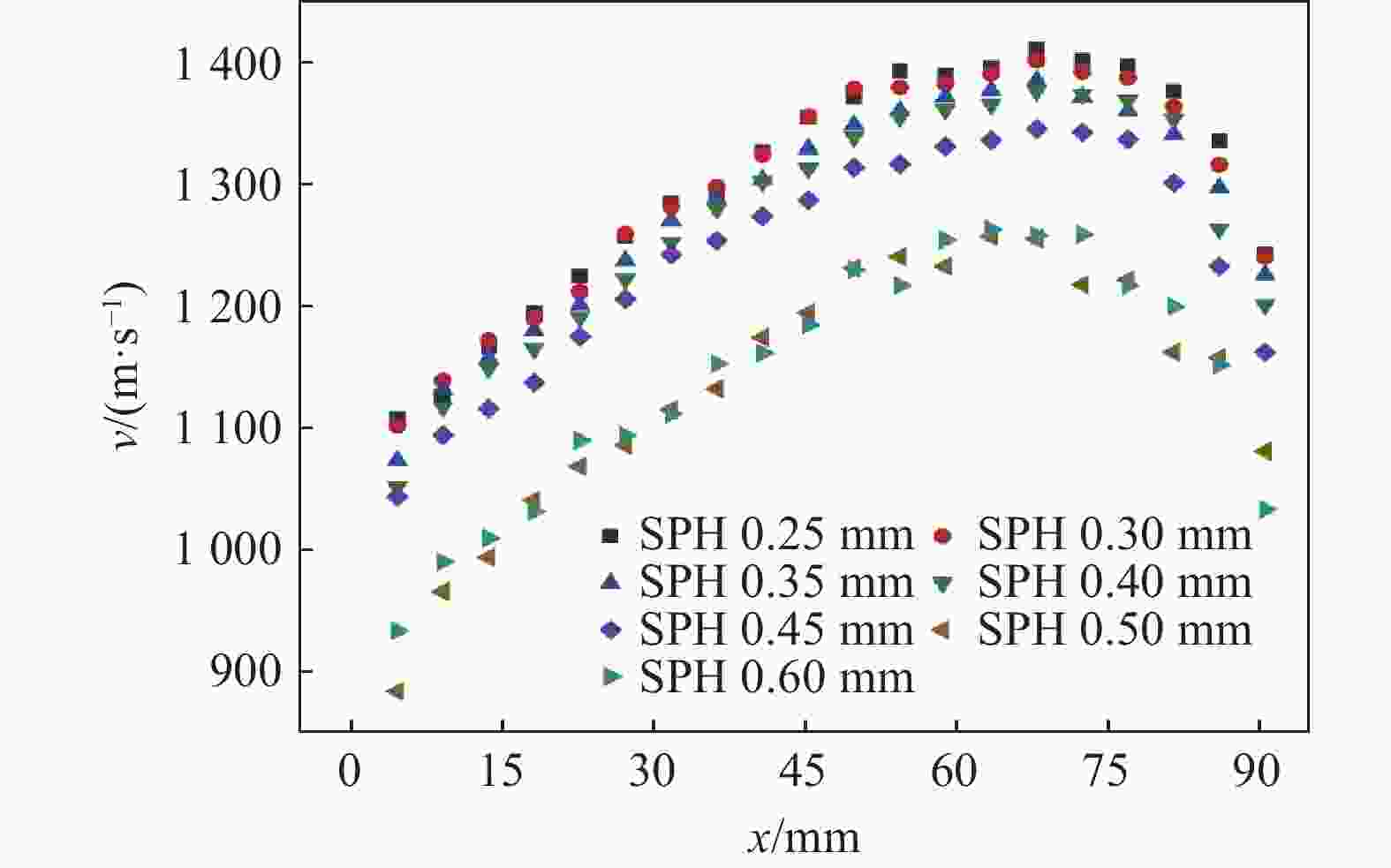
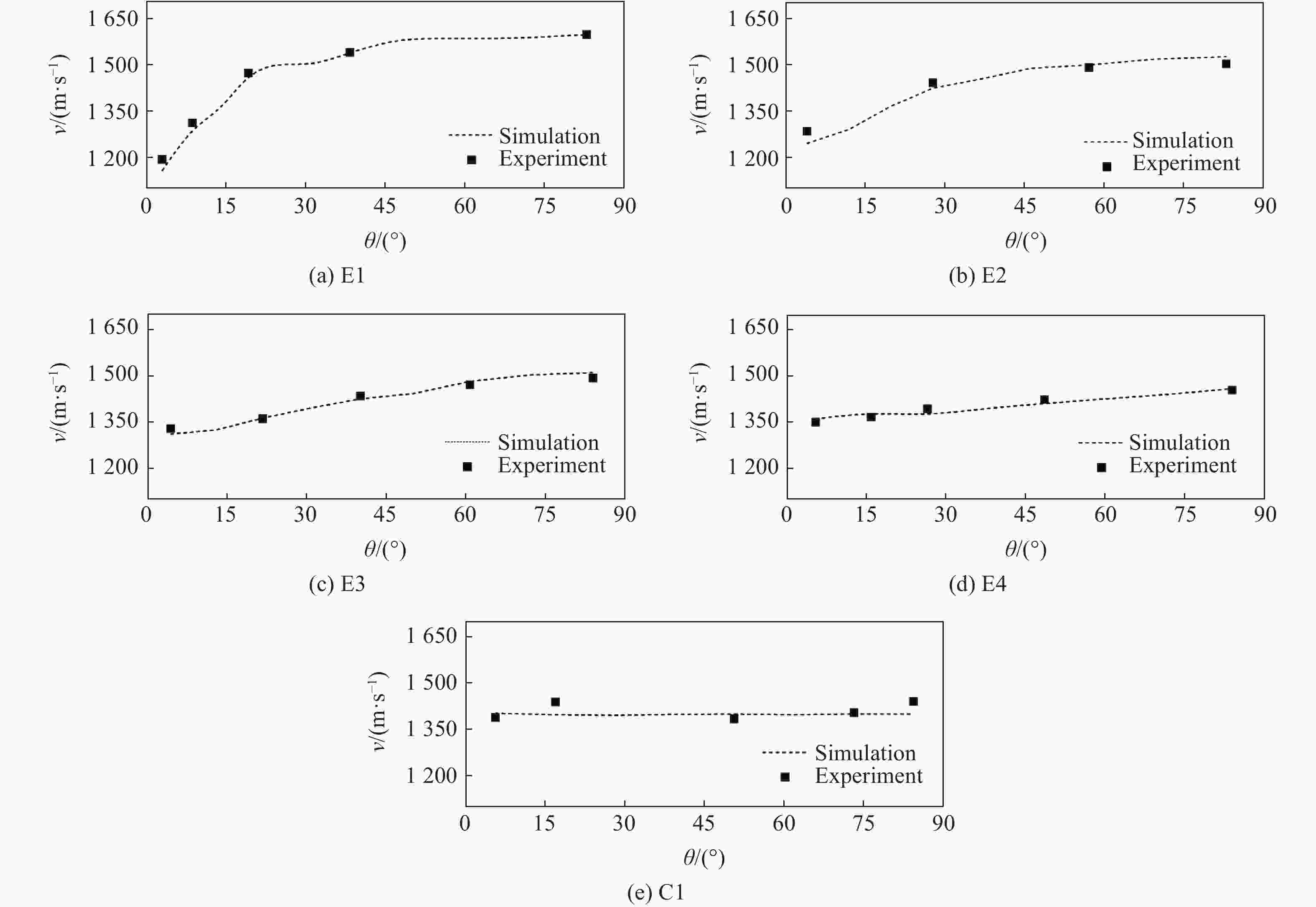
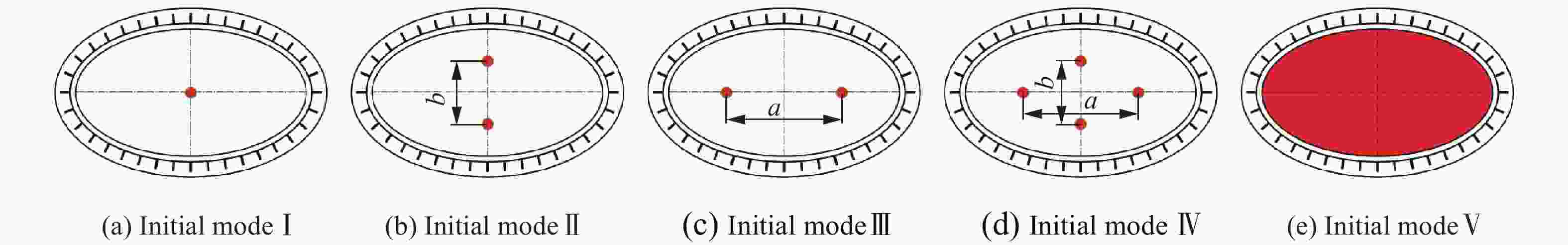
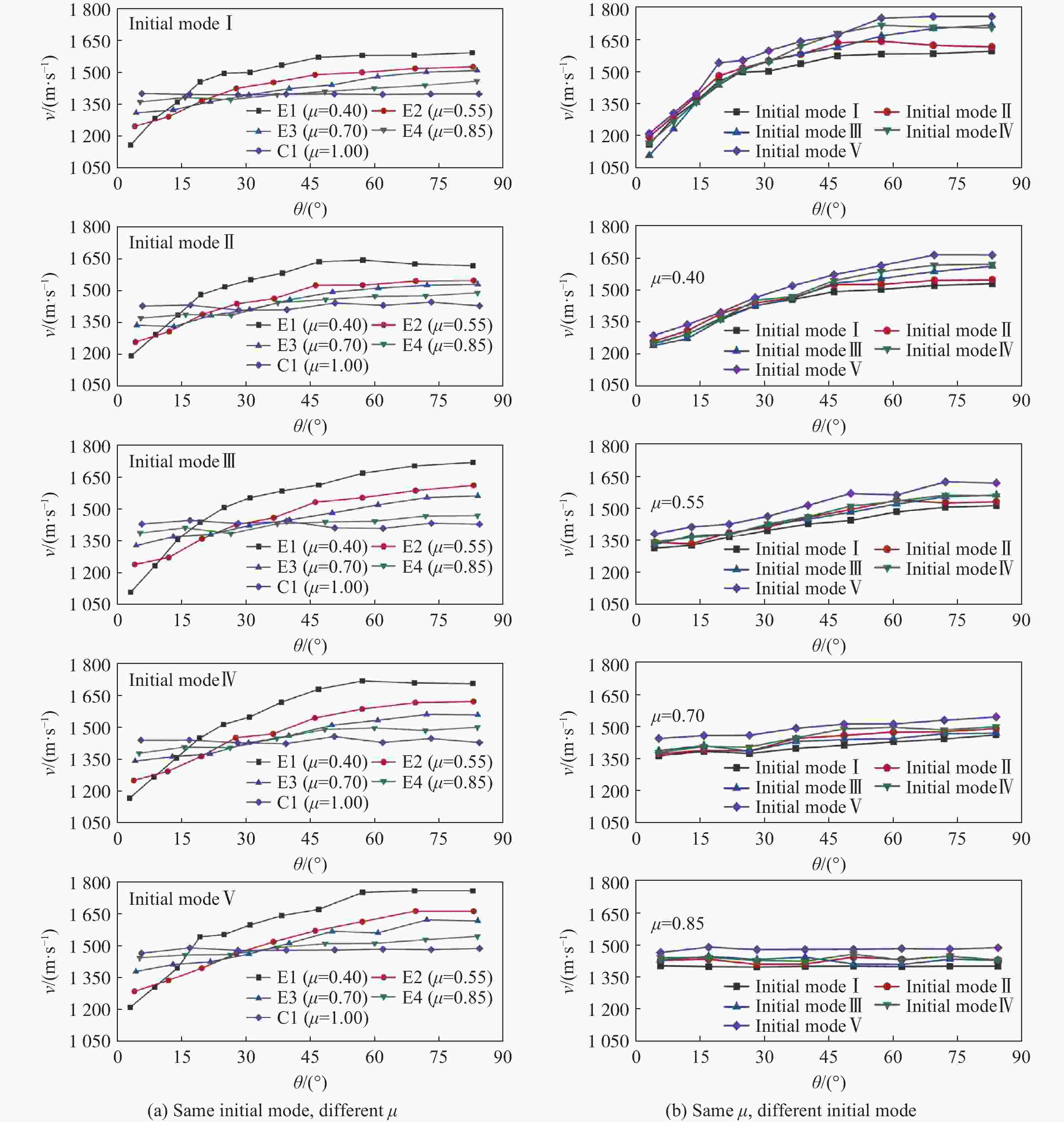
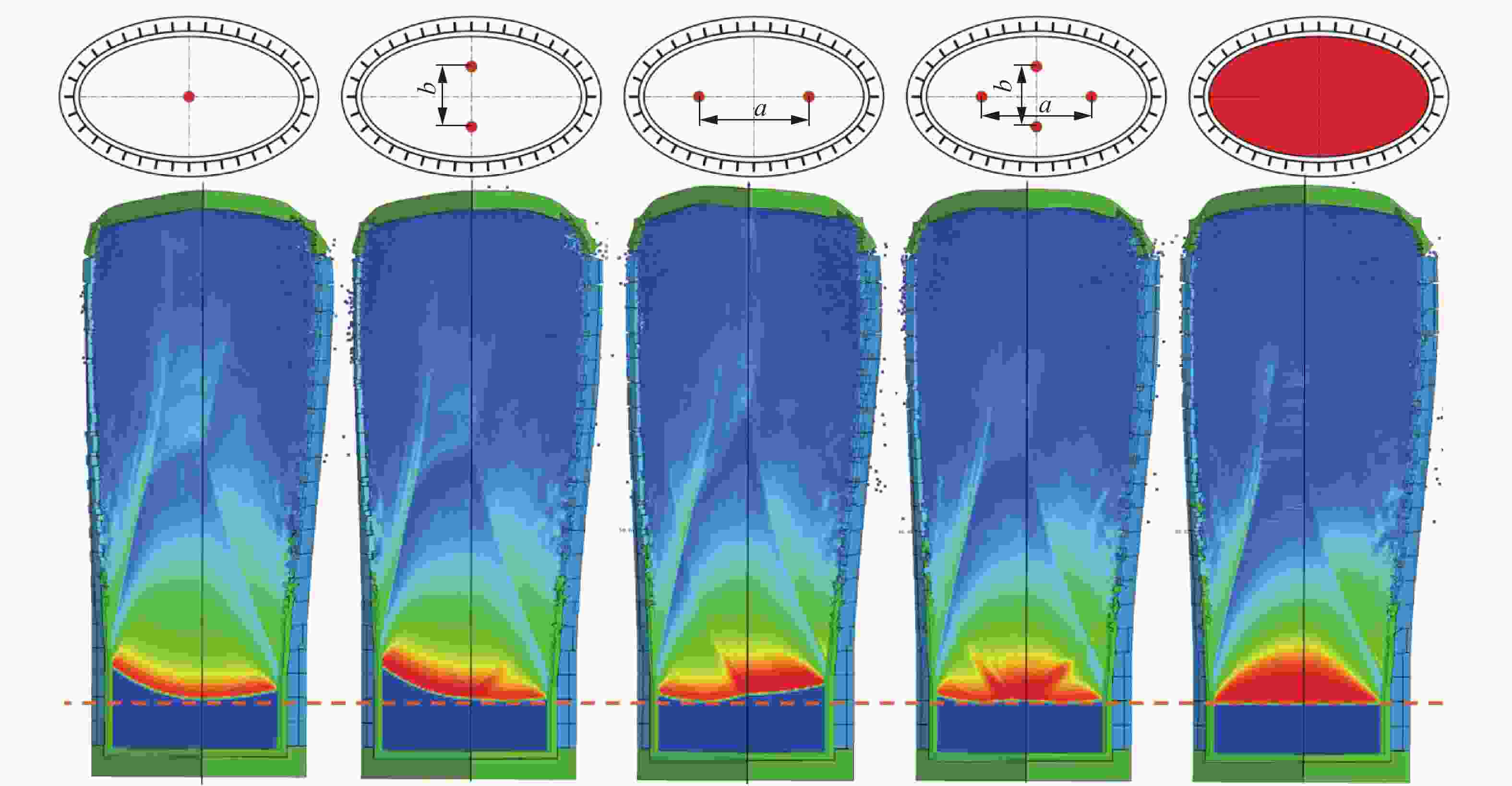
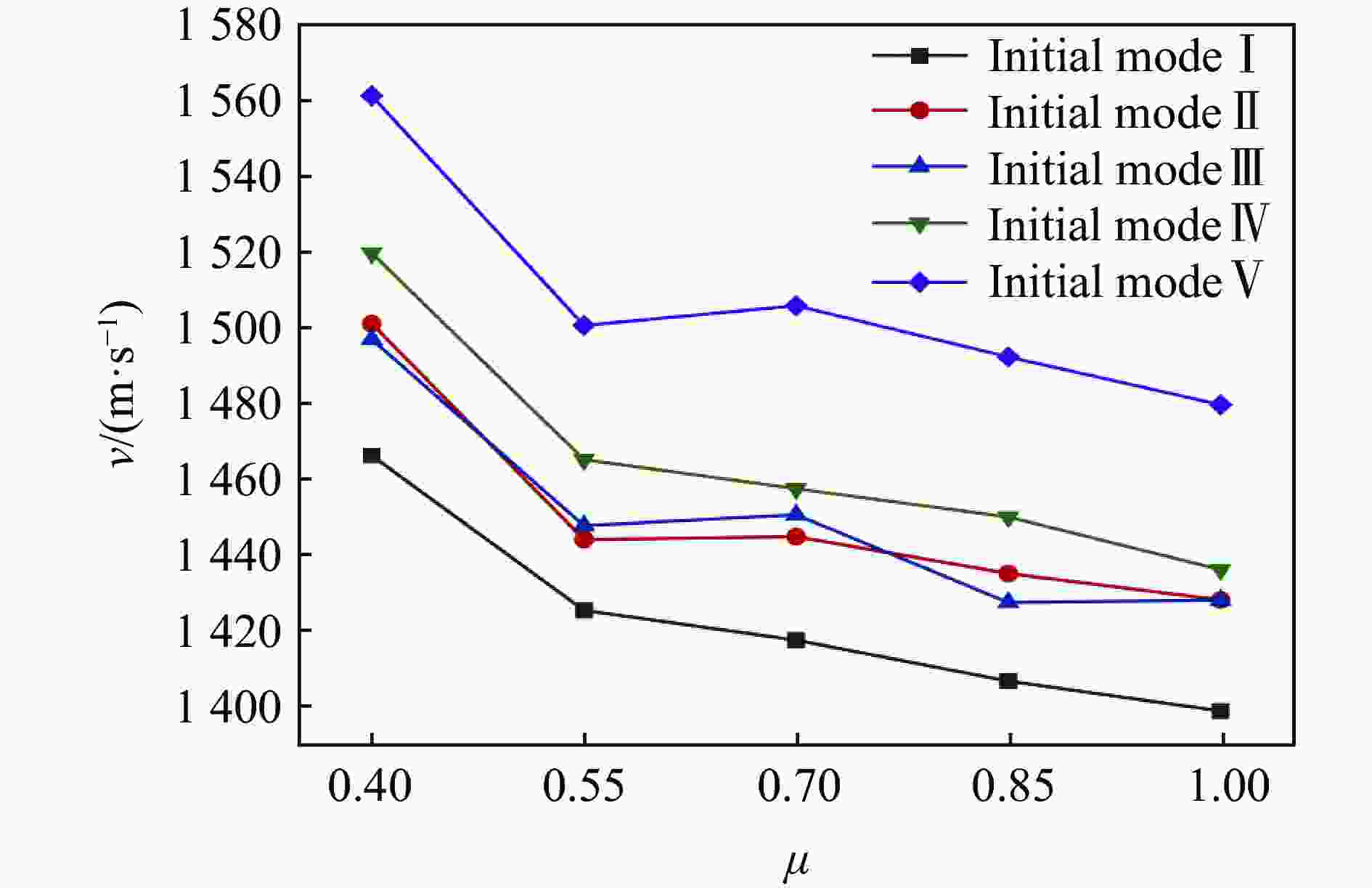
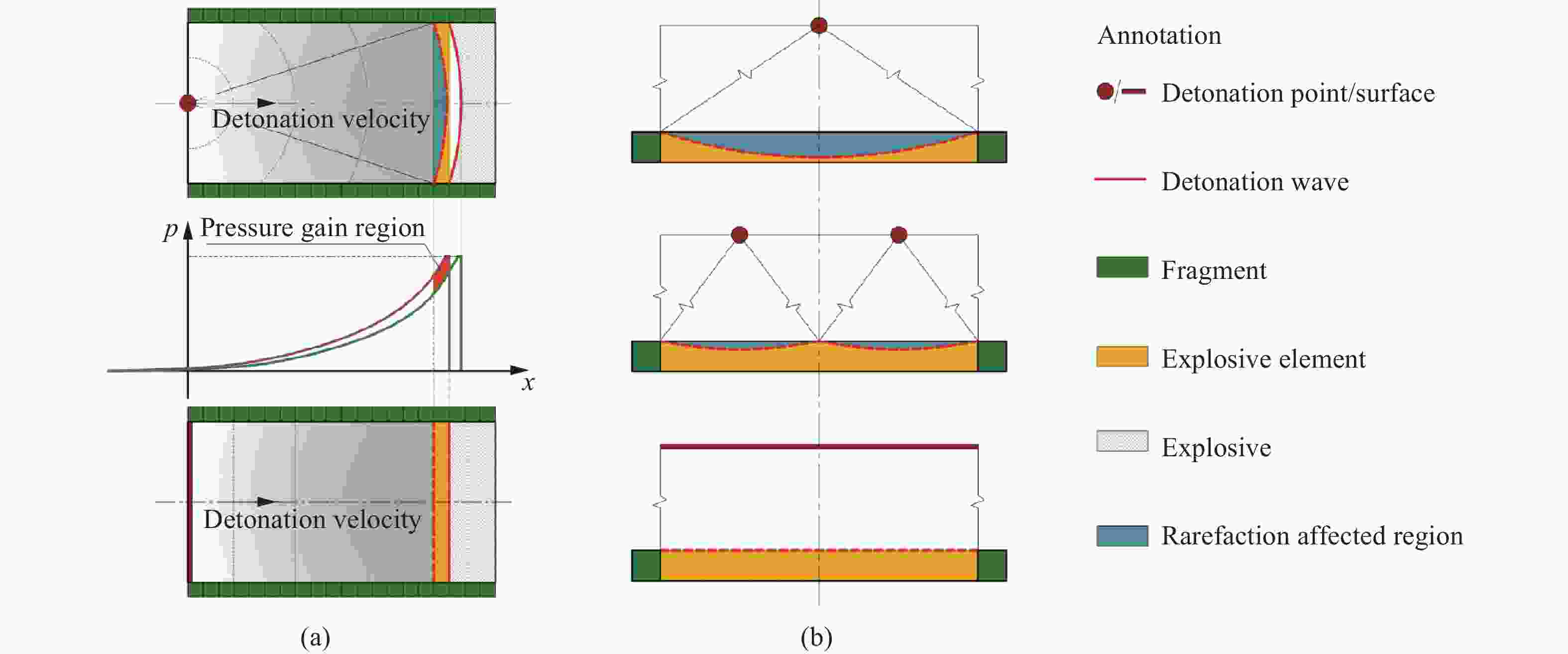
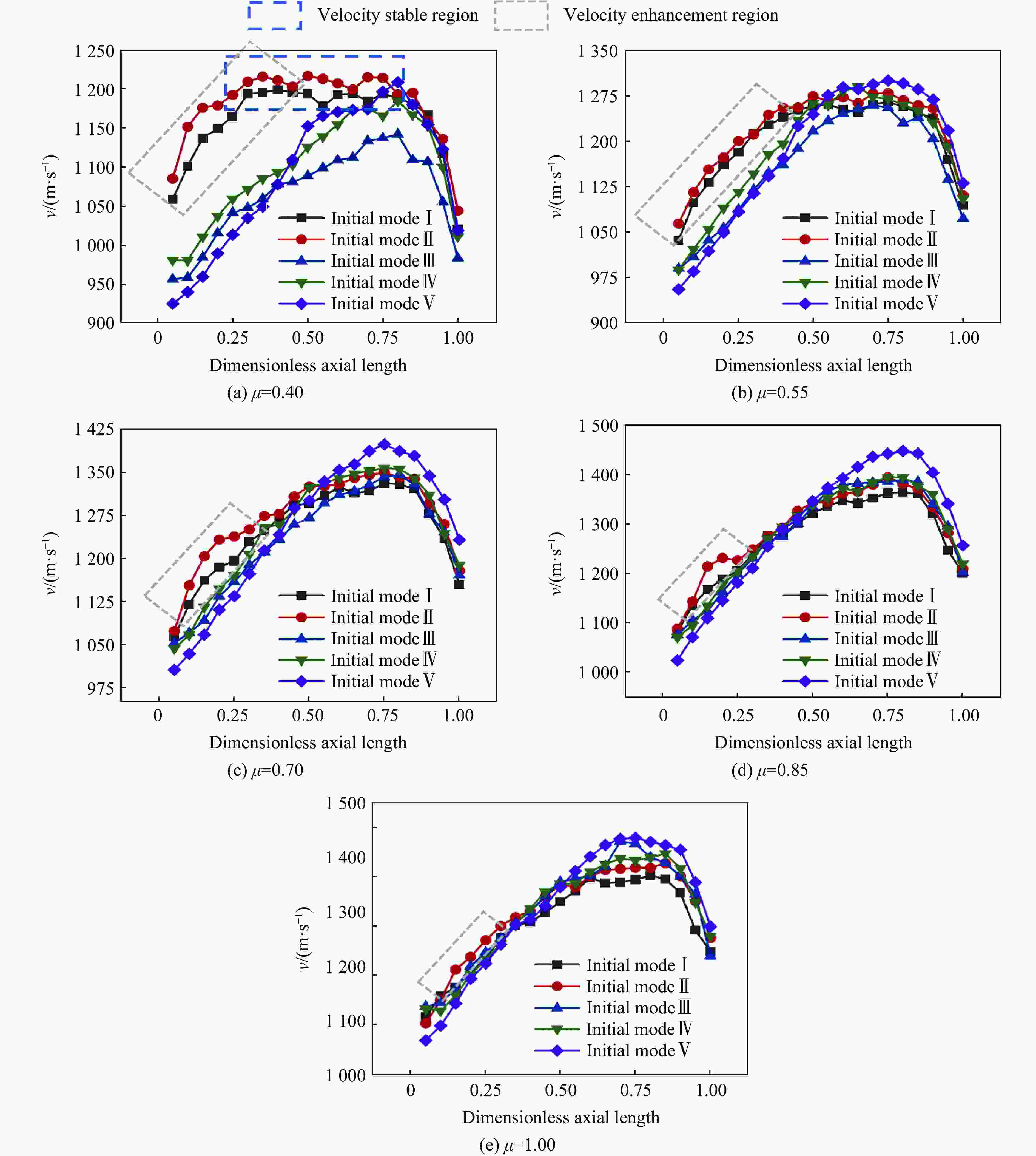
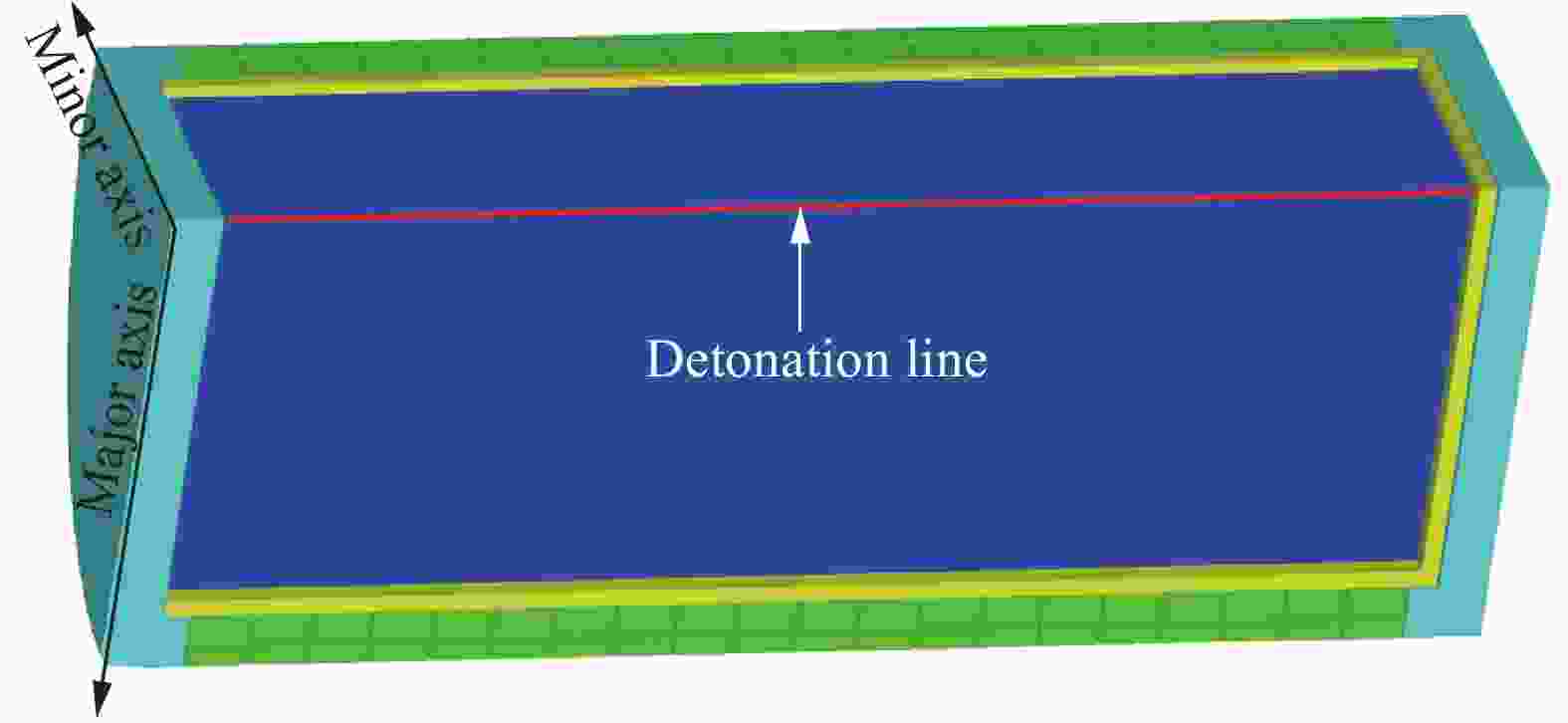
Effect of initiation models on the fragment velocity distribution of elliptical cross-section warhead
-
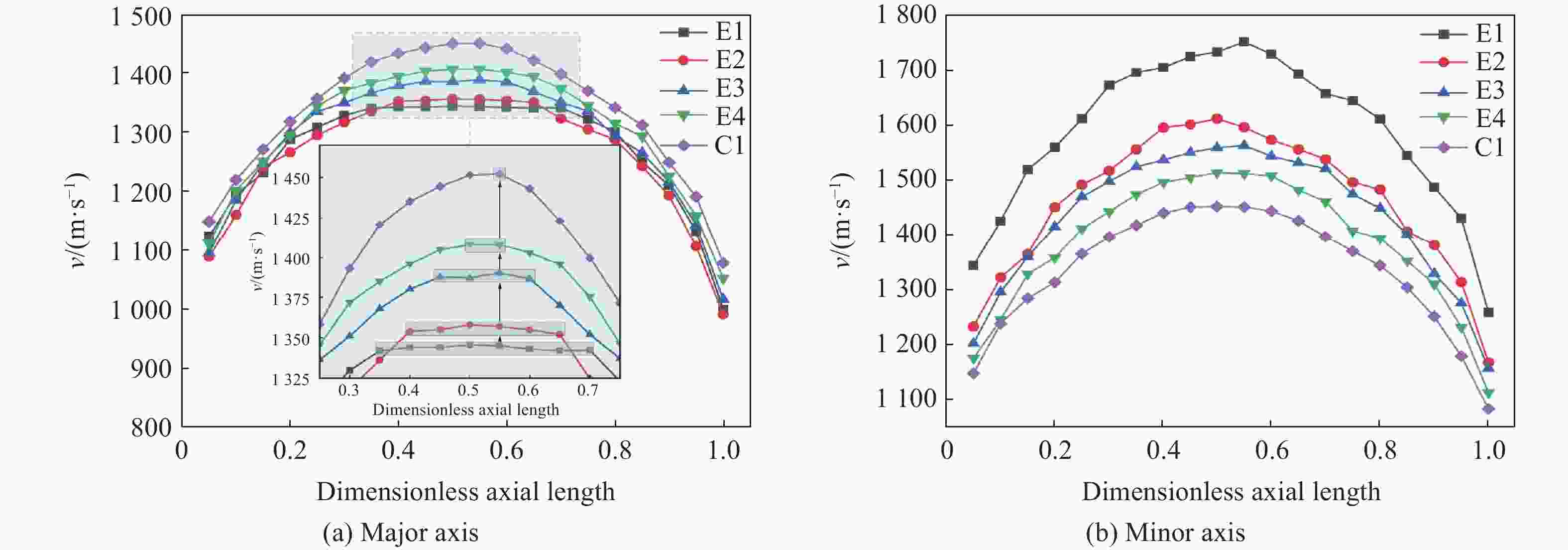
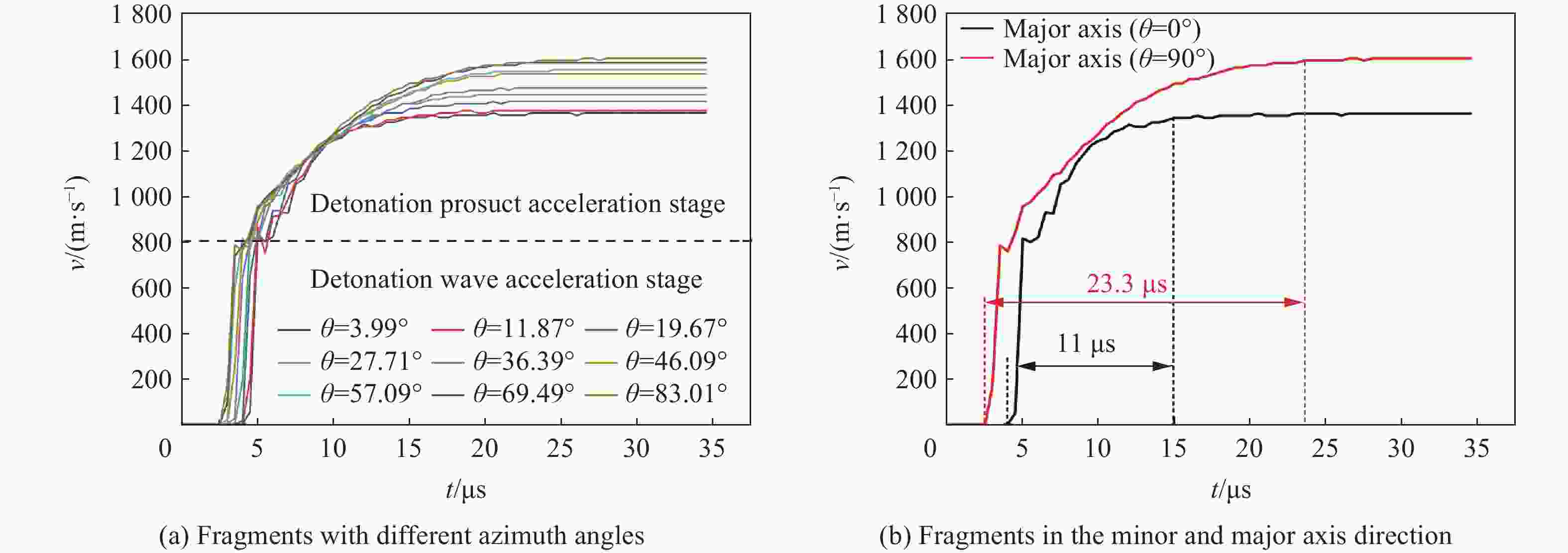
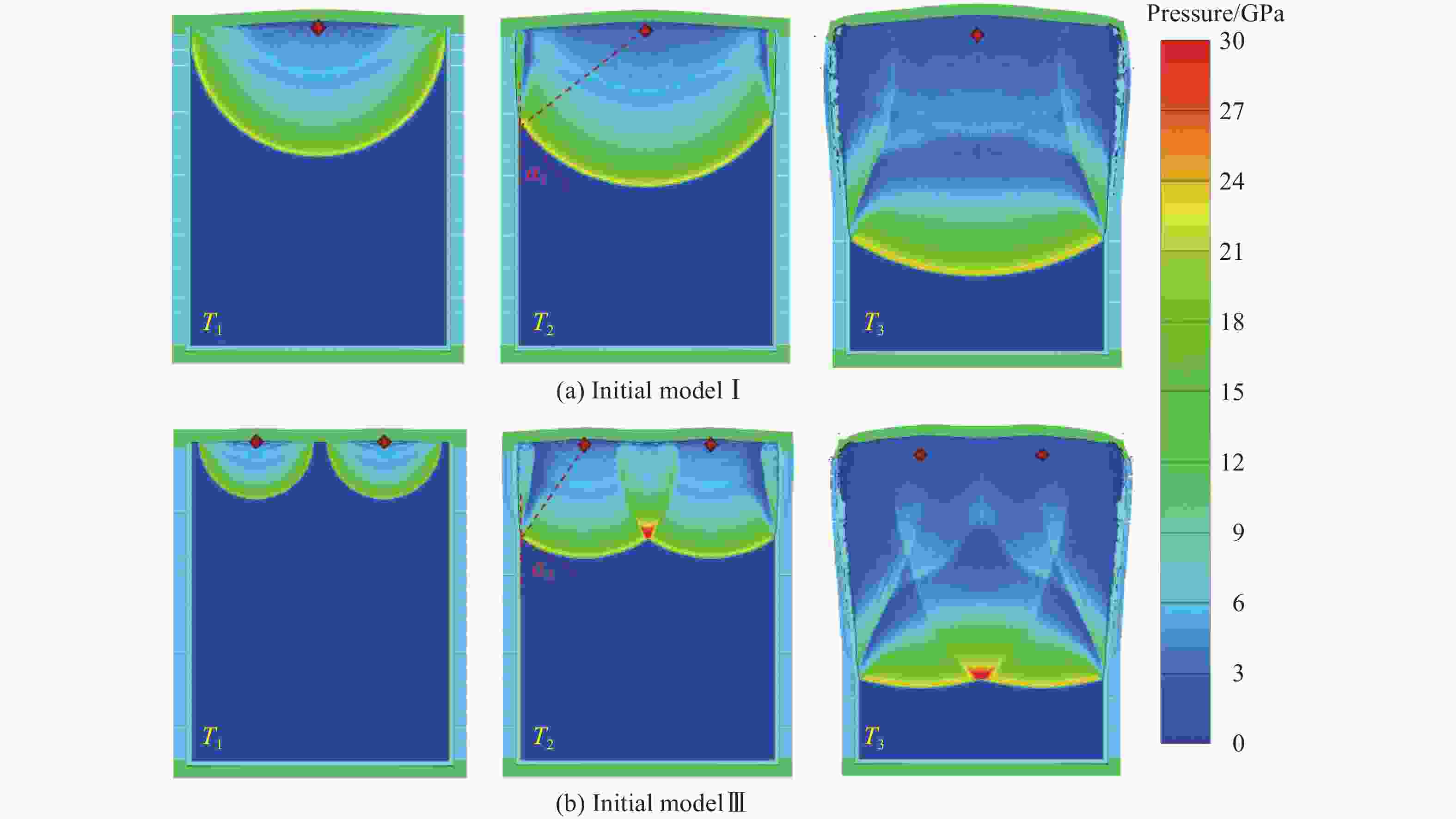
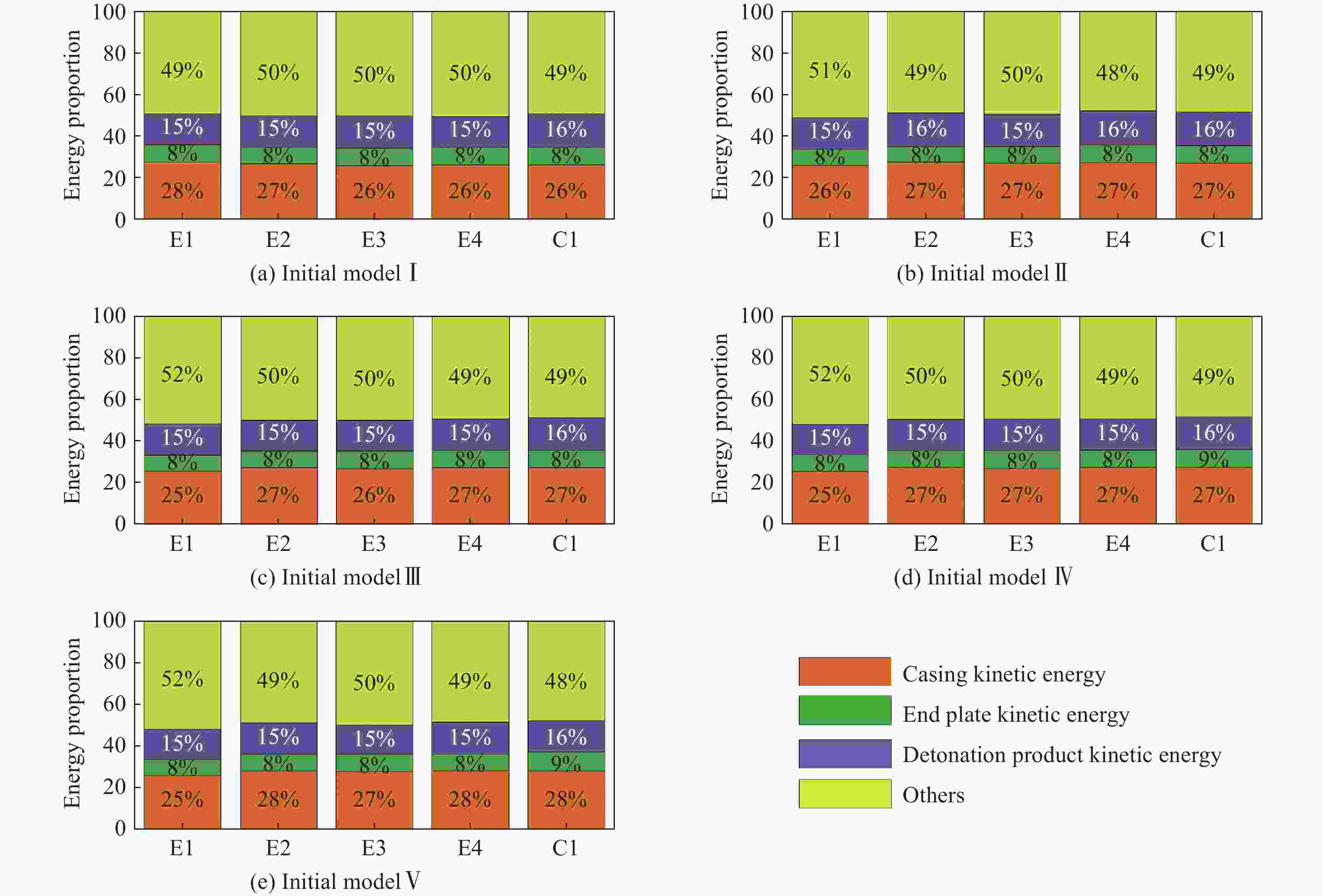
摘要: 为研究椭圆截面战斗部在不同起爆方式下破片速度的分布特性,建立了5种具有不同短长轴比的椭圆截面战斗部数值模拟模型。开展了端面中心单点、短(长)轴中点双点、短长轴中点4点以及端面面起爆5种起爆方式数值模拟研究,分析了不同起爆方式下椭圆截面战斗部破片的速度分布及能量输出特性。研究结果表明:在径向方向,战斗部在不同起爆方式下破片最大径向速度变化规律基本一致,均呈现由长轴至短轴方向对数增长,且随着短长轴比的增大,短长轴方向破片速度差值逐渐减小。然而,不同起爆方式下椭圆截面战斗部最大速度截面上破片速度平均值存在明显差异,具体表现为端面起爆时的破片径向平均速度最高,单点起爆最低,且随着起爆点数量的增加,最大速度截面上的破片的整体平均速度逐渐增大。在轴向方向,受端面稀疏波的影响,不同方位角最大破片速度均出现在靠近非起爆端1/4处,且起爆点在短轴轴线上相较于在长轴轴线上会提高靠近起爆端长轴方向的破片速度,但短轴方向沿轴向的破片速度分布无明显差异。此外,不同起爆方式对椭圆截面装药爆炸能量输出特性无明显影响,其中27%的装药能量转化为壳体动能,有50%的能量被壳体断裂变形以及空气冲击波消耗。Abstract: To investigate the velocity distribution characteristics of elliptical section warhead (ECSW) fragments under different initiation modes, a numerical simulation model was established for five ECSWs with different shape ratios. Numerical simulations were conducted to investigate the velocity distribution and energy output characteristics of fragments from ECSW under five different initiation modes: central single-point initiation, dual-point initiation at the midpoint of the minor (or major) axis, four-point initiation at the midpoint of the major and minor axes, as well as surface-initiated detonation. The research findings suggest that the maximum radial velocity of fragments follows a consistent logarithmic growth pattern in the radial direction across various initiation modes, increasing from the major axis to the minor axis direction. With an increase in the shape ratio, the difference in fragment velocities between the major and minor axis directions gradually decreases. However, the maximum velocity profiles of fragments from elliptical section warheads exhibit noticeable differences in average velocities under different initiation modes. Surface-initiated detonation produces the highest average radial velocity, whereas single-point initiation leads to the lowest. As the number of initiation points increases, the overall average fragment velocity on the maximum velocity profile gradually rises. In the axial direction, the influence of rarefaction waves leads to the maximum fragment velocities occurring near the 1/4 position from the non-initiating end at different azimuthal angles. Initiation points along the minor axis enhance the fragment velocity in the major axis direction near the initiating end compared to initiating points along the major axis. However, there are no significant variations in the axial velocity distribution of fragments in the minor axis direction. The different initiation modes have negligible effects on the energy output characteristics of elliptical section charges. Approximately 27% of the charge energy is converted into shell kinetic energy, while 50% is dissipated through casing fracture deformation and air shock wave propagation.
-
材料 A/MPa B/MPa n C m Tm/K AISI 1045 507 320 0.28 0.064 1.06 1793 表 2 B炸药的JWL状态方程参数
Table 2. JWL state equation parameters of composition B
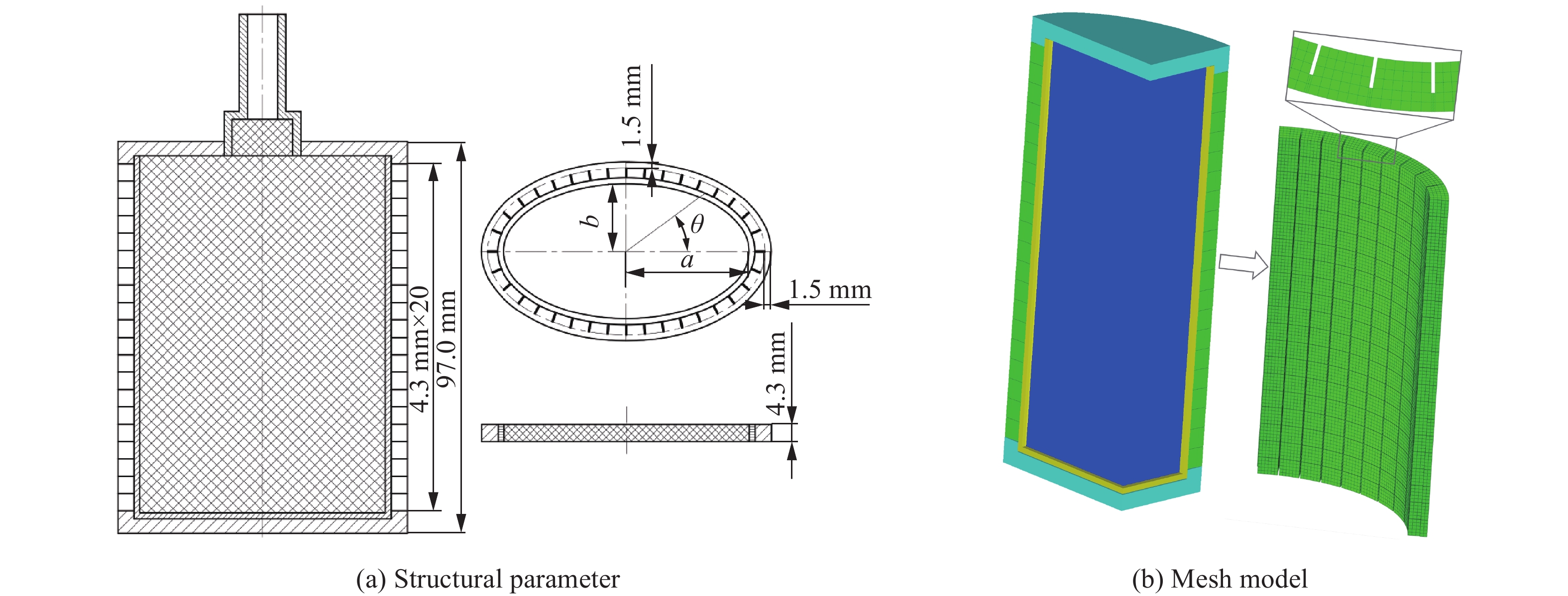
ρ/(g·cm−3) D/(m·s−1) pCJ/GPa C1/GPa C2/GPa r1 r2 ω 1.717 7980 29 542 7.68 4.2 1.1 0.24 表 3 战斗部参数
Table 3. Parameters of warhead
弹体编号 a/mm b/mm μ 壳体厚度/mm E1 35.58 14.23 0.40 3.763 E2 30.34 16.69 0.55 3.956 E3 26.89 18.82 0.70 4.053 E4 24.40 20.74 0.85 4.096 C1 22.50 22.50 1.00 4.108 -
[1] 杨祥, 武海军, 皮爱国, 等. 椭圆截面杀伤战斗部破片初速沿周向分布规律 [J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2018, 38(S2): 178–183. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2018.s2.040.YANG X, WU H J, PI A G, et al. Fragment velocity distribution of elliptical cross-section killing warhead along circumference [J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2018, 38(S2): 178–183. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2018.s2.040. [2] 冯顺山, 蒋建伟, 何顺录, 等. 偏轴心起爆破片初速径向分布规律研究 [J]. 兵工学报, 1993(S1): 12–16.FENG S S, JIANG J W, HE S L, et al. On the pattern of radial distribution pattern of initial velocities of fragments under asymmetrical initiation [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 1993(S1): 12–16. [3] RESNYANSKY A, WILDEGGER-GAISSMAIER A E, KATSELIS G. Directional fragmentation warheads: a theoretical and experimental investigation [C] // 18th International Symposium on Ballistics. San Antonio, TX, USA, 1999: 543–550. [4] HELD M. Velocity enhanced warheads [J]. Journal of Explosives and Propellants, 2001, 17(2): 1–12. [5] HELD M. Aimable fragmenting warhead [C] // 13th International Symposium on Ballistics. Stockholm, Sweden: National Defence Research Establishment, 1992: 539–548. [6] HUANG G Y, LI W, FENG S S. Fragment velocity distribution of cylindrical rings under eccentric point initiation [J]. Propellants, Explosives, Pyrotechnics, 2015, 40(2): 215–220. DOI: 10.1002/prep.201400180. [7] GURNEY R W. The initial velocities of fragments from bombs, shells and grenades: report No 405 [R]. Aberdeen Proving Ground, MD: Ballistic Research Laboratories, 1943. [8] LI W, HUANG G Y, FENG S S. Effect of eccentric edge initiation on the fragment velocity distribution of a cylindrical casing filled with charge [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2015, 80: 107–115. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2015.01.007. [9] LI Y, LI Y H, WEN Y Q. Radial distribution of fragment velocity of asymmetrically initiated warhead [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2017, 99: 39–47. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2016.09.007. [10] LI Y, LI X G, XIONG S H, et al. New formula for fragment velocity in the aiming direction of an asymmetrically initiated warhead [J]. Propellants, Explosives, Pyrotechnics, 2018, 43(5): 496–505. DOI: 10.1002/prep.201800003. [11] LI Y, XIONG S H, LI X G, et al. Mechanism of velocity enhancement of asymmetrically two lines initiated warhead [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2018, 122: 161–174. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2018.07.011. [12] LI Y, CHENG L, WEN Y Q. Fragment velocity formula for reverse detonation driving with opposite initiation [J]. Propellants, Explosives, Pyrotechnics, 2020, 45(12): 1931–1936. DOI: 10.1002/prep.202000162. [13] LI Y, LI X G, WEN Y Q, et al. Detonation driving rules for cylindrical casings under asymmetrical multipoint initiations [J]. Defence Technology, 2023, 23: 35–49. DOI: 10.1016/j.dt.2022.10.001. [14] AN X Y, DONG Y X, LIU J Y, et al. Fragment velocity characteristics of warheads with a hollow core under asymmetrical initiation [J]. Propellants, Explosives, Pyrotechnics, 2019, 44(8): 1049–1058. DOI: 10.1002/prep.201800382. [15] GUO Z W, HUANG G Y, ZHU W, et al. Mechanism and suppression of the effect of axial rarefaction waves on the eccentric initiation effect [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2019, 124: 37–47. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2018.10.009. [16] GUO Z W, HUANG G Y, ZHU W, et al. The fragmentation of D-shaped casing filled with explosive under eccentric initiation [J]. Defence Technology, 2018, 14(5): 417–421. DOI: 10.1016/j.dt.2018.06.006. [17] GUO Z W, HUANG G Y, ZHU W, et al. Fragment velocity distribution of D-shaped casing with multiple fragment layers [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2019, 131: 85–93. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2019.04.027. [18] GUO Z W, HUANG G Y, LIU H, et al. Fragment velocity distribution of the bottom part of D-shaped casings under eccentric initiation [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2020, 144: 103649. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2020.103649. [19] GUO Z W, HUANG G Y, LIU H, et al. Effects of shell thickness on the fragment velocity distribution of D-shaped casing filled with explosive [J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2021, 1721(1): 012018. DOI: 10.1088/1742-6596/1721/1/012018. [20] DING L L, LI Z D, LIANG M Z, et al. The dispersion rule of fragments about the asymmetric shell [J]. Shock and Vibration, 2017, 2017: 9810978. DOI: 10.1155/2017/9810978. [21] DING L L, LI Z D, LU F Y, et al. Rapid assessment of the spatial distribution of fragments about the D-shaped structure [J]. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 10(5): 1–16. DOI: 10.1177/1687814018777594. [22] DING L L, LI Z D, LU F Y, et al. Research into the energy output of asymmetric cylindrical structure under internal explosion loading [J]. Energies, 2018, 11(4): 967. DOI: 10.3390/en11040967. [23] LI Y, WEN Y Q. Experiment and numerical modeling of asymmetrically initiated hexagonal prism warhead [J]. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 2017, 9(1): 1–14. DOI: 10.1177/1687814016687966. [24] 李元, 赵倩, 熊诗辉, 等. 一种异面棱柱战斗部威力特性的数值模拟 [J]. 含能材料, 2019, 27(2): 97–103. DOI: 10.11943/CJEM2018143.LI Y, ZHAO Q, XIONG S H, et al. Numerical modeling on lethality of a faceted prismatic warhead [J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials, 2019, 27(2): 97–103. DOI: 10.11943/CJEM2018143. [25] 刘琛, 李元, 李燕华, 等. 偏心起爆方式对棱柱形定向战斗部破片飞散规律的影响 [J]. 含能材料, 2017, 25(1): 63–68. DOI: 10.11943/j.issn.1006-9941.2017.01.011.LIU C, LI Y, LI Y H, et al. Influence of eccentric initiation ways on fragment dispersion rule of prismatic aimable warhead [J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials, 2017, 25(1): 63–68. DOI: 10.11943/j.issn.1006-9941.2017.01.011. [26] 武敬博, 苟瑞君, 郑俊杰, 等. 六棱柱形战斗部预制破片驱动的数值模拟与试验 [J]. 火炸药学报, 2016, 39(3): 89–94. DOI: 10.14077/j.issn.1007-7812.2016.03.018.WU J B, GOU R J, ZHENG J J, et al. Numerical simulation and experiment of premade fragments droved by hexagonal prism shaped warhead [J]. Chinese Journal of Explosives & Propellants, 2016, 39(3): 89–94. DOI: 10.14077/j.issn.1007-7812.2016.03.018. [27] DENG X M, WU H J, YANG X, et al. Preformed fragment velocity distribution of elliptical cross-section projectile [J]. Latin American Journal of Solids and Structures, 2022, 19(1): e423. DOI: 10.1590/1679-78256835. [28] 邓宇轩, 张先锋, 冯可华, 等. 椭圆截面战斗部爆炸驱动破片作用过程的数值模拟 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2022, 36(2): 025104. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.20210856.DENG Y X, ZHANG X F, FENG K H, et al. Numerical simulation of fragmentation process driven by explosion in elliptical cross-section warhead [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2022, 36(2): 025104. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.20210856. [29] 邓宇轩, 张先锋, 刘闯, 等. 椭圆截面战斗部爆轰驱动壳体的断裂及毁伤特性 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2023, 43(9): 091412. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2023-0135.DENG Y X, ZHANG X F, LIU C, et al. Casing fracture and damage characteristics of an elliptical cross-section warhead under explosive loading [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2023, 43(9): 091412. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2023-0135. [30] 姜斌, 沈波, 薛再清, 等. 椭圆形截面杀伤战斗部破片初速分布特性研究 [J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2022, 43(3): 149–155. DOI: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2022.03.023.JIANG B, SHEN B, XUE Z Q, et al. Study on distribution characteristics of initial velocity of elliptic killing warhead fragment [J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2022, 43(3): 149–155. DOI: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2022.03.023. [31] DYNAMICS C. Release 14. 0 documentation for ANSYS AUTODYN [Z]. 2011. [32] 黄广炎, 刘沛清, 冯顺山. 基于战斗部微圆柱分析的破片飞散特性研究 [J]. 兵工学报, 2010, 31(S1): 215–218.HUANG G Y, LIU P Q, FENG S S. Research on dispersion characteristic of fragment based on micro-column analyses for warhead [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2010, 31(S1): 215–218. [33] 高月光, 冯顺山, 刘云辉, 等. 不同端盖厚度的圆柱形装药壳体破片初速分布 [J]. 兵工学报, 2022, 43(7): 1527–1536. DOI: 10.12382/bgxb.2021.0443.GAO Y G, FENG S S, LIU Y H, et al. Initial velocity distribution of fragments from cylindrical charge shells with different thick end caps [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2022, 43(7): 1527–1536. DOI: 10.12382/bgxb.2021.0443. [34] 李翔宇, 李振铎, 梁民族. D型战斗部破片飞散性及威力场快速计算 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2019, 39(4): 043301. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2017-0420.LI X Y, LI Z D, LIANG M Z. Dispersion properties and rapid calculation of fragment force field of D-shaped fragmentation warhead [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2019, 39(4): 043301. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2017-0420. -






 下载:
下载: