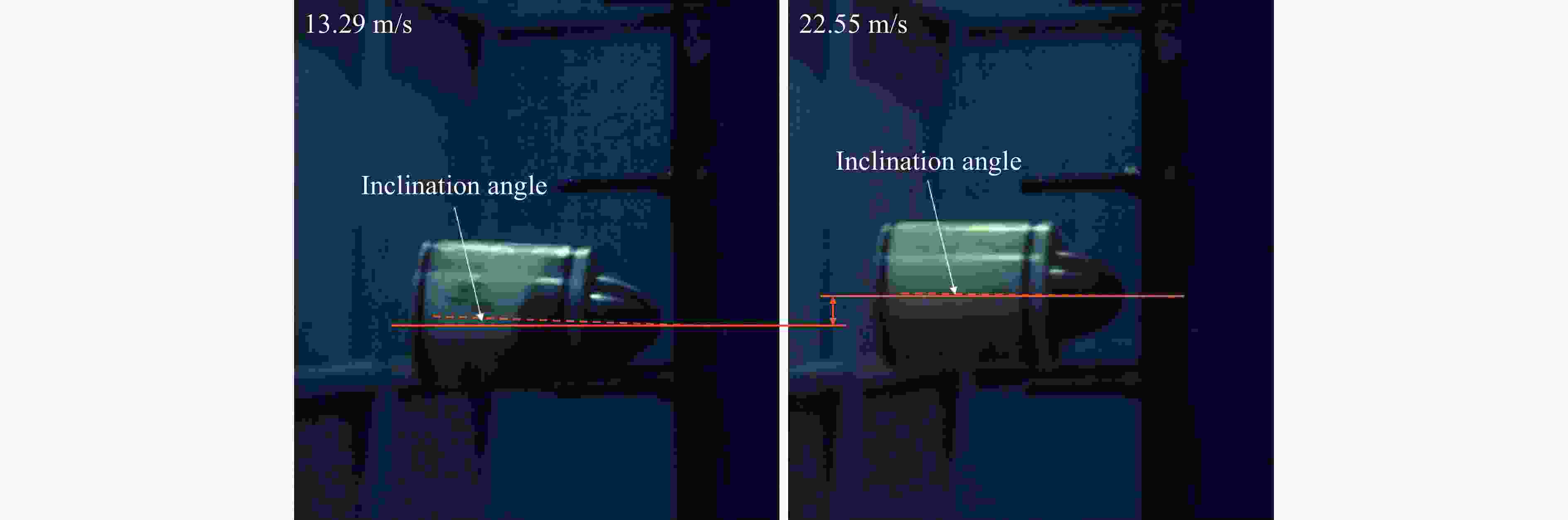
Impact response of TPS folded sandwich structure
-
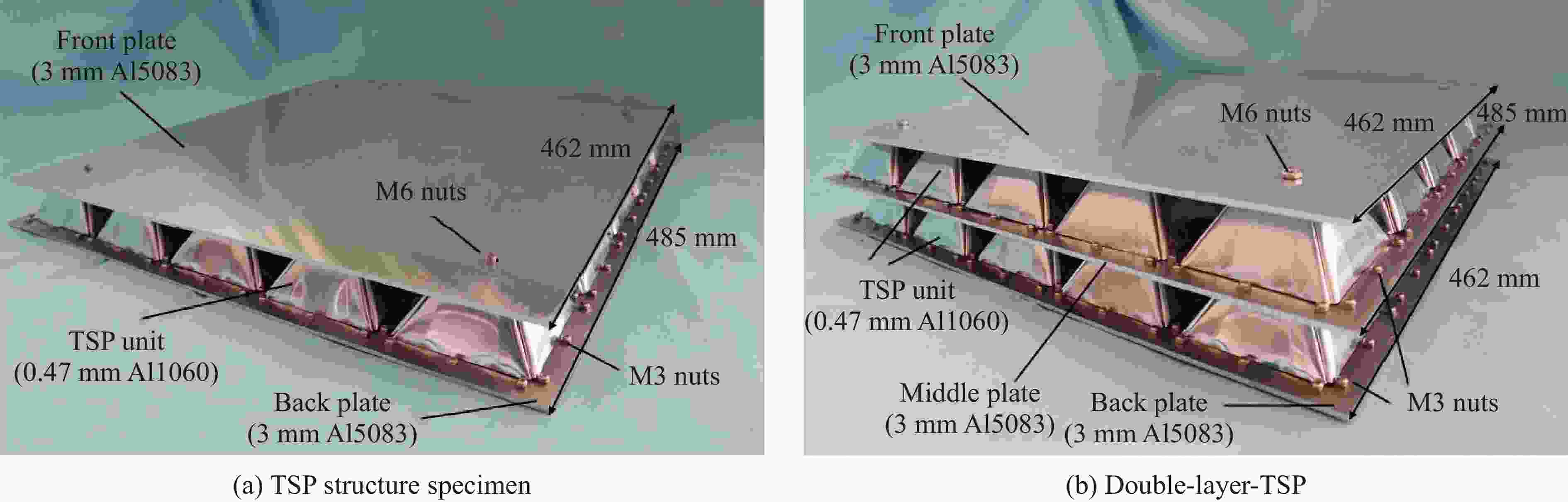
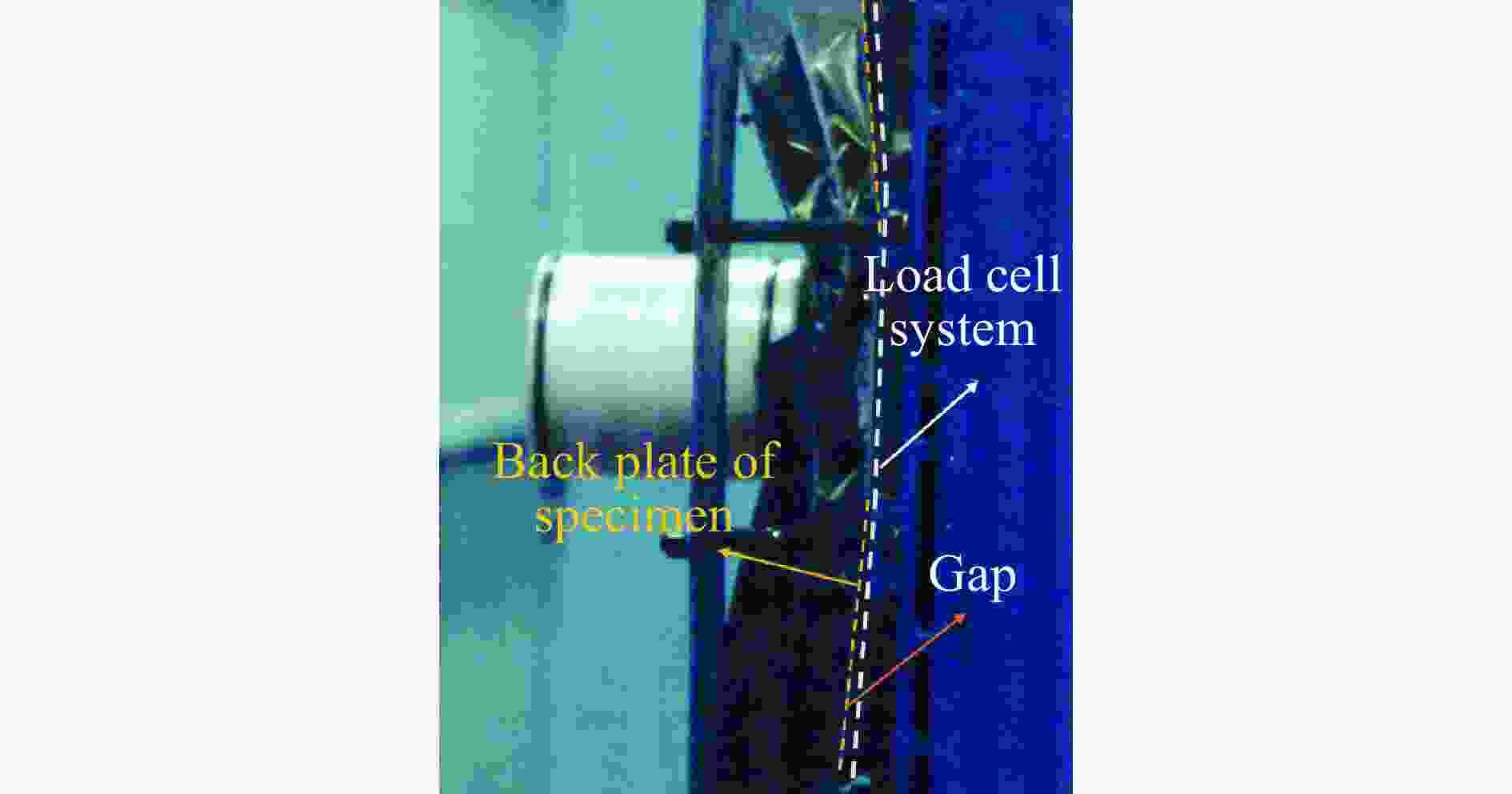
摘要: 多折角梯形台面折纸(truncated square pyramid, TSP)作为新型折叠结构,具有良好的抗冲击、能量吸收特性并具有模块化易加工的特点。基于此结构模块化形成了单层以及多层夹层板,利用空气炮试验装置研究了背板无支撑的夹层结构以及覆层结构,在不同冲击工况、边界条件下结构的冲击防护性能以及吸能特性。通过测量、对比单层夹层结构的位移时程及冲击后的失效模式,对抗冲击性能进行了评估。利用装于背板的多点压力传感器装置,测量冲击作用下覆层结构对背板不同位置的传递力时程,研究不同工况下的缓冲性能。对于背板无支撑夹层工况,背板的残余位移随冲击速度的增大而增大。对于覆层工况,双层覆层有较好的能量吸收和抗冲击性能,相比于单层表现出更充分的芯层利用率。此外,冲击位置通过改变模块单元的变形模式对覆层结构动态响应产生显著影响,尤其影响传递力峰值和峰值出现时间。研究结果可为TSP防护结构的工程设计和应用提供参考。Abstract: As a novel folded structure, the truncated square pyramid (TSP) structure exhibits excellent impact resistance and energy absorption performance. It also has the merit of simple and modulated fabrication of its unit cell. To further verify the performance of TSP sandwich panels under local impact load, impact tests are carried out in this work by using an air cannon testing system. The unit cells are firstly prepared by multi-stage mold-pressing and then modular arranged to form single and multi-layer sandwich panels. The impact protection performance and energy absorption properties of the back-supported cladding cases and unsupported sandwich structures are investigated under different impact scenarios. Their impact resistance performances are evaluated by measuring and comparing the displacement time histories of the single-layer sandwich structures and their deformation modes after impact. For the back-supported cladding cases, a measuring system with five load cells is placed behind the back plate of the cladding and is rigidly supported to record the time history and distribution of the transmitted force of the claddings under impact. Their impact mitigation performances are evaluated by analyzing the recorded force-time histories under various loading scenarios. It is found that the maximum displacement and residual displacement of the back plate increase with the increase of impact velocity for the unsupported cases. For the rigidly supported claddings, the double-layered cladding shows significantly improved energy absorption and impact mitigation performance than the single-layered one. It shows a better utilization of the core, which leads to a reduced initial peak transmitted force. In addition, it is found that the impact position has a significant effect on the dynamic response of the claddings as it changes the peak transmitted force and its occurrence time because of the change in deformation modes. The research results provide a reference for the engineering design and application of TSP sandwich structures.
-
Key words:
- folded structure /
- cladding structure /
- impact test /
- dynamic response /
- impact resistance
-
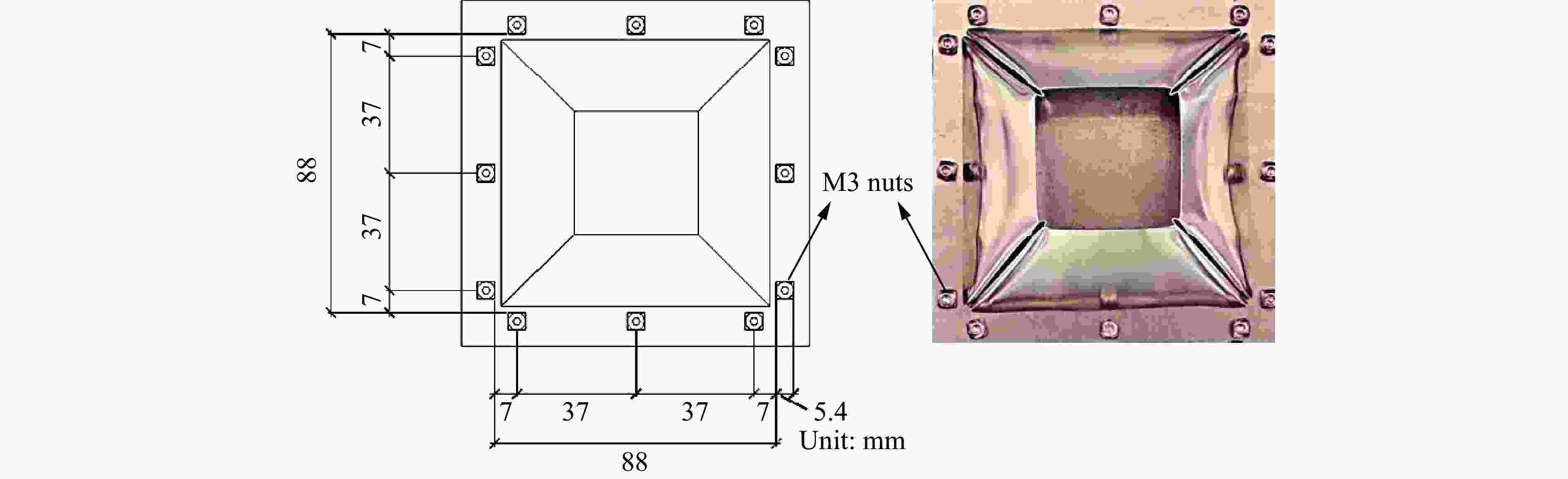
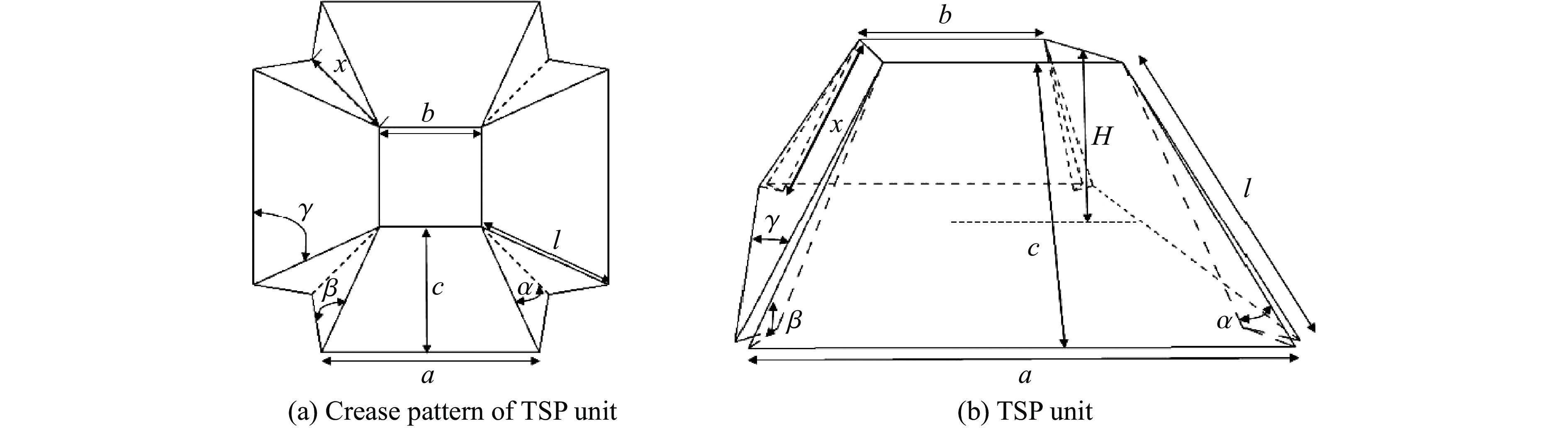
表 1 TSP结构单元尺寸理论参数
Table 1. Theoretical parameters of TSP structural cell size
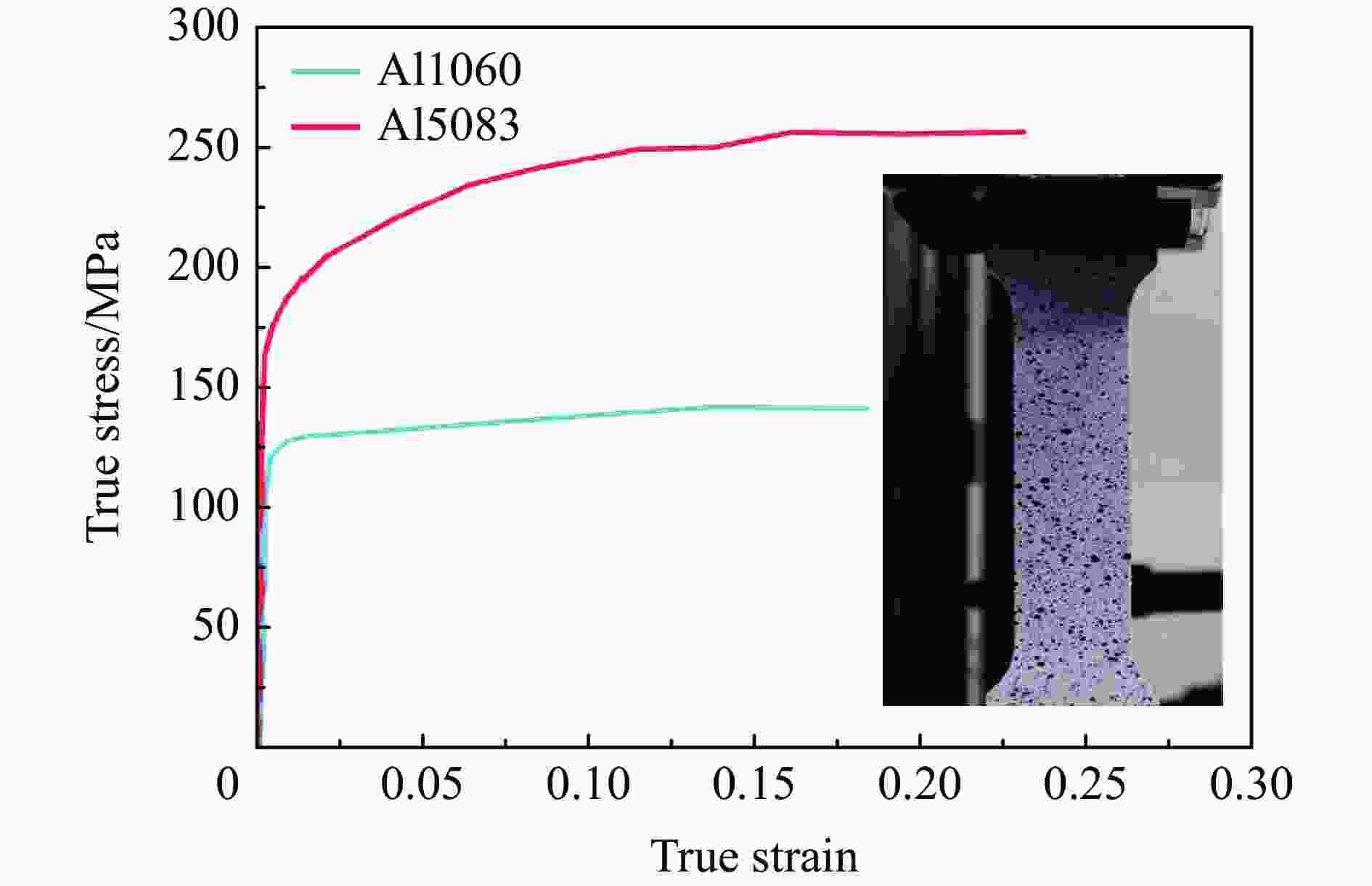
a/mm b/mm H/mm c/mm l/mm γ/(°) β/(°) α/(°) x/mm 80 40 40 44.7 48.9 65.9 54.7 20.9 41.3 表 2 铝板材料性能参数
Table 2. Material properties of Al1060 and Al5083
铝板类型 密度/
(kg·m−3)杨氏模量/
GPa厚度/
mm屈服强度/
MPa泊松比 抗拉强度/
MPa5083铝板 2650 72 3 185 0.3 256 1060铝板 2700 69 0.47 126 0.3 142 表 3 试件的不同冲击场景
Table 3. Impact scenarios for specimens
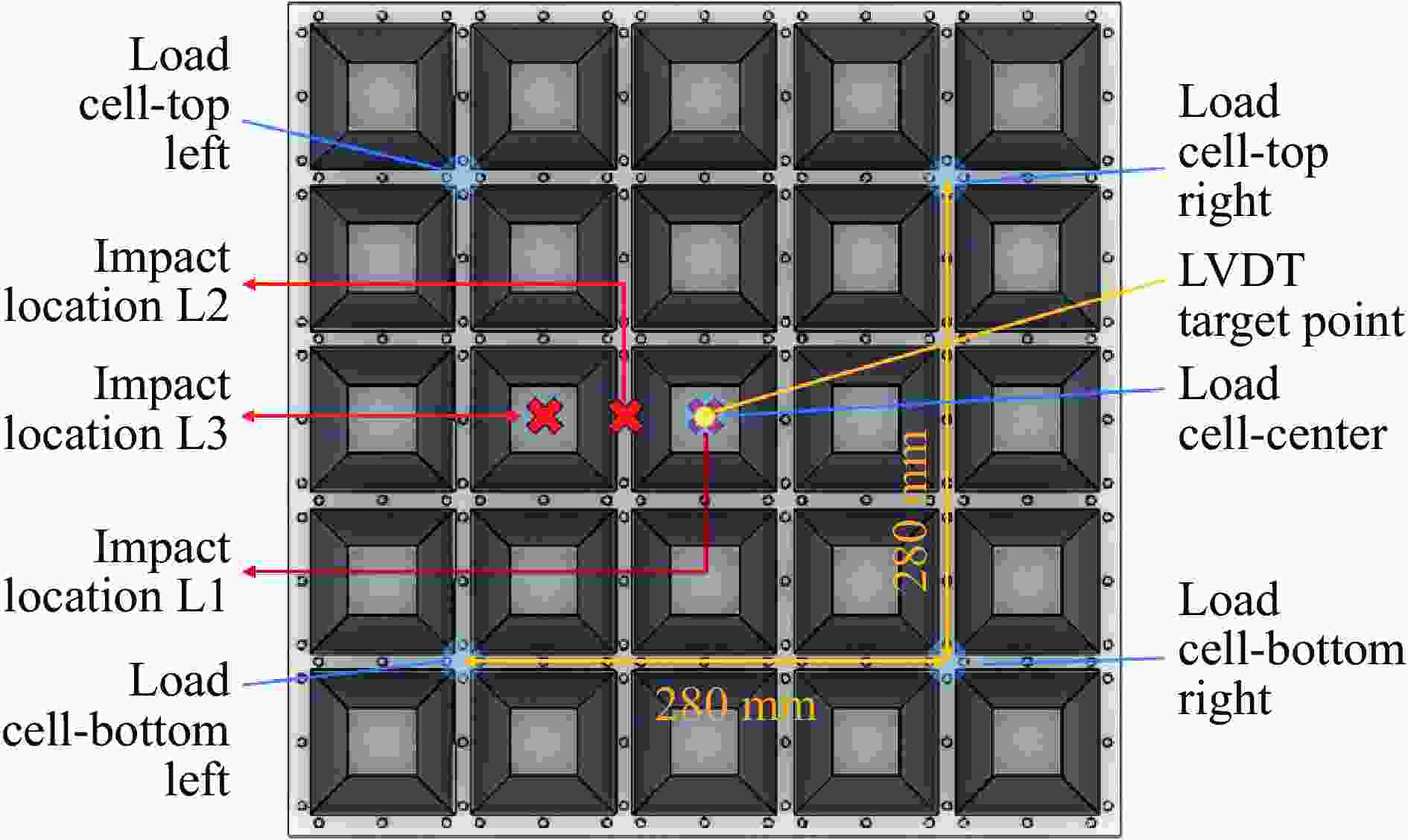
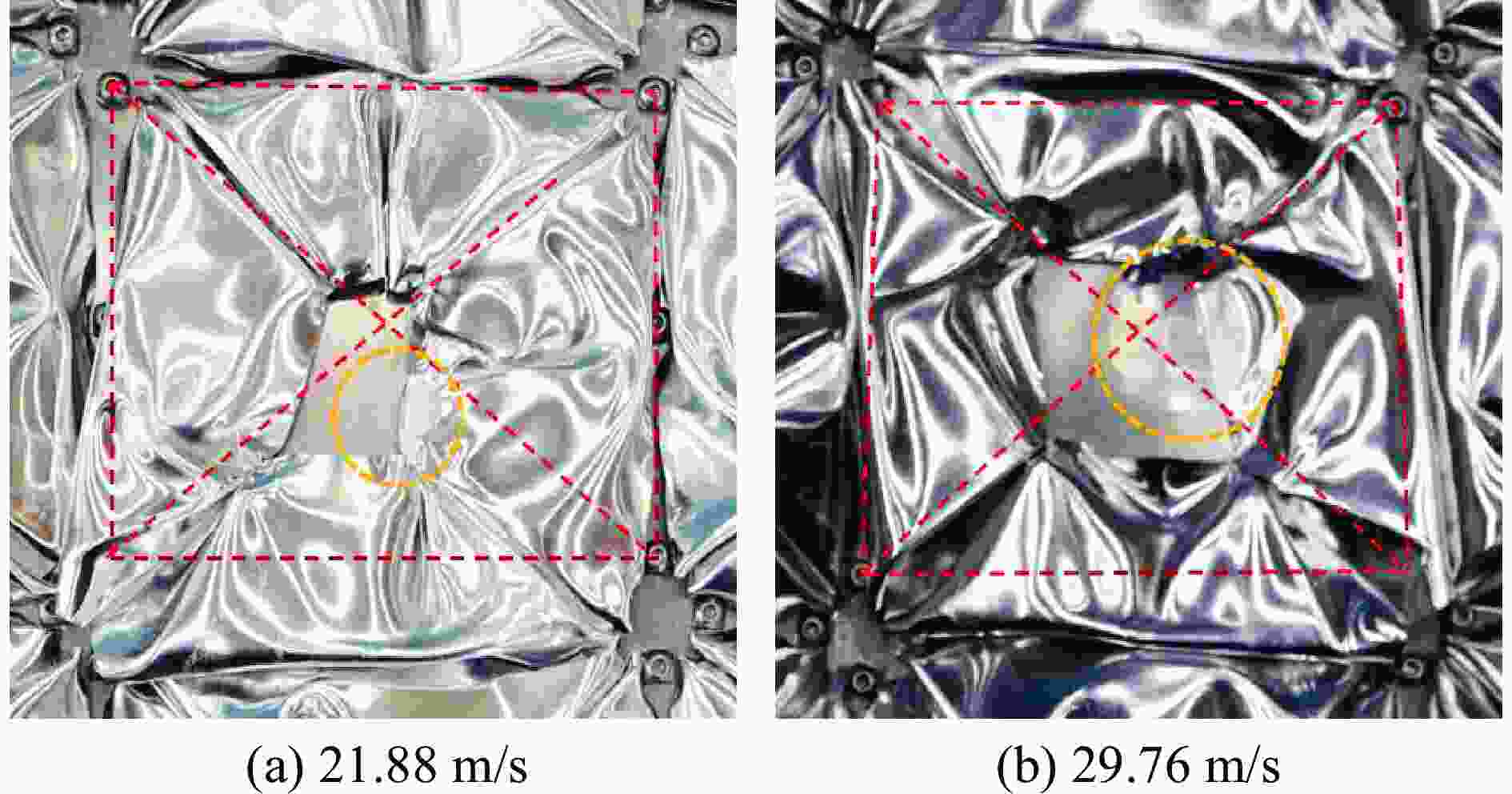
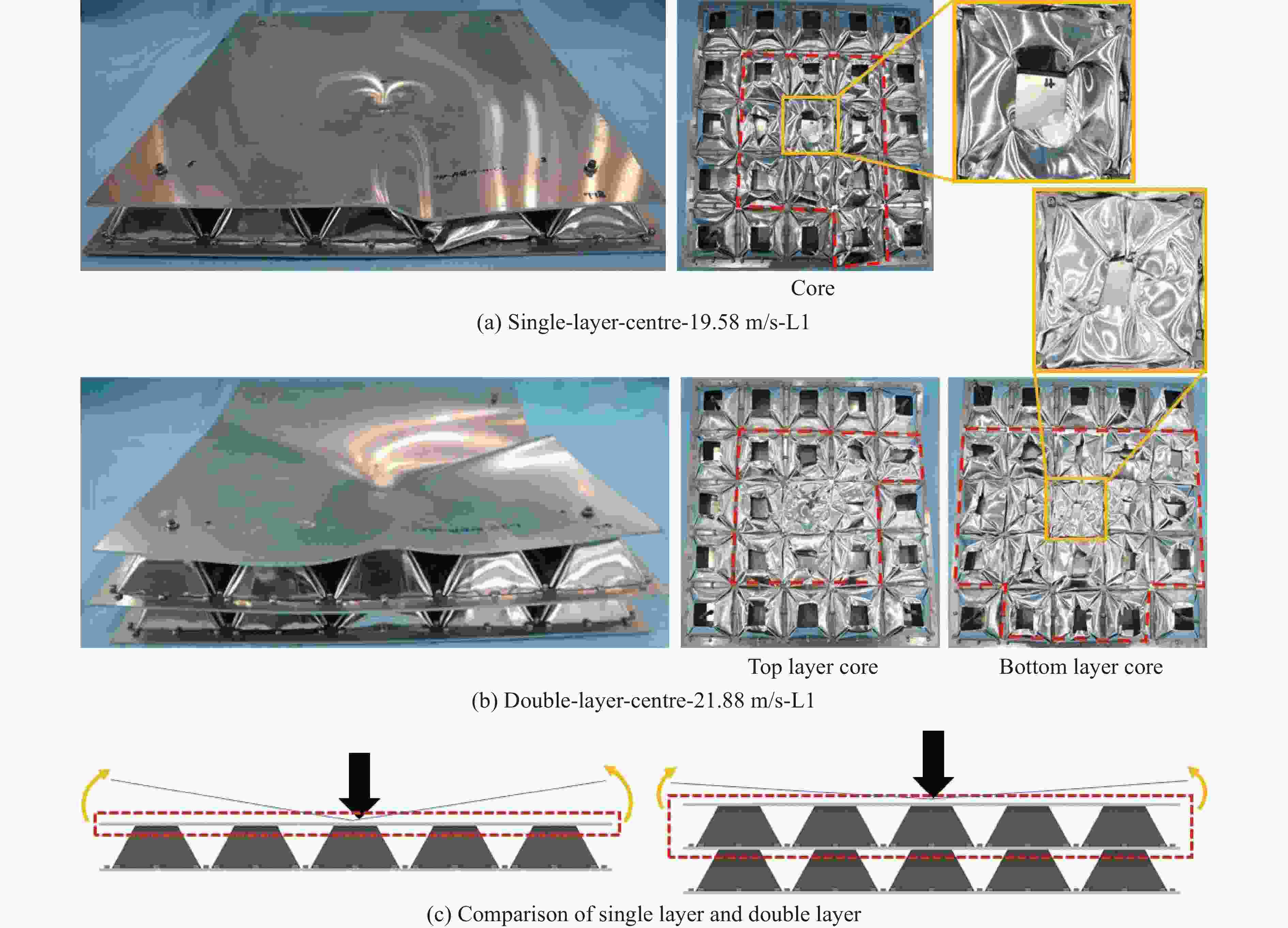
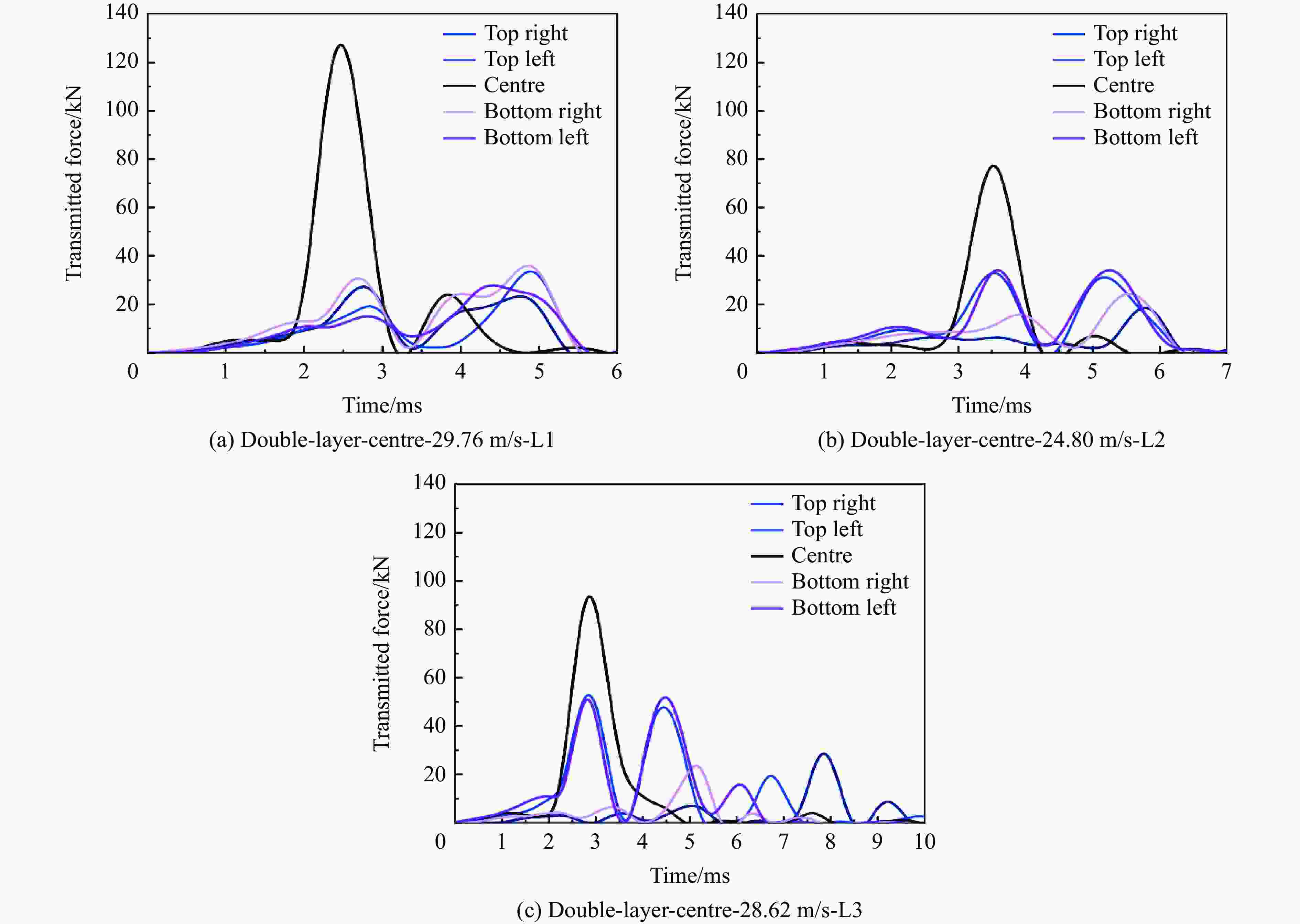
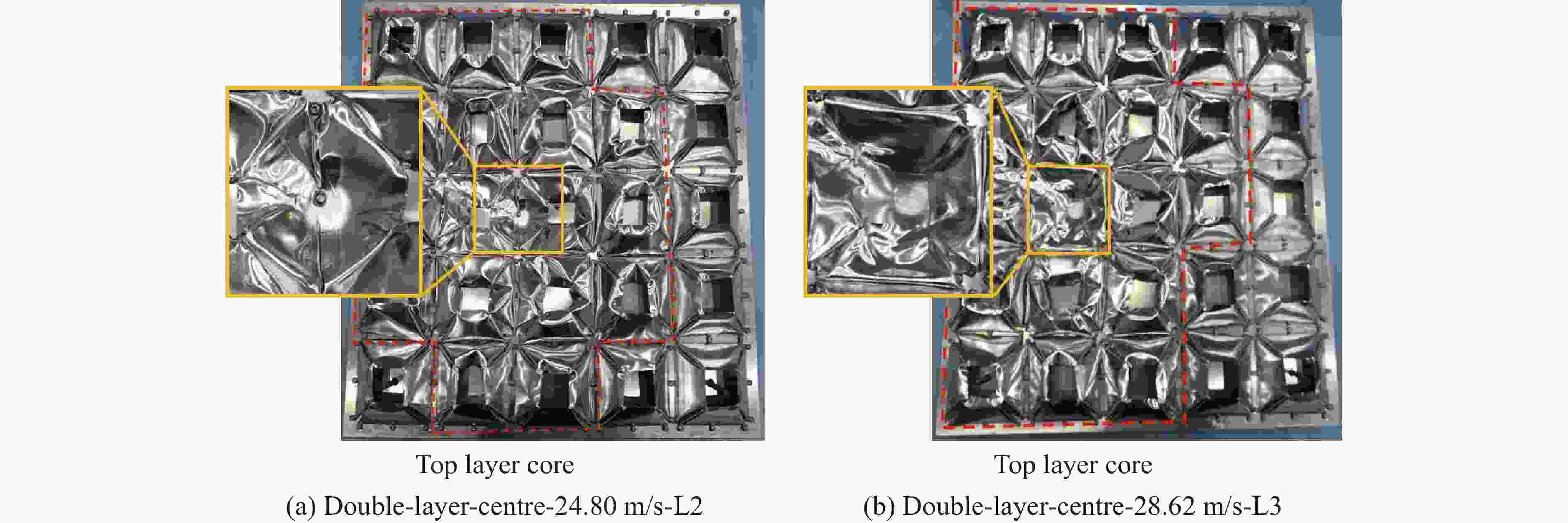
试验编号 试件 芯层层数 弹丸速度/(m·s−1) 冲击位置 冲击能量/J 1 单层TSP(夹层试验) 1 13.29 L1 883 2 单层TSP(夹层试验) 1 17.30 L1 1497 3 单层TSP(夹层试验) 1 18.15 L1 1647 4 单层TSP(夹层试验) 1 22.55 L1 2542 5 单层TSP(覆层试验) 1 19.58 L1 1917 6 双层TSP(覆层试验) 2 21.88 L1 2394 7 双层TSP(覆层试验) 2 29.76 L1 4428 8 双层TSP(覆层试验) 2 24.80 L2 3075 9 双层TSP(覆层试验) 2 28.62 L3 4096 -
[1] ABBADI A, KOUTSAWA Y, CARMASOL A, et al. Experimental and numerical characterization of honeycomb sandwich composite panels [J]. Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, 2009, 17(10): 1533–1547. DOI: 10.1016/j.simpat.2009.05.008. [2] REJAB M R M, CANTWELL W J. The mechanical behaviour of corrugated-core sandwich panels [J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2013, 47: 267–277. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2012.10.031. [3] HEIMBS S, CICHOSZ J, KLAUS M, et al. Sandwich structures with textile-reinforced composite foldcores under impact loads [J]. Composite Structures, 2010, 92(6): 1485–1497. DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2009.11.001. [4] YOO S H, CHANG S H, SUTCLIFFE M P F. Compressive characteristics of foam-filled composite egg-box sandwich panels as energy absorbing structures [J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2010, 41(3): 427–434. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2009.11.010. [5] WANG B, WU L, MA L, et al. Mechanical behavior of the sandwich structures with carbon fiber-reinforced pyramidal lattice truss core [J]. Materials & Design, 2010, 31(5): 2659–2663. DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2009.11.061. [6] MA Q, REJAB M R M, SIREGAR J P, et al. A review of the recent trends on core structures and impact response of sandwich panels [J]. Journal of Composite Materials, 2021, 55(18): 2513–2555. DOI: 10.1177/0021998321990734. [7] 廖就, 李志刚, 梁方正, 等. 高共面/异面抗冲击承载能力的新型蜂窝设计及吸能评估 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2021, 41(8): 083103. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0262.LIAO J, LI Z G, LIANG F Z, et al. Design and evaluation of new honeycomb configurations with high in-plane /out-of-plane loading-carrying capacity under impact [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2021, 41(8): 083103. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0262. [8] TOWNSEND S, ADAMS R, ROBINSON M, et al. 3D printed origami honeycombs with tailored out-of-plane energy absorption behavior [J]. Materials & Design, 2020, 195: 083103. DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2020.108930. [9] PYDAH A, BATRA R C. Crush dynamics and transient deformations of elastic-plastic Miura-ori core sandwich plates [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2017, 115: 311–322. DOI: 10.1016/j.tws.2017.02.021. [10] MA J, DAI H, CHAI S, et al. Energy absorption of sandwich structures with a kirigami-inspired pyramid foldcore under quasi-static compression and shear [J]. Materials & Design, 2021, 206: 083103. DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2021.109808. [11] ZHAI Z, WANG Y, JIANG H. Origami-inspired, on-demand deployable and collapsible mechanical metamaterials with tunable stiffness [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(9): 2032–2037. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1720171115. [12] FANG H, LI S, JI H, et al. Dynamics of a bistable Miura-origami structure [J]. Physical Review E, 2017, 95(5): 052211. DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.95.052211. [13] 邱海, 方虹斌, 徐鉴. 多稳态串联折纸结构的非线性动力学特性 [J]. 力学学报, 2019, 51(4): 1110–1121. DOI: 10.6052/0459-1879-19-115.QIU H, FANG H B, XU J. Nonlinear dynamical characteristics of a multi-stable series origami structure [J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2019, 51(4): 1110–1121. DOI: 10.6052/0459-1879-19-115. [14] YASUDA H, YANG J. Reentrant origami-based metamaterials with negative Poisson’s ratio and bistability [J]. Physical Review Letter, 2015, 114(18): 185502. DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.114.185502. [15] WANG C, ZOU S, ZHAO W, et al. Multi-objective explosion-proof performance optimization of a novel vehicle door with negative Poisson’s ratio structure [J]. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 2018, 58(4): 1805–1822. DOI: 10.1007/s00158-018-2026-z. [16] BIRMAN V, KARDOMATEAS G A. Review of current trends in research and applications of sandwich structures [J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2018, 142: 221–240. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.01.027. [17] STARR C M, KRAUTHAMMER T. Cladding-structure interaction under impact loads [J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2005, 131(8): 1178–1185. DOI: 10.1061/(asce)0733-9445(2005)131:8(1178). [18] TARLOCHAN F. Sandwich structures for energy absorption applications: a review [J]. Materials, 2021, 14(16): 185502. DOI: 10.3390/ma14164731. [19] HOU S, SHU C, ZHAO S, et al. Experimental and numerical studies on multi-layered corrugated sandwich panels under crushing loading [J]. Composite Structures, 2015, 126: 371–385. DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2015.02.039. [20] GHATE N, GOEL M D. Influence of core topology on blast mitigation application of multi-layered honeycomb core sandwich panel [J]. Materials Today Communications, 2023, 36:106531. DOI: 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2023.106531. [21] LI Z, CHEN W, HAO H. Crushing behaviours of folded kirigami structure with square dome shape [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2018, 115: 94–105. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2018.01.013. [22] LI Z, CHEN W, HAO H. Numerical study of open-top truncated pyramid folded structures with interconnected side walls against flatwise crushing [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2018, 132: 537–548. DOI: 10.1016/j.tws.2018.08.023. [23] LI Z, FANG R, YANG Q, et al. Performance of sandwich cladding with modular truncated square pyramid foldcore under projectile impact [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2022, 166: 104258. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2022.104258. [24] CAO B T, HOU B, ZHAO H, et al. On the influence of the property gradient on the impact behavior of graded multilayer sandwich with corrugated cores [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2018, 113: 98–105. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2017.11.017. -






 下载:
下载: